Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Oriented graphene nanoribbons embedded in hexagonal boron nitride trenches
Oriented graphene nanoribbons embedded in hexagonal boron nitride trenches
Graphene nanoribbons are promising candidates for 2D material electrical interconnects; however, the top-down fabrication of nanoribbons has remained a challenge. Here, Chenet al. have used a hexagonal boron nitride template to grow narrow, integrated graphene nanoribbons with small bandgaps.
- Lingxiu Chen
- , Li He
- & Mianheng Jiang
-
Article
| Open Access Intervalley scattering by acoustic phonons in two-dimensional MoS2 revealed by double-resonance Raman spectroscopy
Intervalley scattering by acoustic phonons in two-dimensional MoS2 revealed by double-resonance Raman spectroscopy
Double-resonance Raman scattering is a sensitive spectroscopic probe of the interplay between electrons and phonons in a crystal. Here, the authors unveil the signature of double-resonance intervalley scattering by acoustic phonons in two-dimensional MoS2, underpinning the physics of valley depolarization.
- Bruno R. Carvalho
- , Yuanxi Wang
- & Marcos A. Pimenta
-
Article
| Open Access Liquid-state carbon-13 hyperpolarization generated in an MRI system for fast imaging
Liquid-state carbon-13 hyperpolarization generated in an MRI system for fast imaging
Hyperpolarized MRI uses molecules with a nuclear spin polarization beyond the thermodynamic equilibrium to enhance imaging contrast. Here, Schmidtet al. enable a single MRI system to both generate a hyperpolarized tracer and perform imaging, eliminating the need for an external polarizer.
- A. B. Schmidt
- , S. Berner
- & J. -B. Hövener
-
Article
| Open Access Delayed entanglement echo for individual control of a large number of nuclear spins
Delayed entanglement echo for individual control of a large number of nuclear spins
Single electrons of solid-state defects can be used to detect nearby nuclear spins, but so far only a few at a time have been resolved. Here the authors propose an approach based on delayed entanglement echo that demonstrates improved detection and manipulation capabilities of nuclear spins by an NV centre.
- Zhen-Yu Wang
- , Jorge Casanova
- & Martin B. Plenio
-
Article
| Open Access Perfect X-ray focusing via fitting corrective glasses to aberrated optics
Perfect X-ray focusing via fitting corrective glasses to aberrated optics
X-ray optics are notoriously challenging to fabricate due to the strict tolerances that result from the short wavelength of radiation. Here, Seibothet al. carefully quantify aberrations in complex X-ray lenses and correct them with an easy-to-fabricate broadband phase plate.
- Frank Seiboth
- , Andreas Schropp
- & Christian G. Schroer
-
Article
| Open Access Microstructures define melting of molybdenum at high pressures
Microstructures define melting of molybdenum at high pressures
Molybdenum has long been speculated to undergo an exceptionally steep increase in melting temperature when compressed but without direct experimental evidence. Here authors claim such a direct observation and also report a transition at high pressure and high temperature.
- Rostislav Hrubiak
- , Yue Meng
- & Guoyin Shen
-
Article
| Open Access Direct experimental determination of the topological winding number of skyrmions in Cu2OSeO3
Direct experimental determination of the topological winding number of skyrmions in Cu2OSeO3
Experimental demonstrations of topologically nontrivial states in magnetic films currently rely on indirect comparisons of theoretical models with microscopic images. Here the authors show that resonant X-ray scattering provides direct information on the topology of magnetic textures.
- S. L. Zhang
- , G. van der Laan
- & T. Hesjedal
-
Article
| Open Access Towards high-resolution laser ionization spectroscopy of the heaviest elements in supersonic gas jet expansion
Towards high-resolution laser ionization spectroscopy of the heaviest elements in supersonic gas jet expansion
It is challenging to explore properties of heavy elements as they can only be produced artificially. Here, the authors demonstrate a high resolution spectroscopy method, studying the properties of actinium, which can be extended to the study of other elements located at the end of the periodic table.
