Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access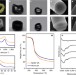 Carbonization of a stable β-sheet-rich silk protein into a pseudographitic pyroprotein
Carbonization of a stable β-sheet-rich silk protein into a pseudographitic pyroprotein
The strength and stability of silk proteins is thought to be related to the high content of β-sheets within their structures. Here, the authors show that when heated at high temperature, and above that of thermal degradation, these β-sheets are transformed into an ordered hexagonal graphitic structure.
- Se Youn Cho
- , Young Soo Yun
- & Hyoung-Joon Jin
-
Article
| Open Access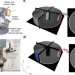 In-operando high-speed tomography of lithium-ion batteries during thermal runaway
In-operando high-speed tomography of lithium-ion batteries during thermal runaway
It is important to understand the mechanisms of thermally induced battery degradation and any safety hazards. Here, the authors use high-speed synchrotron radiation X-ray computed tomography to shed light on the structural and thermal dynamics associated with thermal runaway and failure of commercial Li-ion batteries.
- Donal P. Finegan
- , Mario Scheel
- & Paul R. Shearing
-
Article |
 Transition from near-field thermal radiation to phonon heat conduction at sub-nanometre gaps
Transition from near-field thermal radiation to phonon heat conduction at sub-nanometre gaps
Heat transfer typically occurs by conduction via phonons and radiation via photons, but the distinction between them blurs as surfaces come into contact. Chiloyan et al.study heat transfer between surfaces at sub-nanometre separation and explore the behaviour of phonons as the surfaces approach each other.
- Vazrik Chiloyan
- , Jivtesh Garg
- & Gang Chen
-
Article |
 Ultrasonic hammer produces hot spots in solids
Ultrasonic hammer produces hot spots in solids
The initiation of explosions is thought to result from ‘hot spot’ generation at localized microstructures in energetic material, although experimental evidence has been limited. Here, the authors show controllable hot spot formation in solid composites using an ultrasonic hammer, introducing a new method of study.
- Sizhu You
- , Ming-Wei Chen
- & Kenneth S. Suslick
-
Article |
 Harvesting dissipated energy with a mesoscopic ratchet
Harvesting dissipated energy with a mesoscopic ratchet
Thermoelectric devices convert waste heat to electrical power but suffer from low efficiency. Roche et al.create a mesoscopic heat engine comprising capacitively coupled hot and cold electrical circuits in which thermal fluctuations in the former are converted to potential fluctuations in the latter
- B. Roche
- , P. Roulleau
- & D.C. Glattli
-
Article
| Open Access Description of quantum coherence in thermodynamic processes requires constraints beyond free energy
Description of quantum coherence in thermodynamic processes requires constraints beyond free energy
The statistical nature of standard thermodynamics provides an incomplete picture for individual processes at the nanoscale, and new relations have been developed to extend it. Here, the authors show that by quantifying time-asymmetry it is also possible to characterize how quantum coherence is modified in such processes.
- Matteo Lostaglio
- , David Jennings
- & Terry Rudolph
-
Article |
 Densified network glasses and liquids with thermodynamically reversible and structurally adaptive behaviour
Densified network glasses and liquids with thermodynamically reversible and structurally adaptive behaviour
Degrees of freedom can be frozen in glassy material, which results in a hysteresis in heat capacity under cooling or heating. Here, the authors show that the hysteresis can be minimized at selected thermodynamic conditions, leading to thermally reversible glasses that are isostatically rigid.
- M. Bauchy
- & M. Micoulaut
-
Article
| Open Access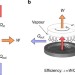 A sublimation heat engine
A sublimation heat engine
Heat engines are designed to convert thermal energy into mechanical work through a thermodynamic cycle. Here, Wells et al. show a cycle based on a sublimation process, where a disk of dry ice that rotates on a hot surface due to the Leidenfrost effect is coupled to a simple electromagnetic generator.
