Abstract
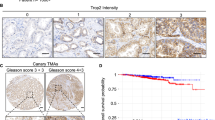
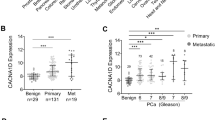
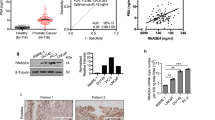
Members of the TRP superfamily of cation channels have homeostatic and regulatory functions in cells and changes in their expression may contribute to malignant growth. Previously, we have demonstrated that the gene of the Ca2+-selective cation channel CaT-L or TRPV6 is not expressed in benign prostate tissues including benign prostate hyperplasia, but is upregulated in prostate cancer. Here, we report on the differential expression of TRPV6 mRNA in prostate tissue obtained from 140 patients with prostate cancer. Using in situ hybridization, TRPV6 transcripts were undetectable in benign prostate tissue, high-grade prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia (n=57), incidental adenocarcinoma and all tumors less than 2.3 cubic centimeter (cc). In prostatectomy specimens from 97 clinically organ-confined tumors, TRPV6 expression correlated significantly with the Gleason score (P=0.032), pathological stage (P<0.001) and extraprostatic extension (P=0.025). Lymph node metastasis (n=17) and androgen-insensitive tumors (n=27) revealed TRPV6 expression in 63 and 67% of cases, respectively. The latter, however, revealed markedly and significantly decreased levels when compared with untreated tumors (P=0.044). In summary, the data demonstrate that TRPV6 expression is associated with prostate cancer progression. Accordingly, TRPV6 represents a prognostic marker and, as a plasma membrane Ca2+ channel, a promising target for new therapeutic strategies to treat advanced prostate cancer.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bonkhoff H, Fixemer T, Hunsicker I and Remberger K . (1999). Am. J. Pathol., 155, 641–647.
Cupp MR, Bostwick DG, Myers RP and Oesterling JE . (1995). J. Urol., 153, 1543–1548.
Hoenderop JGJ, Vennekens R, Müller D, Prenen J, Droogmans G, Bindels RJM and Nilius B . (2001). J. Physiol., 537, 747–761.
Mariot P, Vanoverberghe K, Lalevée N, Rossier MF and Prevarskaya N . (2002). J. Biol. Chem., 277, 10824–10833.
Narayan P, Gajendran V, Taylor SP, Tewari A, Presti Jr JC, Leidich R, Lo R, Palmer K, Shinohara K and Spaulding JT . (1995). Urology, 46, 205–212.
Niemeyer BA, Bergs C, Wissenbach U, Flockerzi V and Trost C . (2001). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 98, 3600–3605.
Partin AW, Kattan MW, Subong EN, Walsh PC, Wojno KJ, Oesterling JE, Scardino PT and Pearson JD . (1997). JAMA, 14, 1445–1451.
Peng J-B, Chen X-Z, Berger UV, Vassilev PM, Tsukaguchi H, Brown EM and Hediger MA . (1999). J. Biol. Chem., 274, 22739–22746.
Steinberg DM, Sauvageot J, Piantadosi S and Epstein JI . (1997). Am. J. Surg. Pathol., 21, 566–576.
Toyota M, Ho C, Ohe-Toyota M, Baylin SB and Issa J-PJ . (1999). Cancer Res., 59, 4535–4541.
Wills ML, Sauvageot J, Partin AW, Gurganus R and Epstein JI . (1998). Urology, 51, 759–764.
Wissenbach U, Niemeyer BA, Fixemer T, Schneidewind A, Trost C, Cavalié A, Reus K, Meese E, Bonkhoff H and Flockerzi V . (2001). J. Biol. Chem., 276, 19461–19468.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported, in part, by the Fonds der Chemischen Industrie, Wilhelm Sander-Stiftung and Landesforschungsförderungsprogramm 0113.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fixemer, T., Wissenbach, U., Flockerzi, V. et al. Expression of the Ca2+-selective cation channel TRPV6 in human prostate cancer: a novel prognostic marker for tumor progression. Oncogene 22, 7858–7861 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1206895
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1206895
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Ascorbate-induced oxidative stress mediates TRP channel activation and cytotoxicity in human etoposide-sensitive and -resistant retinoblastoma cells
Laboratory Investigation (2021)
-
Overexpression of SLC6A1 associates with drug resistance and poor prognosis in prostate cancer
BMC Cancer (2020)
-
Post-mortem histology in transient receptor potential cation channel subfamily V member 6 (TRPV6) under-mineralising skeletal dysplasia suggests postnatal skeletal recovery: a case report
BMC Medical Genetics (2020)
-
Proscillaridin A induces apoptosis and suppresses non-small-cell lung cancer tumor growth via calcium-induced DR4 upregulation
Cell Death & Disease (2018)
-
The calcium–cancer signalling nexus
Nature Reviews Cancer (2017)