Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access X-ray-activated polymerization expanding the frontiers of deep-tissue hydrogel formation
X-ray-activated polymerization expanding the frontiers of deep-tissue hydrogel formation
Photo-crosslinking polymerization facilitates precise control of hydrogel formation for various applications including tissue engineering, but most existing photo-crosslinking methods fail to achieve deep-tissue penetration, especially within bone structures. Here the authors report a strategy of low-dose X-ray-activated polymerization that enables deep-tissue hydrogel formation.
- Hailei Zhang
- , Boyan Tang
- & Gang Han
-
Article
| Open Access Complex activity and short-term plasticity of human cerebral organoids reciprocally connected with axons
Complex activity and short-term plasticity of human cerebral organoids reciprocally connected with axons
Connecting cerebral organoids with an axon bundle models inter-regional projections and enhances neural activity. Optogenetic stimulation induces short-term plasticity, offering insights into macroscopic circuit development and functionality.
- Tatsuya Osaki
- , Tomoya Duenki
- & Yoshiho Ikeuchi
-
Article
| Open Access Silk fibroin hydrogel adhesive enables sealed-tight reconstruction of meniscus tears
Silk fibroin hydrogel adhesive enables sealed-tight reconstruction of meniscus tears
Suture repair is the current clinical treatment for meniscus tears, but inaccessible tears in company with re-tears susceptibility remain unresolved. Here the authors address these issues by developing a meniscus adhesive-based strategy for the seamless and dense reconstruction of torn meniscus.
- Xihao Pan
- , Rui Li
- & Hongwei Ouyang
-
Article
| Open Access Versatile human cardiac tissues engineered with perfusable heart extracellular microenvironment for biomedical applications
Versatile human cardiac tissues engineered with perfusable heart extracellular microenvironment for biomedical applications
The application of engineered cardiac tissues is limited due to their immaturity and lack of functionality. Here, the authors develop an integrated culture platform featuring heart extracellular matrix cultured in a microfluidic chip to facilitate cardiac tissue development for versatile biomedical applications.
- Sungjin Min
- , Suran Kim
- & Seung-Woo Cho
-
Perspective
| Open Access Cellular reprogramming as a tool to model human aging in a dish
Cellular reprogramming as a tool to model human aging in a dish
The development of human cellular models of aging that surpass the limitations of animal models of aging is urgent. Here, the authors explore the opportunities and limitations of cellular reprogramming to create reliable aging in vitro models and their potential for the discovery of anti-aging compounds.
- Patricia R. Pitrez
- , Luis M. Monteiro
- & Lino Ferreira
-
Article
| Open Access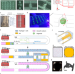 A microfluidic platform integrating functional vascularized organoids-on-chip
A microfluidic platform integrating functional vascularized organoids-on-chip
Vascularization remains a significant challenge in organoid technology. Here, the authors develop a microfluidic platform that enhances organoid growth, function and maturation, by establishing functional perfusable vascular networks.
- Clément Quintard
- , Emily Tubbs
- & Xavier Gidrol
-
Article
| Open Access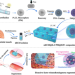 Elastic porous microspheres/extracellular matrix hydrogel injectable composites releasing dual bio-factors enable tissue regeneration
Elastic porous microspheres/extracellular matrix hydrogel injectable composites releasing dual bio-factors enable tissue regeneration
Injectable pro-regenerative biomaterials are vital for developing minimally invasive regenerative treatment, but impeded by brittleness and lack of biological functions. Here the authors address these issues by engineering injectable functionalized composites that facilitate the sequential release of IL-4 and IGF-1 to regulate macrophages and stem cell behavior for enhanced in situ regeneration.
- Yi Li
- , Siyang Liu
- & Meifeng Zhu
-
Article
| Open Access Two way workable microchanneled hydrogel suture to diagnose, treat and monitor the infarcted heart
Two way workable microchanneled hydrogel suture to diagnose, treat and monitor the infarcted heart
Myocardial infarction can lead to malignant arrhythmia and myocardial remodeling. Here, the authors report a microchanneled hydrogel suture for two-way signal communication, pumping drugs on demand, and cardiac repair.
