Abstract
Molecular and stable isotope compositions of hydrate-bound gases collected from 59 hydrate-bearing sites between 2005 to 2019 in the southern and central sub-basins of Lake Baikal are reported. The δ2H of the hydrate-bound methane is distributed between − 310‰ and − 270‰, approximately 120‰ lower than its value in the marine environment, due to the difference in δ2H between the lake water and seawater. Hydrate-bound gases originate from microbial (primary and secondary), thermogenic, and mixed gas sources. Gas hydrates with microbial ethane (δ13C: − 60‰, δ2H: between − 310‰ and − 250‰) were retrieved at approximately one-third of the total sites, and their stable isotope compositions were lower than those of thermogenic ethane (δ13C: − 25‰, δ2H: − 210‰). The low δ2H of ethane, which has rarely been reported, suggests for the first time that lake water with low hydrogen isotope ratios affects the formation process of microbial ethane as well as methane. Structure II hydrates containing enclathrated methane and ethane were collected from eight sites. In thermogenic gas, hydrocarbons heavier than ethane are biodegraded, resulting in a unique system of mixed methane-ethane gases. The decomposition and recrystallization of the hydrates that enclathrate methane and ethane resulted in the formation of structure II hydrates due to the enrichment of ethane.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
Natural gas hydrate enclathrated hydrocarbons occur in marine/lacustrine sediments and sub-permafrost layers. Natural gas hydrates are not only a potential future energy resource1,2,3,4 but also a large reservoir of methane (C1), the second most important greenhouse gas5,6. Gas hydrates are crystalline compounds in which guest molecules are enclathrated in water cages constructed by hydrogen bonds. The differences in the crystal structure caused by the combination of cages of different sizes affect their physicochemical properties, such as hydration number, cage occupancies, and dissociation heat. Three crystallographic structures of natural gas hydrates have been identified as: cubic structure I (sI), cubic structure II (sII), and hexagonal structure H (sH)7,8. sI comprises dodecahedral (512) and tetrakaidecahedral (51262) cages, whereas sII is composed of 512 and hexakaidecahedral (51264) cages. sH has a large icosahedral (51268) cage in its unit cell and can encapsulate larger guest molecules.
Natural hydrocarbon gases can be primarily classified as biogenic or abiogenic gases. Biogenic gases are further divided into two types: microbial and thermogenic. Microbial gases mainly consist of C1 produced under anaerobic conditions by methanogens classified as archaea, and two pathways are known: CO2 reduction and methyl-type fermentation. In contrast, thermogenic gases are produced by the thermal cracking of organic matter in deep sediment layers and contain heavier hydrocarbons, such as ethane (C2), propane (C3), and butane (C4). Additionally, secondary microbial gases produced by microbes during biodegradation of petroleum appear more abundant than primary microbial gases9. To estimate the origin of natural hydrocarbon gases, diagrams have been proposed and refined using the molecular ratio of heavier hydrocarbons to C1 and their carbon isotope ratios10,11,12,13. Recently, a web-based tool was developed to determine the origin of natural gas using machine-learning models14.
C1 is the main component of guest gases in natural gas hydrates found in marine/lacustrine sediments worldwide. It mostly comprises microbial C1 from CO2 reduction, with very few other hydrocarbon components, such as C2 and C3, which generally comprise less than 0.1%15,16,17,18,19. Pure C1 hydrates form sI; thus, the majority of natural gas hydrates found to date belong to sI15.
Cubic structure II (sII) has been discovered in the Caspian Sea20, Gulf of Mexico21, and Sea of Marmara22. Also natural sH hydrates have been retrieved: (1) in the Gulf of Mexico as suggested by the molecular composition of hydrate-bound gases23, and (2) off Vancouver Island, Canada, they were directly confirmed by powder X-ray diffraction and 13C nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy8. Because the cages in sII and sH are larger than those in sI, they can enclathrate C3, C4, and even larger hydrocarbon molecules. For example, the guest gas in the Gulf of Mexico24 contained nearly 15% C3, whereas samples from the Sea of Marmara22 contained approximately 19% C3 and 10% isobutane (i-C4, 2-methylpropane). sH samples from offshore Vancouver Island8 enclathrated methylcyclopentane and methylcyclohexane. Though predominantly methane, thermogenic gases contain large amounts of C2, C3, and C4, and these heavier hydrocarbons decrease the equilibrium pressure of the mixed-gas hydrate and stabilize the system of mixed-gas hydrates7. Molecular fractionation also occurs during gas hydrate crystallization and affects the molecular composition of hydrate-bound gases25,26. Therefore, differences in the molecular composition of natural gas due to their origin determine the diversity of the crystallographic structure of natural gas hydrates.
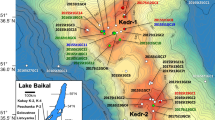
Lake Baikal is divided into three sub-basins: southern, central, and northern. The southern and central sub-basins are separated by the Selenga Delta accommodation zone, and the central and northern sub-basins are separated by the Olkhon Island and the Academician Ridge. During the 1997 Baikal Drilling Project (BDP), gas hydrates were first discovered in sediments at depths of 121 m and 161 m below the lake bed in the southern sub-basin27. Subsequently, researchers have reported that near-surface gas hydrates exist at depths of up to several meters below the lake bottom in the southern and central sub-basins28,29,30,31,32,33,34,35.
In particular, the sII discovered in the Kukuy Canyon (central sub-basin) was a C1 and C2 mixed gas hydrate that contained thermogenic gas but few C3, C4, or larger hydrocarbon molecules31. Laboratory experiments have shown that C1 and C2, both of which are sI-formers, form sII in a mixed system36,37. Because Lake Baikal is the only known place where sII of C1 + C2 systems exist, further studies are needed to determine how such a system occurs.
