Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access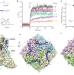 Molecular pathway and structural mechanism of human oncochannel TRPV6 inhibition by the phytocannabinoid tetrahydrocannabivarin
Molecular pathway and structural mechanism of human oncochannel TRPV6 inhibition by the phytocannabinoid tetrahydrocannabivarin
Neuberger et al. report the structure of human channel TRPV6 in complex with a cannabinoid inhibitor tetrahydrocannabivarin (THCV) and explore the pathway taken by the drug to reach binding sites in the portals that connect the membrane environment to the central cavity of the ion channel pore.
- Arthur Neuberger
- , Yury A. Trofimov
- & Alexander I. Sobolevsky
-
Article
| Open Access Crosstalk between regulatory elements in disordered TRPV4 N-terminus modulates lipid-dependent channel activity
Crosstalk between regulatory elements in disordered TRPV4 N-terminus modulates lipid-dependent channel activity
An integrated structural biology approach uncovers the structural complexity of the intrinsically disordered region (IDR) within the TRPV4 ion channel. Multiple stimulatory and inhibitory elements were identified within the IDR that modulate channel activity in a lipid-dependent manner.
- Benedikt Goretzki
- , Christoph Wiedemann
- & Ute A. Hellmich
-
Article
| Open Access TRPV4-Rho GTPase complex structures reveal mechanisms of gating and disease
TRPV4-Rho GTPase complex structures reveal mechanisms of gating and disease
Despite TRPV4’s medical importance, the mechanisms of ligand-mediated channel gating and its regulation by Rho GTPase are unclear. Here, the authors report the structures of TRPV4 in complex with RhoA and ligands, offering atomic-level insights into their functions.
- Do Hoon Kwon
- , Feng Zhang
- & Seok-Yong Lee
-
Article
| Open Access Structure of human TRPV4 in complex with GTPase RhoA
Structure of human TRPV4 in complex with GTPase RhoA
Nadezhdin et al. present structures of human TRPV4 in complex with the GTPase RhoA, in the apo, agonist 4α-PDD and antagonist HC-067047 bound states, uncovering the mechanisms of channel activation, inhibition and disease-causing mutations.
- Kirill D. Nadezhdin
- , Irina A. Talyzina
- & Alexander I. Sobolevsky
-
Article
| Open Access Molecular mechanism of hyperactivation conferred by a truncation of TRPA1
Molecular mechanism of hyperactivation conferred by a truncation of TRPA1
A drastic TRPA1 mutant was identified in patients with CRAMPT syndrome, but it has not been functionally characterized. Here, the authors find this mutant confers gain-of-function by co-assembling with wild type protein to form hyperactive channels.
- Avnika Bali
- , Samantha P. Schaefer
- & Candice E. Paulsen
-
Article
| Open Access Two single-point mutations in Ankyrin Repeat one drastically change the threshold temperature of TRPV1
Two single-point mutations in Ankyrin Repeat one drastically change the threshold temperature of TRPV1
TRPV1 is a noxious heat sensor. Here, authors showed that tailed amphibians express TRPV1 with a reduced heat-activation threshold by substitution of two amino acids in the N-terminal region to contribute to cool-habitat selection.
- Shogo Hori
- , Michihiro Tateyama
- & Osamu Saitoh
-
Article
| Open Access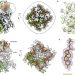 Structural mechanisms of TRPM7 activation and inhibition
Structural mechanisms of TRPM7 activation and inhibition
Authors present the structural mechanisms of TRPM7 spontaneous and agonist-induced opening and inhibition by potent and selective antagonists.
- Kirill D. Nadezhdin
- , Leonor Correia
- & Alexander I. Sobolevsky
-
Article
| Open Access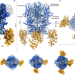 Molecular architecture of the Gαi-bound TRPC5 ion channel
Molecular architecture of the Gαi-bound TRPC5 ion channel
Ion channels could be directly regulated by the alpha subunit of heterotrimeric G-proteins. Here, authors present the cryo-EM structure of an ion channel-Gα complex, TRPC5-Gαi3, and present functional insights into their direct interaction.