- Fangchao Xue
- , Shanlan Zhao
- & Wen Zeng
-
Article
| Open Access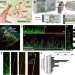 Angiogenesis-on-a-chip coupled with single-cell RNA sequencing reveals spatially differential activations of autophagy along angiogenic sprouts
Angiogenesis-on-a-chip coupled with single-cell RNA sequencing reveals spatially differential activations of autophagy along angiogenic sprouts
The functional heterogeneity of autophagy in endothelial cells during angiogenesis remains incompletely understood. Here, the authors apply a 3D angiogenesis-on-a-chip coupled with single-cell RNA sequencing to find distinct autophagy functions in two different endothelial cell populations during angiogenic sprouting.
- Somin Lee
- , Hyunkyung Kim
- & Noo Li Jeon
-
Q&A
| Open Access A conversation about cultivated meat
A conversation about cultivated meat
Summary: Cultivated or cultured meat is promising to revolutionize the food industry in the coming years to decades, helping to resolve concerns related to the environmental impact and ethical implications linked to conventional meat production. We talked to Dr. Sandhya Sriram, the Group CEO and Co-founder of Shiok Meats Pte. Ltd., Singapore; Prof. Shulamit Levenberg, the former Dean of the Biomedical Engineering Department at the Technion, current Director of the Technion Center for 3D Bioprinting and The Rina & Avner Schneur Center for Diabetes Research, as well as the Co-founder and Chief Scientific Adviser of Aleph Farms, Israel; and Dr. Timothy Olsen, Head of Cultured Meat in the Life Science business at Merck KGaA, Germany; about this relatively new and quickly developing sector. They explain what their teams are working on, including the biggest recent accomplishments, speak about the main challenges facing the field and how they can be resolved, and share their visions about the future of cultivated meat, aiming to provide more equitable and sustainable access to nutritious food for the growing world population.
-
Article
| Open Access Local H2 release remodels senescence microenvironment for improved repair of injured bone
Local H2 release remodels senescence microenvironment for improved repair of injured bone
Senescence microenvironment inhibits tissue repair in elderly individuals. Here, the authors demonstrate that local H2 supply has anti-inflammation and anti-senescence effects, and develop a H2-releasing scaffold to enhance aging bone defect repair.
- Shengqiang Chen
- , Yuanman Yu
- & Qianjun He
-
Article
| Open Access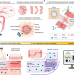 3D bioprinted multilayered cerebrovascular conduits to study cancer extravasation mechanism related with vascular geometry
3D bioprinted multilayered cerebrovascular conduits to study cancer extravasation mechanism related with vascular geometry
Geometrical complexities of blood vessels alter biophysical behaviors of circulating tumor cells, influencing cancer metastasis. Here, the authors develop a 3D bioprinted in vitro brain blood vessel-on-a-chip to investigate continuities between vascular geometry and metastatic cancer development.
- Wonbin Park
- , Jae-Seong Lee
- & Dong-Woo Cho
-
Article
| Open Access Mass production of lumenogenic human embryoid bodies and functional cardiospheres using in-air-generated microcapsules
Mass production of lumenogenic human embryoid bodies and functional cardiospheres using in-air-generated microcapsules
Current methods to generate spheroids are associated with low production throughputs, limiting clinical and industrial translation. Here the authors present a clean ultra-high-throughput in-air microfluidic platform for mass production of lumenogenic embryoid bodies and functional cardiospheres.
- Bas van Loo
- , Simone A. ten Den
- & Jeroen Leijten
-
Article
| Open Access Injectable and biodegradable piezoelectric hydrogel for osteoarthritis treatment
Injectable and biodegradable piezoelectric hydrogel for osteoarthritis treatment
The use of biomaterial scaffolds-based cartilage grafts could potentially innovate the Osteoarthritis (OA) treatment, but has been limited by toxicity concerns and invasive surgical procedures. Here, the authors report an injectable and biodegradable piezoelectric hydrogel with ultrasound activation to offer a minimally invasive approach for OA treatment.
