Volume 42
-
No. 5 May 2024
Young human glial progenitors replace older counterpartsAn illustration of transplanted human glial progenitor cells (red) killing resident human glia (pink) in the adult mouse brain. Vieira et al. show that transplanted young glial progenitors outcompete older or diseased glia, suggesting a therapeutic strategy for neurodegenerative and myelin diseases.
See Vieira et al.
-
No. 4 April 2024
Whole-body imagingImage of a whole mouse body with depth color-coding of a neuronal marker. Mai et al. present wildDISCO, a method for whole-body imaging compatible with standard IgG antibody labeling.
See Mai et al.
-
No. 3 March 2024
Point-of-care monitoringA miniaturized ultrasonic system can provide full-body monitoring and diagnosis. Lin et al. engineer a soft, wireless ultrasound device to measure deep body signals in moving subjects, offering a hands-free solution for continuous, comprehensive health tracking at the point of care.
See Lin et al.
Collection
-
No. 2 February 2024
Focus on protein engineeringArtistic impression of the three data types key to machine learning for functional protein design: structure, sequence and labels. The structure of carbonic anhydrase is shown in front of a background composed of amino acid letters representing sequence data. The hue overlay represents a fitness landscape that experimentally acquired labels help to map.
See Notin et al.
-
No. 1 January 2024
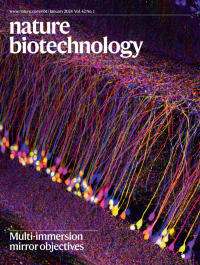
Multi-immersion mirror objectivesNeurons in the mouse hippocampus imaged with the Schmidt objective. Voigt et al. develop a multi-immersion objective based on a mirror instead of a lens.
See Voigt et al.