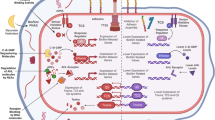
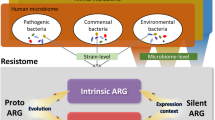
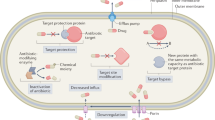
Abstract
Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) is one of the global health challenges of the 21st century that is faced with the twin threats of global climate change and greater longevity, which pose a synergistic risk to the management of AMR. Antimicrobial agents are in high demand due to the challenges faced by increasing life expectancy and the dynamic changes in disease ecology prompted by climate change. In light of global aging and climate change, the complexity and importance of addressing antibiotic resistance are further highlighted by this interplay of issues.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Coque TM, Cantón R, Pérez-Cobas AE, Fernández-de-Bobadilla MD, Baquero F. Antimicrobial resistance in the global health network: known unknowns and challenges for efficient responses in the 21st century. Microorganisms. 2023;11:1050 https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11041050
Coque T, Graham D, Pruden A, So A, Topp E. Bracing for superbugs: strengthening environmental action in the One Health response to antimicrobial resistance. United Nations Environ Programme. 2023. https://doi.org/10.57711/hdq2-xr65.
Murray CJ, Ikuta KS, Sharara F, Swetschinski L, Aguilar GR, Gray A, et al. Global burden of bacterial antimicrobial resistance in 2019: a systematic analysis. Lancet. 2022;399:629–55. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(21)02724-0
LUISA A. Tackling antimicrobial resistance: from science to pharmaceuticals policy. 2023.
Lambraki IA, Cousins M, Graells T, Léger A, Abdelrahman S, Desbois AP, et al. Governing antimicrobial resistance (AMR) in a changing climate: a participatory scenario planning approach applied to Sweden in 2050. Front Public Health. 2022;10:831097 https://doi.org/10.3389/fpubh.2022.831097
Jesudason T. A new research agenda to combat antimicrobial resistance. Lancet Infect Dis. 2023;23:e281 https://doi.org/10.1016/S1473-3099(23)00446-2
Bloom DE, Cadarette D. Infectious disease threats in the twenty-first century: strengthening the global response. Front Immunol. 2019;10:549 https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2019.00549
Longevity TLH. Tackling antimicrobial resistance to protect healthy ageing. 2023. 4:e584. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2666-7568(23)00218-0.
Augustine S, Bonomo R. Taking stock of infections and antibiotic resistance in the elderly and long-term care facilities: A survey of existingand upcoming challenges. Eur J Microbiol Immunol. 2011;1:190–7. https://doi.org/10.1556/EuJMI.1.2011.3.2
Organization WH. Antimicrobial resistance 21 November 2023 [Available from: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/antimicrobial-resistance.
Hodin MW. Antimicrobial resistance: a major threat to the promise of healthy aging. Health Affairs Forefront. 2023. https://doi.org/10.1377/forefront.20230110.717379.
Meinen A, Tomczyk S, Wiegand FN, Sin MA, Eckmanns T, Haller S. Antimicrobial resistance in Germany and Europe–A systematic review on the increasing threat accelerated by climate change. J Health Monit. 2023;8:93 https://doi.org/10.25646/11404
Li W, Liu C, Ho HC, Shi L, Zeng Y, Yang X, et al. Association between antibiotic resistance and increasing ambient temperature in China: An ecological study with nationwide panel data. Lancet Regional Health–West Pac. 2023;30:100628 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lanwpc.2022.100628
Qamar MU. Impact of climate change on antimicrobial resistance dynamics: an emerging One Health challenge. Fut Microbiol 2023;18:535–9. https://doi.org/10.2217/fmb-2023-0022
Waits A, Emelyanova A, Oksanen A, Abass K, Rautio A. Human infectious diseases and the changing climate in the Arctic. Environ Int. 2018;121:703–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2018.09.042
Magnano San Lio R, Favara G, Maugeri A, Barchitta M, Agodi A. How antimicrobial resistance is linked to climate change: an overview of two intertwined global challenges. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2023;20:1681 https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20031681
Butler MS, Henderson IR, Capon RJ, Blaskovich MA. Antibiotics in the clinical pipeline as of December 2022. J Antibiotics. 2023;76:431–73. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41429-023-00629-8
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Maryam Shafaati: Conceptualization, Data Curation, Writing-Original Draft, Writing- Review & Editing. Mohammadreza Salehi: Data Curation, Writing-Original Draft, Writing- Review & Editing.Maryam Zare: Data Curation, Writing- Review & Editing.All authors critically reviewed and approved the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Shafaati, M., Salehi, M. & Zare, M. The twin challenges of longevity and climate change in controlling antimicrobial resistance. J Antibiot (2024). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41429-024-00730-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41429-024-00730-6