- Tra Vinikoor
- , Godwin K. Dzidotor
- & Thanh D. Nguyen
-
Article
| Open Access Chronological adhesive cardiac patch for synchronous mechanophysiological monitoring and electrocoupling therapy
Chronological adhesive cardiac patch for synchronous mechanophysiological monitoring and electrocoupling therapy
Flexible electronic hydrogels that allow conformal tissue integration, online precision diagnosis, and simultaneous tissue regeneration are desired for advancing the treatment of myocardial infarction. Here, the authors report a chronological adhesive hydrogel patch integrating diagnostic and therapeutic functions through mechanophysiological monitoring and electrocoupling therapy.
- Chaojie Yu
- , Mingyue Shi
- & Junjie Li
-
Article
| Open Access Mechanically induced pyroptosis enhances cardiosphere oxidative stress resistance and metabolism for myocardial infarction therapy
Mechanically induced pyroptosis enhances cardiosphere oxidative stress resistance and metabolism for myocardial infarction therapy
Therapeutic options for myocardial infarction therapy remain limited. Here the authors report the application of an optimized liquid crystal substrate in the mass production and effective preconditioning of cardiospheres, which could generate cardiospheres with improved cell bioactivity and resistance to oxidative stress for myocardial infarction therapy.
- Yingwei Wang
- , Qi Li
- & Zheng Wu
-
Article
| Open Access An osteoinductive and biodegradable intramedullary implant accelerates bone healing and mitigates complications of bone transport in male rats
An osteoinductive and biodegradable intramedullary implant accelerates bone healing and mitigates complications of bone transport in male rats
Current limb salvage techniques for the treatment of the osteopathic non-unions still have several drawbacks that may prolong the duration of treatment. Here, Lin et al., propose using an osteoinductive (BMP-2 eluting) intramedullary and biodegradable implant to achieve early bony bridging and show that pin tract infection or docking site non-union can be avoided in experimental animal models of large bone defects.
- Sien Lin
- , Hirotsugu Maekawa
- & Yunzhi Peter Yang
-
Article
| Open Access In situ activation of flexible magnetoelectric membrane enhances bone defect repair
In situ activation of flexible magnetoelectric membrane enhances bone defect repair
Biomaterials that can be non-invasively activated to promote bone growth would be useful tools to repair bone defects in patients with comorbidities like inflammation or impaired osteogenesis. Here, the authors develop a composite membrane that can be stimulated by an external magnetic field and use it to correct skull defects in rats treated to reflect such comorbidities.
- Wenwen Liu
- , Han Zhao
- & Xuliang Deng
-
Article
| Open Access Drug screening at single-organoid resolution via bioprinting and interferometry
Drug screening at single-organoid resolution via bioprinting and interferometry
Traditional 2D cell culture platforms do not accurately reflect the physiology of human tumors. Here, authors combine bioprinting and high-speed live cell interferometry with machine learning to measure drug sensitivity at single-organoid resolution in a label-free manner.
- Peyton J. Tebon
- , Bowen Wang
- & Alice Soragni
-
Article
| Open Access Hydrogel-in-hydrogel live bioprinting for guidance and control of organoids and organotypic cultures
Hydrogel-in-hydrogel live bioprinting for guidance and control of organoids and organotypic cultures
Organ-like 3D cultures are advanced model system for biology and medicine limited by their uncontrolled cell self-assembly. Here, the authors develop a hydrogel-in-hydrogel bioprinting approach to dynamically control the growth landscape of a broad range of living 3D cell cultures.