The authors continuously investigated near-surface gas hydrates in Lake Baikal within the framework of the multi-phase gas hydrate project (MHP) from 2009 to 2019. Of the 60 hydrate-bearing structures discovered by 2019 (Fig. 1), 48 sites were discovered by the MHP38,39. The water depths at sites where gas hydrates were recovered range from 396 m (Goloustnoe) to 1508 m (Novosibirsk-2)38. In this study, all gas data obtained so far in the MHP, along with previously reported hydrate-bound gas data33,40,41,42, were analyzed to understand the origin of hydrate-bound gases and their diversity in Lake Baikal.
Results
The gas analysis results are shown in Figs. 2 and 3. These data were obtained from 668 hydrate-bound gas samples collected at each site and the median value for each site was plotted. Of these samples, 479 were analyzed in this study, while the others, i.e. 93 and 96, respectively, were analyzed in previous works33,41. For the eight sites where double structure (sI and sII) gas hydrates were obtained, inferred crystallographic structures are specified on the graph. The mixing lines between the microbial and thermogenic origins in Fig. 2a,c are plotted for C1 δ13C, C2 δ13C, and C1/(C2 + C3), with assumed end members, respectively, of − 67‰, − 65‰, and 100,000 for microbial origin, and − 44‰, − 25‰, and 20 for thermogenic origin.
Empirical diagrams of hydrate-bound gases. (a) C1/(C2 + C3) plotted against C1 δ13C, based on the classification of Milkov and Etiope13; (b) C1 δ2H plotted against C1 δ13C, based on the classification of Milkov and Etiope13; and (c) C2 δ13C plotted against C1 δ13C, based on the classification of Milkov15. The data for Malenky, Bolshoy, Malyutka, P-2, K-0, K-2 and Goloustnoe are sourced partly from Hachikubo et al.33. The data for Kedr and Kedr-2 are sourced partly from Hachikubo et al.41.
Stable isotope compositions of C2 and C3. (a) Relation between C2 δ2H and C2 δ13C. (b) Relation between C3 δ13C and C2 δ13C. The data for Malenky, Bolshoy, Malyutka, P-2, K-0, K-2 and Goloustnoe are sourced partly from Hachikubo et al.33. The data for Kedr and Kedr-2 are sourced partly from Hachikubo et al.41.
Figure 2a shows the relationship between C1 δ13C and C1/(C2 + C3) plotted in the empirical diagram13. More than 20 of the 60 total sites have C1 δ13C between − 68‰ and − 65‰ and C1/(C2 + C3) concentrated around 1000–5000, which means that microbial gas is enclathrated in more than one-third of the hydrate-bearing sites in Lake Baikal. However, along the mixing line from the microbial to thermogenic regions, C1 δ13C increases with a decrease in C1/(C2 + C3), passing through the mixed region of microbial and thermogenic gases to thermogenic gas (e.g., K-4, PosolBank, Kedr, and Kedr-2). For the eight sII hydrate data points, C1/(C2 + C3) is nearly constant at 6–7. Furthermore, C1 δ13C seems independent of the crystallographic structure at the same sites but differs considerably in K-3 and K-pockmark. This is because the hydrate-bearing sediment cores are different, even at the same site, indicating that the characteristics of the hydrate-bound gas can change markedly with slight differences in location. Gorevoy Utes43,44 is one of the two oil seep sites and plots in the field of secondary microbial gas (Fig. 2a)9. Another point, ZelenSeep, also plots near the Gorevoy Utes. Most of the data plotted for the thermogenic origin overlap with the field of secondary microbial gas.
Figure 2b shows the relationship between C1 δ13C and C1 δ2H, which is also plotted in an empirical diagram13. The isotopic fractionation of C1 between the gas and hydrate phases is negligible when considering gas origins using a diagram45. C1 δ13C tends to increase with C1 δ2H. In a diagram by Whiticar12, hydrate-bound C1 in Lake Baikal is interpreted to be of microbial origin via methyl-type fermentation31,32,33,46. However, the latest diagram by Milkov and Etiope13 shows that most of the C1 δ13C values below − 60‰ overlap completely with the microbial origin via CO2 reduction and may possibly be of an early mature origin. Therefore, it is difficult to determine the origin of C1 in Fig. 2b.
Figure 2c shows the relationship between C1 δ13C and C2 δ13C plotted on an empirical diagram15. All data are distributed in an "L" shape along the mixing line. This is because the composition of C2 in the microbial gas is so small that even a small amount of thermogenic gas with a large C2 composition can considerably affect and increase C2 δ13C during the mixing of microbial and thermogenic gases. As shown in Fig. 2c, hydrate-bound gases of natural gas hydrates in Lake Baikal can be classified into three categories: (1) both C1 and C2 of microbial origin, (2) C1 primarily of microbial origin, C2 primarily of thermogenic origin, and (3) both C1 and C2 of thermogenic origin.
Figure 3a shows that the relationship between C2 δ13C and C2 δ2H is similar to that in Fig. 2b for C1. This diagram was first proposed by Hachikubo et al.33, who showed that both C2 δ13C and C2 δ2H in P-2 were relatively lower than those at other sites (approximately − 60‰ and − 285‰, respectively). The amount of data increased over the next 10 years of investigation, and it is mostly concentrated in the area of the diagram interpreted as thermogenic C2 (C2 δ13C: − 25‰, C2 δ2H: − 210‰). In contrast, a group of C2 δ13C of approximately − 60‰, which corresponds to microbial C2, has low C2 δ2H ranging from − 310‰ to − 250‰. Therefore, the C2 δ2H of microbial gas is apparently lower than that of the thermogenic gas.
