Abstract
BACKGROUND: Obesity is frequently associated with an increase in the early inflammation marker C-reactive protein (CRP), insulin resistance and changes in lipoprotein metabolism. Increased CRP is known as an independent cardiovascular risk factor. Since the apolipoproteins (apo) E and CIII components of HDL are associated with reduced cardiovascular risk and since apoE has in vitro anti-inflammatory effect, we have investigated the relationships between apoE, apoCIII (in apoB and non apoB containing lipoproteins) and CRP in obese adults.
METHODS: The following parameters from 34 healthy obese fasting women (age 22–64 y, body mass index (BMI) 28–68 kg/m2) were measured: (1) ApoE and apoCIII, in total plasma, in apoB- (E LpB, CIII LpB) and non-apoB-containing lipoproteins (E LpnonB, CIII LpnonB); (2) CRP and cytokine secreted by adipose tissue (TNF-α and its soluble receptor TNFR2); (3) triglyceride, HDL-cholesterol, systolic blood pressure, diastolic blood pressure, waist and hip circumferences, insulin, glucose. HOMA, a marker of insulin sensitivity, and the ratio E/CIII in LpB and LpnonB were calculated.
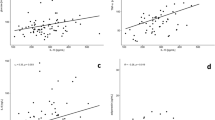
RESULTS: CRP was positively correlated with BMI (P<0.05), waist circumference (WC, P<0.05), triglyceride (P<0.05) and negatively correlated with apoE (P<0.01) and E LpnonB (P<0.05). Two multiple regression models including parameters related to CRP with a P<0.25 were run stepwise to assess their independent contribution to CRP concentration. In the first model (including BMI, WC, HOMA, insulin, triglyceride, apoE, E LpnonB), apoE was the best predictor of CRP (P=0.01) together with triglyceride (P=0.02) and BMI (P=0.08). The second model took into account E/CIII LpnonB ratio with the parameters included in the first model. In this second model, E/CIII LpnonB was the best predictor of CRP (P=0.007), explaining 39% of CRP variance.
CONCLUSION: ApoE is strongly correlated with CRP and could have an anti-inflammatory effect in vivo in obese subjects. This correlation could be limited to LpnonB lipoproteins, depending on their apoE and CIII relative content.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ford ES . Body mass index, diabetes, and C-reactive protein among U.S. adults Diabetes Care 1999 12: 1971–1977.
Visser M, Bouter LMMGM, Wener MH, Harris TB . Elevated C-reactive protein levels in overweight and obese adults JAMA 1999 282: 2131–2135.
Cook DG, Mendall MA, Whincup PH, Carey IM, Ballam L, Morris JE, Miller GJ, Strachan DP . C-reactive protein concentration in children: relationship to adiposity and other cardiovascular risk factor Atherosclerosis 2000 149: 139–150.
Hak AE, Stehouwer CD, Bots ML, Polderman KH, Schalkwijk CG, Westendorp IC, Hofman A, Witteman JC . Association of C-reactive protein with measures of obesity, insulin resistance and subclinical atherosclerosis in healthy, middle-aged women Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 1999 19: 1986–1991.
Yudkin JS, Stehouwer CD, Emeis JJ, Coppack SW . C-reactive protein in healthy subjects: associations with obesity, insulin resistance and endothelial dysfunction: a potential role for cytokines originating from adipose tissue? Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 1999 19: 972–978.
Danesh J, Muir J, Wong YK, Ward M, Gallimore JR, Pepys MB . Risk factors for coronary heart disease and acute-phase proteins. A population-based study Eur Heart J 1999 20: 954–959.
Ross R . Atherosclerosis—an inflammatory disease New Engl J Med 1999 340: 115–126.
Liuzzo G, Biasucci LM, Gallimore JR, Grillo RL, Rebuzzi AG, Pepys MB, Maseri AM . The pronostic value of C-reactive protein and serum amyloid a protein in severe unstable angina New Engl J Med 1994 331: 417–424.
Haverkate F, Thompson SG, Pyke SDM, Gallimore JR, Pepys MB . Production of C-reactive protein and risk of coronary events in stable and unstable angina Lancet 1997 349: 462–466.