- Anna Urciuolo
- , Giovanni Giuseppe Giobbe
- & Nicola Elvassore
-
Article
| Open Access Cultured meat platform developed through the structuring of edible microcarrier-derived microtissues with oleogel-based fat substitute
Cultured meat platform developed through the structuring of edible microcarrier-derived microtissues with oleogel-based fat substitute
Cultured meat (CM) is a sustainable alternative for meat, providing similar eating experience and nutrition. Here the authors present and fully characterize a CM platform from cellularized edible microcarriers and oleogel-based fat substitute.
- Feng-Chun Yen
- , Jovana Glusac
- & Marcelle Machluf
-
Article
| Open Access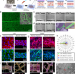 Leaf-venation-directed cellular alignment for macroscale cardiac constructs with tissue-like functionalities
Leaf-venation-directed cellular alignment for macroscale cardiac constructs with tissue-like functionalities
Recapitulating the native architecture of myocardium is crucial to engineering functional cardiac tissues. Here, the authors develop a leaf-venation-directed strategy for macroscale cardiac constructs with tissue-like structural, mechanical, and electrophysiological properties.
- Mao Mao
- , Xiaoli Qu
- & Dichen Li
-
Article
| Open Access Modeling of three-dimensional innervated epidermal like-layer in a microfluidic chip-based coculture system
Modeling of three-dimensional innervated epidermal like-layer in a microfluidic chip-based coculture system
Skin-nerve crosstalk is a major element of skin physiological pathology. Here the authors report a 3D innervated epidermal keratinocyte layer as a sensory neuron-epidermal keratinocyte coculture model on a microfluidic chip using the slope-based air-liquid interfacing culture and spatial compartmentalization.
- Jinchul Ahn
- , Kyungeun Ohk
- & Sang-Hoon Lee
-
Article
| Open Access Emergent collective organization of bone cells in complex curvature fields
Emergent collective organization of bone cells in complex curvature fields
It remains unclear how cells respond to complex extracellular geometries at the mesoscale. Here, the authors study the organization of bone cells in landscapes with varying curvatures, observing a preference for local concavities, multicellular bridging, and collective stress fiber orientation.
- Sebastien J. P. Callens
- , Daniel Fan
- & Amir A. Zadpoor
-
Article
| Open Access Bioengineered liver crosslinked with nano-graphene oxide enables efficient liver regeneration via MMP suppression and immunomodulation
Bioengineered liver crosslinked with nano-graphene oxide enables efficient liver regeneration via MMP suppression and immunomodulation
Bioengineered livers using decellularized scaffolds have been considered as an alternative to donor organs. Here, the authors modulate biophysical properties of decellularized scaffolds by crosslinking with nano-graphene oxide, thereby greatly enhancing therapeutic efficacy of bioengineered livers.
- Da-Hyun Kim
- , Min-Ji Kim
- & Kyung-Sun Kang
-
Article
| Open Access Light-driven biological actuators to probe the rheology of 3D microtissues
Light-driven biological actuators to probe the rheology of 3D microtissues
The mechanical properties of biological tissues are key to their integrity and function. Here, the authors engineer 3D microtissues from optogenetically modified fibroblasts and use light to quantify tissue elasticity and strain propagation using their own constituent cells as internal actuators.
- Adrien Méry
- , Artur Ruppel
- & Thomas Boudou
-
Article
| Open Access Volumetric additive manufacturing of pristine silk-based (bio)inks
Volumetric additive manufacturing of pristine silk-based (bio)inks
Volumetric additive manufacturing of protein scaffolds has a wide range of possible biomedical applications. Here the authors report on the bioprinting of unmodified silk sericin and silk fibroin inks with shape-memory and tuneable mechanical properties and demonstrate the potential of the inks in different applications.
- Maobin Xie
- , Liming Lian
- & Yu Shrike Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Implantable niche with local immunosuppression for islet allotransplantation achieves type 1 diabetes reversal in rats
Implantable niche with local immunosuppression for islet allotransplantation achieves type 1 diabetes reversal in rats
Islet transplantation for type 1 diabetes management is hindered by the life-long need for immunosuppressive medications. Here, the authors report an islet encapsulation device with local anti-rejection drug release that achieves long-term diabetes reversal in male rats and reduces drug-related toxicity.
