Abstract
Background: Recent hypertension trials have demonstrated the importance of achieving goal blood pressures to reduce the risk of target organ damage. In patients with moderate to severe hypertension, the use of high-dose monotherapy and/or combinations of drugs are necessary to achieve these goals. Fixed-dose combination products may be useful in these patients by reducing the number of daily doses required to control blood pressure.
Objective: The objective of the present study was to evaluate the efficacy and safety of a therapeutic interchange between high-dose calcium channel blocker therapy and a fixed-dose combination of amlodipine/ benazepril (Lotrel®; Novartis Pharmaceuticals, USA) in patients with moderate to severe hypertension.
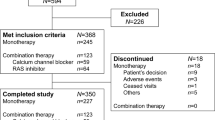
Methods: A total of 75 patients were switched from amlodipine (n = 25), felodipine (n = 25), and nifedipine-GITS (n = 25) to amlodipine/benazepril. Twenty-eight of the 75 patients (37%) were taking either a beta-blocker or a diuretic in addition to the high-dose calcium channel blocker prior to the switch. Blood pressure control, side effects and the cost of the therapeutic interchange were evaluated in the year following the therapeutic interchange.
Results: Sixty-six of the 75 (88%) patients were successfully switched with maintenance of blood pressure control and without the development of new dose-limiting side effects. Reasons for treatment failure after the therapeutic interchange included loss of blood pressure control in five patients and the development of new dose-limiting side effects in four patients. These side effects included cough in three patients and rash in one patient. After accounting for differences in drug acquisition cost and costs related to the switch (clinic and emergency room and laboratory tests), a cost savings of $16030 for all 75 patients was realised in the first year. The per patient-per year cost savings was $214.
Conclusions: Our data indicate that a therapeutic interchange from selected high-dose calcium channel blockers to a fixed-dose combination of amlodipine/ benazepril can be successfully accomplished in the majority of patients.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 digital issues and online access to articles
$119.00 per year
only $9.92 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hansson L et alEffects of intensive blood-pressure lowering and low-dose aspirin inpatients with hypertension: principal results of the Hypertension Optimal Treatment (HOT) randomized trial Lancet 1998 351 1755–1762
Hansson L et alEffect of angiotensin-converting-enzyme inhibition compared with conventional therapy on cardiovascular morbidity and mortality in hypertension: the Captopril Prevention Project (CAPP) Randomised Trial Lancet 1999 353 611–616
Sutton JM, Bagby SP Non-traditional combination pharmacotherapy of hypertension Clev Clin J Med 1992 59 459–468
Sakurai Y et alManagement of severe hypertension with nifedipine in combination with clonidine or propranolol Arzneimittelforschung 1980 30 674–678
Frishman WH et alComparison of amlodipine and benazepril monotherapy to amlodipine plus benazepril inpatients with systemic hypertension: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group study J Clin Pharmacol 1995 35 1060–1066
Price-Chek PT Version 2.16. St. Louis (MO). Medi-Span, Inc. 2000
Joint National Committee on Detection P, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Pressure The Sixth Report of the Joint National Committee on the Prevention, Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Pressure (JNC VI) Arch Intern Med 1997 157 2413–2446
Frishman WH et alA multifactorial trial design to assess combination therapy in hypertension: treatment with bisoprolol and hydrochlorothiazide Arch Intern Med 1994 154 1461–1468
Epstein M, Bakris G Newer approaches to antihypertensive therapy: use of fixed-dose combination therapy Arch Intern Med 1996 156 1969–1978
Gradman AH et alCombined enalapril and felodipine extended release (ER) for systemic hypertension Am J Cardiology 1997 79 431–435
Mohiuddin SM, Hilleman DE Substituting nifedipine-GITS for immediate-release calcium channel antagonist inpatients with stable angina pectoris Curr Ther Res 1991 50 546–552
Lorman L, Borysiuk L Replacing lovastin with pravastatin: effect on serum lipids and costs AJHP 1995 52 1078–1082
Nael H Formulary conversion from glipizide to glyburide: cost-minimization analysis Hosp Pharm 1995 30 467–469, 472–474
Oh T, Franko T Comprehensive therapeutic interchange program in a community hospital Am J Hosp Pharm 1991 48 1471–1478
Sotek AJ, Krofeod L Therapeutic interchange of fluoxetine and sertraline: experience in the clinical setting Am J Hosp Pharm 1994 52 2279–2281
Lindgren-Furmaga E, Schuna A, Wolf N Cost of switching hypertensivepatients from enalapril maleate to lisinopril Am J Hosp Pharm 1991 48 276–279
Rosen A, Kay B, Halecky D Implementing a therapeutic interchange program in an institutional setting PT 1995 20 711–717
Yusuf S et alEffects of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor, ramipril, on cardiovascular events in high-riskpatients. The Heart Outcomes Prevention Evaluation Study Investigators N Engl J Med 2000 342 145–153
Pahor M et alTherapeutic effects of calcium antagonists and other antihypertensive drugs Circulation 2000 102 (Suppl II) II–519
Hansson L et alRandomized trial of effects of calcium antagonists compared with diuretics and beta-blockers on cardiovascular morbidity and mortality in hypertension: the Nordic Diltiazem (NORDIL) Study Lancet 2000 356 359–365
Brown MJ et alMorbidity and mortality inpatients randomized to double-blind treatment with a long-acting calcium channel blocker or diuretic in the International Nifedipine-GITS Study: Intervention as a Goal in Hypertension Treatment (INSIGHT) Lancet 2000 356 366–372
ALLHAT Collaborative Research Group Major cardiovascular events in hypertensivepatients randomized to doxazosin vs chlorthalidone JAMA 2000 283 1967–1975
World Health Organisation-International Society of Hypertension Blood Pressure Lowering Treatment Trialists’ Collaboration Protocol for prospective collaborative overviews of major randomized trials of blood-pressure lowering treatments J Hypertens 1998 16 127–137
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hilleman, D., Reyes, A., Wurdeman, R. et al. Efficacy and safety of a therapeutic interchange from high-dose calcium channel blockers to a fixed-dose combination of amlodipine/benazepril in patients with moderate-to-severe hypertension. J Hum Hypertens 15, 559–565 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.jhh.1001230
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.jhh.1001230
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Systematic literature review of the methodology for developing pharmacotherapeutic interchange guidelines and their implementation in hospitals and ambulatory care settings
European Journal of Clinical Pharmacology (2019)
-
Efficacy of fixed-dose amlodipine and losartan combination compared with amlodipine monotherapy in stage 2 hypertension: a randomized, double blind, multicenter study
BMC Research Notes (2011)