Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Bidirectional ATP-driven transport of cobalamin by the mycobacterial ABC transporter BacA
Bidirectional ATP-driven transport of cobalamin by the mycobacterial ABC transporter BacA
ABC transporters are generally considered to be unidirectional. Here, the authors develop a fluorescence-based transport assay and show that the mycobacterial ABC transporter BacA instead acts as a bidirectional transporter for cobalamin.
- Mark Nijland
- , Solène N. Lefebvre
- & Dirk J. Slotboom
-
Article
| Open Access Molecular basis for inhibiting human glucose transporters by exofacial inhibitors
Molecular basis for inhibiting human glucose transporters by exofacial inhibitors
Human glucose transporters (GLUTs), particularly GLUT1 and GLUT3, are potential anticancer therapy targets. Here, Nan Wang et al. use an engineered GLUT 3 variant to identify an exofacial GLUT3 inhibitor, SA47, and elucidate the drug’s inhibitory mechanism.
- Nan Wang
- , Shuo Zhang
- & Nieng Yan
-
Article
| Open Access Metabolite trafficking enables membrane-impermeable-terpene secretion by yeast
Metabolite trafficking enables membrane-impermeable-terpene secretion by yeast
The engineering of metabolite secretion from microorganisms can lead to many applications in synthetic biology. In this article, the authors engineer a metabolite trafficking system for the secretion of medicinal terpenes.
- So-Hee Son
- , Jae-Eung Kim
- & Ju Young Lee
-
Article
| Open Access Combinatorial GxGxE CRISPR screen identifies SLC25A39 in mitochondrial glutathione transport linking iron homeostasis to OXPHOS
Combinatorial GxGxE CRISPR screen identifies SLC25A39 in mitochondrial glutathione transport linking iron homeostasis to OXPHOS
Combinatorial Gene×Gene×Environment CRISPR screen targeting human SLC25 transporter family enables the identification of SLC25A39 in mitochondrial glutathione import and its coordination with mitochondrial iron import in supporting OXPHOS.
- Xiaojian Shi
- , Bryn Reinstadler
- & Hongying Shen
-
Article
| Open Access The dopamine transporter antiports potassium to increase the uptake of dopamine
The dopamine transporter antiports potassium to increase the uptake of dopamine
The dopamine transporter, DAT, controls dopamine signaling by facilitating its reuptake using the Na+ gradient as driving force. Here, the authors uncover that an antiport of K+ ions also contributes to setting the rate of DAT-mediated dopamine clearance.
- Solveig G. Schmidt
- , Mette Galsgaard Malle
- & Claus J. Loland
-
Article
| Open Access CRISPR-assisted rational flux-tuning and arrayed CRISPRi screening of an l-proline exporter for l-proline hyperproduction
CRISPR-assisted rational flux-tuning and arrayed CRISPRi screening of an l-proline exporter for l-proline hyperproduction
Corynebacterium glutamicum is a major workhorse in industrial biomanufacturing of amino acids. Here, the authors employ CRISPR-assisted rational flux-tuning and CRISPRi screening of a L-proline exporter to covert a wild-type C. glutamicum to a hyperproducer of L-proline.
- Jiao Liu
- , Moshi Liu
- & Jibin Sun
-
Article
| Open Access Structural basis of terephthalate recognition by solute binding protein TphC
Structural basis of terephthalate recognition by solute binding protein TphC
The presence of the gene encoding the solute binding protein TphC has been shown to permit the uptake of terephthalate (TPA), which is the breakdown product of Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) plastic. Here the authors present a structural characterization of TphC in both open and TPA-bound closed conformations.
- Trishnamoni Gautom
- , Dharmendra Dheeman
- & Neil Dixon
-
Article
| Open Access Development of a mugineic acid family phytosiderophore analog as an iron fertilizer
Development of a mugineic acid family phytosiderophore analog as an iron fertilizer
Iron is an essential plant nutrient that is poorly bioavailable in alkaline soils, resulting in reduced agricultural productivity. Here, the authors report the synthesis of stable and cheap iron-chelator, proline-2’-deoxymugineic acid (PDMA), and demonstrate its utility as potential fertilizer.
- Motofumi Suzuki
- , Atsumi Urabe
- & Kosuke Namba
-
Article
| Open Access Insights into SusCD-mediated glycan import by a prominent gut symbiont
Insights into SusCD-mediated glycan import by a prominent gut symbiont
In Bacteroidetes, SusCD complexes mediate uptake of large nutrients across the outer membrane. SusCD structures in the apo state and in complex with β2,6 fructo-oligosaccharides reveal several substrate molecules in the binding cavity and suggest details of the pedal bin mechanism employed in glycan import.