- Jesus Paez-Mayorga
- , Jocelyn Nikita Campa-Carranza
- & Alessandro Grattoni
-
Article
| Open Access Bead-jet printing enabled sparse mesenchymal stem cell patterning augments skeletal muscle and hair follicle regeneration
Bead-jet printing enabled sparse mesenchymal stem cell patterning augments skeletal muscle and hair follicle regeneration
Current mesenchymal stem cell (MSC) transplantation practices are limited by the loss or reduced performance of MSCs. Here the authors develop a bead-jet printer for intraoperative formulation and printing of MSCs-laden Matrigel beads to improve skeletal muscle and hair follicle regeneration.
- Yuanxiong Cao
- , Jiayi Tan
- & Shaohua Ma
-
Article
| Open Access Endowing universal CAR T-cell with immune-evasive properties using TALEN-gene editing
Endowing universal CAR T-cell with immune-evasive properties using TALEN-gene editing
Host versus graft reaction is a major impediment to CAR-T cell immune therapy in allogeneic settings. Authors show here that CAR-T cells, engineered to be deficient in MHC I expression but to express the NK inhibitor HLA-E, are resistant to destruction by both T and NK cells of the host.
- Sumin Jo
- , Shipra Das
- & Julien Valton
-
Article
| Open Access Molecularly cleavable bioinks facilitate high-performance digital light processing-based bioprinting of functional volumetric soft tissues
Molecularly cleavable bioinks facilitate high-performance digital light processing-based bioprinting of functional volumetric soft tissues
Soft tissue fabrication using digital light processing remains challenging. Here the authors present a molecular cleavage approach to achieve high-performance bioprinting of constructs with tissue-matching mechanical properties and structural complexity.
- Mian Wang
- , Wanlu Li
- & Yu Shrike Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access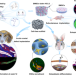 An instantly fixable and self-adaptive scaffold for skull regeneration by autologous stem cell recruitment and angiogenesis
An instantly fixable and self-adaptive scaffold for skull regeneration by autologous stem cell recruitment and angiogenesis
Limited stem cells and mismatched interface fusion have plagued biomaterial-mediated cranial reconstruction. Here, the authors engineer an instantly fixable and self-adaptive scaffold to promote calcium chelation and interface integration, regulate macrophage M2 polarization, and recruit endogenous stem cells.
- Gonggong Lu
- , Yang Xu
- & Xingdong Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access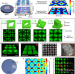 High-throughput production of functional prototissues capable of producing NO for vasodilation
High-throughput production of functional prototissues capable of producing NO for vasodilation
Protoissues have received a lot of attention for studying cell interaction and for biomedical engineering. Here, the authors demonstrate a high-throughput, bottom-up approach to assemble spatial programmable prototissues based on the magnetic Archimedes affect and demonstrate biomedical application for producing NO for vasodilation.
- Xiangxiang Zhang
- , Chao Li
- & Xiaojun Han
-
Article
| Open Access Mechanical control of innate immune responses against viral infection revealed in a human lung alveolus chip
Mechanical control of innate immune responses against viral infection revealed in a human lung alveolus chip
Mechanical forces in lungs facilitate breathing motions. Here the authors use a microfluidic human lung alveolus chip to study influenza infection and find that mechanical forces from active chips also induce innate inflammatory responses via, at least partially, signaling from TRPV4 and RAGE, thereby implicating them as potential therapeutic targets for lung inflammation.
- Haiqing Bai
- , Longlong Si
- & Donald E. Ingber
-
Article
| Open Access Tissue extracellular matrix hydrogels as alternatives to Matrigel for culturing gastrointestinal organoids
Tissue extracellular matrix hydrogels as alternatives to Matrigel for culturing gastrointestinal organoids
The culture of gastrointestinal organoids relies on Matrigel that has several drawbacks for clinical application. Here, the authors report the feasibility of gastrointestinal tissue-mimetic matrices as effective alternatives to Matrigel for organoid culture and transplantation.
