Abstract
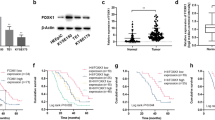
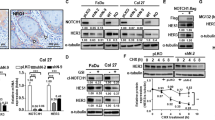
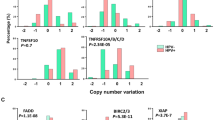
Previous studies have shown early region 1A (E1A) gene to inhibit the proliferation of tumour cells with wild-type, but not mutant, p53. E1A has also been shown to downregulate c-erb-B-2/neu expression, resulting in inhibition of growth in c-erb-B-2/neu overexpressing tumour cells. In this study, we have investigated the effect of E1A expression on four head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC) cell lines that do not overexpress c-erb-B-2/neu. Cell cycle and Western blot analysis show E1A-mediated induction of apoptosis in all cell lines examined. This induction of apoptosis was independent of the p53 status as it occurred in the cell lines with wild-type, mutated or deleted p53. However, there was no evidence of E1A-induced apoptosis in a p53+ve normal human fibroblast cell line, 1BR3. Analysis of apoptosis in the SCC cell lines demonstrated E1A-mediated downregulation of EGFR, which was overexpressed in each of these cell lines. Overexpression of an exogenously introduced EGFR, under the control of an E1A-insensitive heterologous promoter, blocked E1A induction of apoptosis in these cells. Therefore, E1A-mediated downregulation of EGFR expression appears to be the cause, rather than a consequence of E1A-induced apoptosis in these SCC cell lines. Previous studies have shown downregulation of EGFR expression by PML. Interestingly, E1A expression in the HNSCC cells altered the pattern of PML distribution and induced the level of PML protein, thus suggesting that E1A-mediated downregulation of EGFR may occur via direct or indirect interactions with PML. These findings demonstrate a novel pathway by which E1A can induce apoptosis and identify EGFR as a potential target for the development of therapeutic strategies against epithelial malignancies, the majority of which have abnormal EGFR expression.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alcalay M, Tomassoni L, Colombo E, Stoldt S, Grignani F, Fagioli M, Szekely L, Helin K and Pelicci PG . (1998). Mol. Cell. Biol., 18, 1084–1093.
Askujarvi G . (1979). J. Mol. Biol., 134, 143–158.
Averbuch SD . (2002). Clin. Cancer Res., 8, 1–3.
Borrelli E, Hen R and Chambon P . (1984). Nature, 312, 608–612.
Branton PE, Bayley ST and Graham FL . (1985). Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 780, 67–94.
Chang JY, Xia W, Shao R and Hung MC . (1996). Oncogene, 13, 1405–1412.
Chang JY, Xia W, Shao R, Sorgi F, Hortobagyi GN, Huang L and Hung MC . (1997). Oncogene, 14, 561–568.
Chiou SK, Rao L and White E . (1994). Mol. Cell. Biol., 14, 2556–2563.
Davies DE and Chamberlin SG . (1996). Biochem. Pharmacol, 51, 1101–1110.
Duque PM, Alonso C, Sanchez-Prieto R, Lleonart M, Martinez C, de Buitrago GG, Cano A, Quintanilla M and, Ramon y Cajal S . (1999). Cancer Gene Ther., 6, 554–563.
Dyck JA, Maul GG, Miller Jr WH, Chen JD, Kakizuka A and Evans RM . (1994). Cell, 76, 333–343.
Faha B, Harlow E and Lees E . (1993). J. Virol., 67, 2456–2465.
Ferguson B, Krippl B, Andrisani O, Jones N, Westphal H and Rosenberg M . (1985). Mol. Cell. Biol., 5, 2653–2661.
Fogal V, Gostissa M, Sandy P, Zacchi P, Sternsdorf T, Jensen K, Pandolfi PP, Will H, Schneider C and Del Sal G . (2000). EMBO J., 19, 6185–6195.
Frisch SM and Dolter KE . (1995). Cancer Res., 55, 5551–5555.