- Declan A. Gray
- , Joshua B. R. White
- & Bert van den Berg
-
Article
| Open Access An electrostatic switching mechanism to control the lipid transfer activity of Osh6p
An electrostatic switching mechanism to control the lipid transfer activity of Osh6p
Osh6p and Osh7p are yeast lipid transfer proteins (LTPs) that must transiently interact with membranes but how they escape from the electrostatic attraction of the plasma membrane is unclear. Here authors show that Osh6p reduces its avidity for anionic membranes once it captures PS or PI4P, due to a molecular lid closing its lipid-binding pocket.
- Nicolas-Frédéric Lipp
- , Romain Gautier
- & Guillaume Drin
-
Article
| Open Access ABCB1 protects bat cells from DNA damage induced by genotoxic compounds
ABCB1 protects bat cells from DNA damage induced by genotoxic compounds
Bats possess an extended lifespan compared to most mammals of their size, and have a low cancer incidence. Here the authors show that several bat species exhibit resistance to genotoxic agents that is in part attributable to high expression of the ABCB1 transporter.
- Javier Koh
- , Yoko Itahana
- & Koji Itahana
-
Article
| Open Access Tracking carrier protein motions with Raman spectroscopy
Tracking carrier protein motions with Raman spectroscopy
Acyl carrier proteins (ACPs), a universal and highly conserved carrier of acyl intermediates during fatty acid and polyketide synthesis, are difficult to visualise. Here, the authors developed a facile, Raman spectroscopy-based method to detect ACP-substrate interactions.
- Samuel C. Epstein
- , Adam R. Huff
- & Louise K. Charkoudian
-
Article
| Open Access Inward- and outward-facing X-ray crystal structures of homodimeric P-glycoprotein CmABCB1
Inward- and outward-facing X-ray crystal structures of homodimeric P-glycoprotein CmABCB1
P-glycoprotein, an ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporter, extrudes a large variety of xenobiotics from the cell which protects tissues from toxins. Here authors solve a pair of X-ray structures of homodimeric P-glycoprotein and resolve structural elements proposed to participate in the mechanism of the transporter.
- Atsushi Kodan
- , Tomohiro Yamaguchi
- & Hiroaki Kato
-
Article
| Open Access Direct protein-lipid interactions shape the conformational landscape of secondary transporters
Direct protein-lipid interactions shape the conformational landscape of secondary transporters
Secondary transporters catalyse substrate translocation across the cell membrane but the role of lipids during the transport cycle remains unclear. Here authors used hydrogen-deuterium exchange mass spectrometry and molecular dynamics simulations to understand how lipids regulate the conformational dynamics of secondary transporters.
- Chloe Martens
- , Mrinal Shekhar
- & Argyris Politis
-
Article
| Open Access Designing a norepinephrine optical tracer for imaging individual noradrenergic synapses and their activity in vivo
Designing a norepinephrine optical tracer for imaging individual noradrenergic synapses and their activity in vivo
The noradrenergic system plays numerous physiological roles but tools to study it are scarce. Here the authors develop a fluorescent analogue of norepinephrine that can be used to label noradrenergic neurons and the synaptic vesicles, and use it to measure single synaptic vesicle release sites in living mice.
- Matthew Dunn
- , Adam Henke
- & Dalibor Sames
-
Article
| Open Access CryoEM structure of the human SLC4A4 sodium-coupled acid-base transporter NBCe1
CryoEM structure of the human SLC4A4 sodium-coupled acid-base transporter NBCe1
Na+-coupled acid-base membrane transport proteins regulate blood pressure, ion homeostasis and acid-base chemistry. Here the authors present the 3.9 Å resolution cryoEM structure of the sodium-bicarbonate cotransporter NBCe1 and characterize its ion coordination site and ion accessibility pathway with mutagenesis experiments.
- Kevin W. Huynh
- , Jiansen Jiang
- & Ira Kurtz
-
Article
| Open Access Structures and transport dynamics of a Campylobacter jejuni multidrug efflux pump
Structures and transport dynamics of a Campylobacter jejuni multidrug efflux pump
Multidrug efflux pumps significantly contribute for bacteria resistance to antibiotics. Here the authors present the structure of Campylobacter jejuni CmeB pump combined with functional FRET assays to propose a transport mechanism where each CmeB protomers is functionally independent from the trimer.
