Abstract
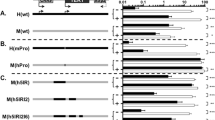
Activation of telomerase, which has been frequently associated with cellular immortality, may constitute a key step in the development of human cancer. De-repression in the expression of its catalytic subunit hTERT gene has been proposed to directly link to the telomerase activation in tumor cells. Little is known about the mechanism how the hTERT gene is repressed in telomerase-negative mortal cells. This study was conducted, using an expression cloning approach, with the aim of identifying the gene(s) responsible for repressing the hTERT gene expression. Using this genetic screen, we isolated the transcription factor Mad as a repressor. Mutation of its DNA binding sites caused significant de-repression of hTERT promoter activity in mortal cells. This Mad-mediated repression of the hTERT promoter in mortal cells was counteracted by ectopic expression of Myc. The antagonism between Mad and Myc was also observed with an endogenous hTERT promoter. Their potential roles in differential hTERT promoter activities were further supported by the relative amounts of Mad and Myc proteins detected in immortal and mortal cells. Thus, Mad may be a direct negative regulator of hTERT in mortal cells and this repression mechanism can be inhibited by induction of Myc in immortal cells.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ayer DE, Kretzner L and Eisenman RN . 1993 Cell 72: 211–222
Blackwood EM, Luscher B and Eisenman RN . 1992 Genes Dev 6: 71–80
Bodnar AG, Quellette M, Frolkis M, Holt SE, Chiu C-P, Morin GB, Harley CB, Shay JW, Lichtsteiner S and Wright WE . 1998 Science 279: 349–352
Cole MD and McMahon SB . 1999 Oncogene 18: 2916–2924
Cong Y-S, Wen J and Bacchetti S . 1999 Hum Mol Genet 8: 137–142
Cuthbert AP, Bond J, Trott DA, Gill S, Broni J, Marriott A, Khoudoli G, Parkinson EK, Cooper CS and Newbold RF . 1999 J Natl Cancer Inst 91: 37–45
Dang CV . 1999 Mol Cell Biol 19: 1–11
Grandori C and Eisenman RN . 1997 Trends Biochem 22: 177–181
Greenberg RA, O'Hagan RC, Deng H, Xiao Q, Hann SR, Adams RR, Lichtsteiner S, Chin L, Morin GB and DePinho RA . 1999 Oncogene 18: 1219–1226
Greider CW . 1998 Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95: 90–92
Hensler PJ, Annab LA, Barrett JC and Pereira-Smith OM . 1994 Mol Cell Biol 14: 2291–2297
Holt SE, Wright WE and Shay JW . 1997 Eur J Cancer 33: 761–766
Horikawa I, Cable PL, Afshari C and Barrett JC . 1999 Cancer Res 59: 826–830
Horikawa I, Oshimura M and Barrett JC . 1998 Mol Carcinog 22: 65–72
Kilian A, Bowtell DDL, Abud HE, Hime GR, Venter DJ, Keese PK, Duncan EL, Reddel RR and Jefferson RA . 1997 Hum Mol Genet 6: 2011–2019
Kim TK and Maniatis T . 1996 Science 273: 1717–1719
Meyerson M, Counter CM, Eaton EN, Ellisen LW, Steiner P, Caddle SD, Ziaugra L, Beijersbergen RL, Davidoff MJ, Liu Q, Bacchetti S, Haber DA and Weinberg RA . 1997 Cell 90: 785–795
Nakamura TM, Morin GB, Chapman KB, Weinrich SL, Andrews WH, Lingner J, Harley CB and Cech TR . 1997 Science 277: 955–959
Ning YJ, Weber JL, Killary AM, Ledbetter DH, Smith JR and Pereira-Smith OM . 1991 Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 88: 5635–5639
Nugent CI and Lundblad V . 1998 Genes Dev 12: 1073–1085
Ogata T, Oshimura M, Namba M, Fujii M, Oishi M and Ayusawa D . 1995 Japan J Cancer Res 86: 35–40
Oh S, Song Y-H, Kim U-J, Yim J and Kim TK . 1999a Biochem Biophys Res Com 263: 361–365
Oh S, Song Y-H, Yim J and Kim TK . 1999b J Biol Chem 274: 37473–37478
Ohmura H, Tahara H, Suzuki M, Ide T, Shimizu M and Yoshida MA . 1995 Japan J Cancer Res 86: 899–904
Schreiber-Agus N and DePinho RA . 1998 Bioessays 20: 808–818
Sedivy JM . 1998 Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95: 9078–9081
Serrano M, Lin AW, McCurrach ME, Beach D and Lowe SW . 1997 Cell 88: 593–602
Shay JW . 1999 J Natl Cancer Inst 91: 4–6
Takakura M, Kyo S, Kanaya T, Hirano H, Takeda J, Yutsudo M and Inoue M . 1999 Cancer Res 59: 551–557
Vaziri H and Benchimol S . 1998 Curr Biol 8: 279–282
Wright WE and Shay JW . 1995 Trends Cell Biol 5: 293–297
Wu K-J, Grandori C, Amacker M, Simon-Vermot N, Polack A, Lingner J and Dalla-Favera R . 1999 Nature Genet 21: 220–224
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Creative Research Initiatives of the Korean Ministry of Science and Technology, Republic of Korea.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Oh, S., Song, YH., Yim, J. et al. Identification of Mad as a repressor of the human telomerase (hTERT) gene. Oncogene 19, 1485–1490 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1203439
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1203439
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Analysis of matched primary and recurrent BRCA1/2 mutation-associated tumors identifies recurrence-specific drivers
Nature Communications (2022)
-
Targeting telomerase for cancer therapy
Oncogene (2020)
-
Diverse regulatory manners of human telomerase reverse transcriptase
Cell Communication and Signaling (2019)
-
Molecular regulation of telomerase activity in aging
Protein & Cell (2011)
-
Epigenetic plasticity of hTERT gene promoter determines retinoid capacity to repress telomerase in maturation-resistant acute promyelocytic leukemia cells
Leukemia (2010)