Figure 3b shows the relationship between C2 δ13C and C3 δ13C. The thermogenic gases are concentrated at approximately − 25‰ and − 10‰ for C2 δ13C and C3 δ13C, respectively. Based on the empirical diagram15, the value of C2 δ13C at approximately − 42‰ is interpreted as an approximate boundary between microbial and thermogenic C2. C3 δ13C is above 0‰ in K-2 (sI), K-4 (sI and sII), K-10 (sI and sII), K-pockmark (sI), St. Petersburg, Krest, and Seep13 in the field of thermogenic C2. In contrast, C3 δ13C is generally below − 30‰ in the field of microbial C2.
Discussion
Structure II hydrates in Lake Baikal
The sII hydrates from the Gulf of Mexico and Sea of Marmara contained large amounts (> 10%) of C3 and C4, whereas in Lake Baikal the ratio of C3 and C4 in the hydrate-bound gas is < 0.5% in the sII hydrates (Table S1). Therefore, C1 and C2 mixed-gas systems are responsible for the appearance of sII in Lake Baikal. Pure C1 and C2 hydrates each form sI, but in C1 and C2 mixed-gas systems, sII appears at certain mixing ratios36,37. In Lake Baikal, sII hydrates, in which the hydrate-bound gas was 85% C1 and 15% C2, were retrieved at Kukuy K-2 in 200531,32,33,46. Generally, the sII hydrate is adjacent to the sI hydrate with 1–4% C2, forming a "double structure". Current understanding of the process is that the formation processes of double-structure gas hydrates in Lake Baikal have been discussed extensively34,46,47,48. The formation of sI hydrates blocked the gas supply channel, causing dissolution of sI hydrates and secondary formation of sII hydrates by enrichment of C2 from the dissociated gas34,47. A detailed investigation of the sII hydrates at Kedr and Kedr-2 revealed that besides C2 also C3, i-C4, n-butane (n-C4), and neopentane (neo-C5, 2,2-dimethylpropane) are enriched in the crystals41. The sII hydrates are identified at eight sites: Kukuy K-2, K-3, K-4, K-10, and K-pockmark in the central sub-basin and PosolBank, Kedr, and Kedr-2 in the southern sub-basin. The C1/(C2 + C3) ratios of these hydrate-bound gases are concentrated at approximately 6–7 (Fig. 2a), and the contribution of C3 is negligible compared to that of C2 (Table S1). The homogeneous gas composition of sII hydrates over a wide area of Lake Baikal can be explained by the decomposition processes of C1 and C2 mixed gas hydrates and the concentration of C241,49.
The C1 and C2 mixed-gas system that gives rise to sII hydrates in Lake Baikal is established by the relative depletion of heavier hydrocarbons, such as C3 and C4 (Table S1). For example, in Kedr and Kedr-2, the maximum compositions of C3, i-C4, n-C4, and neo-C5 in the hydrate-bound gas were 0.3% and 270, 25, and 540 ppm, respectively41. These low compositions are likely due to biodegradation. In the area of Fig. 3b where C2 is of thermogenic origin (δ13C > − 42‰), C3 δ13C is widely distributed from − 20 to + 10‰, suggesting the effect of biodegradation. For example, C3 is selectively affected by microbial alteration and exhibits anomalous C3 δ13C50. C1-rich dry gas, large C1 δ13C (− 55‰ to − 35‰), and large CO2 δ13C (> + 2‰) have been proposed as characteristics of secondary microbial C19. The molecular and stable isotope compositions of CO2 in the hydrate-bound gas are unknown; however, the CO2 δ13C in the sediment gas around the hydrate crystals reaches + 20‰ (Kedr) and + 30‰ (Kedr-2)41, indicating the generation of secondary microbial C1. With two exceptions (Kukuy K-2 and K-10), the hydrate-bound gases of the sII crystals plot in the area of secondary microbial gases in Fig. 2a. Thus, at most sites in Lake Baikal, where thermogenic gas is supplied from a deeper sediment layer, hydrocarbons heavier than C3 are selectively and microbially degraded, resulting in the appearance of C1 and C2 mixed gas, further dissociation of sI hydrate, and the formation of sII hydrate adjacent to sI.
Hydrogen isotope compositions of methane in hydrate-bound gas
The C1 δ2H of hydrate-bound gas in marine sediments is generally concentrated between approximately − 200‰ to − 190‰ for microbial gas and is greater for thermogenic gas, reaching approximately − 140‰ for gas hydrates retrieved offshore of Vancouver Island and Costa Rica15. The distribution of C1 δ2H of the thermogenic gas ranges from − 300‰ to − 100‰11 and from − 350‰ to − 100‰13. In addition, C1 δ2H tends to increase with C1 δ13C11,12. The factors that determine the C1 δ2H of thermogenic gas have not yet been clarified; however, it can be assumed that hydrogen isotope exchange occurs between C1 and environmental water. Based on the effect of temperature on the hydrogen isotope fractionation between C1 and hydrogen, and between hydrogen and water51, the hydrogen isotope fractionation between C1 and water can be expected to be smaller at higher temperatures. If the thermogenic gas produced by the decomposition of organic matter exchanges isotopically with environmental water during decomposition, the C1 δ2H of thermogenic gas in the deep sediment layers becomes greater than that of microbial gas produced in shallower sediment layers.
The C1 δ2H of hydrate-bound gas in Lake Baikal is generally concentrated around − 310‰ for microbial gas and increases to − 280‰ to − 270‰ for gases of thermogenic origin (Fig. 2b). The difference in C1 δ2H between the seawater and freshwater environments is approximately + 120‰. The δ2H of lake bottom water is reported to be − 123 ± 2‰52, whereas the δ2H of seawater is approximately 0‰ as a standard hydrogen stable isotope. Accordingly, the difference in C1 δ2H between them can be attributed to the difference in the δ2H of the environmental water.