- Chih-Chia Su
- , Linxiang Yin
- & Edward W. Yu
-
Article
| Open Access Structure and function of the divalent anion/Na+ symporter from Vibrio cholerae and a humanized variant
Structure and function of the divalent anion/Na+ symporter from Vibrio cholerae and a humanized variant
Divalent anion/Na+ symporter (DASS) transporters move intermediates of the Krebs cycle across the cell membrane. Here the authors present the substrate-bound structures of VcINDY, a DASS from Vibrio cholerae, which provide insights into the underlying transport mechanism.
- Rongxin Nie
- , Steven Stark
- & Min Lu
-
Article
| Open Access Cholesterol-mediated allosteric regulation of the mitochondrial translocator protein structure
Cholesterol-mediated allosteric regulation of the mitochondrial translocator protein structure
The outer mitochondrial membrane translocator protein (TSPO) mediates several mitochondrial functions and binds cholesterol with a high affinity. Here the authors use solid-state NMR to show that cholesterol binding to TSPO results in allosteric changes that modulate TSPO oligomerization.
- Garima Jaipuria
- , Andrei Leonov
- & Markus Zweckstetter
-
Article
| Open Access Cationic amino acid transporters play key roles in the survival and transmission of apicomplexan parasites
Cationic amino acid transporters play key roles in the survival and transmission of apicomplexan parasites
Apicomplexans are parasites that use membrane transporters to scavenge essential nutrients from the host. Here the authors identify and characterize two apicomplexans transporters showing that these are crucial for cationic amino acid uptake, parasite survival and virulence.
- Esther Rajendran
- , Sanduni V. Hapuarachchi
- & Giel G. van Dooren
-
Article
| Open Access Mitochondrial ATP transporter depletion protects mice against liver steatosis and insulin resistance
Mitochondrial ATP transporter depletion protects mice against liver steatosis and insulin resistance
Adenine nucleotide translocase (ANT) 2 promotes ADP/ATP exchange across the mitochondrial inner membrane. Choet al. show that liver specific Ant2 deletion increases uncoupled respiration and protects mice against fatty liver and obesity-induced insulin resistance.
- Joonseok Cho
- , Yujian Zhang
- & Naohiro Terada
-
Article
| Open Access Major sulfonate transporter Soa1 in Saccharomyces cerevisiae and considerable substrate diversity in its fungal family
Major sulfonate transporter Soa1 in Saccharomyces cerevisiae and considerable substrate diversity in its fungal family
Sulfonates are a major source of sulphur for soil microbes but their cellular uptake is still not fully understood. Here the authors show thatSaccharomyces cerevisiae YIL166C(SOA1)encodes for an inorganic sulphur transporter that can also function as a sulfonate and choline sulphate transporter.
- Sylvester Holt
- , Harish Kankipati
- & Johan M. Thevelein
-
Article
| Open Access A quantized mechanism for activation of pannexin channels
A quantized mechanism for activation of pannexin channels
Pannexins are oligomeric plasma membrane channels that allow permeation of ions and large molecules. Here the authors show that human Pannexin 1 activation is a multistep event, where modification of each monomer opens the channel to a unique conductance state and fine tunes its activity.
- Yu-Hsin Chiu
- , Xueyao Jin
- & Douglas A. Bayliss
-
Article
| Open Access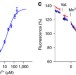 Structural and mechanistic basis of proton-coupled metal ion transport in the SLC11/NRAMP family
Structural and mechanistic basis of proton-coupled metal ion transport in the SLC11/NRAMP family
Cellular uptake of transition metal ions is mediated by members of the SLC11/NRAMP family. Here the authors determine the structural and functional properties of EcoDMT, a bacterial SLC11 transporter, gathering molecular insight into its transport mechanism and proton coupling process.
- Ines A. Ehrnstorfer
- , Cristina Manatschal
- & Raimund Dutzler
-
Article
| Open Access Coupled ATPase-adenylate kinase activity in ABC transporters
Coupled ATPase-adenylate kinase activity in ABC transporters
ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporters hydrolyse ATP to transport molecules across the cell membrane. Here Vogelet al. show that the ABC exporter MsBA can couple ATP hydrolyse to an adenylate kinase activity that seems to be predominant at low ATP levels and a general feature of ABC exporters.
- Hundeep Kaur
- , Andrea Lakatos-Karoly
- & Clemens Glaubitz
-
Article
| Open Access Coupled binding mechanism of three sodium ions and aspartate in the glutamate transporter homologue GltTk
Coupled binding mechanism of three sodium ions and aspartate in the glutamate transporter homologue GltTk
In neurons and glia, glutamate transporters catalyse the reuptake of this neurotransmitter by coupling it with cation transport. Here the authors combine X-ray crystallography and molecular dynamics simulations of the archeal glutamate transporter GltTkto get insight into the coupled transport mechanism.