- R. Ferrer
- , A. Barzakh
- & A. Zadvornaya
-
Article
| Open Access Effect of hydrogen on the integrity of aluminium–oxide interface at elevated temperatures
Effect of hydrogen on the integrity of aluminium–oxide interface at elevated temperatures
Hydrogen gas can drive detachment of protective surface oxides from metal substrates and this process is accelerated at moderately elevated temperatures relevant to applications. Here the authors use environmental transmission electron microscopy to monitor associated void coalescence processes and clarify roles that diffusion and hydrogen-vacancy complexes play.
- Meng Li
- , De-Gang Xie
- & Zhi-Wei Shan
-
Article
| Open Access Portraying entanglement between molecular qubits with four-dimensional inelastic neutron scattering
Portraying entanglement between molecular qubits with four-dimensional inelastic neutron scattering
Showing the presence of quantum entanglement in a system means it is beyond a classical description, but this is difficult to do experimentally. Here, the authors show how four-dimensional inelastic neutron scattering can quantify entanglement, demonstrating the method on a supramolecular dimer.
- E. Garlatti
- , T. Guidi
- & S. Carretta
-
Article
| Open Access Local self-uniformity in photonic networks
Local self-uniformity in photonic networks
The interaction between photonic bandgap materials and light is largely determined by the wavelength-scale material structure. Here, Sellerset al. develop a new metric of network structural order and demonstrate its connection to the photonic bandgap of an amorphous gyroid network.
- Steven R. Sellers
- , Weining Man
- & Marian Florescu
-
Article
| Open Access Three-dimensional surface topography of graphene by divergent beam electron diffraction
Three-dimensional surface topography of graphene by divergent beam electron diffraction
Graphene, and other 2D materials, do not exist as strictly planar sheets but instead have topographic ripples on the sub-nanometre scale. Here, Latychevskaiaet al. present a method to non-invasively image ripples in 2D materials with a single-shot, wide-area, electron diffraction measurement.
- Tatiana Latychevskaia
- , Wei-Hao Hsu
- & Ing-Shouh Hwang
-
Article
| Open Access In situ study on atomic mechanism of melting and freezing of single bismuth nanoparticles
In situ study on atomic mechanism of melting and freezing of single bismuth nanoparticles
The atomic mechanisms of reversible phase transitions are challenging to probe experimentally. Here, the authors induce melting and freezing processes in bismuth nanoparticles inside a high-resolution electron microscope, observing the atom-level stages of this phase transition pathway in real time.
- Yingxuan Li
- , Ling Zang
- & Chuanyi Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Quantum lock-in force sensing using optical clock Doppler velocimetry
Quantum lock-in force sensing using optical clock Doppler velocimetry
Existing force sensors are designed for driving frequencies above tens of kHz due to heating and sensitivity loss. Here the authors demonstrate precise force metrology for below kHz frequency range by combining the Doppler-shifted optical transition in trapped ion and quantum lock-in technique.
- Ravid Shaniv
- & Roee Ozeri
-
Article
| Open Access Electron–acoustic phonon coupling in single crystal CH3NH3PbI3 perovskites revealed by coherent acoustic phonons
Electron–acoustic phonon coupling in single crystal CH3NH3PbI3 perovskites revealed by coherent acoustic phonons
Carrier mobility is a basic semiconductor property. Manteet al., use femtosecond lasers to investigate coherent acoustic phonons and relate their deformation potentials to estimate the intrinsic electron and hole mobilities of CH3NH3PbI3 single crystals to be 2,800 and 9,400 cm2 V−1 s−1, respectively.
- Pierre-Adrien Mante
- , Constantinos C. Stoumpos
- & Arkady Yartsev
-
Article
| Open Access Ultrahigh-resolution imaging of water networks by atomic force microscopy
Ultrahigh-resolution imaging of water networks by atomic force microscopy
The structure of water in the first layer on surfaces is essential to our understanding of various phenomena, such as surface wettability and heterogeneous catalysis. Here, the authors use atomic force microscopy with a CO-functionalized tip to image water defects on copper surface at atomic resolution.
