Abstract
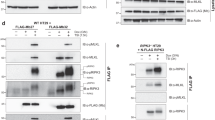
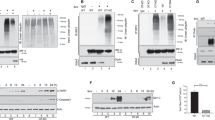
We have investigated the effect of inducing apoptosis in BJAB and Jurkat cells on the cellular content of several polypeptide chain initiation factors. Serum deprivation results in inhibition of protein synthesis and induction of apoptosis in BJAB cells; at early times, there is selective degradation of polypeptide initiation factor eIF4G but no major losses of other key initiation factors. The disappearance of full length eIF4G is accompanied by the appearance of smaller forms of the protein, including a major product of approximately 76 kDa. Apoptosis induced by cycloheximide results in similar effects. Both total cytoplasmic eIF4G and eIF4G associated with eIF4E are degraded with a half-life of 2–4 h under these conditions. Treatment of serum-starved or cycloheximide-treated cells with Z-VAD.FMK or Z-DEVD.FMK, which inhibit caspases required for apoptosis, protects eIF4G from degradation and blocks the appearance of the ca. 76 kDa product. Exposure of BJAB cells to rapamycin rapidly inhibits protein synthesis but does not lead to acute degradation of eIF4G. In both BJAB and Jurkat cells induction of apoptosis with anti-Fas antibody or etoposide also results in the selective loss of eIF4G, which is inhibitable by Z-VAD.FMK. These data suggest that eIF4G is selectively targeted for cleavage as cells undergo apoptosis and is a substrate for proteases activated during this process.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Clemens, M., Bushell, M. & Morley, S. Degradation of eukaryotic polypeptide chain initiation factor (eIF) 4G in response to induction of apoptosis in human lymphoma cell lines. Oncogene 17, 2921–2931 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1202227
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1202227
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Heterogeneity and specialized functions of translation machinery: from genes to organisms
Nature Reviews Genetics (2018)
-
A ribosome-related signature in peripheral blood CLL B cells is linked to reduced survival following treatment
Cell Death & Disease (2016)
-
Behavioural and biochemical changes in maternally separated Sprague–Dawley rats exposed to restraint stress
Metabolic Brain Disease (2016)
-
A role for eukaryotic initiation factor 4B overexpression in the pathogenesis of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma
Leukemia (2014)
-
Analysis of the protein expression changes during taxol-induced apoptosis under translation inhibition conditions
Molecular and Cellular Biochemistry (2010)