Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access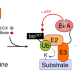 BioE3 identifies specific substrates of ubiquitin E3 ligases
BioE3 identifies specific substrates of ubiquitin E3 ligases
Here, the authors describe BioE3, a biotin-based method to discriminate direct substrates of ubiquitin E3 ligases of interest from mere interactors using proximity proteomics. BioE3 responds to chemical treatments, and works with RING- and HECT-type E3s, as well as ubiquitin-likes (e.g., SUMO).
- Orhi Barroso-Gomila
- , Laura Merino-Cacho
- & James D. Sutherland
-
Article
| Open Access Multiple E3 ligases control tankyrase stability and function
Multiple E3 ligases control tankyrase stability and function
The poly(ADP-ribosyl)transferases, tankyrase 1 and 2, are regulated by RNF146-mediated K48-linked polyubiquitylation and degradation. Here the authors show that this is opposed by K11-linked diubiquitylation by RING-UIM E3 ligases RNF114 and 166 and further impacted by several PAR-binding E3 ligases.
- Jerome Perrard
- & Susan Smith
-
Article
| Open Access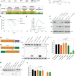 A TRIM21-based bioPROTAC highlights the therapeutic benefit of HuR degradation
A TRIM21-based bioPROTAC highlights the therapeutic benefit of HuR degradation
Overexpression of human antigen R (HuR) correlates with high grade tumours and poor patient prognosis. Here, the authors engineer a TRIM21 biological PROTAC to demonstrate the benefit of a targeted protein degradation approach to deplete HuR, resulting in tumour growth inhibition in pre-clinical cancer models by altering the HuR-regulated proteome.
- Alice Fletcher
- , Dean Clift
- & James Hunt
-
Article
| Open Access Decoding of the ubiquitin code for clearance of colliding ribosomes by the RQT complex
Decoding of the ubiquitin code for clearance of colliding ribosomes by the RQT complex
The colliding ribosomes are ubiquitinated by the sensor protein Hel2, leading to noncanonical subunit dissociation by the ribosome associated quality control trigger (RQT) complex. Here the authors reveal the decoding mechanism of the ribosome ubiquitin code by the RQT complex.
- Yoshitaka Matsuo
- , Takayuki Uchihashi
- & Toshifumi Inada
-
Article
| Open Access Cooperative assembly of p97 complexes involved in replication termination
Cooperative assembly of p97 complexes involved in replication termination
This study describes how p97Ufd1-Npl4 and the UBA-UBX protein Ubxn7 disassemble vertebrate replisomes during replication termination, and it provides novel insights into how p97 complexes assemble with UBA-UBX proteins on ubiquitylated substrates
- Olga V. Kochenova
- , Sirisha Mukkavalli
- & Johannes C. Walter
-
Article
| Open Access A distinct mammalian disome collision interface harbors K63-linked polyubiquitination of uS10 to trigger hRQT-mediated subunit dissociation
A distinct mammalian disome collision interface harbors K63-linked polyubiquitination of uS10 to trigger hRQT-mediated subunit dissociation
Collided ribosomes are marked by ubiquitination to induce quality control mechanisms. Here, authors show that mammalian disomes form a distinct structural interface, in which uS10 K63-linked polyubiquitination is critical for ribosome dissociation.
- Momoko Narita
- , Timo Denk
- & Toshifumi Inada
-
Article
| Open Access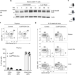 The ubiquitin ligase Cul5 regulates CD4+ T cell fate choice and allergic inflammation
The ubiquitin ligase Cul5 regulates CD4+ T cell fate choice and allergic inflammation
Cytokine signaling influences the differentiation of CD4+ T cells into varying functional subsets. Here the authors show that an E3 ubiquitin ligase Cul5 alters TH2 and TH9 development and absence of Cul5 in T cells results in higher levels of allergy-associated IL-4 and IL-9 secreting T cells.