- Jongdae Won
- , Jinsung Kim
- & Hyung Ho Lee
-
Article
| Open Access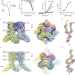 Human TRPV1 structure and inhibition by the analgesic SB-366791
Human TRPV1 structure and inhibition by the analgesic SB-366791
Small molecules targeting transient receptor potential (TRP) channels might be used to control pain. Here, Neuberger et al. report cryo-EM structures of human TRPV1 in the absence of added ligands or in the presence of the TRPV1-specific antagonist SB-366791, providing insights for the design of new promising analgesics.
- Arthur Neuberger
- , Mai Oda
- & Alexander I. Sobolevsky
-
Article
| Open Access Structure-guided peptide engineering of a positive allosteric modulator targeting the outer pore of TRPV1 for long-lasting analgesia
Structure-guided peptide engineering of a positive allosteric modulator targeting the outer pore of TRPV1 for long-lasting analgesia
TRPV1 as a drug target suffers from side effects of hypothermia. Here, authors engineer a peptide, sRhTx, as a positive allosteric modulator of TRPV1 channel. It potentiates the activity of TRPV1 to reversibly ablate pain-sensing nerve terminals for long-lasting analgesia without changing mice body temperature.
- Heng Zhang
- , Jia-Jia Lin
- & Fan Yang
-
Article
| Open Access Cannabinoid non-cannabidiol site modulation of TRPV2 structure and function
Cannabinoid non-cannabidiol site modulation of TRPV2 structure and function
TRPV2 is activated by temperature and cannabinoids. Here, the authors have used cryo-EM and electrophysiology to identify a cannabinoid binding site distinct from that of cannabidiol as a possible drug target for treatment of inflammation and immune-mediated diseases.
- Liying Zhang
- , Charlotte Simonsen
- & Peter M. Zygmunt
-
Article
| Open Access The human TRPA1 intrinsic cold and heat sensitivity involves separate channel structures beyond the N-ARD domain
The human TRPA1 intrinsic cold and heat sensitivity involves separate channel structures beyond the N-ARD domain
The authors report how the cold and heat sensing properties of the pain receptor TRPA1 are separately modulated by the C-terminal intracellular domain, and in concert with either the S1–S4 or the S5–S6 transmembrane domain.
- Lavanya Moparthi
- , Viktor Sinica
- & Peter M. Zygmunt
-
Article
| Open Access Vanilloid-dependent TRPV1 opening trajectory from cryoEM ensemble analysis
Vanilloid-dependent TRPV1 opening trajectory from cryoEM ensemble analysis
Cryo-EM often yields multiple protein conformations within a single dataset. Using the thermal titration methods and cryo-EM, Do Hoon Kwon et al. elucidate the conformational trajectory of the TRPV1 with resiniferatoxin (RTx) bound.
- Do Hoon Kwon
- , Feng Zhang
- & Seok-Yong Lee
-
Article
| Open Access Structural insights into TRPV2 activation by small molecules
Structural insights into TRPV2 activation by small molecules
A non-selective calcium channel transient receptor potential vanilloid 2 (TRPV2) is a potential drug target. Here, the authors employ cryo-electron microscopy, in silico docking, and electrophysiology to identify a binding site for an activator 2-aminoethoxydiphenyl borate (2-APB) in this channel.
- Ruth A. Pumroy
- , Anna D. Protopopova
- & Vera Y. Moiseenkova-Bell
-
Article
| Open Access Structural basis for Ca2+ activation of the heteromeric PKD1L3/PKD2L1 channel
Structural basis for Ca2+ activation of the heteromeric PKD1L3/PKD2L1 channel
Hetero-oligomeric TRP-like channels such as PKD1L3/PKD2L1 play crucial roles in a range of physiological and pathophysiological processes. Here, the authors present the cryo-EM structures of a minimal functional murine PKD1L3/PKD2L1 complex in the absence and presence of calcium and further supported through structure-guided mutagenic studies, they discuss the mechanism of calcium-induced channel activation.