Two processes are involved in the formation of microbial C1: CO2 reduction and methyl-type fermentation. Previously, it was thought that the hydrogen in C1 is derived from environmental water via CO2 reduction, whereas a certain percentage of hydrogen is derived from the original organic matter via methyl-type fermentation12,53. Based on this, a diagram12,53 was proposed that could discriminate between CO2 reduction and methyl-type fermentation by C1 δ2H. It was considered a useful method for evaluating the origin of C1. However, it has been suggested that, even for C1 produced via methyl-type fermentation, the hydrogen in C1 is exchanged with water in the environment54,55. Therefore, C1 δ2H strongly reflects the information of environmental water, and the C1 δ2H of natural gas hydrates in Lake Baikal (freshwater environment) is interpreted to be distinct from natural gas hydrates from seawater due to the difference in the δ2H of water (0‰ for seawater compared to − 123‰ for lake water).
In Fig. 2b, the group with C1 δ2H in the range of − 298‰ to − 281‰ and C1 δ13C in the range of − 70‰ to − 63‰ is distinct from the other microbial plots. Except for Belkamen, Tonky, K-12, and Solzan, eight of these sites belong to the Gydratny and Olkhon faults in the central sub-basin. Although the details are unknown, it is possible that the origin of the water involved in methanogenesis in these fault systems differs from those at other sites. Gorevoy Utes is an oil seep site43,44, with C1 δ13C of − 45‰ and C1 δ2H of − 308‰, and is plotted farther away from the other areas (Fig. 2b). It is outside the thermogenic area with a C1/(C2 + C3) ratio of 274 (Fig. 2a) and small compositions of C2 and C3, indicating the effect of secondary microbial gas. Anaerobic biodegradation of heavier hydrocarbons likely results in this gas composition44. However, the very low C1 δ2H of the Gorevoy Utes cannot be explained at this stage. ZelenSeep42 is also an oil seep site, and its characteristics for hydrate-bound gas are similar to those of the Gorevoy Utes (Fig. 2a,b).
Microbial ethane and propane
Although information on ethanogens is still scarce, ethane with a small δ13C (< − 40‰) suggests an in situ microbial origin56. Experiments on biologically generated hydrocarbons in anaerobic sediments showed lower C2 δ13C values, ranging from − 55‰ to − 35‰57. The method of C2 formation by ethanogens is not yet understood; however, a process involving the reduction of acetic acid has been proposed58. Ethanogens are considered less competitive than methanogens59, therefore C2 compositions are very low compared to C1 compositions. In this study, the sites in the area of microbial C2 in Fig. 2c corresponded to sites where C1/(C2 + C3) was generally above 1000 (Fig. 2a).
There are several reports of microbial C2 in hydrate-bound gases in other marine areas. Charlou et al.60 analyzed gas hydrates collected in the Congo-Angola Basin and reported a C2 δ13C of − 61.4‰ for hydrate-bound gas. Milkov et al.61 reported stable isotope compositions of hydrate-bound gas collected during the Ocean drilling Program (ODP) Leg 204 at the Hydrate Ridge offshore Oregon and found C2 δ13C in the range between − 50‰ and − 30‰. Sassen and Curiale16 reported a C2 δ13C value of − 52.6‰ in hydrate-bound gas collected from the Makassar Strait in Indonesia, which they attributed to microbial C2. Lorenson and Collett62 analyzed the void gas and gas in pressure cores obtained from gas hydrate accumulation areas in the Bay of Bengal and reported a C2 δ13C of − 64‰ to − 52‰. Microbiological experimental work with Lake Baikal sediments showed the possibility of producing C2 as well as C1 by microbes63. Therefore, there are many cases in which microbial C2 produced in situ in shallow sediment layers is enclathrated into hydrate crystals. Figure 2c shows that there are 21 sites where gas hydrates enclathrate microbial C2, which represents approximately one-third of the total 60 hydrate-bearing sites in Lake Baikal.
Little is known regarding the hydrogen isotope ratios of microbial C2. Figure 3a presents valuable information on C2 δ2H in hydrate-bound gases, following a previous study33. Stable isotope compositions of thermogenic C2 concentrate with C2 δ13C and C2 δ2H values of approximately by − 25‰ and − 210‰, respectively, and C2 δ2H decreases with C2 δ13C. Microbial C2 is widely distributed, with C2 δ13C ranging from − 70‰ to − 60‰ and C2 δ2H from − 310‰ to − 250‰. This trend is similar to the relationship between C1 δ13C and C1 δ2H, suggesting that lake water with low hydrogen isotope ratios is also involved in the formation of microbial C2.
Although little information is available on microbial C3, a mechanism has been proposed by Hinrichs et al. for its formation from acetate and hydrogen58, in which it has been noted that C3 δ13C was greater than C2 δ13C, and Fig. 3b satisfies this relationship. In the area of microbial C2 where C2 δ13C is below − 42‰, C3 δ13C is also relatively low, ranging from − 40‰ to − 30‰, indicating that microbial C3 is more depleted in13C than thermogenic C3.
The reason for the presence of C3 in the samples of hydrate-bound gas of sI, even if only a small percentage, is still unclear. Due to its molecular size, C3 cannot be enclathrated in the 51262 cages of sI, but it can be enclathrated in the 51264 cages of sII. Therefore, it is possible that C3 adsorbs onto sediment particles and/or gas hydrate crystals and can be encaged if a small amount of sII crystals are present.
Origin of hydrate-bound gas in Lake Baikal
Based on the characteristics of the molecular and isotopic compositions of hydrate-bound gases, the origin of the hydrate-bound gases in Lake Baikal is discussed from a geological perspective. The hydrate-bound gases in Lake Baikal can be classified into three main categories:
-
(1)
Thermogenic gas derived from crude oil, in some cases accompanied by secondary microbial gas;
-
(2)
Thermogenic gas rising up from deep sedimentary layers through faults, mixed with microbial gas in shallow layers;
-
(3)
Microbial gas formed in shallow sedimentary layers.
