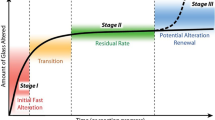
Abstract
The remarkable chemical durability of silicate glass makes it suitable for a wide range of applications. The slowdown of the aqueous glass corrosion kinetics that is frequently observed at long time is generally attributed to chemical affinity effects (saturation of the solution with respect to silica). Here, we demonstrate a new mechanism and highlight the impact of morphological transformations in the alteration layer on the leaching kinetics. A direct correlation between structure and reactivity is revealed by coupling the results of several structure-sensitive experiments with numerical simulations at mesoscopic scale. The sharp drop in the corrosion rate is shown to arise from densification of the outer layers of the alteration film, leading to pore closure. The presence of insoluble elements in the glass can inhibit the film restructuring responsible for this effect. This mechanism may be more broadly applicable to silicate minerals.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lasaga, A. C., Soler, J. M., Gabor, J., Burch, T. E. & Nagy, K. L. Chemical weathering rate laws and global geochemical cycles. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 58, 2361–2386 (1994).
Nugent, M. A., Brantley, S. L., Pantano, C. G. & Maurice, P. A. The influence of natural mineral coating on feldspar wheathering. Nature 395, 588–591 (1998).
Kump, L., Brantley, S. L. & Arthur, M. A. Chemical weathering, atmospheric CO2 and climate. Earth Planet. Sci. Rev. 28, 611–667 (2000).
Scholze, H. Durability investigation of siliceous man-made mineral fibers: A critical review. Glastechnische Berichte Glass Sci. Tech. 61, 161–171 (1988).
Filgueras, M. R., Latorre, G. & Hench, L. L. Solution effects on the surface reaction of bioactive glasses. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 27, 445–453 (1993).
Pisciella, P., Crisucci, S., Karamanov, A. & Pelino, M. Chemical durability of glasses obtained by vitrification of industrial wastes. Waste Management 21, 1–9 (2001).
Hench, L. L. & Clark, D. E. Physical chemistry of glass surface. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 28, 83–105 (1978).
Scholze, H. Glass water interactions. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 102, 1–10 (1988).
Conradt, R. Chemical durability of oxide glasses in aqueous solutions: A review. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 91, 728–735 (2008).
Werme, L. O. et al. Chemical corrosion of highly radioactive borosilicate nuclear waste glass under simulated repository conditions. J. Mater. Res. 5, 1130–1146 (1990).
Abraitis, P. K. et al. The kinetics and mechanisms of simulated British Magnox waste glass dissolution as a function of pH, silicic acid activity, and time in low temperature aqueous systems. Appl. Geochem. 15, 1399–1416 (2000).
Pierce, E. M. et al. Accelerated weathering of a high-level and pu-bearing lanthanide borosilicate waste glass in a can-in-canister configuration. Appl. Geochem. 22, 1841–1859 (2007).
Ewing, R. C. in Scientific Basis for Nuclear Waste Management Vol. 1 (ed. McCarthy, J. M.) 57–68 (1978).
Lutze, W., Malow, G., Ewing, R. C., Jercinovic, M. J. & Keil, K. Alteration of basalt glasses: Implications for modelling the long-term stability of nuclear waste glasses. Nature 314, 252–255 (1985).
Casey, W. H. & Bunker, B. C. Mineral-water interface geochemistry. Rev. Mineral. 23, 397–426 (1990).
Bunker, B. C. Molecular mechanisms for corrosion of silica and silicate glasses. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 179, 300–308 (1994).
Alekseyev, V. A., Medvedeva, L. S., Prisyagina, N. I., Meshalkin, S. S. & Balabin, A. I. Change in the dissolution rates of alkali feldspars as a result of secondary mineral precipitation and approach to equilibrium. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 61, 1125–1142 (1997).
Abraitis, P. K., McGrail, B. P., Trivedi, D. P., Livens, F. R. & Vaughan, D. J. Single-pass flow-trough experiments on a simulated waste in alkaline media at 40 ∘C. J. Nucl. Mater. 280, 196–205 (2000).
Grambow, B. & Muller, R. First-order dissolution rate law and the role of surface layers in glass performance assessment. J. Nucl. Mater. 298, 112–124 (2001).
Casey, W. H., Westrich, H. R., Banfiled, J. F., Ferruzzi, G. & Arnold, G. W. Leaching and reconstruction at the surfaces of dissolving chain-silicate minerals. Nature 366, 253–256 (1993).
Tsomaia, N., Brantley, S. L., Hamilton, J. P., Pantano, C. G. & Mueller, K. T. NMR evidence for formation of octahedral and tetrahedral Al and repolymerisation of Si network during dissolution of aluminosilicate glass and crystal. Am. Mineral. 88, 54–67 (2003).
Grambow, B. Uhlig’s Corrosion Handbook 2nd edn 411–437 (Wiley, 2000).
Barkatt, A., Macedo, P. B., Gibson, B. C. & Montrose, C. J. Modelling of waste performance and system release. Mater. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc. 44, 3–13 (1985).
Delage, F., Ghaleb, D. & Dussossoy, J. L. A mechanistic model for understanding nuclear waste glass dissolution. J. Nucl. Mater. 190, 191–197 (1992).
Xing, S. B., Buechele, A. C. & Pegg, I. L. Effect of surface layers on the dissolution of nuclear waste glasses. Mater. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc 333, 541–548 (1994).
Gin, S., Ribet, I. & Couillard, M. Role and properties of the gel formed during nuclear glass alteration: Importance of gel formation conditions. J. Nucl. Mater. 298, 1–10 (2001).
Chick, L. A. & Pederson, L. R. The relationship between layer thickness and leach rate for nuclear waste glasses. Mater. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc. 26, 635–642 (1984).