- Gary G. Wells
- , Rodrigo Ledesma-Aguilar
- & Khellil Sefiane
-
Article |
 Visualization and thermodynamic encoding of single-molecule partition function projections
Visualization and thermodynamic encoding of single-molecule partition function projections
It is challenging to determine thermodynamic quantities for single molecules. Here, the authors access single-molecule thermodynamic information via a microscopic and computational study of a confined molecule, for which the resulting patterns represent a real-space equilibrium probability distribution.
- Carlos-Andres Palma
- , Jonas Björk
- & Johannes V. Barth
-
Article |
 Hydrodynamic phonon transport in suspended graphene
Hydrodynamic phonon transport in suspended graphene
Hydrodynamic phonon transport occurs when phonons are able to drift over macroscopic distances, leading to the breakdown of Fourier’s law of heat conduction. Here, the authors predict that this regime occurs in suspended graphene at higher temperatures than bulk materials.
- Sangyeop Lee
- , David Broido
- & Gang Chen
-
Article |
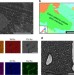 Deviation from high-entropy configurations in the atomic distributions of a multi-principal-element alloy
Deviation from high-entropy configurations in the atomic distributions of a multi-principal-element alloy
Alloys containing multiple elements of equal distributions are known to show enhanced properties as they tend to form single phases. Here, the authors demonstrate that even in cases of elemental segregation and chemical ordering, these alloys can still maintain enhanced properties.
- Louis J. Santodonato
- , Yang Zhang
- & Peter K Liaw
-
Article |
 Mechanical instability at finite temperature
Mechanical instability at finite temperature
How do fluctuations alter the dynamics of phase transitions in crystal near a mechanical instability? To answer this question, here Mao et al. present a square lattice-based analytic model showing that large entropic effects can take place at nonzero temperature near the transition.
- Xiaoming Mao
- , Anton Souslov
- & T. C. Lubensky
-
Article
| Open Access Size dependence of phase transitions in aerosol nanoparticles
Size dependence of phase transitions in aerosol nanoparticles
Although phase transitions are fundamental for understanding aerosol particles, current models are insufficient to explain observations at the nanoscale. Here, the authors present a method for investigating droplets, suggesting particle size is a key determinant in the phase diagram of nanoparticles.
- Yafang Cheng
- , Hang Su
- & Ulrich Pöschl
-
Article |
 A microscopic steam engine implemented in an optical tweezer
A microscopic steam engine implemented in an optical tweezer
Heat engines are widely used in our daily life, hence there is interest in miniaturized versions. Here, Quinto-Su demonstrates a micrometer-sized piston steam engine in an optical tweezer, whereby a single colloidal particle is periodically driven by microscopic vapour explosions and optical forces.
- Pedro A. Quinto-Su
-
Article |
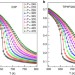 Widom line and dynamical crossovers as routes to understand supercritical water
Widom line and dynamical crossovers as routes to understand supercritical water
Liquid and gas phases are indistinguishable at supercritical conditions. Here, Gallo et al.show that this convention is not precisely true for supercritical water on approaching its critical point due to the existence of the Widom line, which separates a liquid-like and a gas-like regime on its two sides.
- P. Gallo
- , D. Corradini
- & M. Rovere
-
Article
| Open Access Observing classical nucleation theory at work by monitoring phase transitions with molecular precision
Observing classical nucleation theory at work by monitoring phase transitions with molecular precision
Many nanoscale systems can form ordered microphases through non-classical multistep nucleation. Here, the authors report that glucose isomerase, which is known to exhibit the characteristics of multi-step nucleation in 3D, nucleates along the pathway predicted by classical nucleation theory in 2D.
- Mike Sleutel
- , Jim Lutsko
- & Dominique Maes
-
Article |
 Freezing-in orientational disorder induces crossover from thermally-activated to temperature-independent transport in organic semiconductors
Freezing-in orientational disorder induces crossover from thermally-activated to temperature-independent transport in organic semiconductors
The electronic properties of organic charge-transfer complexes are highly coupled to their crystallographic structures. Goetz et al.show that the librational motion can mediate a glass-like transition, resulting in a transition from temperature-activated to temperature-independent charge transport.