Frisch SM and Mymryk JS . (2002). Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol., 3, 441–452.
Fry DW, Kraker AJ, McMichaE1A, Ambroso LA, Nelson JM, Leopold WR, Connors RW and Bridges AJ . (1994). Science, 265, 1093–1095.
Graham FL and Prevec L . (1991). Methods in Molecular Biology: Gene Transfer and Expression Protocols. Murray EJ (ed). Human Press Inc.: Clifton, NJ, pp 109–128.
de Groot R, Foulkes N, Mulder M, Kruijer W and Sassone-Corsi P . (1991). Mol. Cell. Biol., 11, 192–201.
Grooteclaes ML and Frisch SM . (2000). Oncogene, 19, 3823–3828.
He Y, Zeng Q, Drenning SD, Melhem MF, Tweardy DJ, Huang L and Rubin Grandis J . (1998). J. Nat. Cancer Inst., 90, 1080–1087.
Irish JC and Bernstein A . (1993) Laryngoscope, 103, 42–52.
Ishii S, Xu Y, Stratton RH, Roe BA, Merlino GT and Pastan I . (1985). Procl. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 82, 4920–4924.
Jensen K, Shiels C and Freemont PS . (2001). Oncogene, 20, 7223–7233.
Kao HT and Nevins JR . (1984). Mol. Cell. Biol., 4, 2792–2810.
Lee WP, Liao Y, Robinson D, Kung HJ, Liu ET and Hung MC . (1999). Mol. Cell. Biol., 19, 8075–8082.
Lill NL, Douillard P, Awwad RA, Ota S, Lupher Jr ML, Miyake S, Meissner-Lula N, Hsu VW and Band H . (2000). J. Biol. Chem., 275, 367–377.
Lowe SW, Jacks T, Housman DE and Ruley HE . (1994). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 91, 2026–2030.
Lowe SW and Ruley HE . (1993). Genes Dev., 7, 535–545.
Ludes-Meyers JH, Subler MA, Shivakumar CV, Munoz RM, Jiang P, Bigger JE, Brown DR, Deb SP and Deb S . (1996). Mol. Cell. Biol., 16, 6009–6019.
Mal A, Poon RY, Howe PH, Toyoshima H, Hunter T and Harter ML . (1996). Nature, 380, 262–265.
Maul GG, Yu E, Ishov AM and Epstein AL . (1995). J. Cell. Biochem., 59, 498–513.
de Melker AA, van der Horst G, Calafat J, Jansen H and Borst J . (2001). J. Cell Sci., 114, 2167–2178.
Mymryk JS . (1996). Oncogene, 13, 1581–1599.
Nishi H, Senoo M, Nishi KH, Murphy B, Rikiyama T, Matsumura Y, Habu S and Johnson AC . (2001). J. Biol. Chem., 276, 41717–41724.
Prudenziati M, Sirito M, van Dam H and Ravazzolo R . (2000). Int. J. Cancer, 88, 943–948.
Rusch V, Baselga J, Cordon-Cardo C, Orazem J, Zaman M, Hoda S, McIntosh J, Kurie J and Dmitrovsky E . (1993). Cancer Res., 53, 2379–2385.
Saha V, Young BD and Freemont PS . (1998). J. Cell. Biochem. Suppl., 30–31, 264–276.
Salomon DS, Normanno N, Ciardiello F, Brandt R, Shoyab M and Todaro GJ . (1995). Breast Cancer Res. Treat., 33, 103–114.
Sartor M, Steingrimsdottir H, E1Amin F, Gaken J, Warnakulasuriya S, Partridge M, Thakker N, Johnson NW and Tavassoli M . (1999). Br. J. Cancer, 80, 79–86.
Sassone-Corsi P and Borrelli E . (1987). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 84, 6430–6433.
Sheikh MS, Carrier F, Johnson AC, Ogdon SE and Fornace Jr AJ . (1997). Oncogene, 15, 1095–1101.
de Stanchina E, McCurrach ME, Zindy F, Shieh SY, Ferbeyre G, Samuelson AV, Prives C, Roussel MF, Sherr CJ and Lowe SW . (1998). Genes Dev., 12, 2434–2442.