Each category can be associated to specific geological and geographical environments of Lake Baikal. Geological factors that affect gas hydrate formation in the central sub-basin are large amounts of deltaic deposits submitted to significant heating, the presence/absence of major faults, and oil seeping into the subsurface sediments. Oil seepage at the lake floor has been reported at two sites in the central sub-basin: Gorevoy Utes43,44 and ZelenSeep42. The hydrate-bound gases in these locations are of thermogenic origin, although there are signs of anaerobic biodegradation44 and of the influence of secondary microbial gas. The Selenga Delta is located in the southern part of the central sub-basin. It has the thickest lake sediment in Lake Baikal, of approximately 9 km, with abundant organic matter and it experiences frequent earthquakes. Hydrate-bound gases in the Kukuy Canyon (K-0 to K-17, Fig. 1) consist of thermogenic gases supplied from deeper sedimentary layers mixed with microbial gases in shallow layers at various mixing ratios. As mentioned previously, the C1 δ2H is greater at Seep 13, Krest, Unshuy, Uhkhan, Novosibirsk, Novosibirsk-2, St. Petersburg, and St. Petersburg-2 in the central sub-basin than at other sites (Fig. 2b). The Olkhon and Gydratny faults in the central sub-basin extend all the way up from the basement64, in a region where the sediment thickness reaches 7.5 km65. Thus, water with a greater δ2H than lake water is supplied from deeper sedimentary layers through the faults, possibly affecting the values of C1 δ2H at these sites.
In contrast, on the southeastern slope of the central sub-basin, with a few exceptions, microbial gases are predominant at most sites from Enkhaluk to Barguzin. No major faults are present in these sites. Based on the formation mechanism of mud volcanoes, such as on Academician Ridge66, hydrate-bound gases are microbially produced in relatively shallow layers, that is, from the lake bottom to a depth of 300–400 m, where the maximum temperature is approximately 40 °C.
The sedimentary layers are sufficiently thick, and major faults exist near Goloustnoe, PosolBank, PosolBank-2, PosolCanyon, and PosolCanyon-2 in the southern sub-basin, and the characteristics of the hydrate-bound gas are similar to those of the Kukuy Canyon. Faults are also adjacent to Malenky, Bolshoy, and Malyutka28,29. Although the gases at these sites are considered microbial gases33, the stable isotope ratios of C2 indicate that they are slightly contaminated by thermogenic gases (Figs. 2b and 3a). There is also the influence of coal deposits at Kedr, Kedr-2, and Mamay67, and gas hydrate enclathrates thermogenic gas accompanied by secondary microbial gas41.
Despite the existence of faults, Unshuy, Ukhan, and Novosibirsk-2 in the central sub-basin show small C2 δ13C values, indicating microbial gas. P-2, P-3, and Krasny Yar in the southern sub-basin are located in the periphery of the Selenga Delta, and their hydrate-bound gases are expected to be similar to those of the Kukuy Canyon in the central sub-basin; however, they are microbial gases. Further studies are required to explain these discrepancies. In conclusion, microbial gases (C1, C2, and C3) exist everywhere in the shallow sediments of Lake Baikal, and a mixing of small amount of thermogenic gas eliminates any trace of microbial C2. These gases form gas hydrates in subsurface sediments and display a rich diversity of gas compositions and crystallographic structures.
Materials and methods
In the multi-phase gas hydrate project during 2009–2019, 11 cruises (VER09-03, VER10-03, VER11-01, VER12-03, VER13-03, VER14-03, VER15-03, VER16-03, VER17-03, VER18-03, and VER19-03) were conducted, and natural gas hydrates were sampled at 52 sites (Fig. 1). Detailed information on these sites is described in previous reports35,38,39. In this study, 668 hydrate-bound gas data points were organized according to sampling site. Hydrate-bound sediment cores were obtained using a gravity corer onboard R/V G. Yu. Vereshchagin. Gas hydrate samples in the sediments were collected rapidly and the hydrate-bound gases were stored in glass vials (5 mL) with butyl septum stoppers. From 2005 to 2013, gas hydrate crystals were placed in syringes (50 mL) and connected to a vial with a needle for a hydrate-bound gas sampling method33; however, after 2014, a water displacement method was used41. To avoid microbial alteration, 0.3 mL of a preservative (50 wt% aqueous solution of benzalkonium chloride) was introduced into the vials using a syringe.
The details of the gas analysis are similar to those described in previous studies33,41. Gas chromatography (GC-14B for 2005–2011 and GC-2014 for 2012–2019, Shimadzu, Kyoto, Japan) was used to analyze the molecular composition of the hydrocarbons. Both instruments consisted of a glass-packed column (Shimadzu Sunpak-S; length 2 m, inner diameter 3 mm), a thermal conductivity detector, and a frame ionization detector. The detectors were connected in series. The analytical error estimated by multiple injections of the standard gases was < 1.2% for each gas component. As crystallographic analysis was not conducted in this study, the crystallographic structure of the gas hydrate was estimated by the C2 composition in hydrocarbons according to the method in the previous work41. For the stable isotope analysis of hydrocarbons, continuous-flow isotope-ratio mass spectrometry (DELTA plus XP, Thermo Finnigan, Waltham, MA, USA for 2005–2013 and DELTA V, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA for 2014–2019) was used. In all cases, a gas chromatograph (TRACE GC Ultra, Thermo Finnigan/Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) equipped with a Carboxen-1006PLOT capillary column (length 30 m, inner diameter 0.32 mm, film thickness 15 μm, Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA) was connected to the mass spectrometer. The stable isotope compositions are reported as δ values (in ‰).
where R denotes the 13C/12C or 2H/1H ratio. δ13C and δ2H were given with reference to the V-PDB and V-SMOW standards, respectively, and were determined using NIST RM8544 (NBS19) for δ13C and NIST RM8561 (NGS3) for δ2H. The analytical precisions for hydrocarbon (C1–C3) δ13C and δ2H were 0.3‰ and 1‰, respectively.