McGrail, B. P., Icenhower, J. P. & Cordova, E. A. Origins of discrepancies between kinetic rate law theory and experiments in the Na2O–B2O3–SiO2 system. Mater. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc. 713, 537–546 (2002).
Hodson, M. E. The influence of Fe-rich coatings on the dissolution of anorthite at pH 2.6. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 67, 3355–3363 (2003).
Advocat, T., Jollivet, P., Crovisier, J. L. & Del Nero, M. Long-term alteration mechanisms in water for SON68 radioactive borosilicate glass. J. Nucl. Mater. 298, 55–62 (2001).
Scheetz, B. E. et al. The role of boron in monitoring the leaching of borosilicate glass waste forms. Mater. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc. 44, 129–134 (1985).
Galoisy, L., Pelegrin, E., Arrio, M. A., Ildefonse, P. & Calas, G. Evidence for 6-coordinated zirconium in inactive nuclear waste glasses. J. Am. Ceram. Soc 82, 2219–2224 (1999).
Angeli, F., Gaillard, M., Charpentier, T. & Jollivet, P. Influence of zirconium on the structure of pristine and leached soda-lime borosilicate glasses: Towards a quantitative approach by 17O MQMAS NMR. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 354, 3713–3722 (2008).
Porod, G. in Small Angle X-ray Scattering (eds Glatter, O. & Kratky, O.) 17–52 (Academic, 1982).
Brunauer, S., Emmett, P. H. & Teller, E. Adsorption of gases in multilmolecular layers. J. Am. Chem. Soc 60, 309–319 (1938).
Calo, J. M. & Hall, P. J. The applications of small angle scattering techniques to porosity characteristics in carbons. Carbon 42, 1299–1304 (2004).
Devreux, F., Ledieu, A., Barboux, P. & Minet, Y. Leaching of borosilicate glasses. II. Model and Monte Carlo simulations. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 343, 13–25 (2004).
Ledieu, A., Devreux, F., Barboux, P., Sicard, L. & Spalla, O. Leaching of borosilicate glasses. I. Experiments. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 343, 3–12 (2004).
Bourcier, W. L., Pfeiffer, D. W., Knauss, K. G., McKeegan, K. D. & Smith, D. K. A kinetic model for borosilicate glass dissolution affinity of a surface alteration layer. In scientific basis for nuclear waste management. Mater. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc. 176, 209–216 (1990).
Grambow, B. A general rate equation for nuclear waste glass corrosion. Mater. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc. 44, 15–27 (1985).
Linard, Y., Advocat, T., Jégou, C. & Richet, P. Thermochemistry of nuclear glasses: Application to weathering studies. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 289, 135–143 (2001).
Gin, S., Jégou, C., Frugier, P. & Minet, Y. Theoretical consideration on the application of the Aagaard-Helgeson rate law to the dissolution of silicate minerals and glasses. Chem. Geol. 255, 14–24 (2008).
Chave, T., Frugier, P., Ayral, A. & Gin, S. Solid state diffusion during nuclear glass residual alteration in solution. J. Nucl. Mater. 362, 466–473 (2007).
Ferrand, K., Abdelouas, A. & Grambow, B. Water diffusion in the simulated French nuclear waste SON 68 contacting silica rich solutions: Experimental and modeling. J. Nucl. Mater. 355, 54–67 (2006).
Liu, Y. C., Wang, Q. & Lu, L. H. Water confined in nanopores: Its molecular distribution and diffusion at lower density. Chem. Phys. Lett. 381, 210–215 (2003).
Crovisier, J. L., Advocat, T. & Dussossoy, J. L. Nature and role of natural alteration gels formed on the surface of ancient volcanic glasses (Natural analogs of waste containment glasses). J. Nucl. Mater. 321, 91–109 (2003).
Casey, H. W., Westrich, H. R., Arnold, G. W. & Banfield, J. F. The surface chemistry of dissolving labradorite feldspar. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 53, 821–832 (1989).
Aagaard, P. & Helgeson, H. C. Thermodynamic and kinetic constraints on reaction rates among minerals and aqueous solutions. I. Theoretical considerations. Am. J. Sci. 282, 237–285 (1982).
Lasaga, A. C. Fundamental approaches in describing mineral dissolution and precipitation rates. Rev. Mineral. 31, 23–86 (1995).
Oelkers, E. H. General kinetic description of multioxide silicate mineral and glass dissolution. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 65, 3703–3719 (2001).
Acknowledgements
We acknowledge the help of Wahib Saikaly at CP2M (Marseille, France) for the scanning transmission electron microscopy experiments and the assistance of Laurent Dupuy at BiophyResearch (Marseille, France) for the ToF-SIMS experiments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Supplementary information
Supplementary Information
Supplementary Information (PDF 407 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cailleteau, C., Angeli, F., Devreux, F. et al. Insight into silicate-glass corrosion mechanisms. Nature Mater 7, 978–983 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1038/nmat2301
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nmat2301
This article is cited by
-
Corrosion of glaze in the marine environment: study on the green-glazed pottery from the Southern Song “Nanhai I” shipwreck (1127–1279 A.D.)
Heritage Science (2023)
-
Impact of a Mn-oxidizing bacterial strain on the dissolution and browning of a Mn-bearing potash-lime silicate glass
npj Materials Degradation (2023)
-
A review of glass corrosion: the unique contribution of studying ancient glass to validate glass alteration models
npj Materials Degradation (2023)
-
Study on the regulation of luminescence properties of SBGCS: Tb3+ glass for LEDs applications
Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Electronics (2023)
-
A comparative study of the dissolution mechanisms of amorphous and crystalline feldspars at acidic pH conditions
npj Materials Degradation (2022)