Stein RW, Corrigan M, Yaciuk P, WhE1An J and Moran E . (1990). J. Virol., 64, 4421–4427.
Stein R and Ziff E . (1984). Mol. Cell Biol., 4, 2792–2801.
Tavassoli M, Soltaninia J, Rudnicka J, Mashanyare D, Johnson N and Gäken J . (2002). Carcinogenesis, 23, 1569–1576.
Theodoro JG, Shore GC and Branton PE . (1995). Oncogene, 11, 467–474.
Thomas A and White E . (1998). Genes Dev., 12, 1975–1985.
Tian XX, Chan JYH, Pang JCS, Chen J, He JH, To TSS, Leung SF and Ng HK . (1999). Br. J. Cancer, 81, 994–1001.
Vallian S, Chin K and Chang K . (1998). Mol. Cell. Biol., 18, 7147–7156.
Vallian S, Gäken JA, Trayner ID, Gingold EB, Kouzarides T, Chang KS and Farzaneh F . (1997). Exp. Cell. Res., 237, 371–382.
Weis K, Rambaud S, Lavau C, Jansen J, Carvalho T, Carmo-Fonseca M, Lamond A and Dejean A . (1994). Cell, 76, 345–356.
Whyte P, Buchkovich KJ, Horowitz JM, Friend SH, Raybuck M, Weinberg RA and Harlow E . (1988). Nature, 334, 124–129.
Woodburn JR . (1999). Pharmacol. Ther., 82, 241–250.
Wu WS, Vallian S, Seto E, Yang WM, Edmondson D, Roth S and Chang KS . (2001). Mol. Cell. Biol., 21, 2259–2268.
Yan DH, Chang LS and Hung MC . (1991). Oncogene, 6, 343–345.
Yeudall WA, Jakus J, Ensley JF and Robbins KC . (1997). Mol. Carcinog., 18, 89–96.
Yu D, Matin A, Xia W, Sorgi F, Huang L and Hung MC . (1995). Oncogene, 11, 1383–1388.
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to Dr M-C Hung, Department of Molecular and Cellular Oncology, MD Anderson Cancer Center for the E1A vectors, to Prof. William Gullick Department of Biosciences, University of Kent at Canterbury for EGFR antibody and for advice on EGFR expression analysis, Dr Kun-San Chang, Department of Molecular Pathology, MD Anderson Cancer Center for PML antibody and advise on PML analysis. We would like to thank Dr Barry Gusterson, Department of Pathology, University of Glasgow for HN5, Dr Andrew Yeudall, Department of Craniofacial Development, Guy's Dental Institute for HN30 and Dr Stephen Prime, Department of Oral and Dental Science, University of Bristol for H357 cell lines. MF was supported by a studentship awarded by Guy's, King's and St Thomas's Dental Institute. This work was supported by grants from the Royal Society and European Union (EU).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Flinterman, M., Gäken, J., Farzaneh, F. et al. E1A-mediated suppression of EGFR expression and induction of apoptosis in head and neck squamous carcinoma cell lines. Oncogene 22, 1965–1977 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1206190
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1206190
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Apoptin interacts with and regulates the activity of protein kinase C beta in cancer cells
Apoptosis (2015)
-
Evaluation of apoptogenic adenovirus type 5 oncolytic vectors in a Syrian hamster head and neck cancer model
Cancer Gene Therapy (2014)
-
Apoptin induces apoptosis by changing the equilibrium between the stability of TAp73 and ΔNp73 isoforms through ubiquitin ligase PIR2
Apoptosis (2012)
-
Identification of genes differentially expressed as result of adenovirus type 5- and adenovirus type 12-transformation
BMC Genomics (2009)
-
PML involvement in the p73-mediated E1A-induced suppression of EGFR and induction of apoptosis in head and neck cancers
Oncogene (2009)