Data availability
All the gas data are reported in the Supplementary Information.
References
Milkov, A. V. Global estimates of hydrate-bound gas in marine sediments: How much is really out there?. Earth Sci. Rev. 66, 183–197. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.earscirev.2003.11.002 (2004).
Makogon, Y. F., Holditch, S. A. & Makogon, T. Y. Natural gas-hydrates: A potential energy source for the 21st Century. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 56, 14–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.petrol.2005.10.009 (2007).
Boswell, R. & Collett, T. S. Current perspectives on gas hydrate resources. Energy Environ. Sci. 4, 1206–1215. https://doi.org/10.1039/C0EE00203H (2011).
Yu, Y.-S., Zhang, X., Liu, J.-W., Lee, Y. & Li, X.-S. Natural gas hydrate resources and hydrate technologies: A review and analysis of the associated energy and global warming challenges. Energy Environ. Sci. 11, 5611–5668. https://doi.org/10.1039/D1EE02093E (2021).
Milkov, A. V. & Sassen, R. Two-dimensional modeling of gas hydrate decomposition in the northwestern Gulf of Mexico: Significance to global change assessment. Glob. Planet Change 36, 31–46. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0921-8181(02)00162-5 (2003).
Kennedy, M., Mrofka, D. & von der Borch, C. Snowball Earth termination by destabilization of equatorial permafrost methane clathrate. Nature 453, 642–645. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature06961 (2008).
Sloan, E. D. & Koh, C. A. Clathrate Hydrates of Natural Gases (CRC Press, 2008).
Lu, H. et al. Complex gas hydrate from the Cascadia margin. Nature 445, 303–306. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature05463 (2007).
Milkov, A. V. Worldwide distribution and significance of secondary microbial methane formed during petroleum biodegradation in conventional reservoirs. Org. Geochem. 42, 184–207. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.orggeochem.2010.12.003 (2011).
Bernard, B. B., Brooks, J. M. & Sackett, W. M. Natural gas seepage in the Gulf of Mexico. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 31, 48–54. https://doi.org/10.1016/0012-821X(76)90095-9 (1976).
Schoell, M. Multiple origins of methane in the earth. Chem. Geol. 71, 1–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/0009-2541(88)90101-5 (1988).
Whiticar, M. J. Carbon and hydrogen isotope systematics of bacterial formation and oxidation of methane. Chem. Geol. 161, 291–314. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0009-2541(99)00092-3 (1999).
Milkov, A. V. & Etiope, G. Revised genetic diagrams for natural gases based on a global dataset of >20,000 samples. Org. Geochem. 125, 109–120. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.orggeochem.2018.09.002 (2018).
Snodgrass, J. E. & Milkov, A. V. Web-based machine learning tool that determines the origin of natural gases. Comput. Geosci. 145, 104595. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cageo.2020.104595 (2020).
Milkov, A. V. Molecular and stable isotope compositions of natural gas hydrates: a revised global dataset and basic interpretations in the context of geological settings. Org. Geochem. 36, 681–702. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.orggeochem.2005.01.010 (2005).
Sassen, R. & Curiale, J. A. Microbial methane and ethane from gas hydrate nodules of the Makassar Strait, Indonesia. Org. Geochem. 37, 977–980. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.orggeochem.2006.04.016 (2006).
Kim, J.-H. et al. Inferences on gas transport based on molecular and isotopic signatures of gases at acoustic chimneys and background sites in the Ulleung Basin. Org. Geochem. 43, 26–38. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.orggeochem.2011.11.004 (2012).
Kida, M. et al. Chemical and crystallographic characterizations of natural gas hydrates recovered from a production test site in the eastern Nankai Trough. Mar. Pet. Geol. 66, 396–403. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2015.02.019 (2015).
Rodrigues, L. F. et al. Molecular and isotopic composition of hydrate-bound, dissolved and free gases in the Amazon deep-sea fan and slope sediments, Brazil. Geosciences 9, 73. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences9020073 (2019).
Ginsburg, G. D. et al. Gas hydrates of the southern Caspian. Int. Geol. Rev. 34, 765–782. https://doi.org/10.1080/00206819209465635 (1992).
Davidson, D. W. et al. Laboratory analysis of a naturally occurring gas hydrate from sediment of the Gulf of Mexico. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 50, 619–623. https://doi.org/10.1016/0016-7037(86)90110-9 (1986).
Bourry, C. et al. Free gas and gas hydrates from the Sea of Marmara, Turkey. Chemical and structural characterization. Chem. Geol. 264, 197–206. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemgeo.2009.03.007 (2009).
Sassen, R. & MacDonald, I. R. Evidence of structure H hydrate, Gulf of Mexico continental slope. Org. Geochem. 22, 1029–1032. https://doi.org/10.1016/0146-6380(94)90036-1 (1994).
Brooks, J. M., Kennicutt, M. C., Fay, R. R., McDonald, T. J. & Sassen, R. Thermogenic gas hydrates in the Gulf of Mexico. Science 225, 409–411. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.225.4660.409 (1984).
Sassen, R., Sweet, S. T., DeFreitas, D. A. & Milkov, A. V. Exclusion of 2-methylbutane (isopentane) during crystallization of structure II gas hydrate in sea-floor sediment, Gulf of Mexico. Org. Geochem. 31, 1257–1262. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0146-6380(00)00144-3 (2000).