- Qiang Su
- , Mengying Chen
- & Yigong Shi
-
Article
| Open Access Extracellular cap domain is an essential component of the TRPV1 gating mechanism
Extracellular cap domain is an essential component of the TRPV1 gating mechanism
Structural and functional characterization of the full-length TRPV1 channel from the thirteen-lined ground squirrel reveal the architecture of the extracellular cap domain and the intracellular C-terminus, and suggest a role of the cap domain in TRPV1 conductance and ion selectivity.
- Kirill D. Nadezhdin
- , Arthur Neuberger
- & Alexander I. Sobolevsky
-
Article
| Open Access Evidence that the TRPV1 S1-S4 membrane domain contributes to thermosensing
Evidence that the TRPV1 S1-S4 membrane domain contributes to thermosensing
The TRPV1 ion channel is a heat-sensing receptor that is also activated by vanilloid compounds, but the molecular underpinnings of thermosensing have remained elusive. Here authors use in solution NMR on the isolated human TRPV1 S1-S4 domain and show that this domain undergoes a non-denaturing temperature-dependent transition with a high thermosensitivity.
- Minjoo Kim
- , Nicholas J. Sisco
- & Wade D. Van Horn
-
Article
| Open Access Molecular mechanisms underlying menthol binding and activation of TRPM8 ion channel
Molecular mechanisms underlying menthol binding and activation of TRPM8 ion channel
Menthol in mints elicits a coolness sensation by selective activation of TRPM8 ion channel. Here authors dock menthol to TRPM8 and systematically validate their menthol binding models with thermodynamic mutant cycle analysis in functional tests, and shed light on TRPM8 activation by menthol at the atomic level.
- Lizhen Xu
- , Yalan Han
- & Fan Yang
-
Article
| Open Access Visualizing structural transitions of ligand-dependent gating of the TRPM2 channel
Visualizing structural transitions of ligand-dependent gating of the TRPM2 channel
The transient receptor potential channel member 2 (TRPM2) ion channel has a function in redox-dependent signaling. Here the authors present the cryo-EM structures of zebrafish TRPM2 in the ligand-free form, with Ca2+ and both ADP-ribose/Ca2+ and observe two-fold symmetric quaternary structure rearrangements in the ligand-bound structures that likely represent intermediate gating states.
- Ying Yin
- , Mengyu Wu
- & Seok-Yong Lee
-
Article
| Open Access Conformational ensemble of the human TRPV3 ion channel
Conformational ensemble of the human TRPV3 ion channel
Transient receptor potential vanilloid channel 3 (TRPV3) responds to temperature and sensitizes upon repeated stimulation with either heat or agonists. Here authors present the cryo-EM structures of apo and sensitized human TRPV3 and describe the structural basis of sensitization.
- Lejla Zubcevic
- , Mark A. Herzik Jr.
- & Seok-Yong Lee
-
Article
| Open Access Structural basis for PtdInsP2-mediated human TRPML1 regulation
Structural basis for PtdInsP2-mediated human TRPML1 regulation
Transient receptor potential mucolipin 1 (TRPML1) is a lysosomal channel which maintains the low pH and calcium levels for lysosomal function. Here authors use structural biology and electrophysiology to show how lipids bind and allosterically activate TRPML1.
- Michael Fine
- , Philip Schmiege
- & Xiaochun Li
-
Article
| Open Access Preventing acute asthmatic symptoms by targeting a neuronal mechanism involving carotid body lysophosphatidic acid receptors
Preventing acute asthmatic symptoms by targeting a neuronal mechanism involving carotid body lysophosphatidic acid receptors
Acute bronchoconstriction is the leading cause of asthmatic sudden death following allergen exposure. The authors show that the systemic increase of LPA following inhaled allergen or bradykinin challenge activates the carotid bodies through TRPV1 and LPA-specific receptors and that systemic TRPV1 and LPA-specific receptor antagonists ameliorate acute bronchoconstriction.