- Albert Guskov
- , Sonja Jensen
- & Dirk Jan Slotboom
-
Article
| Open Access Crystal structure of bacterial haem importer complex in the inward-facing conformation
Crystal structure of bacterial haem importer complex in the inward-facing conformation
Pathogenic bacteria acquire iron from heme cofactors imported by ABC heme transporters. Here the authors present crystal structures of Burkholderia cenocepaciaheme importer BhuUV with and without the heme-binding protein BhuT, gathering mechanistic insight into the catalytic cycle of heme import.
- Youichi Naoe
- , Nozomi Nakamura
- & Hiroshi Sugimoto
-
Article
| Open Access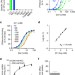 Transition metal ion FRET uncovers K+ regulation of a neurotransmitter/sodium symporter
Transition metal ion FRET uncovers K+ regulation of a neurotransmitter/sodium symporter
The neurotransmitter transporter SERT counter transport K+ to transport serotonin. Here the authors show that the activity of the prokaryotic orthologue LeuT is also modulated by this cation, suggesting a general regulatory role for K+on neutrotrasmitter:sodium symporters function.
- Christian B. Billesbølle
- , Jonas S. Mortensen
- & Claus J. Loland
-
Article
| Open Access ATP-dependent substrate transport by the ABC transporter MsbA is proton-coupled
ATP-dependent substrate transport by the ABC transporter MsbA is proton-coupled
ABC exporters mediate the translocation of cytotoxic compounds to the cell exterior via ATP hydrolysis. Here, the authors show that the bacterial transporter MsbA requires additional energy from the transmembrane electrochemical proton gradient to facilitate drug transport.
- Himansha Singh
- , Saroj Velamakanni
- & Hendrik W. van Veen
-
Article
| Open Access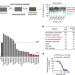 A phosphotyrosine switch regulates organic cation transporters
A phosphotyrosine switch regulates organic cation transporters
Organic cation transporters are important drug transporters that influence therapeutic outcomes. Here, the authors find that these transporters are regulated by tyrosine phosphorylation and propose that tyrosine kinase inhibitors can influence drug transporter function through post-translational mechanisms.
- Jason A. Sprowl
- , Su Sien Ong
- & Navjotsingh Pabla
-
Article
| Open Access Outward- and inward-facing structures of a putative bacterial transition-metal transporter with homology to ferroportin
Outward- and inward-facing structures of a putative bacterial transition-metal transporter with homology to ferroportin
Iron export from vertebrate cells is mediated by ferroportin, which is suppressed by the peptide hormone hepcidin. Taniguchi et al. present crystal structures of a putative bacterial ferroportin homologue in both outward- and inward-facing states, providing insight into its transport mechanism.
- Reiya Taniguchi
- , Hideaki E. Kato
- & Osamu Nureki
-
Article
| Open Access Structures of FolT in substrate-bound and substrate-released conformations reveal a gating mechanism for ECF transporters
Structures of FolT in substrate-bound and substrate-released conformations reveal a gating mechanism for ECF transporters
Substrate specificity of ECF transporters is determined by the transmembrane EcfS protein subunit. Here Zhao et al.present substrate-bound and substrate-released structures of a bacterial folate transporter EcfS and suggest a gating mechanism for ECF transporters.
- Qin Zhao
- , Chengcheng Wang
- & Peng Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Insect glycerol transporters evolved by functional co-option and gene replacement
Insect glycerol transporters evolved by functional co-option and gene replacement
Insects can accumulate high levels of glycerol as an adaptive response to dessication and freezing. Here, the authors show that glycerol transporters evolved from water-selective channels that co-opted the glycerol transport function of ancestral aquaglyceroporins in the oldest lineages of insects.
- Roderick Nigel Finn
- , François Chauvigné
- & Joan Cerdà
-
Article |
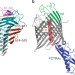 Translocation path of a substrate protein through its Omp85 transporter
Translocation path of a substrate protein through its Omp85 transporter
The two-partner secretion system transports proteins across the bacterial outer membrane but the molecular mechanisms involved are poorly understood. Here, Baud et al. use site-specific crosslinking to track the path of a protein substrate through the β-barrel of its Omp85 transporter.