- K. P. Goetz
- , A. Fonari
- & O. D. Jurchescu
-
Article |
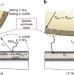 Deciphering the scaling of single-molecule interactions using Jarzynski’s equality
Deciphering the scaling of single-molecule interactions using Jarzynski’s equality
Adhesion forces depend on the strength and density of the individual molecular interactions of which they are composed. Here, the authors use surface force apparatus and atomic force microscopy to experimentally probe the scaling of single-molecule interactions into macroscopic properties.
- Sangeetha Raman
- , Thomas Utzig
- & Markus Valtiner
-
Article |
 Explaining why simple liquids are quasi-universal
Explaining why simple liquids are quasi-universal
Researchers refer to the approximate invariance in the structure and dynamics of simple liquids among different pair models as quasi-universality, while little is known about its origin. Here, Becher et al.show that the pair potential as a sum of exponential terms fulfils the quasuniversality.
- Andreas K. Bacher
- , Thomas B. Schrøder
- & Jeppe C. Dyre
-
Article
| Open Access Self-propagating high-temperature synthesis for compound thermoelectrics and new criterion for combustion processing
Self-propagating high-temperature synthesis for compound thermoelectrics and new criterion for combustion processing
The existing methods to synthesize thermoelectric materials remain constrained to multi-step processes that are usually time and energy consuming. Here, Su et al.use a fast, one-step combustion approach to synthesize various compounds, which holds promise for scalable industrial processing.
- Xianli Su
- , Fan Fu
- & Ctirad Uher
-
Article |
 The unlikely Carnot efficiency
The unlikely Carnot efficiency
Carnot efficiency is the highest theoretically possible efficiency that a heat engine can have. Verley et al.use the fluctuation theorem to show that the Carnot value is the least likely efficiency in the long time limit.
- Gatien Verley
- , Massimiliano Esposito
- & Christian Van den Broeck
-
Article |
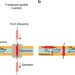 Spontaneous transmembrane helix insertion thermodynamically mimics translocon-guided insertion
Spontaneous transmembrane helix insertion thermodynamically mimics translocon-guided insertion
Insertion of proteins into a membrane bilayer driven by the Sec translocon is aided by the attributes of the inserted peptides. Here, Ulmschneider et al.measure the free energies of various insertion events and suggest that the membrane interface plays an important role in translocon-guided TM helix insertion.
- Martin B. Ulmschneider
- , Jakob P. Ulmschneider
- & Stephen H. White
-
Article |
 Evidence of Stranski–Krastanov growth at the initial stage of atmospheric water condensation
Evidence of Stranski–Krastanov growth at the initial stage of atmospheric water condensation
Water condensation on surfaces occurs in nature everywhere, but the study of its initial stage at ambient conditions is very challenging. Here, Song et al.address this issue using thermal controlled atomic force microscopy and identify a mixture of layer-by-layer and island-like modes.
- Jie Song
- , Qiang Li
- & Mingdong Dong
-
Article |
 A structural signature of liquid fragility
A structural signature of liquid fragility
Glass fragility characterises the rate of change in viscosity as a liquid is cooled towards the glass transition temperature. Here, the authors demonstrate via neutron diffraction that the rate at which structural ordering occurs within the melt correlates with kinetic fragility in a range of metallic glass samples.
- N. A. Mauro
- , M. Blodgett
- & K. F. Kelton
-
Article |
 Stabilizing colloidal crystals by leveraging void distributions
Stabilizing colloidal crystals by leveraging void distributions
It is challenging to prepare colloidal crystals with long-range order for their applications. Mahynski et al. propose a method to achieve this goal through tailoring energy loss of absorbed polymers in crystal voids to selectively stabilize one crystal structure among its competing polymorphs.