- Akitoshi Shiotari
- & Yoshiaki Sugimoto
-
Article
| Open Access A general patterning approach by manipulating the evolution of two-dimensional liquid foams
A general patterning approach by manipulating the evolution of two-dimensional liquid foams
Ostwald ripening is thermodynamically favoured in many liquid and gas systems, where small particles tend to dissolve into large ones. Against this effect, Huanget al. use patterned microstructures to guide the evolution of two-dimensional liquid foams as a platform for the assembly of nanoparticles.
- Zhandong Huang
- , Meng Su
- & Yanlin Song
-
Article
| Open Access Interfacial Ca2+ environments in nanocrystalline apatites revealed by dynamic nuclear polarization enhanced 43Ca NMR spectroscopy
Interfacial Ca2+ environments in nanocrystalline apatites revealed by dynamic nuclear polarization enhanced 43Ca NMR spectroscopy
Solid-state NMR can in principle be used to study calcium environments in biomaterials such as bones/teeth, but43Ca lacks receptivity. Here the authors present an approach to acquire 43Ca data for hydroxyapatite at its natural isotopic abundance, distinguishing between core and surface Ca sites.
- Daniel Lee
- , César Leroy
- & Gaël De Paëpe
-
Article
| Open Access Sub-wavelength modulation of χ(2) optical nonlinearity in organic thin films
Sub-wavelength modulation of χ(2) optical nonlinearity in organic thin films
Materials with spatially modulated nonlinear optical properties are used for quasi-phase matching. Here, Yanet al. exploit the nonlinearity of intermolecular charge transfer states together with oblique-angle deposition to achieve nanoscale modulation of the second-order susceptibility.
- Yixin Yan
- , Yakun Yuan
- & Noel C. Giebink
-
Article
| Open Access Direct visualization of hydrogen absorption dynamics in individual palladium nanoparticles
Direct visualization of hydrogen absorption dynamics in individual palladium nanoparticles
It remains unclear why energy storage systems with nanoscale constituents are less susceptible to stress-induced damage than their bulk counterparts. Here, the authors probe in real time the intercalation-driven phase transitions of nanoscale palladium hydride, finding that these nanoparticles are able to fix crystallographic flaws as they form.
- Tarun C. Narayan
- , Fariah Hayee
- & Jennifer A. Dionne
-
Article
| Open Access Purely antiferromagnetic magnetoelectric random access memory
Purely antiferromagnetic magnetoelectric random access memory
Magnetoelectric coupling allows switching of magnetic states via gate voltage pulses. Here the authors propose and demonstrate a purely antiferromagnetic magnetoelectric random access memory based on Cr2O3, reporting 50-fold reduction of writing threshold compared to ferromagnetic counterparts.
- Tobias Kosub
- , Martin Kopte
- & Denys Makarov
-
Article
| Open Access Bio-inspired self-shaping ceramics
Bio-inspired self-shaping ceramics
Shaping ceramics into complex forms is a formidable goal. Here, the authors present an approach to self-shaping ceramics, inspired by self-folding processes in plants, in which the ceramic microstructure is embedded with aligned platelets that control the orientation of heat-induced shrinkage.
- Fabio L. Bargardi
- , Hortense Le Ferrand
- & André R. Studart
-
Article
| Open Access Folding of xylan onto cellulose fibrils in plant cell walls revealed by solid-state NMR
Folding of xylan onto cellulose fibrils in plant cell walls revealed by solid-state NMR
The polysaccharide xylan binds to cellulose microfibrils in the plant cell wall, but the nature of this interaction remains unclear. Here Simmonset al. show that while xylan forms a threefold helical screw in solution it forms a twofold screw to bind cellulose microfibrils in the plant cell wall.
- Thomas J. Simmons
- , Jenny C. Mortimer
- & Paul Dupree
-
Article
| Open Access Electronic single-molecule identification of carbohydrate isomers by recognition tunnelling
Electronic single-molecule identification of carbohydrate isomers by recognition tunnelling
Carbohydrates are common biological molecules, but display huge stereochemical complexity that often cannot be elucidated by mass spectrometry. Here the authors show that recognition tunnelling can distinguish individual stereoisomers, utilizing picomole quantities of analytes.