- Nicholas G. Jendzjowsky
- , Arijit Roy
- & Richard J. A. Wilson
-
Article
| Open Access The conformational wave in capsaicin activation of transient receptor potential vanilloid 1 ion channel
The conformational wave in capsaicin activation of transient receptor potential vanilloid 1 ion channel
The capsaicin receptor TRPV1 has been structurally characterized, but the capsaicin activation dynamics remain elusive. Here authors use fluorescent unnatural amino acid incorporation, computational modeling and Φ-analysis to derive the capsaicin-bound open state model and reveal the capsaicin induced conformational changes.
- Fan Yang
- , Xian Xiao
- & Jie Zheng
-
Article
| Open Access TRPV1 SUMOylation regulates nociceptive signaling in models of inflammatory pain
TRPV1 SUMOylation regulates nociceptive signaling in models of inflammatory pain
SUMOylation is a post translational modification. Here the authors show that TRPV1, which conveys thermal nociception, is SUMOylated in DRGs in inflammatory conditions and contributes to pain behavior in mice.
- Yan Wang
- , Yingwei Gao
- & Yong Li
-
Article
| Open Access Copper sulfide nanoparticles as a photothermal switch for TRPV1 signaling to attenuate atherosclerosis
Copper sulfide nanoparticles as a photothermal switch for TRPV1 signaling to attenuate atherosclerosis
Capsaicin prevents atherosclerotic plaque formation by activating TRPV1 cation channels, but its toxicity precludes its use in clinical settings. Here, Tang and colleagues use copper sulfide nanoparticles as a photothermal switch to locally and temporally activate TRPV1 in vascular smooth muscle cells and reduce plaque formation without apparent toxicity.
- Wen Gao
- , Yuhui Sun
- & Bo Tang
-
Article
| Open Access Arrestin-biased AT1R agonism induces acute catecholamine secretion through TRPC3 coupling
Arrestin-biased AT1R agonism induces acute catecholamine secretion through TRPC3 coupling
Angiotensin II type 1 receptor (AT1R)-mediated acute catecholamine release is modulated by β-arrestin. Here the authors show that β-arrestin-1 recruits the Ca2+channel TRPC3 and the PLCγ to the AT1R-β-arrestin complex, triggering G protein-independent calcium influx and catecholamine secretion.
- Chun-Hua Liu
- , Zheng Gong
- & Jin-Peng Sun
-
Article
| Open Access Nicotinamide is an endogenous agonist for a C. elegans TRPV OSM-9 and OCR-4 channel
Nicotinamide is an endogenous agonist for a C. elegans TRPV OSM-9 and OCR-4 channel
TRPV are cation channels activated by physical and chemical stimuli. Here the authors show that nicotinamide is a soluble, endogenous agonist for orthologous TRPV channels fromC. elegans and Drosophila, unveiling a metabolic-based regulation for TRPV channel activity.
- Awani Upadhyay
- , Aditya Pisupati
- & Wendy Hanna-Rose
-
Article
| Open Access Inhibition of TRPV1 channels by a naturally occurring omega-9 fatty acid reduces pain and itch
Inhibition of TRPV1 channels by a naturally occurring omega-9 fatty acid reduces pain and itch
TRPV1 channels are known to mediate pathological pain and itch. Here, the authors find a naturally occurring fatty acid, oleic acid, acts as a TRPV1 antagonist and can modulate capsaicin and histamine-mediated pain and itch response in mouse models.
- Sara L. Morales-Lázaro
- , Itzel Llorente
- & Tamara Rosenbaum
-
Article
| Open Access Cold sensitivity of TRPA1 is unveiled by the prolyl hydroxylation blockade-induced sensitization to ROS
Cold sensitivity of TRPA1 is unveiled by the prolyl hydroxylation blockade-induced sensitization to ROS
The transient receptor potential ankyrin 1 (TRPA1) is a cation channel that is involved in nociceptive pain sensing. Here, the authors show that hydroxylation of a proline in the N terminus of TRPA1 renders it sensitive to reactive oxygen species resulting from noxious cold.