- Binod Kumar
- , Natania S. Field
- & Paula M. Oliver
-
Article
| Open Access Active conformation of the p97-p47 unfoldase complex
Active conformation of the p97-p47 unfoldase complex
The p97 unfoldase is an essential and abundant enzyme that segregates its substrates from macromolecular complexes and organelle membranes. Here, authors determined the structure of human p97 in the act of unfolding an authentic substrate.
- Yang Xu
- , Han Han
- & Peter S. Shen
-
Article
| Open Access Regulated interaction of ID2 with the anaphase-promoting complex links progression through mitosis with reactivation of cell-type-specific transcription
Regulated interaction of ID2 with the anaphase-promoting complex links progression through mitosis with reactivation of cell-type-specific transcription
Tissue-specific transcriptional activity is silenced in mitotic cells. Here the authors reveal a general phosphorylation-dependent mechanism of recognition for the anaphase-promoting complex (APC) substrates, and show that the APC targets ID2 during the establishment of post-mitotic transcription.
- Sang Bae Lee
- , Luciano Garofano
- & Anna Lasorella
-
Article
| Open Access The 20S as a stand-alone proteasome in cells can degrade the ubiquitin tag
The 20S as a stand-alone proteasome in cells can degrade the ubiquitin tag
The 20S particle is part of the 26S proteasome, but also exists as a free complex. Here, the authors outline signature activities of the 20S and combine chemical, structural, functional and proteomic assays to show that the 20S can degrade ubiquitin tags along with conjugated substrates.
- Indrajit Sahu
- , Sachitanand M. Mali
- & Michael H. Glickman
-
Article
| Open Access OTULIN inhibits RIPK1-mediated keratinocyte necroptosis to prevent skin inflammation in mice
OTULIN inhibits RIPK1-mediated keratinocyte necroptosis to prevent skin inflammation in mice
OTULIN is a negative regulator of linear ubiquitination, and its deficiency in human causes multi-organ inflammations including the skin. Here the authors show, by combining various genetic tools with epidermis-specific Otulin knockout mice, that Otulin suppresses skin inflammation predominantly by inhibiting RIPK1-mediated keratinocytes necroptosis.
- Hannah Schünke
- , Ulrike Göbel
- & Manolis Pasparakis
-
Article
| Open Access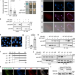 UXT chaperone prevents proteotoxicity by acting as an autophagy adaptor for p62-dependent aggrephagy
UXT chaperone prevents proteotoxicity by acting as an autophagy adaptor for p62-dependent aggrephagy
p62/SQSTM1 acts as a key mediator in the selective autophagy of protein aggregates, or aggrephagy. Here the authors identify the prefoldin-like chaperone UXT as an autophagy adaptor of p62 dependent aggrephagy and show that ectopic UXT expression delays motor neuron degeneration in a Xenopus model.
- Min Ji Yoon
- , Boyoon Choi
- & Chungho Kim
-
Article
| Open Access Phase separation by the polyhomeotic sterile alpha motif compartmentalizes Polycomb Group proteins and enhances their activity
Phase separation by the polyhomeotic sterile alpha motif compartmentalizes Polycomb Group proteins and enhances their activity
The conserved SAM motif of Polycomb Repressive Complex 1 subunit Ph has been shown to play an important role in chromatin organization. Here, the authors study the effect of Ph SAM on chromatin in vitro, showing that it induces the formation of concentrated, phase-separated condensates, which enhance the ubiquitin ligase activity of PRC1.
- Elias Seif
- , Jin Joo Kang
- & Nicole J. Francis
-
Article
| Open Access UBB pseudogene 4 encodes functional ubiquitin variants
UBB pseudogene 4 encodes functional ubiquitin variants
Ubiquitin pseudogenes are present in many organisms but whether they encode functional proteins has remained unclear. Here, the authors show that human UBB pseudogene 4 produces ubiquitin variants with amino acid compositions and cellular functions that are distinct from canonical ubiquitin.