- JongOne Im
- , Sovan Biswas
- & Peiming Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Complementarity of PALM and SOFI for super-resolution live-cell imaging of focal adhesions
Complementarity of PALM and SOFI for super-resolution live-cell imaging of focal adhesions
Live cell super-resolution imaging requires a high temporal resolution, which remains a challenge. Here the authors combine photo-activated localization microscopy (PALM) with super-resolution optical fluctuation imaging (SOFI) to achieve high spatiotemporal resolution and quantitative imaging of focal adhesion dynamics.
- Hendrik Deschout
- , Tomas Lukes
- & Aleksandra Radenovic
-
Article
| Open Access Imaging electric field dynamics with graphene optoelectronics
Imaging electric field dynamics with graphene optoelectronics
Detection of electric fields, central to chemical and biological processes, has been limited to measurements of current (e.g., electrodes) and secondary reporters (e.g., fluorescent dyes). Here, the authors demonstrate an optical platform capable of imaging electric field dynamics with high spatio-temporal resolution.
- Jason Horng
- , Halleh B. Balch
- & Feng Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Imaging high-speed friction at the nanometer scale
Imaging high-speed friction at the nanometer scale
It has been a challenge to characterize microscopic origins of friction at high velocities. Here authors extend atomic force microscopy to develop a dynamic technique combining force sensitivity and spatial resolution and able to probe, at each image pixel, frictional forces at velocities up to several cm per second.
- Per-Anders Thorén
- , Astrid S. de Wijn
- & David B. Haviland
-
Article
| Open Access Nanoscale assembly of superconducting vortices with scanning tunnelling microscope tip
Nanoscale assembly of superconducting vortices with scanning tunnelling microscope tip
Scanning tunneling microscope (STM) is a powerful tool but local control of superconductivity with the STM tip is still lacking. Here, Geet al. show the use of an STM tip to control the local pinning in a superconductor through the heating effect, allowing to manipulate single superconducting vortex at nanoscale.
- Jun-Yi Ge
- , Vladimir N. Gladilin
- & Victor V. Moshchalkov
-
Article
| Open Access Scanning superlens microscopy for non-invasive large field-of-view visible light nanoscale imaging
Scanning superlens microscopy for non-invasive large field-of-view visible light nanoscale imaging
Rare subcellular events can be tracked by correlating structural-information gathered by imaging with specific-molecule fluorescent identification. Here, the authors achieve this correlation in a quick and non-invasive way using microsphere-based scanning superlens microscopy.
- Feifei Wang
- , Lianqing Liu
- & Wen Jung Li
-
Article
| Open Access Interrogation of bimetallic particle oxidation in three dimensions at the nanoscale
Interrogation of bimetallic particle oxidation in three dimensions at the nanoscale
Understanding bimetallic alloy oxidation is key to design of hollow-structured binary oxides and their optimization for applications, e.g., as catalysts. Here the authors combine real-time imaging and chemically-sensitive electron tomography to uncover unexpected complexity in possible morphological outcomes of bimetallic oxidation.
- Lili Han
- , Qingping Meng
- & Huolin L. Xin
-
Article
| Open Access Rapid mapping of polarization switching through complete information acquisition
Rapid mapping of polarization switching through complete information acquisition
Resolution of classical piezoresponse force microscopy is limited in data acquisition rates and energy scales. Here, Somnath et al. report an approach for rapid probing of ferroelectric switching using direct strain detection of material response to probe bias, enabling spectroscopic imaging at a rate of 3,504 times faster the current state of the art.
- Suhas Somnath
- , Alex Belianinov
- & Stephen Jesse
-
Article
| Open Access Dynamic nuclear magnetic resonance field sensing with part-per-trillion resolution
Dynamic nuclear magnetic resonance field sensing with part-per-trillion resolution
The measurement of high magnetic fields has been limited to sensitivities in the nanotesla range. Here, the authors report advances in high-field magnetometry based on nuclear magnetic resonance, achieving resolution in the order of picoteslas or one part per trillion in relative terms.
