Abstract
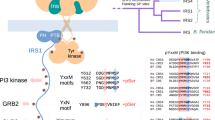
Shc and IRS-1 (and their relatives) are cytoplasmic docking proteins that possess phosphotyrosine-binding (PTB) domains, through which they bind specific activated receptor tyrosine kinases (RTK). The subsequent phosphorylation of Shc or IRS-1 creates binding sites for the SH2 domains of multiple signaling proteins, leading to the activation of intracellular biochemical pathways. The PTB domains of Shc and IRS-1 both recognize autophosphorylation sites in RTKs with the consensus sequence NPXpY, but show distinct abilities to bind stably to RTKs such as the TrkA nerve growth factor receptor and the insulin receptor. In vitro analysis has suggested that residues N-terminal to the NPXpY motif may determine the affinity with which phosphopeptide ligands are recognized by the Shc and IRS-1 PTB domains. Unlike IRS-1, the Shc PTB domain binds poorly to the insulin-receptor (IR) β subunit in vitro, owing to its low affinity for the NPXpY autophosphorylation site at Tyr 960 of the IR. As a consequence, Shc does not bind stably to the activated IR in cells. We show that substitution of Ser 955, five residues N-terminal to the Tyr 960 autophosphorylation site (the −5 position), with Ile alters the target specificity of the IR such that it stably associates with Shc in insulin-stimulated cells. A triple substitution of the −5, −8 and −9 residues relative to Tyr 960 of the IR to the corresponding amino acids found in the Shc PTB domain binding site of TrkA results in even stronger binding of the IR to Shc in vivo. The variant IRs with enhanced ability to bind Shc showed an increased ability to activate the MAPK pathway in response to insulin stimulation. These results demonstrate that subtle differences in residues N-terminal to NPXpY autophosphorylation sites determine the ability of RTKs to bind specific PTB domain proteins in vivo, and thus modify the signaling properties of activated receptors.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Backer JM., Myers MJ, Shoelson SE, Chin DJ, Sun XJ, Miralpeix M, Hu P, Margolis B, Skolnik EY, Schlessinger J and White MF. . 1992 EMBO J. 11: 3469–3479.
Blaikie P, Immanuel D, Wu J, Li N, Yainik V and Margolis B. . 1994 J. Biol. Chem. 269: 32031–32034.
Borg JP, Ooi J, Levy E and Margolis B. . 1996 Mol. Cell. Biol. 16: 6229–6241.
Di Guglielmo GM, Baass PC, Ou WJ, Posner BI and Bergeron JJ. . 1994 EMBO J. 13: 4269–4277.
Eck MJ, Dhe-Paganon, S, Trüb T, Nolte RT and Shoelson SE. . 1996 Cell 85: 695–705.
Feener EP, Backer JM, King GL, Wilden PM, Sun XJ, Kahn CR and White M.F. . 1993 J. Biol. Chem. 268: 11256–11264.
Fiore F, Zambrano N, Minopoli G, Donini V, Duilio A and Russo T. . 1995 J. Biol. Chem. 270: 30853–30856.
He W, O'Neil TJ and Gustafson TA. . 1995 J. Biol. Chem. 270: 23258–23262.
Kavanaugh WM and Williams LT. . 1994 Science 266: 1862–1865.
Kuriyan J and Cowburn D. . 1997 Ann. Rev. Biophys. Biomol. Struct. 26: 259–288.
Li SC, Songyang Z, Vincent SJ, Zwahlen C, Wiley S, Cantley L, Kay LE, Forman-Kay J and Pawson T. . 1997 Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci USA 94: 7204–7209.
O'Neill TJ, Craparo A and Gustafson TA. . 1994 Mol. Cell. Biol. 14: 6433–6442.
Pawson T and Scott JD. . 1997 Science 278: 2075–2080.
Pelicci G, Lanfrancone L, Grignani F, McGlade J, Cavallo F, Forni G, Nicoletti I, Grignani F, Pawson T and Pelicci PG. . 1992 Cell 70: 93–104.
Songyang Z, Margolis B, Chaudhuri M, Shoelson SE and Cantley LC. . 1995 J. Biol. Chem. 270: 14863–14866.
Stephens RM, Loeb DM, Copeland TD, Pawson T, Greene LA and Kaplan DR. . 1994 Neuron 12: 691–705.
van der Geer P, Wiley S, Gish GD, Lai VK, Stephens R, White MF, Kaplan D and Pawson T. . 1996a Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 93: 963–968.
van der Geer P, Wiley S, Gish GD and Pawson T. . 1996b Curr. Biol. 6: 1435–1444.
van der Geer P, Wiley S, Lai VK-M, Olivier JP, Gish G, Stephens R, Kaplan D, Shoelson S and Pawson T. . 1995 Curr. Biol. 5: 404–412.
White MF, Livingston JN, Backer JM, Lauris V, Dull TJ, Ullrich A and Kahn CR. . 1988 Cell 54: 641–649.
Wolf G, Trub T, Ottinger E, Groninga L, Lynch A, White MF, Miyazaki M, Lee J and Shoelson SE. . 1995 J. Biol. Chem. 270: 27407–7410.
Zhou MM, Ravichandran KS, Olejniczak EF, Petros AM, Meadows RP, Sattler M, Harlan JE, Wade WS, Burakoff SJ and Fesik SW. . 1995 Nature 378: 584–592.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by grants from the National Cancer Institute of Canada (NCIC), the Medical Research Council of Canada (MRC) and the Protein Engineering Network of Centres of Excellence and a Howard Hughes Medical International Scholar Award to T Pawson. T Pawson is a distinguished scientist of the MRC. Peter van der Geer acknowledges a postdoctoral fellowship from the NCIC.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
van der Geer, P., Wiley, S. & Pawson, T. Re-engineering the target specificity of the insulin receptor by modification of a PTB domain binding site. Oncogene 18, 3071–3075 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1202879
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1202879