Abstract
OBJECTIVE: The purpose of the present study was to investigate the continuing validity of the hypothesis that leptin is a physiologically important regulator of food intake, using the human leptin mutant R128Q leptin.
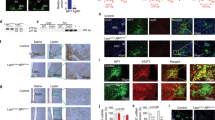
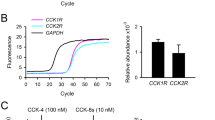
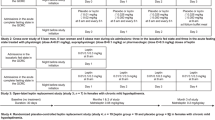
DESIGN: In a cellular proliferation assay, based on BAF-3 cells transfected with the murine ObRb receptor, R128Q leptin was shown to be devoid of agonistic activity and to competitively inhibit the proliferative effects of leptin. To determine whether R128Q leptin was also an antagonist of leptin in vivo, the leptin mutant was injected intracerebroventricularly (i.c.v.) into rats in the absence and presence of leptin. R128Q was also injected intraperitoneally (i.p.) into ob/ob and into db/db mice expressing, respectively, either normal or defective ObRb receptors.
RESULTS: R128Q was shown to be a competitive antagonist of leptin induced cellular proliferation in vitro. Surprisingly, in vivo R128Q leptin produced a strong dose-dependent decrease in food intake, and was only slightly less potent than leptin itself. In fasted rats, the inhibitory effects of leptin and R128Q leptin (i.c.v.) on post-fast refeeding were additive. Finally, R128Q leptin produced the same inhibition of food intake as leptin when injected i.p. in ob/ob mice and, like leptin, was inactive after i.p. injection to db/db mice.
CONCLUSION: R128Q leptin is a leptin agonist in vivo, but behaves as an antagonist against leptin induced proliferation in vitro. The data demonstrate that the human leptin mutant R128Q leptin is not a suitable tool for investigating the physiological actions of leptin.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Brunner, L., Whitebread, S., Leconte, I. et al. A peptide leptin antagonist reduces food intake in rodents. Int J Obes 23, 463–469 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ijo.0800842
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ijo.0800842