- Simon Gross
- , Christoph Barmet
- & Klaas P. Pruessmann
-
Article
| Open Access Kaleidoscopic imaging patterns of complex structures fabricated by laser-induced deformation
Kaleidoscopic imaging patterns of complex structures fabricated by laser-induced deformation
Complex surface micro- and nanostructures can be useful in many device applications, but are challenging in terms of controllability, low cost and high throughput. Here the authors have fabricated quasi 3D structures by the thermal deformation of simple two-dimensional laser-induced patterns.
- Haoran Zhang
- , Fengyou Yang
- & Qian Liu
-
Article
| Open Access Laser-induced phase separation of silicon carbide
Laser-induced phase separation of silicon carbide
Laser beam-induced processing is industrially relevant but often challenging to study in terms of underlying phase transformations. Here authors characterize formation of thin, phase-separated carbon and silicon layers on a silicon carbide substrate by laser-induced melting and solidification.
- Insung Choi
- , Hu Young Jeong
- & Keon Jae Lee
-
Correspondence
| Open Access Correspondence: Strongly-driven Re+CO2 redox reaction at high-pressure and high-temperature
Correspondence: Strongly-driven Re+CO2 redox reaction at high-pressure and high-temperature
- D. Santamaria-Perez
- , C. McGuire
- & A. Muñoz
-
Correspondence
| Open Access Correspondence: Reply to ‘Strongly-driven Re+CO2 redox reaction at high-pressure and high-temperature’
Correspondence: Reply to ‘Strongly-driven Re+CO2 redox reaction at high-pressure and high-temperature’
- Mario Santoro
- , Federico A. Gorelli
- & Julien Haines
-
Article
| Open Access A stable lithium-rich surface structure for lithium-rich layered cathode materials
A stable lithium-rich surface structure for lithium-rich layered cathode materials
Surface modification of high-capacity lithium-rich layered oxides for improved capacity retention is an active area of battery materials research. Here authors demonstrate lithium-rich layered surfaces with a framework matching the host's, but with nickel atoms regularly arranged between layers.
- Sangryun Kim
- , Woosuk Cho
- & Jang Wook Choi
-
Article
| Open Access All-gas-phase synthesis of UiO-66 through modulated atomic layer deposition
All-gas-phase synthesis of UiO-66 through modulated atomic layer deposition
Thin films of metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) are promising for catalysis, gas storage, and microelectronics. Here, the authors introduce a vapour-phase synthesis of UiO-66 thin films, beginning with modulated atomic layer deposition of porous, amorphous films, followed by acetic acid vapour-enabled crystallization to the MOF structure.
- Kristian Blindheim Lausund
- & Ola Nilsen
-
Article
| Open Access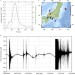 Prompt gravity signal induced by the 2011 Tohoku-Oki earthquake
Prompt gravity signal induced by the 2011 Tohoku-Oki earthquake
Earthquakes have been theorised to produce gravity signals that may arrive before seismic waves, but until now they had not been detected. Montagneret al. have detected prompt gravity signals from the 2011 Tohoku-Oki earthquake thus allowing an early warning of earthquakes before seismic wave arrival.
- Jean-Paul Montagner
- , Kévin Juhel
- & Philippe Lognonné
-
Article
| Open Access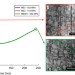 Phase transformation strengthening of high-temperature superalloys
Phase transformation strengthening of high-temperature superalloys
Nanoscale processes may directly impact macroscopic mechanical behaviour. Here authors describe a ‘phase-transformation strengthening’ mechanism in nickel-based high temperature alloys, allowing suppression of deleterious deformation processes at elevated temperatures by specific alloying elements.
- T. M. Smith
- , B. D. Esser
- & M. J. Mills
-
Article
| Open Access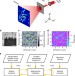 Phase retrieval by coherent modulation imaging
Phase retrieval by coherent modulation imaging
Robust coherent diffractive imaging generally requires many exposures that may damage samples. Here, the authors develop a single-shot X-ray imaging method applicable to general samples for materials and biological sciences, also enabling imaging of dynamic processes, using a pulsed X-ray laser.
