Abstract
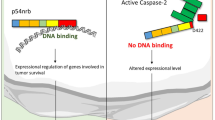
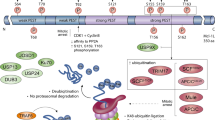
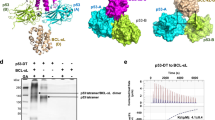
The MDM2 oncogene product is a regulator of the p53 tumor suppressor. MDM2 is cleaved by Caspase 3 (CPP32) during apoptosis after aspartic acid-361, generating a 60 kd fragment. Here we report that human tumor cell lines often express high levels of a 60 kd MDM2 isoform (p60) in the absence of apoptosis. We demonstrate that p60 is a product of caspase cleavage of full length MDM2 after residue 361. The protease that cleaves MDM2 in non-apoptotic cells appears to be distinct from the apoptosis-specific Caspase 3, since Caspase 3 substrate poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) is not cleaved in cells producing p60. The p60 form of MDM2 is a significant fraction of the p53-bound MDM2 protein in certain tumor cells, suggesting that it functions in the regulation of p53. p60 is also detected in breast tumors overexpressing MDM2. These observations suggest that MDM2 is regulated by caspase processing in non-apoptotic cells, and may account for the MDM2 proteins of similar mobility seen in tumors and other cell lines.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pochampally, R., Fodera, B., Chen, L. et al. A 60 kd MDM2 isoform is produced by caspase cleavage in non-apoptotic tumor cells. Oncogene 17, 2629–2636 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1202206
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1202206
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Efficacy of SCF drug conjugate targeting c-KIT in gastrointestinal stromal tumor
BMC Medicine (2022)
-
Tau affects P53 function and cell fate during the DNA damage response
Communications Biology (2020)
-
Comprehensive assessment of TP53 loss of function using multiple combinatorial mutagenesis libraries
Scientific Reports (2020)
-
Structurally novel steroidal spirooxindole by241 potently inhibits tumor growth mainly through ROS-mediated mechanisms
Scientific Reports (2016)
-
Upregulated p53 expression activates apoptotic pathways in wild-type p53-bearing mesothelioma and enhances cytotoxicity of cisplatin and pemetrexed
Cancer Gene Therapy (2012)