Mendall MA, Patel P, Ballam L, Strachan D, Northfield TC . C-reactive protein and its relation to cardiovascular risk factors: a population based cross sectional study Br Med J 1996 312: 1061–1065.
Kern PA, Saghizageh M, Ong JM, Bosch RJ, Deem R, Simsolo RB . The expression of tumor necrosis factor in human adipose tissue. Regulation by obesity, weight loss and relationship to lipoprotein lipase J Clin Invest 1995 95: 2111–2119.
Torre-Amione G, Vooletich MT, Farmer JA . Role of tumor necrosis factor-alpha in the progression of heart failure: therapeutic implications Drugs 2000 59: 745–751.
Van der PT, van Deventer SJ, Hack CE, Wolbink GJ, Aarden LA, Buller HR, Ten Cate JW . Effects on leukocytes after injection of tumor necrosis factor into healthy humans Blood 1992 79: 693–698.
Hotamisligil GS, Budavari A, Murray DL, Spiegelman BM . Reduced tyrosine kinase activity of the insulin receptor in obesity diabetes: central role of tumor necrosis factor α J Clin Invest 1994 94: 1543–1549.
Hotamisligil GS, Armer P, Atkinson RL, Spiegelman BM . Differential regulation of the p80 tumor necrosis factor receptor in human obesity and insulin resistance Diabetes 1997 46: 451–455.
Hardardottir I, Grünfeld C, Feingold KR . Effects of endotoxin and cytokines on lipid metabolism Curr Opin Lipidol 1994 5: 207–215.
Kahn BB, Flier JS . Obesity and insulin resistance J Clin Invest 2000 106: 473–481.
Reaven GM . Role of insulin resistance in human disease Diabetes 1988 37: 1595–1607.
Austin MA . Plasma triglycerides and coronary heart disease Arterioscler Thromb 1991 11: 2–14.
Mahley RW . Plasma lipoproteins: apolipoprotein structure and function J Lipid Res 1984 25: 1277–1294.
Havel RJ, Kane JP, Kashyap ML . Interchange of apolipoproteins between chylomicrons and high density lipoproteins during alimentary lipemia in man J Clin Invest 1973 52: 32–38.
Berman M, Hall M, Levy RI, Eisenberg S, Bilheimer DW, Phair RD, Goebel RH . Metabolism of apoB and apoC lipoproteins in man: kinetics studies in normal and hyperlipoproteinemic subjects J Lipid Res 1978 19: 38–56.
Blum CB . Dynamics of apoE metabolism in humans J Lipid Res 1982 23: 1308–1316.
Eisenberg S, Olivecrona T . Very low Density lipoprotein. Fate of phospholipids, cholesterol and apolipoprotein C during lipolysis in vitro J Lipid Res 1979 20: 614–623.
Nestel PJ, Huff MW, Billington T, Fidge NH . Changes in the plasma lipoprotein distribution of apolipoprotein CII, CIII1, CIII2 and apoB after heparin-induced lipolysis Biochim Biophys Acta 1982 712: 94–102.
Gibson JC, Brown WV . Effect of lipoprotein lipase and hepatic triglycerides lipase activity on the distribution of apolipoprotein E among the plasma lipoproteins Atherosclerosis 1988 75: 45–55.
Jeppensen J, Hollenbeck CB, Zhou MY, Coulston AM, Jones C, Chen YD, Reaven GM . Relation between insulin resistance, hyperinsulinemia, postheparin plasma lipoprotein lipase activity and postprandial lipemia Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 1995 15: 320–324.
Che YD, Facchini F, Landau C, Hollenbeck CB, Reaven GM . Plasma postheparin lipoprotein lipase activity is decreased in normal individuals who are resistant to insulin mediated glucose uptake Endocrinol Metab 1994 1: 153–158.
Bard JM, Charles MA, Juhan-Vague I, Vague P, André P, Safar M, Fruchart JC, Eschwège E, on behalf of the BIGPRO study group . Accumulation of triglycerides-rich lipoproteins in subjects with abdominal obesity. The biguanides and the prevention of the risk of obesity (BIGPRO)1-study Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 2001 21: 407–414.