Milkov, A. V. et al. Ethane enrichment and propane depletion in subsurface gases indicate gas hydrate occurrence in marine sediments at southern Hydrate Ridge offshore Oregon. Org. Geochem. 35, 1067–1080. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.orggeochem.2004.04.003 (2004).
Kuzmin, M. I. et al. The first find of gas-hydrates in the sedimentary rocks of lake Baikal. Dokl. Earth Sci. 362, 1029–1031 (1998).
Van Rensbergen, P. et al. Sublacustrine mud volcanoes and methane seeps caused by dissociation of gas hydrates in Lake Baikal. Geology 30, 631–634. https://doi.org/10.1130/0091-7613(2002)030%3c0631:SMVAMS%3e2.0.CO;2 (2002).
Matveeva, T. V. et al. Gas hydrate accumulation in the subsurface sediments of Lake Baikal (Eastern Siberia). Geo-Mar. Lett. 23, 289–299. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00367-003-0144-z (2003).
Khlystov, O. M. New findings of gas hydrates in the Baikal bottom sediments. Russ. Geol. Geophys. 47, 979–981 (2006).
Kida, M. et al. Coexistence of structure I and II gas hydrates in Lake Baikal suggesting gas sources from microbial and thermogenic origin. Geophys. Res. Lett. 33, L24603. https://doi.org/10.1029/2006GL028296 (2006).
Kida, M. et al. Natural gas hydrates with locally different cage occupancies and hydration numbers in Lake Baikal. Geochem. Geophys. Geosyst. 10, Q05003. https://doi.org/10.1029/2009GC002473 (2009).
Hachikubo, A. et al. Molecular and isotopic characteristics of gas hydrate-bound hydrocarbons in southern and central Lake Baikal. Geo-Mar. Lett. 30, 321–329. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00367-010-0203-1 (2010).
Poort, J. et al. Low thermal anomalies associated with double structure gas hydrates in K-2 mud volcano, Lake Baikal. Geo-Mar. Lett. 32, 407–417. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00367-012-0292-0 (2012).
Khlystov, O. et al. Gas hydrate of Lake Baikal: Discovery and varieties. J. Asian Earth Sci. 62, 162–166. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jseaes.2012.03.009 (2013).
Subramanian, S., Kini, R. A., Dec, S. F. & Sloan, E. D. Jr. Evidence of structure II hydrate formation from methane + ethane mixtures. Chem. Eng. Sci. 55, 1981–1999. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0009-2509(99)00389-9 (2000).
Subramanian, S., Ballard, A. L., Kini, R. A., Dec, S. F. & Sloan, E. D. Jr. Structural transitions in methane + ethane gas hydrates—part I: Upper transition point and applications. Chem. Eng. Sci. 55, 5763–5771. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0009-2509(00)00162-7 (2000).
Khlystov, O. M., Khabuev, A. V., Minami, H., Hachikubo, A. & Krylov, A. A. Gas hydrates in Lake Baikal. Limnol. Freshwater Biol. 1, 66–70. https://doi.org/10.31951/2658-3518-2018-A-1-66 (2018).
Khlystov, O. M. et al. The position of gas hydrates in the sedimentary strata and in the geological structure of Lake Baikal. In World Atlas of Submarine Gas Hydrates in Continental Margins (eds. Mienert, J. et al.) 465–471 (Springer, 2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-81186-0_39.
Manakov, A. Yu. et al. Structural studies of Lake Baikal natural gas hydrates. J. Struct. Chem. 60, 1437–1455. https://doi.org/10.1134/S0022476619090087 (2019).
Hachikubo, A. et al. Characteristics of hydrate-bound gas retrieved at the Kedr mud volcano (southern Lake Baikal). Sci. Rep. 10, 14747. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-71410-2 (2020).
Khlystov, O. M. et al. A new oil and gas seep in Lake Baikal. Pet. Chem. 62, 475–481. https://doi.org/10.1134/s096554412205005x (2022).
Khlystov, O. M. et al. Oil in the lake of world heritage. Dokl. Earth Sci. 415, 682–685. https://doi.org/10.1134/S1028334X07050042 (2007).
Kalmychkov, G. V., Egorov, A. V., Hachikubo, A. & Khlystov, O. M. Hydrocarbon gases of the Gorevoi Utes underwater oil-gas seep (Lake Baikal, Russia). Russ. Geol. Geophys. 60, 1188–1194. https://doi.org/10.15372/RGG2019110 (2007).
Hachikubo, A. et al. Isotopic fractionation of methane and ethane hydrates between gas and hydrate phases. Geophys. Res. Lett. 34, L21502. https://doi.org/10.1029/2007GL030557 (2007).
Hachikubo, A. et al. Model of formation of double structure gas hydrates in Lake Baikal based on isotopic data. Geophys. Res. Lett. 36, L18504. https://doi.org/10.1029/2009GL039805 (2009).
Manakov, A. Yu., Khlystov, O. M., Hachikubo, A. & Ogienko, A. G. A physicochemical model for the formation of gas hydrates of different structural types in K-2 mud volcano (Kukui Canyon, Lake Baikal). Rus. Geol. Geophys. 54, 475–482. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rgg.2013.03.009 (2013).
Manakov, A. Yu. et al. Structure, morphology, and composition of natural gas hydrates sampled in the Kedr-1 mud volcano (Lake Baikal). J. Struct. Chem. 62, 889–896. https://doi.org/10.1134/S0022476621060081 (2021).
Hachikubo, A. et al. Dissociation heat of mixed-gas hydrate composed of methane and ethane. In Proc. 6th Int. Conf. on Gas Hydrates, 6–10 July, 2008 (2008). http://hdl.handle.net/2429/2694.