- Suran Kim
- , Sungjin Min
- & Seung-Woo Cho
-
Article
| Open Access Using CRISPR-Kill for organ specific cell elimination by cleavage of tandem repeats
Using CRISPR-Kill for organ specific cell elimination by cleavage of tandem repeats
How double strand breaks (DSBs) are repaired within the plant 45S rDNA repeats is unclear. Here, the authors show that Cas9-mediated DSBs in 45S rDNA are mainly repaired by cNHEJ and describe CRISPR-Kill as a tool for organ-specific cell elimination by targeting functional repetitive DNA in Arabidopsis.
- Angelina Schindele
- , Fabienne Gehrke
- & Holger Puchta
-
Article
| Open Access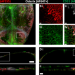 Quantitative 3D imaging of the cranial microvascular environment at single-cell resolution
Quantitative 3D imaging of the cranial microvascular environment at single-cell resolution
Vascularization is critical for cranial bone growth, maintenance, and healing, but it remains unknown how blood vessels are spatially distributed in the calvarium, and how they interact with skeletal progenitors during these processes. Here, the authors apply a quantitative light-sheet imaging platform to visualize and analyze the relationship between blood vessels and skeletal progenitors throughout the murine calvarium.
- Alexandra N. Rindone
- , Xiaonan Liu
- & Warren L. Grayson
-
Article
| Open Access Engineered whole cut meat-like tissue by the assembly of cell fibers using tendon-gel integrated bioprinting
Engineered whole cut meat-like tissue by the assembly of cell fibers using tendon-gel integrated bioprinting
Mammalian cell-based cultured meat has mostly been unstructured, leaving a demand for artificial steak-like meat. Here the authors present an assembled steak-like tissue of bovine skeletal muscle, adipose tissue, and blood capillary tissue fabricated by tendon-gel integrated printing technology.
- Dong-Hee Kang
- , Fiona Louis
- & Michiya Matsusaki
-
Article
| Open Access Microchannelled alkylated chitosan sponge to treat noncompressible hemorrhages and facilitate wound healing
Microchannelled alkylated chitosan sponge to treat noncompressible hemorrhages and facilitate wound healing
Developing effective treatments for noncompressible hemorrhages remains a challenge. Here the authors engineer alkylated chitosan sponges with highly interconnective microchannels and demonstrate anti-infective activity, as well as higher pro-coagulant, hemostatic and wound healing capacities compared to clinically-used materials in rat and pig liver models.
- Xinchen Du
- , Le Wu
- & Meifeng Zhu
-
Article
| Open Access Microfluidic device with brain extracellular matrix promotes structural and functional maturation of human brain organoids
Microfluidic device with brain extracellular matrix promotes structural and functional maturation of human brain organoids
Brain organoids derived from human pluripotent stem cells can model human brain development and disease, though current culture systems fail to ensure reliable production of high-quality organoids. Here the authors combine human brain extracellular matrix and culture in a microfluidic device to promote structural and functional maturation of human brain organoids.
- Ann-Na Cho
- , Yoonhee Jin
- & Seung-Woo Cho
-
Article
| Open Access 4D polycarbonates via stereolithography as scaffolds for soft tissue repair
4D polycarbonates via stereolithography as scaffolds for soft tissue repair
Shape memory scaffolds are needed for minimally invasive tissue repair and void filling. Here the authors report on the development of 4D printed polycarbonate-based scaffolds with surface degradation properties which fill voids without deforming tissue and allow for tissue ingrowth with reduced immune response.
- Andrew C. Weems
- , Maria C. Arno
- & Andrew P. Dove
-
Article
| Open Access Vapor-phased fabrication and modulation of cell-laden scaffolding materials
Vapor-phased fabrication and modulation of cell-laden scaffolding materials
Current methods for the modular assembly of biomaterials are associated with limitations. Here the authors implement vapor-phase deposition to fabricate 3D polymeric materials that permit biomolecule functionalization, tunable mass transport and mechanical properties, as well as control over boundaries between compartments, and analyze the behavior of 3D encapsulated cells.