- Marie-Line Dubois
- , Anna Meller
- & François-Michel Boisvert
-
Article
| Open Access Requirement for p62 acetylation in the aggregation of ubiquitylated proteins under nutrient stress
Requirement for p62 acetylation in the aggregation of ubiquitylated proteins under nutrient stress
The autophagy receptor p62 mediates the assembly and removal of ubiquitylated protein aggregates by forming p62 bodies. Here, the authors identify an acetylation-dependent mechanism that regulates formation and autophagic clearance of p62 bodies under nutrient-deficient conditions.
- Zhiyuan You
- , Wen-Xue Jiang
- & Wei Liu
-
Article
| Open Access K27-linked ubiquitination of BRAF by ITCH engages cytokine response to maintain MEK-ERK signaling
K27-linked ubiquitination of BRAF by ITCH engages cytokine response to maintain MEK-ERK signaling
BRAF drives MEK/ERK activation to facilitate tumorigenesis. Here, the authors show that in response to pro-inflammatory cytokines, ITCH mediates a non-proteolytic ubiquitination and activation of BRAF, which in turn sustains MEK/ERK signaling to facilitate melanoma cell growth.
- Qing Yin
- , Tao Han
- & Lixin Wan
-
Article
| Open Access Structural basis of specific H2A K13/K15 ubiquitination by RNF168
Structural basis of specific H2A K13/K15 ubiquitination by RNF168
Ubiquitination of histone H2A can occur on distinct lysine residues, but how each site is recognised by the specific E3 ligase remains poorly understood. Here the authors demonstrate that the E3 ligase RNF168 binds the acidic patch on the nucleosome surface, directing the E2 to the target lysine K13/K15.
- Velten Horn
- , Michael Uckelmann
- & Hugo van Ingen
-
Article
| Open Access Discovery of a potent HMG-CoA reductase degrader that eliminates statin-induced reductase accumulation and lowers cholesterol
Discovery of a potent HMG-CoA reductase degrader that eliminates statin-induced reductase accumulation and lowers cholesterol
Accumulated HMG-CoA reductase (HMGCR) limits the cholesterol-lowering effect of statins via a feedback loop. Here the authors developed a compound that degrades HMGCR, thus decreasing cholesterol levels and reducing atherosclerotic plaques.
- Shi-You Jiang
- , Hui Li
- & Bao-Liang Song
-
Article
| Open Access Structural dynamics of the E6AP/UBE3A-E6-p53 enzyme-substrate complex
Structural dynamics of the E6AP/UBE3A-E6-p53 enzyme-substrate complex
Oncoprotein E6 facilitates the E6AP-catalyzed ubiquitination of p53. Here, the authors study the structural basis of this process by qualitative and quantitative cross-linking mass spectrometry, providing insights into E6AP-E6-p53 complex assembly and the conformational dynamics that enable p53 ubiquitination.
- Carolin Sailer
- , Fabian Offensperger
- & Florian Stengel
-
Article
| Open Access SKP2- and OTUD1-regulated non-proteolytic ubiquitination of YAP promotes YAP nuclear localization and activity
SKP2- and OTUD1-regulated non-proteolytic ubiquitination of YAP promotes YAP nuclear localization and activity
Regulation of Yes-associated protein (YAP) through the Hippo pathway is well established, but its Hippo-independent regulation remains to be elucidated. Here, the authors show that non-proteolytic ubiquitination presents another means of YAP regulation, promoting its nuclear localization and activity.
- Fan Yao
- , Zhicheng Zhou
- & Li Ma
-
Article
| Open Access FAN1 interaction with ubiquitylated PCNA alleviates replication stress and preserves genomic integrity independently of BRCA2
FAN1 interaction with ubiquitylated PCNA alleviates replication stress and preserves genomic integrity independently of BRCA2
FANCD2-associated nuclease 1 (FAN1) is a key protein involved in the metabolism of DNA and in human pathologies. Here, the authors show that FAN1 directly interacts with PCNA at stalled replication forks to control their progression and prevent their collapse.