- Fucai Zhang
- , Bo Chen
- & Ian K. Robinson
-
Article
| Open Access Structure-conserving spontaneous transformations between nanoparticles
Structure-conserving spontaneous transformations between nanoparticles
Ambient chemical transformations between nanoparticles are poorly explored in materials science. Here, the authors find that two atomically precise, isomorphic clusters of gold and silver can convert between each other in solution through a series of alloy clusters, preserving structure, topology, and metal-ligand stoichiometry.
- K. R. Krishnadas
- , Ananya Baksi
- & Thalappil Pradeep
-
Article
| Open Access High-energy electron emission from metallic nano-tips driven by intense single-cycle terahertz pulses
High-energy electron emission from metallic nano-tips driven by intense single-cycle terahertz pulses
High-energy electron sources are powerful tools for investigating dynamics at atomic and subatomic scales. Here, Li and Jones demonstrate the terahertz-driven emission of electrons with energies exceeding five kiloelectronvolts from nano-tips and study its dependence on the tip radius.
- Sha Li
- & R. R. Jones
-
Article
| Open Access Origin and structure of polar domains in doped molecular crystals
Origin and structure of polar domains in doped molecular crystals
Doping can introduce structural distortions in a molecular crystal in the form of polar domains. Here, the authors combine pyroelectric measurements and computation to reveal the molecular structure of such domains in centrosymmetric α-glycine crystals doped with L-amino acids.
- E. Meirzadeh
- , I. Azuri
- & I. Lubomirsky
-
Article
| Open Access Following lithiation fronts in paramagnetic electrodes with in situ magnetic resonance spectroscopic imaging
Following lithiation fronts in paramagnetic electrodes with in situ magnetic resonance spectroscopic imaging
Magnetic resonance imaging is a promising non-invasive approach to visualize paramagnetic materials in devices, but the short lifetime of signals currently limits its use. Here, the authors develop an approach which overcomes this hurdle to spectroscopically image lithiation fronts during battery operation.
- Mingxue Tang
- , Vincent Sarou-Kanian
- & Elodie Salager
-
Article
| Open Access Atomic intercalation to measure adhesion of graphene on graphite
Atomic intercalation to measure adhesion of graphene on graphite
Analysis of the mechanical properties of two-dimensional materials is important for device development. Here, the authors report a microscopic method for measuring the adhesion of graphene on top of highly ordered pyrolytic graphite, which exploits atomic-scale blisters formed upon neon atom intercalation.
- Jun Wang
- , Dan C. Sorescu
- & Petro Maksymovych
-
Article
| Open Access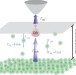 Time-resolved single dopant charge dynamics in silicon
Time-resolved single dopant charge dynamics in silicon
Probing individual impurities will become increasingly important as devices shrink towards the nanoscale. Here Rashidi et al., introduce a method based on time-resolved scanning tunnelling spectroscopy of surface dangling bonds to investigate the dynamics of individual dopants in silicon.
- Mohammad Rashidi
- , Jacob A. J. Burgess
- & Robert A. Wolkow
-
Article
| Open Access Scattering-type scanning near-field optical microscopy with low-repetition-rate pulsed light source through phase-domain sampling
Scattering-type scanning near-field optical microscopy with low-repetition-rate pulsed light source through phase-domain sampling
Low repetition rate lasers are suitable for studying nonlinear optical phenomena, while near-field microscopy allows high spatial resolution for nanomaterial characterisation. Here, Wang et al. enable scattering-type near-field microscopy with low repetition rate lasers through phase-domain sampling.
- Haomin Wang
- , Le Wang
- & Xiaoji G. Xu
-
Article
| Open Access Self-assembly of acetate adsorbates drives atomic rearrangement on the Au(110) surface
Self-assembly of acetate adsorbates drives atomic rearrangement on the Au(110) surface
The efficiency of a catalyst relies on the stability of intermediates on its surface. Here, the authors find that van der Waals interactions between acetate adsorbates on Au(110) provide a small but necessary energy contribution to stabilize the acetate and drive restructuring of the Au surface.
- Fanny Hiebel
- , Bonggeun Shong
- & Cynthia M. Friend

 Quantum coherence selective 2D Raman–2D electronic spectroscopy
Quantum coherence selective 2D Raman–2D electronic spectroscopy