- Chih-Yu Wu
- , Ting-Ying Wu
- & Hsien-Yeh Chen
-
Article
| Open Access Microfluidic platform accelerates tissue processing into single cells for molecular analysis and primary culture models
Microfluidic platform accelerates tissue processing into single cells for molecular analysis and primary culture models
Existing methods for tissue dissociation are inefficient and lead to variable outcomes and biases. Here, the authors present a microfluidic platform that combines digestion, disaggregation and filtration of tissue to allow single cell analysis and RNA sequencing.
- Jeremy A. Lombardo
- , Marzieh Aliaghaei
- & Jered B. Haun
-
Article
| Open Access Janus 3D printed dynamic scaffolds for nanovibration-driven bone regeneration
Janus 3D printed dynamic scaffolds for nanovibration-driven bone regeneration
Fabrication of dynamic, reversible and biocompatible scaffolds with non-invasive external triggers has so far been limited. Here, the authors report on the creation of 3D printed scaffolds with Janus structure that produce nanovibrations when exposed to ultrasound, promoting bone regeneration.
- Sandra Camarero-Espinosa
- & Lorenzo Moroni
-
Article
| Open Access Concomitant control of mechanical properties and degradation in resorbable elastomer-like materials using stereochemistry and stoichiometry for soft tissue engineering
Concomitant control of mechanical properties and degradation in resorbable elastomer-like materials using stereochemistry and stoichiometry for soft tissue engineering
The creation of biomaterials which are resorbable and have biomimetic mechanical properties is key to successful tissue engineering. Here the authors report on the creation of a new biopolymer where the mechanical properties can be tuned by changing the ratios of cis:trans double bonds in the backbone.
- Mary Beth Wandel
- , Craig A. Bell
- & Matthew L. Becker
-
Review Article
| Open Access Plant-based and cell-based approaches to meat production
Plant-based and cell-based approaches to meat production
Large-scale meat production can have negative impacts on public health, the environment and animal welfare. In this Review, the authors consider plant-based and cell-based approaches to meat production and the challenges they face.
- Natalie R. Rubio
- , Ning Xiang
- & David L. Kaplan
-
Article
| Open Access Modeling early stage atherosclerosis in a primary human vascular microphysiological system
Modeling early stage atherosclerosis in a primary human vascular microphysiological system
Human microphysiological systems (MPS) have some advantages over animal models to study the mechanisms of disease. Here the authors use a tissue-engineered blood vessel MPS to create a model of early stage atherosclerosis and assess the effect of several drugs.
- Xu Zhang
- , Muath Bishawi
- & George A. Truskey
-
Article
| Open Access Developmental GABA polarity switch and neuronal plasticity in Bioengineered Neuronal Organoids
Developmental GABA polarity switch and neuronal plasticity in Bioengineered Neuronal Organoids
Brain organoids are important tools to study early development and disease but little is known of their network activity and plasticity. Here the authors generate iPSC-derived neuronal organoids that display early network formation and maturation with evidence for a GABA polarity switch and long-term potentiation.
- Maria-Patapia Zafeiriou
- , Guobin Bao
- & Wolfram-Hubertus Zimmermann
-
Article
| Open Access Mechano-modulatory synthetic niches for liver organoid derivation
Mechano-modulatory synthetic niches for liver organoid derivation
3D liver organoids hold great promise for regenerative medicine but the use of ill-defined matrices limits their potential. Here, the authors generate human and mouse liver organoids using a chemically defined matrix, and reveal a link between matrix stiffness and organoid growth that does not require acto-myosin contraction.
- Giovanni Sorrentino
- , Saba Rezakhani
- & Kristina Schoonjans

 A patient-specific lung cancer assembloid model with heterogeneous tumor microenvironments
A patient-specific lung cancer assembloid model with heterogeneous tumor microenvironments