- Nathan A. Mahynski
- , Athanassios Z. Panagiotopoulos
- & Sanat K. Kumar
-
Article |
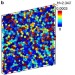 Multiple reentrant glass transitions in confined hard-sphere glasses
Multiple reentrant glass transitions in confined hard-sphere glasses
Wall–fluid interactions are known to have a large influence on the physics of confined glasses. Here, the authors observe a multiple re-entrant glass transition for a polydisperse hard-sphere system confined between two surfaces, when the wall separation distance is of the order of a few particle diameters.
- Suvendu Mandal
- , Simon Lang
- & Fathollah Varnik
-
Article |
 Momentum-resolved hidden-order gap reveals symmetry breaking and origin of entropy loss in URu2Si2
Momentum-resolved hidden-order gap reveals symmetry breaking and origin of entropy loss in URu2Si2
URu2Si2 undergoes a prominent phase transition to an ordered state of unknown nature. Using high-resolution 3D ARPES, Bareille et al. image an abrupt symmetry reconstruction of its heavy-fermion electronic structure that could explain the origin of the ordered state and its missing entropy.
- C. Bareille
- , F. L. Boariu
- & A. F. Santander-Syro
-
Article |
 The key role of vibrational entropy in the phase transitions of dithiazolyl-based bistable magnetic materials
The key role of vibrational entropy in the phase transitions of dithiazolyl-based bistable magnetic materials
Some organic radicals are diamagnetic at low temperatures but switch to a paramagnetic state at higher temperatures. Vela at al. now present computer simulations that indicate this phase change is a result of vibrational entropy, which causes the radicals to organize into neat stacks.
- Sergi Vela
- , Fernando Mota
- & Jordi Ribas-Arino
-
Article |
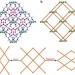 Giant negative linear compression positively coupled to massive thermal expansion in a metal–organic framework
Giant negative linear compression positively coupled to massive thermal expansion in a metal–organic framework
Negative linear compressibility in materials is usually accompanied by a thermal contraction upon heating. Here, the authors report a metal organic framework that breaks this rule, exhibiting large intrinsic negative linear compressibility coinciding with strong positive thermal expansion.
- Weizhao Cai
- & Andrzej Katrusiak
-
Article |
 Work extraction and thermodynamics for individual quantum systems
Work extraction and thermodynamics for individual quantum systems
Traditionally, thermodynamics deals with the study of macroscopic systems comprised of a large number of particles. Skrzypczyk et al. present a framework—including a thermal bath and work-storage device—to extract the optimal amount of work from individual quantum systems.
- Paul Skrzypczyk
- , Anthony J. Short
- & Sandu Popescu
-
Article |
 Interfacial mobility scale determines the scale of collective motion and relaxation rate in polymer films
Interfacial mobility scale determines the scale of collective motion and relaxation rate in polymer films
Interfacial mobility in thin polymer films is crucial for their technological applications. Here, Hanakata et al.provide computational evidence for a general relationship between the scale of interfacial mobility and collective motion within the films, which explains their glass transition behaviour.
- Paul Z. Hanakata
- , Jack F. Douglas
- & Francis W. Starr
-
Article |
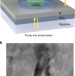 Electrochemically tunable thermal conductivity of lithium cobalt oxide
Electrochemically tunable thermal conductivity of lithium cobalt oxide
Materials with variable and reversible thermal conductivities are important in technologies, and yet such materials are rare. Here, Cho et al. report in situmeasurements of thermal conductivity of lithium cobalt oxide, and show how to reversibly modulate thermal conductivities over a considerable range.
- Jiung Cho
- , Mark D. Losego
- & Paul V. Braun
-
Article |
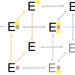 Physiological sodium concentrations enhance the iodide affinity of the Na+/I− symporter
Physiological sodium concentrations enhance the iodide affinity of the Na+/I− symporter
Thyroid hormone synthesis requires import of iodide ions through the Na+/I− symporter, however its affinity for iodide is surprisingly low. Using a statistical thermodynamics approach, Nicola et al. show that sodium ion binding enhances iodide affinity, revealing a mechanism for iodide transport.