- Catherine Baud
- , Jérémy Guérin
- & Françoise Jacob-Dubuisson
-
Article |
 A female gametocyte-specific ABC transporter plays a role in lipid metabolism in the malaria parasite
A female gametocyte-specific ABC transporter plays a role in lipid metabolism in the malaria parasite
Production of male and female forms of the malaria parasite in an infected person is crucial for transmission of the disease. Here, Tran et al.show that an ABC transporter protein of the parasite, expressed in the female cells, modulates lipid accumulation and formation of sexual cells.
- Phuong N. Tran
- , Simon H. J. Brown
- & Alexander G. Maier
-
Article |
 Export of a single drug molecule in two transport cycles by a multidrug efflux pump
Export of a single drug molecule in two transport cycles by a multidrug efflux pump
Secondary multidrug transporters use ion concentration gradients to power the removal of drug molecules from cells. Here, Fluman et al. demonstrate that the bacterial transporter MdfA can catalyse the efflux of divalent cations in two consecutive transport cycles where each charged moiety is transported as if it were a separate substrate.
- Nir Fluman
- , Julia Adler
- & Eitan Bibi
-
Article
| Open Access Proton-coupled sugar transport in the prototypical major facilitator superfamily protein XylE
Proton-coupled sugar transport in the prototypical major facilitator superfamily protein XylE
Glucose transporters are a medically important class of membrane proteins often deregulated in diseases such as Type 2 diabetes. Here, Wisedchaisri et al. report the crystal structure of XylE in an inward-facing open conformation to provide a general mechanism of substrate transport for the sugar porter family of proteins.
- Goragot Wisedchaisri
- , Min-Sun Park
- & Tamir Gonen
-
Article
| Open Access Arrayed lipid bilayer chambers allow single-molecule analysis of membrane transporter activity
Arrayed lipid bilayer chambers allow single-molecule analysis of membrane transporter activity
The development of small volume chamber arrays has greatly facilitated high throughput biological assays of soluble proteins. Here, Watanabe et al.adapt this approach to develop an arrayed lipid bilayer chamber system for single molecule level measurements of membrane transporter activity.
- Rikiya Watanabe
- , Naoki Soga
- & Hiroyuki Noji
-
Article
| Open Access Molecular architecture and the structural basis for anion interaction in prestin and SLC26 transporters
Molecular architecture and the structural basis for anion interaction in prestin and SLC26 transporters
Prestin is an anion transporter-like protein in the mammalian inner ear that amplifies sound-induced vibration by voltage-driven structural rearrangements. Here, Gorbunov et al. show that this electromechanical activity is controlled by the binding of anions to a central cavity within the protein core.
- Dmitry Gorbunov
- , Mattia Sturlese
- & Dominik Oliver
-
Article |
 Activity of the mitochondrial calcium uniporter varies greatly between tissues
Activity of the mitochondrial calcium uniporter varies greatly between tissues
The flow of calcium into the mitochondrial matrix is mediated by the mitochondrial calcium uniporter. Fieniet al. apply patch-clamp techniques to mitoplasts isolated from different mouse and Drosophilatissues and find that the mitochondrial calcium uniporter activity varies depending on the tissue studied.
- Francesca Fieni
- , Sung Bae Lee
- & Yuriy Kirichok
-
Article
| Open Access Distant residues mediate picomolar binding affinity of a protein cofactor
Distant residues mediate picomolar binding affinity of a protein cofactor
Flavodoxin requires tight binding of its FMN cofactor to be active, but the residues involved are unknown. In this biophysical study, FMN binding is shown to change from nanomolar to picomolar affinity on extremely slow protein relaxation and the residues responsible for cofactor binding are identified.
- Yves J.M. Bollen
- , Adrie H. Westphal
- & Carlo P.M. van Mierlo
-
Article
| Open Access ABCA4 is an N-retinylidene-phosphatidylethanolamine and phosphatidylethanolamine importer
ABCA4 is an N-retinylidene-phosphatidylethanolamine and phosphatidylethanolamine importer
In mammalian cells, ABC transporter proteins were thought to exclusively export a range of substrates out of cells. Quazi and colleagues show that, in retinal photoreceptor cells, ABCA4 is acting as an importer of phospholipids and that mutations known to cause Stargardt disease decrease its activity.
- Faraz Quazi
- , Stepan Lenevich
- & Robert S. Molday

 LDL receptor-related protein 5 selectively transports unesterified polyunsaturated fatty acids to intracellular compartments
LDL receptor-related protein 5 selectively transports unesterified polyunsaturated fatty acids to intracellular compartments