Abstract
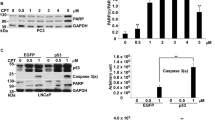
In this study we characterize the connections between p53-dependent G1 cell cycle arrest, transcriptional activation of the protein and the increase of its intracellular steady-state concentration. Several cell lines expressing wild-type p53 protein were treated with increasing concentrations of DNA-damaging drug camptothecin. Lower doses of the drug caused transcriptional activation of p53, but no accumulation of the protein was detected. Only after a certain threshold dose of camptothecin does the amount of the protein rapidly increase and reach its plateau levels. The threshold dose was different for different cell lines, but the general non-linear profile was similar. Increase of p53 level was accompanied by additional transcriptional activation of some p53 target genes (i.e. waf1), but not the others (mdm2). We demonstrate here that transcriptional activation of p53 after the treatment of camptothecin is not sufficient to cause p53-dependent G1 cell cycle arrest. The latter is observable only after the inrease of steady-state level of p53. Low drug concentrations, although accompanied by transcriptional activation of p53, do not cause either p53 protein accumulation nor cell cycle arrest at G1. We propose a model for p53 acting as a part of cellular sensor system detecting the severity of DNA damage.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Avemann K, Knippers R, Koller T and Sogo J. . 1998 Mol. Cell. Biol. 8: 3206–3034.
Barak Y, Juven T, Haffner R and Oren M. . 1993 EMBO J. 12: 461–468.
Canman C, Gilmer T, Coutts S and Kastan M. . 1995 Genes Dev. 12: 600–611.
Carrier F, Georgel PT, Pourguier P, Blake M, Kontny HU, Antinore MJ, Gariboldi M, Myers TG, Weinstein JN, Pommier Y and Fornace Jr AJ. . 1999 Mol. Cell. Biol. 19: 1673–1685.
Chao C, Saito S, Kang J, Anderson CW, Appella E and Xu Y. . 2000 EMBO J. 19: 4967–4975.
Chen X, Ko L, Jayaraman L and Prives C. . 1996 Genes Dev. 10: 2438–2451.
Chernov M, Ramana C, Adler V and Stark G. . 1998 Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 95: 2284–2289.
Cox LS, Hupp T, Midgley CA and Lane DP . 1995 EMBO J. 14: 2099–2105.
Deptala A, Li X, Bedner E, Cheng W, Traganos F and Darzynkiewicz Z. . 1999 Int. J. Oncol. 15: 861–871.
Di Leonardo A, Linke S, Clarkin K and Wahl G. . 1994 Genes Dev. 8: 2540–2551.
Dulic V, Kaufmann W, Wilson S, Tlsty T, Lees E, Harper J, Elledge S and Reed S. . 1994 Cell 76: 1013–1023.
El-Deiry WS, Tokino T, Velculescu VE, Levy DB, Parsons R, Trent JM, Lin D, Mercer WE, Kinzler KW and Vogelstein B. . 1993 Cell 75: 817–825.
Ewen M. . 1996 J. Lab. Clin. Med. 128: 355–360.
Fu L, Minden M and Benchimol S. . 1996 EMBO J. 15: 4392–4401.
Gorospe M, Wang X and Holbrook NJ. . 1998 Mol. Cell. Biol. 18: 1400–1407.
Graeber T, Peterson J, Tsai M, Monica K, Fornace AJ and Giaccia A. . 1994 Mol. Cell. Biol. 14: 6264–6277.
Haapajärvi T, Pitkanen K, Tsubari M and Laiho M. . 1997 Mol. Cell. Biol. 17: 3074–3080.
Han J, Sabbatini P, Perez D, Rao L, Modha D and White E. . 1996 Genes Dev. 10: 461–477.
Harper JW, Adami GR, Wei N, Keyomarsi K and Elledge SJ. . 1993 Cell 75: 805–816.
Haupt Y, Maya R, Kazaz A and Oren M. . 1997 Nature 387: 296–299.
Jimenez GS, Nister M, Stommel JM, Beeche M, Barcarse EA, Zhang XQ, O'Gorman S and Wahl GM. . 2000 Nat. Genet. 26: 37–43.
Kastan MB. . 1993 Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 339: 291–293; discussion 295–296.
Kastan MB, Onyekwere O, Sidransky D, Vogelstein B and Craig RW. . 1991 Cancer Res. 51: 6304–6311.
Kastan MB, Zhan Q, El-Deiry WS, Carrier F, Jacks T, Walsh WV, Plunkett BS, Vogelstein B and Fornace AJJ. . 1992 Cell 71: 587–597.