Blankenhorn DH, Alaupovic P, Wickham E, Chin HP, Azen SP . Prediction of angiographic change in native human coronary arteries and aortocoronary bypass grafts Circulation 1990 81: 470–476.
Hodis HN, Mack WJ, Azen SP, Alaupovic P, Podoga JM, Labree L, Hemphill LC, Kramsch DM, Blakenhorn DH . Triglyceride- and cholesterol-rich lipoproteins have a differential effect on mild/moderate and severe lesion progression as assessed by quantitative coronary angiography in a controlled trial of lovastatin Circulation 1994 90: 42–49.
Shimano H, Yamada N, Katsuki M, Yamamoto K, Gotoda T, Harada K, Shimada M, Yazaki Y . Plasma lipoprotein metabolism in transgenic mice overexpressing apolipoprotein E. Accelerated clearance of lipoproteins containing apolipoprotein B J Clin Invest 1992 90: 2084–2091.
Nikouli IR, Curtiss LK . An apolipoprotein E synthetic peptide targets to lipoproteins in plasma and mediates both cellular lipoprotein interactions in vitro and acute clearance of cholesterol-rich lipoproteins in vivo J Clin Invest 1998 101: 223–234.
Zhu Y, Bellosta S, Langer C, Bernini F, Pitas RE, Mahley RW, Assman G, Eckardstein AV . Low dose expression of a human apolipoprotein E transgene in macrophages restores cholesterol efflux capacity of apolipoprotein E-deficient mouse plasma Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1998 95: 7585–7590.
Boisvert WA, Black AS, Curtiss LK . Apolipoprotein AI reduces free cholesterol accumulation in atherosclerotic lesions of apoE-deficient mice transplanted with apolipoprotein E-expressing macrophages Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 1999 19: 525–530.
Zhang SH, Reddick RL, Piedrarita JA, Maeda N . Spontaneous hypercholesterolemia and arterial lesions in mice lacking apolipoprotein E Science 1992 258: 468–472.
Plump AS, Smith JD, Hayek T, Aalto-Setälä K, Walsh A, Verstuyft JG, Rubin EM, Breslow JL . Severe hypercholesterolemia and atherosclerosis in apoE deficient mice created by homologous recombinaison in ES cell Cell 1992 71: 343–353.
Piedrarita JA, Zhang SH, Hagamon JR, Oliver PM, Maeda N . Generation of mice carrying a mutant apolipoprotein E gene inactivated by gene targeting in embryonic stem cells Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1992 89: 4471–4475.
Hasty AH, Linton MF, Swift LL, Fazio S . Determination of the lower threshold of apolipoprotein E resulting in remnant lipoprotein clearance J Lipid Res 1999 40: 1529–1538.
Arai T, Rinninger F, Varban L, Fairchild-Huntress V, Liang C-P, Chen W, Seo T, Deckelbaum R, Huszar D, Tall AR . Decreased selective uptake of high density lipoprotein cholesteryl esters in apolipoprotein E knock-out mice Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1999 96: 12050–12055.
Schaefer EJ, Gregg RE, Ghiselli G, Forte TM, Ordovas JM, Zech LA, Brewer HB . Familial apolipoprotein E deficiency J Clin Invest 1986 78: 1206–1219.
Scheer WD, Boudreau DA, Malcom GT, Middaugh JP . Apolipoprotein E and atherosclerosis in Alaska natives Atherosclerosis 1995 114: 197–202.
Klezovitch O, Formato M, Cherchi GM, Weissgraber KH, Scanu AM . Structural determinants in the C-terminal domain of apolipoprotein E mediating binding to the protein core of human aortic biglycan J Biol Chem 2000 275: 18913–18918.
Paka L, Goldberg IJ, Obunike JC, Choi SY, Saxena U, Goldberg ID, Pillarisetti S . Perlecan mediates the anti proliferative effect of apolipoprotein E on smooth muscle cells J Biol Chem 1999 274: 36403–36408.
Pepe MG, Curtiss LK . ApoE is a biologically active constituent of the normal immunoregulatory lipoprotin, LDL-in J Immunol 1986 3716: 3723.