- Juan P. Nicola
- , Nancy Carrasco
- & L. Mario Amzel
-
Article |
 An unconventional bilayer ice structure on a NaCl(001) film
An unconventional bilayer ice structure on a NaCl(001) film
The complication of water adsorption on surfaces goes well beyond a simple hexagonal bilayer model predicted by the ice rule. Chen et al.observe an extended cyclical pattern of water tetramers on an insulator surface, which is attributable to the formation of periodic Bjerrum defects at high density.
- Ji Chen
- , Jing Guo
- & En-Ge Wang
-
Article |
 An electrochemical system for efficiently harvesting low-grade heat energy
An electrochemical system for efficiently harvesting low-grade heat energy
Thermoelectric devices can convert low-grade heat sources into electricity, but suffer from low efficiency. Here, Lee et al.present a thermally regenerative electrochemical device with copper hexacyanoferrate electrode material, which enables efficient heat-to-electricity energy conversion.
- Seok Woo Lee
- , Yuan Yang
- & Yi Cui
-
Article |
 A quantum diffractor for thermal flux
A quantum diffractor for thermal flux
The Josephson effect produces a supercurrent between two superconductors separated by an insulator, but it also leads to more exotic effects like electric quantum diffraction. Here, the authors show the appearance of Fraunhofer diffraction for thermal currents in a thermally biased Josephson junction.
- Maria José Martínez-Pérez
- & Francesco Giazotto
-
Article |
 Understanding water’s anomalies with locally favoured structures
Understanding water’s anomalies with locally favoured structures
Water shows various anomalies, but an understanding of their microscopic origin is still missing. Russo and Tanaka introduce a new structural order parameter in simulations and identify locally favoured structures whose formation is responsible for the anomalies and supercooled water's stability against ice crystallization.
- John Russo
- & Hajime Tanaka
-
Article
| Open Access Glassiness and exotic entropy scaling induced by quantum fluctuations in a disorder-free frustrated magnet
Glassiness and exotic entropy scaling induced by quantum fluctuations in a disorder-free frustrated magnet
Spin liquids and spin ices arise when spins arranged on a lattice have several states that are close in energy, a phenomenon referred to as frustration. Here, Klich et al.show that quantum fluctuations can induce a spin liquid to freeze into a glassy state.
- I. Klich
- , S.-H. Lee
- & K. Iida
-
Article
| Open Access Unexpectedly high pressure for molecular dissociation in liquid hydrogen by electronic simulation
Unexpectedly high pressure for molecular dissociation in liquid hydrogen by electronic simulation
Studying the high pressure phase diagram of hydrogen experimentally or by simulations presents significant challenges. Here, the authors apply a combined molecular dynamics and many-body quantum Monte Carlo approach, finding that the molecular liquid phase is stable at higher pressures than previously believed.
- Guglielmo Mazzola
- , Seiji Yunoki
- & Sandro Sorella
-
Article
| Open Access Restoration of the third law in spin ice thin films
Restoration of the third law in spin ice thin films
In bulk, the spin ice Dy2Ti2O7 has posed an enigma because – due to its slow dynamics – it is unclear whether and how the material will reach a zero entropy state at zero temperature. Here, the authors show that in thin films of Dy2Ti2O7a zero entropy state is induced at 0.4 K, plausibly by lattice strain.
- L. Bovo
- , X. Moya
- & S.T. Bramwell
-
Article |
 Thermotropic phase boundaries in classic ferroelectrics
Thermotropic phase boundaries in classic ferroelectrics
Morphotropic phase boundaries, which separate two competing phases of different chemical composition, are the crucial ingredient for lead-based piezoelectrics. Here, the authors show that similar enhanced properties and analogous thermotropic phase boundaries can occur in simple, lead-free ferroelectrics.
