Abstract
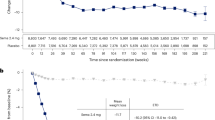
A double-blind, double-dummy, randomised, multicentre study to compare the efficacy and tolerability of lercanidipine with losartan. Patients with mild to moderate hypertension (supine diastolic blood pressure (DBP) 95–115 mm Hg) were enrolled and underwent a placebo run-in period of 14–30 days before random allocation to lercanidipine tablets 10 mg once-daily (n = 234) or losartan tablets 50 mg once-daily (n = 231) during the assessment period (approximately 16 weeks). Titration to lercanidipine 20 mg once-daily (two 10 mg tablets) or losartan 100 mg once-daily (two 50 mg tablets) was allowed after 8 weeks, if necessary. At the end of the study, 71% of patients who received lercanidipine tablets had achieved normalised DBP (ie, ⩽90 mm Hg) and 81% had responded to treatment (ie, DBP ⩽90 mm Hg or a decrease in DBP ⩾10 mm Hg). The corresponding numbers in the losartan tablets group were 65% and 78%, respectively. In those patients who required dose titration, there was evidence of a greater response with lercanidipine tablets than with losartan tablets. Both treatments were well tolerated with a low incidence of adverse drug reactions and a low withdrawal rate. In conclusion, the antihypertensive effects of lercanidipine tablets were comparable with those of losartan tablets; both treatments gave a high response rate for an antihypertensive monotherapy and were very well tolerated.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 digital issues and online access to articles
$119.00 per year
only $9.92 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ramsay LE et al. Guidelines for management of hypertension: report of the third working party of the British Hypertension Society J Hum Hypertens 1999; 13: 569–592
Circo A . Active dose findings for lercanidipine in a double-blind, placebo-controlled design inpatients with mild to moderate hypertension J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 1997; 29 (Suppl 2): S21–S25
Barbagallo M, Barbagallo-Sangiorgi G . Efficacy and tolerability of lercanidipine in monotherapy in elderlypatients with isolated systolic hypertension Aging (Milano) 2000; 12: 375–379
Herbette LG, Vecchiarelli M, Leonardi A . Lercanidipine: short plasma half-life, long duration of action. A molecular model to rationalize its pharmacokinetic properties J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 1997; 29 (Suppl 1): S19–S24
Morisco C, Trimarco B . Efficacy and tolerability of lercanidipine in comparison to and in combination with atenolol inpatients with mild to moderate hypertension in a double-blind controlled study J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 1997; 29 (Suppl 2): S26–S30
Notarbartolo A, Rengo F, Scafidi V, Acanfora D . Long-term effects of lercanidipine on the lipoprotein and apolipoprotein profile ofpatients with mild-to-moderate essential hypertension Cur Therapeut Res Clin Exper 1999; 60: 228–236
Barbagallo Sangiorgi G, Putignano E, Calcara L, Barbagallo M . Efficacy and tolerability of lercanidipine versus captopril inpatients with mild to moderate hypertension in a double-blind controlled study J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 1997; 29 (Suppl 2): S36–S39
Policicchio D, Magliocca R, Malliani A . Efficacy and tolerability of lercanidipine inpatients with mild to moderate essential hypertension: a comparative study with slow-release nifedipine J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 1997; 29 (Suppl 2): S31–S35
Goa KL, Wagstaff AJ . Losartan potassium: a review of its pharmacology, clinical efficacy and tolerability in the management of hypertension Drugs 1996; 51: 820–845
Chan JC et al. Randomised, double-blind, parallel group study of the antihypertensive efficacy and safety to losartan potassium compared with felodipine in elderlypatients with mild to moderate hypertension J Hum Hypertens 1995; 9: 765–771
Cafiero M, Giasi M . Long-term (12-month) treatment with lercanidipine inpatients with mild to moderate hypertension J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 1997; 29 (Suppl 2): S45–S49
Circo A . Active dose findings for lercanidipine in a double-blind, placebo-controlled design inpatients with mild to moderate hypertension J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 1997; 29 (Suppl 2): S21–S25
Hedner T et al. A comparison of the angiotensin II antagonists valsartan and losartan in the treatment of essential hypertension Am J Hypertens 1999; 12: 414–417
Borghi C et al. The use of lercanidipine can improve the individual tolerability to dihydropyridine calcium blockers in hypertensivepatients [abstract]. Tenth European Meeting on Hypertension; 2000 May 29–Jun 3; Göteborg, Sweden J Hypertens 2000; 18 (Suppl): S155
Kumar P, Clarke M (eds). Clinical Medicine 4th edition Harcourt Brace and Company: London 1998
Aranda P et al. Therapeutic efficacy and tolerability of lercanidipine versus candesartan, alone or in combination, in mild–moderate essential hypertensives [abstract] J Hypertens 2000; 18 (Suppl 2): S152
Sànchez A et al. Comparative evaluation of the antihypertensive efficacy and tolerability of lercanidipine and irbesartan [abstract] 4th European Meeting on Calcium Antagonists 1999; 27–29 Oct, Amsterdam
Acknowledgements
This study was sponsored by Napp Pharmaceuticals Limited. The authors would like to acknowledge the work of the other investigators in this study and the help of Mrs T Roberts, Mrs C O'Brien, Dr C McDonald, and Dr A Greenough for their help in preparing this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
James, I., Jones, A. & Davies, P. A randomised, double-blind, double-dummy comparison of the efficacy and tolerability of lercanidipine tablets and losartan tablets in patients with mild to moderate essential hypertension. J Hum Hypertens 16, 605–610 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.jhh.1001430
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.jhh.1001430