James, A. T. & Burns, B. J. Microbial alteration of subsurface natural gas accumulations. Am. Assoc. Pet. Geol. Bull. 68, 957–960. https://doi.org/10.1306/AD46169C-16F7-11D7-8645000102C1865D (1984).
Horibe, Y. & Craig, H. D/H fractionation in the system methane-hydrogen-water. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 59, 5209–5217. https://doi.org/10.1016/0016-7037(95)00391-6 (1995).
Seal, R. R. & Shanks, W. C. Oxygen and hydrogen isotope systematics of Lake Baikal, Siberia: Implications for paleoclimate studies. Limnol. Oceanogr. 43, 1251–1261. https://doi.org/10.4319/lo.1998.43.6.1251 (1998).
Whiticar, M. J., Faber, E. & Schoell, M. Biogenic methane formation in marine and freshwater environments: CO2 reduction vs. acetate fermentation—Isotope evidence. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 50, 693–709. https://doi.org/10.1016/0016-7037(86)90346-7 (1986).
Sugimoto, A. & Wada, E. Hydrogen isotopic composition of bacterial methane: CO2/H2 reduction and acetate fermentation. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 59, 1329–1337. https://doi.org/10.1016/0016-7037(95)00047-4 (1995).
de Graaf, W., Wellsbury, P., Parkes, R. J. & Cappenberg, T. E. Comparison of acetate turnover in methanogenic and sulfate-reducing sediments by radiolabeling and stable isotope labeling and by use of specific inhibitors: evidence for isotopic exchange. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 62, 772–777. https://doi.org/10.1128/aem.62.3.772-777.1996 (1996).
Taylor, S. W., Sherwood Lollar, B. & Wassenaar, L. I. Bacteriogenic ethane in near-surface aquifers: Implications for leaking hydrocarbon well bores. Environ. Sci. Technol. 34, 4727–4732. https://doi.org/10.1021/es001066x (2000).
Oremland, R. S., Whiticar, M. J., Strohmaier, F. E. & Kiene, R. P. Bacterial ethane formation from reduced ethylated compounds in anoxic sediments. Geochem. Cosmochim. Acta 52, 1895–1904. https://doi.org/10.1016/0016-7037(88)90013-0 (1988).
Hinrichs, K.-U. et al. Biological formation of ethane and propane in the deep marine subsurface. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 103, 14684–14689. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0606535103 (2006).
Katz, B. J. Microbial processes and natural gas accumulations. Open Geol. J. 5, 75–83. https://doi.org/10.2174/1874262901105010075 (2011).
Charlou, J. L. et al. Physical and chemical characterization of gas hydrates and associated methane plumes in the Congo-Angola Basin. Chem. Geol. 205, 405–425. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemgeo.2003.12.033 (2004).
Milkov, A. V., Claypool, G. E., Lee, Y.-J. & Sassen, R. Gas hydrate systems at Hydrate Ridge offshore Oregon inferred from molecular and isotopic properties of hydrate-bound and void gases. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 69, 1007–1026. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gca.2004.08.021 (2005).
Lorenson, T. D. & Collett, T. S. National Gas Hydrate Program Expedition 01 offshore India; gas hydrate systems as revealed by hydrocarbon gas geochemistry. Mar. Petrol. Geol. 92, 477–492. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2017.11.011 (2018).
Pavlova, O. N. et al. Production of gaseous hydrocarbons by microbial communities of Lake Baikal bottom sediments. Microbiology 83, 798–804. https://doi.org/10.1134/S0026261714060137 (2014).
Seminsky, K. Zh., Cheremnykh, A. S., Khlystov, O. M. & Akhmanov, G. G. Fault zones and stress fields in the sedimentary fill of Lake Baikal: Tectonophysical approach for seismic and hydroacoustic data interpretation. Russ. Geol. Geophys. 63, 840–855. https://doi.org/10.2113/RGG20204293 (2022).
Hutchinson, D. R. et al. Bottom simulating reflector in Lake Baikal. EOS Trans. Am. Geophys. Union 72, 307–308 (1991).
Khlystov, O. M. et al. Shallow-rooted mud volcanism in Lake Baikal. Mar. Petrol. Geol. 102, 580–589. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2019.01.005 (2019).
Rasskazov, S. V. et al. Sediments in the Tertiary Tankhoi field, South Baikal basin: Stratigraphy, correlation and structural transformations in the Baikal region. Geodyn. Tectonophys. 5, 993–1032. https://doi.org/10.5800/GT-2014-5-4-0165 (2014).
Acknowledgements
We appreciate the assistance of the shipboard crews of RV G. Yu. Vereshchagin during the Lake Baikal expeditions. We are grateful to anonymous reviewers for their constructive comments and suggestions. This work was supported by funding agencies in Japan (Japan Society for the Promotion of Science KAKENHI 21254006, 21360219, 24404026, 26303021, 16H05760, 20H04304, and 22K03712). The work was also supported by the project of LIN SB RAS (FWSR-2021-0006 (121032300223-1)), the Ministry of Science and Higher Education of the Russian Federation (grant No. 121031700321-3), IGC SB RAS # IX.127.1.2. (0350-2019-0004), and RSF-19-17-00226.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
A.H. designed the study, performed gas analysis and drafted the manuscript; H.M., H.S., S.Y., and A.K. conducted the fieldwork onboard R/V; G.K. supported gas sampling and analysis; J.P. conceived the model of gas hydrate formation; M.D. revised and edited the manuscript; A.M. supported sampling of gas hydrates and O.K. organized the research cruise, reasoned and discovered hydrate-containing sites in Lake Baikal. All authors contributed to the drafts and gave final approval for publication.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Hachikubo, A., Minami, H., Sakagami, H. et al. Characteristics and varieties of gases enclathrated in natural gas hydrates retrieved at Lake Baikal. Sci Rep 13, 4440 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-023-31669-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-023-31669-7
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.