- Tom T.A. Lummen
- , Yijia Gu
- & Venkatraman Gopalan
-
Article |
 Co-operativity in a nanocrystalline solid-state transition
Co-operativity in a nanocrystalline solid-state transition
Co-operativity is an effect where initial reaction events influence later events. Here, White et al.find evidence for co-operativity in the cation exchange process of nanocrystals, as cadmium selenide transforms into the copper selenide phase.
- Sarah L. White
- , Jeremy G. Smith
- & Prashant K. Jain
-
Article |
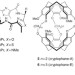 A very stable complex of a modified marine cyclopeptide with chloroform
A very stable complex of a modified marine cyclopeptide with chloroform
Typically dispersion forces are weak interactions, and host–guest chemistry is dominated by more powerful events such as hydrogen bonding. Here, the authors show extremely high binding between a modified marine peptide and chloroform, driven by dispersion interactions with the chlorine atoms.
- Gebhard Haberhauer
- , Áron Pintér
- & Sascha Woitschetzki
-
Article |
 Stabilization of a linear nanomechanical oscillator to its thermodynamic limit
Stabilization of a linear nanomechanical oscillator to its thermodynamic limit
Micro- and nano-scale oscillators are finding usage in novel sensors, but their performance is limited by their sensitivity to external perturbations. Here, the authors report an optomechanical technique to stabilize a nanomechanical beam to its thermodynamic limit.
- Emanuel Gavartin
- , Pierre Verlot
- & Tobias J. Kippenberg
-
Article |
 A solid–solid phase transition in carbon dioxide at high pressures and intermediate temperatures
A solid–solid phase transition in carbon dioxide at high pressures and intermediate temperatures
It is desirable for scientists to be able to predict the structures, spectra and phase diagrams of molecular crystals using ab initio computation. Li et al. demonstrate such an approach, which is able to determine the phase behaviour of solid carbon dioxide at a range of pressures and temperatures.
- Jinjin Li
- , Olaseni Sode
- & So Hirata
-
Article |
 Model studies of force-dependent kinetics of multi-barrier reactions
Model studies of force-dependent kinetics of multi-barrier reactions
In chemical reactions, inner barriers, which precede the rate-determining transition state, are kinetically invisible but mechanistically significant. On an example of reduction of macrocyclic disulphides, the authors quantify these inner barriers by studying the reaction rate as a function of applied force.
- Yancong Tian
- , Timothy J. Kucharski
- & Roman Boulatov
-
Article |
 Evidence of two distinct local structures of water from ambient to supercooled conditions
Evidence of two distinct local structures of water from ambient to supercooled conditions
Liquid water shows anomalous behaviour, which is expected to be related with critical phenomena below its melting temperature. Taschinet al.experimentally identify two intermolecular vibrational modes that provide evidence for the coexistence of high-density and low-density water forms.
- A. Taschin
- , P. Bartolini
- & R. Torre
-
Article |
 Thermodynamic behaviour of supercritical matter
Thermodynamic behaviour of supercritical matter
A physical description of supercritical fluids remains challenging because common approximations for solids and gases do not apply to liquids. Bolmatov et al. identify a liquid/gas dynamic crossover of specific heat above the critical point, and formulate a theory to shed light on its nature.
- Dima Bolmatov
- , V. V. Brazhkin
- & K. Trachenko
-
Article
| Open Access Semiclassical Monte-Carlo approach for modelling non-adiabatic dynamics in extended molecules
Semiclassical Monte-Carlo approach for modelling non-adiabatic dynamics in extended molecules
Many interesting chemical problems like photosynthesis and photovoltaics involve non-adiabatic dynamical phenomena, which are difficult to predict theoretically. Here, the authors develop a new numerical method capable of recovering quantum interferences that are neglected by conventional methods.
- Vyacheslav N. Gorshkov
- , Sergei Tretiak
- & Dmitry Mozyrsky

 Self-assembly of dynamic orthoester cryptates
Self-assembly of dynamic orthoester cryptates