Ishigami M, Swertfeger DK, Granholm NA, Hui DY . Apolipoprotein E inhibits platelet derived growth factor-induced vascular smooth muscle cell migration and proliferation by suppressing signal transduction and preventing cell entry to G1 phase J Biol Chem 1998 273: 20156–20161.
Barger SW, Harmon AD . Microglial activation by Alzheimer amyloïd precursor protein and modulation by apolipoprotein E Nature 1997 388: 878–881.
La Du MJ, Shah JA, Reardon CA, Getz GS, Bu G, Hu J, Guo L, Eldik LJV . Apolipoprotein E receptor mediates the effects of β-amyloid on astrocyte cultures J Biol Chem 2000 275: 33974–33980.
Desai K, Bruckdorfer R, Hutton RA, Owen JS . Binding of apolipoprotein E-rich high density lipoprotein particles by saturable sites on human blood platelets inhibits agonist-induced platelet aggregation J Lipid Res 1989 30: 831–840.
Zhou MY, Paulsson G, Hansson GK . Hypercholesterolemia is associated with a T helper (Th)1/Th2 switch of the auto-immune response in atherosclerotic apoE-knockout mice J Clin Invest 1998 101: 1717–1725.
Friedewald WT, Levy RI, Fredrickson DS . Estimation of the concentration of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol in plasma, without use of the preparative ultracentrifuge Clin Chem 1972 18: 499–502.
Matthews DR, Hosker JP, Rudenski AS, Naylor BA, Treacher DF, Turner RC . Homeostatic model assessment: insulin resistance and β cell function from fasting glucose and insulin concentrations in man Diabetologia 1985 28: 412–419.
Alaupovic P, McConathy WJ, Fesmire J, Tavella M, Bard JM . Profiles of apolipoproteins and apolipoprotein B-containing lipoprotein particles in dyslipoproteinemia Clin Chem 1988 34 (8B): B13–B27.
Menzel H-J, Utermann G . Apolipoprotein E phenotyping from serum by Western Blotting Electrophoresis 1986 7: 492–495.
Kelly ME, Clay MA, Mistry MJ, Hsieh-li HM, Harmony JAK . Apolipoprotein E inhibition of proliferation of mitrogen-activated T lymphocytes: production of Interleukine 2 with reduced biological activity Cell Immunol 1994 159: 124–139.
Song H, Saito K, Fujigaki S, Noma A, Ishiguro H, Nagatsu T, Seishima M . II-1β and TNFα suppress apolipoprotein (apo) E secretion and apo-AI expression in HepG2 cells Cytokine 1998 10: 275–280.
Panichi V, Migliori M, De Pietro S, Taccola D, Andreini B, Metelli MR, Giovannini L, Palla R . The link of biocompatibility to cytokine production Kidney Int 2000 58: 96–103.
Mahley RW . Apolipoprotein E: from atherosclerosis to Alzheimer's disease and beyond Curr Opin Lipidol 1999 10: 207–217.
Curtiss LK, Boisvert WA . Apolipoprotein E and atherosclerosis Curr Opin Lipidol 2000 11: 243–251.
Mazzone T . Apolipoprotein E secretion by macrophages: its potential physiological functions Curr Opin Lipidol 1996 7: 303–307.
Yudkin JS, Kumari M, Humphries SE, Mohamed-Ali V . Inflammation, obesity, stress and coronary heart disease: is interleukine-6 the link? Atherosclerosis 2000 148: 209–214.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by la Direction de la Recherche Clinique University Hospital, CHU Hôtel-Dieu, Nantes, France.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bach-Ngohou, K., Nazih, H., Nazih-Sanderson, F. et al. Negative and independent influence of apolipoprotein E on C-reactive protein (CRP) concentration in obese adults. Potential anti-inflammatory role of apoE in vivo. Int J Obes 25, 1752–1758 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ijo.0801833
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ijo.0801833
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Body fat and circulating leukocytes in children
International Journal of Obesity (2006)
-
Qualitative and quantitative effects of APOE genetic variation on plasma C-reactive protein, LDL-cholesterol, and apoE protein
Genes & Immunity (2006)
-
Apolipoprotein E kinetics: influence of insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes
International Journal of Obesity (2002)