- Takahito Miyake
- , Saki Nakamura
- & Shuji Kaneko
-
Article |
 ZBTB20 regulates nociception and pain sensation by modulating TRP channel expression in nociceptive sensory neurons
ZBTB20 regulates nociception and pain sensation by modulating TRP channel expression in nociceptive sensory neurons
The upregulation of TRP ion channels is implicated in pain processing. In this study, the authors show that the zinc-finger protein ZBTB20 is responsible for TRP channel upregulation, and eliminating ZBTB20 from pain-sensing neurons in mouse models of pain results in the reduction of pain-like sensation.
- An-Jing Ren
- , Kai Wang
- & Weiping J. Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access TRPV channel-mediated calcium transients in nociceptor neurons are dispensable for avoidance behaviour
TRPV channel-mediated calcium transients in nociceptor neurons are dispensable for avoidance behaviour
TRPs are calcium-permeable channels involved in the sensing of damaging stimuli but the relationship between calcium influx and pain behaviour has been elusive. Here the authors find that the TRP channel OSM-9 functions as an ion channel in vivo in C. elegans, and establish residues that are critical for worm pain-like behaviour.
- Amanda S. Lindy
- , Puja K. Parekh
- & Wolfgang B. Liedtke
-
Article |
 Molecular mechanism of the assembly of an acid-sensing receptor ion channel complex
Molecular mechanism of the assembly of an acid-sensing receptor ion channel complex
Polycystic kidney disease family proteins form heteromeric complexes with transient receptor potential channel subunits of the TRPP subfamily. Yu and colleagues find that the polycystic kidney disease protein, PKD1L3, is an ion channel pore-forming subunit in the acid-sensing PKD1L3/TRPP3 complex.
- Yong Yu
- , Maximilian H. Ulbrich
- & Jian Yang
-
Article |
 Cardioprotection by Klotho through downregulation of TRPC6 channels in the mouse heart
Cardioprotection by Klotho through downregulation of TRPC6 channels in the mouse heart
Mice that cannot produce the hormone Klotho show various aging-related phenotypes. Here, Xie and colleagues reveal that Klotho protects the heart of mice from stress-induced remodelling by inhibiting exocytosis of the TRPC6 ion channel in cardiomyocytes.
- Jian Xie
- , Seung-Kuy Cha
- & Chou-Long Huang
-
Article |
 Transient activation of specific neurons in mice by selective expression of the capsaicin receptor
Transient activation of specific neurons in mice by selective expression of the capsaicin receptor
The ability to spatially and temporally control excitation of neuronsin vivo is an invaluable tool. By expressing the TRPV1 receptor in specific neuronal populations, Güler et al. have developed a rapid and noninvasive method to stimulate neuronal activity by the simple administration of capsaicin.
- Ali D. Güler
- , Aundrea Rainwater
- & Richard D. Palmiter
-
Article
| Open Access Activation of TRPC6 channels is essential for lung ischaemia–reperfusion induced oedema in mice
Activation of TRPC6 channels is essential for lung ischaemia–reperfusion induced oedema in mice
The signalling cascade involved in lung ischaemia–reperfusion-induced oedema is poorly understood. Using knockout mice, Weissmannet al. propose a model in which reactive oxygen species production by endothelial NOX2 leads to phospholipase C-γ activation, DAG kinase inhibition and subsequent TRPC6 activation.
- Norbert Weissmann
- , Akylbek Sydykov
- & Alexander Dietrich
-
Article |
 TRPV3 regulates nitric oxide synthase-independent nitric oxide synthesis in the skin
TRPV3 regulates nitric oxide synthase-independent nitric oxide synthesis in the skin
Nitric oxide can be produced by nitric oxide synthase or by nitrite reduction, but whether the latter occurs inside cells is unknown. Here, the TRPV3 ion channel is shown to induce nitrite-dependent nitric oxide production in keratinocytes, where it has a role in thermosensory behaviour and wound healing.
- Takashi Miyamoto
- , Matt J. Petrus
- & Ardem Patapoutian

 Structural basis of the activation of TRPV5 channels by long-chain acyl-Coenzyme-A
Structural basis of the activation of TRPV5 channels by long-chain acyl-Coenzyme-A