Kristjuhan A, Jaks V, Rimm I, Tooming T and Maimets T. . 1998 Oncogene 16: 2413–2418.
Kristjuhan A and Maimets T. . 1995 Eur. J. Biochem. 234: 827–831.
Kubbutat MH, Jones SN and Vousden KH. . 1997 Nature 387: 299–303.
Lakin ND and Jackson SP. . 1999 Oncogene 18: 7644–7655.
Lane DP. . 1992 Nature 358: 15–16.
Li G and Ho VC. . 1998 Br. J. Dermatol. 139: 3–10.
Li R, Waga S, Hannon GJ, Beach D and Stillman B. . 1994 Nature 371: 534–537.
Lowe S, Schmitt E, Smith S, Osborne B and Jacks T. . 1993 Nature 362: 847–849.
Lu X, Burbidge SA, Griffin S and Smith HM. . 1996 Oncogene 13: 413–418.
Maltzman W and Czyzyk L. . 1984 Mol. Cell. Biol. 4: 1689–1694.
Maxwell S, Roth J and Mukhopadhyay T. . 1996 Electrophoresis 17: 1772–1775.
May P and May E. . 1999 Oncogene 18: 7621–7636.
Miyashita T, Krajewski S, Krajewska M, Wang HG, Lin HK, Liebermann DA, Hoffman B and Reed JC. . 1994 Oncogene 9: 1799–1805.
Momand J, Zambetti GP, Olson DC, George D and Levine AJ. . 1992 Cell 69: 1237–1245.
Nelson W and Kastan M. . 1994 Mol. Cell. Biol. 14: 1815–1823.
Offer H, Wolkowicz R, Matas D, Blumenstein S, Livneh Z and Rotter V. . 1999 FEBS Lett. 450: 197–204.
Okamoto K and Beach D. . 1994 EMBO J. 13: 4816–4822.
Okamoto K and Prives C. . 1999 Oncogene 18: 4606–4615.
Oliner JD, Kinzler KW, Meltzer PS, George DL and Vogelstein B. . 1992 Nature 358: 80–83.
Perry ME, Piette J, Zawadzki JA, Harvey D and Levine AJ. . 1993 Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 90: 11623–11627.
Radford I. . 1994 Int. J. Radiat. Biol. 66: 557–560.
Ryan AJ, Squires S, Strutt HL and Johnson RT. . 1991 Nucleic Acids Res. 19: 3295–3300.
Selkirk J, He C, Patterson R and Merrick B. . 1996 Electrophoresis 17: 1764–1771.
Selvakumaran M, Lin H, Miyashita T, Wang H, Krajewski S, Reed J, Hoffman B and Liebermann D. . 1994 Oncogene 9: 1791–1798.
Shaw P, Bovey R, Tardy S, Sahli R, Sordat B and Costa J. . 1992 Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 89: 4495–4499.
Shieh SY, Ahn J, Tamai K, Taya Y and Prive C. . 2000 Genes Dev. 14: 289–300.
Waga S, Hannon GJ, Beach D and Stillman B. . 1994 Nature 369: 574–578.
Wu X, Bayle JH, Olson D and Levine AJ. . 1993 Genes Dev. 7: 1126–1132.
Xiong Y, Hannon GJ, Zhang H, Casso D, Kobayashi R and Beach D. . 1993 Nature 366: 701–704.
Zhang W, Randhawa G, Guo X and Deisseroth A. . 1994 Cell Growth Differ. 5: 705–710.
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr Arnold Levine, Princeton University, for 10(1) cell line, Dr Marikki Laiho for critically reviewing the manuscript; Drs Jane Lehtmaa and Ain Kaare, Clinic of Hematology and Oncology, Tartu University for opportunity to use flow cytometer and for personal help. This work has been partly supported by contract QLG7-CT-1999-00851 from the European Community and grant no.4029 from Estonian Science Foundation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jaks, V., Jõers, A., Kristjuhan, A. et al. p53 protein accumulation in addition to the transactivation activity is required for p53-dependent cell cycle arrest after treatment of cells with camptothecin. Oncogene 20, 1212–1219 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1204232
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1204232
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Truncating mutations of PPM1D are found in blood DNA samples of lung cancer patients
British Journal of Cancer (2015)
-
The Glial Response to CNS HIV Infection Includes p53 Activation and Increased Expression of p53 Target Genes
Journal of Neuroimmune Pharmacology (2007)
-
E2F-1 overexpression sensitizes colorectal cancer cells to camptothecin
Cancer Gene Therapy (2003)