- Antonio Porro
- , Matteo Berti
- & Josef Jiricny
-
Article
| Open Access Variation in auxin sensing guides AUX/IAA transcriptional repressor ubiquitylation and destruction
Variation in auxin sensing guides AUX/IAA transcriptional repressor ubiquitylation and destruction
The phytohormone auxin is sensed by SCFTIR1-AUX/IAA receptors leading to AUX/IAA repressor ubiquitylation and turnover. Here the authors show that IAA6 and IAA19 differ in their ubiquitylation and turnover dynamics, differentially contributing to auxin sensing and enabling discrimination of auxin concentrations.
- Martin Winkler
- , Michael Niemeyer
- & Luz Irina A. Calderón Villalobos
-
Article
| Open Access Uncovering the SUMOylation and ubiquitylation crosstalk in human cells using sequential peptide immunopurification
Uncovering the SUMOylation and ubiquitylation crosstalk in human cells using sequential peptide immunopurification
Ubiquitylation and SUMOylation are two important related post-translational modifications. Here the authors present an approach for the simultaneous identification and quantification of protein-wide SUMO and ubiquitin sites from a single sample, uncovering widespread crosstalk between the two modifications.
- Frédéric Lamoliatte
- , Francis P. McManus
- & Pierre Thibault
-
Article
| Open Access ISGylation controls exosome secretion by promoting lysosomal degradation of MVB proteins
ISGylation controls exosome secretion by promoting lysosomal degradation of MVB proteins
Multivesicular bodies (MVB) are endosomal compartments that can either fuse with the plasma membrane for the secretion of exosomes, or fuse with the lysosome and be degraded along with their contents. Here, the authors show that ISGylation of the MVB protein TSG101 impairs exosome secretion and acts as a regulator of MVB fate.
- Carolina Villarroya-Beltri
- , Francesc Baixauli
- & Francisco Sánchez-Madrid
-
Article
| Open Access Open-gate mutants of the mammalian proteasome show enhanced ubiquitin-conjugate degradation
Open-gate mutants of the mammalian proteasome show enhanced ubiquitin-conjugate degradation
The proteasome plays a key role in proteostasis by mediating the degradation of ubiquitinated substrates. Here the authors show that an open-gate mutant of the proteasome is hyperactive towards a subset of substrates and can effectively delay the accumulation of toxic protein aggregates.
- Won Hoon Choi
- , Stefanie A. H. de Poot
- & Min Jae Lee
-
Article |
 The Parkinson’s-associated protein DJ-1 regulates the 20S proteasome
The Parkinson’s-associated protein DJ-1 regulates the 20S proteasome
Mutations in the gene encoding DJ-1 are associated with early-onset familial forms of Parkinson’s disease, and several different molecular functions have been attributed to this protein. Moscovitz et al.show that DJ-1 physically binds the 20S proteasome and inhibits its degradation activity.
- Oren Moscovitz
- , Gili Ben-Nissan
- & Michal Sharon
-
Article |
 Rad23 escapes degradation because it lacks a proteasome initiation region
Rad23 escapes degradation because it lacks a proteasome initiation region
Rad23 accompanies ubiquitinated substrates to the proteasome for destruction but manages to avoid degradation. In this study, Fishbainet al.show that Rad23 escapes because it lacks an effective initiation region; therefore, the proteasome is unable to engage the protein and unfold it.
- Susan Fishbain
- , Sumit Prakash
- & Andreas Matouschek
-
Article
| Open Access C-terminal UBA domains protect ubiquitin receptors by preventing initiation of protein degradation
C-terminal UBA domains protect ubiquitin receptors by preventing initiation of protein degradation
Rad23 and Dsk2 bind polyubiquitylated proteins and escort them to the proteasome for destruction. In this study, Heinenet al.investigate the molecular mechanisms that protect the C-terminal UBA domains of Rad23 and Dsk2 from proteasomal destruction.
- Christian Heinen
- , Klàra Ács
- & Nico P. Dantuma

 VCF1 is a p97/VCP cofactor promoting recognition of ubiquitylated p97-UFD1-NPL4 substrates
VCF1 is a p97/VCP cofactor promoting recognition of ubiquitylated p97-UFD1-NPL4 substrates