Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Atomic-scale observation of localized phonons at FeSe/SrTiO3 interface
Atomic-scale observation of localized phonons at FeSe/SrTiO3 interface
The authors characterize the phonon modes at the FeSe/SrTiO3 interface with atomically resolved electron energy loss spectroscopy and correlate them with accurate atomic structure in an electron microscope. They find several phonon modes highly localized at the interface, one of which engages in strong interactions with the electrons in FeSe.
- Ruochen Shi
- , Qize Li
- & Peng Gao
-
Article
| Open Access 3D printable strong and tough composite organo-hydrogels inspired by natural hierarchical composite design principles
3D printable strong and tough composite organo-hydrogels inspired by natural hierarchical composite design principles
The preparation of composite hydrogels can allow for mechanical properties to be enhanced, and hierarchical structures can be effective. Here, the authors report improved mechanical properties by the addition of ceramic platelets to an organohydrogel in direct ink writing.
- Quyang Liu
- , Xinyu Dong
- & Wei Zhai
-
Article
| Open Access Controlled condensation by liquid contact-induced adaptations of molecular conformations in self-assembled monolayers
Controlled condensation by liquid contact-induced adaptations of molecular conformations in self-assembled monolayers
Surface condensation is predetermined and is typically adjusted by chemical or topographical surface modification. Here, the authors report on a strategy to control the surface condensation behavior by adjusting molecular conformations in self-assembled monolayers.
- Guoying Bai
- , Haiyan Zhang
- & Yufeng Liu
-
Article
| Open Access Beyond nothingness in the formation and functional relevance of voids in polymer films
Beyond nothingness in the formation and functional relevance of voids in polymer films
Voids are known to impact the properties of materials, but the nanovoids also present are less well understood than macroscopic voids. Here, the authors utilise 3D imaging and graph theory to study nanovoid formation and impact on material properties.
- Falon C. Kalutantirige
- , Jinlong He
- & Qian Chen
-
Article
| Open Access Low-nuclearity CuZn ensembles on ZnZrOx catalyze methanol synthesis from CO2
Low-nuclearity CuZn ensembles on ZnZrOx catalyze methanol synthesis from CO2
The ideal metal selection and atomic-level arrangement for catalysts in CO2 hydrogenation are still uncertain. Here, copper is identified as the most effective promoter for enhancing ZnZrOx catalysts when precisely structured into CuZn ensembles, offering new insights for designing superior catalysts for CO2-based methanol synthesis.
- Thaylan Pinheiro Araújo
- , Georgios Giannakakis
- & Javier Pérez-Ramírez
-
Article
| Open Access Vapor-induced phase-separation-enabled versatile direct ink writing
Vapor-induced phase-separation-enabled versatile direct ink writing
The extrusion-based three-dimensional printing of polymers, metals, and composites requires elevated temperatures and may lead to diverse undesirable defects on printed parts. Here, the authors develop a vapor-induced phase separation printing technique to construct polymeric, metallic, and composite parts by using a polymer as a binder.
- Marc Sole-Gras
- , Bing Ren
- & Yong Huang
-
Article
| Open Access Wide field-of-hearing metalens for aberration-free sound capture
Wide field-of-hearing metalens for aberration-free sound capture
Achieving a wide angular response in single layer acoustic metalenses is challenging. By leveraging perfect acoustic symmetry conversion, the authors realize an aberration free metalens with a wide field-of-hearing, up to 140 degrees.
- Dongwoo Lee
- , Beomseok Oh
- & Junsuk Rho
-
Article
| Open Access Rewritable printing of ionic liquid nanofilm utilizing focused ion beam induced film wetting
Rewritable printing of ionic liquid nanofilm utilizing focused ion beam induced film wetting
With a helium focused ion beam, an ionic liquid can undergo induced wetting to flow into a desired pattern on a surface in a controllable, rewriteable manner. Combined with electrochemical deposition, patterned solid materials can be produced.
- Haohao Gu
- , Kaixin Meng
- & Hao Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Observation of Kekulé vortices around hydrogen adatoms in graphene
Observation of Kekulé vortices around hydrogen adatoms in graphene
Kekulé vortices in hexagonal lattices can host fractionalized charges at zero magnetic field, but have remained out of experimental reach. Here, the authors report a Kekulé vortex in the local density states of graphene around a chemisorbed hydrogen adatom.
- Yifei Guan
- , Clement Dutreix
- & Vincent T. Renard
-
Article
| Open Access Crosslinking-induced patterning of MOFs by direct photo- and electron-beam lithography
Crosslinking-induced patterning of MOFs by direct photo- and electron-beam lithography
Precise and scalable patterning is essential for the use of metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) in solid-state electronics and photonics. Here, the authors report on resistance-free, direct photo- and electron-beam lithography of MOF films using crosslinking chemistry.
- Xiaoli Tian
- , Fu Li
- & Jinghong Li
-
Article
| Open Access Deuteration-enhanced neutron contrasts to probe amorphous domain sizes in organic photovoltaic bulk heterojunction films
Deuteration-enhanced neutron contrasts to probe amorphous domain sizes in organic photovoltaic bulk heterojunction films
The use of conventional X-ray scattering techniques is challenging to detect donor-acceptor contrast within amorphous intermixing regions. Here, the authors apply neutron scattering and targeted deuteration to enhance the contrast by one order of magnitude and reveal short-range aggregations of d-Y6.
- Guilong Cai
- , Yuhao Li
- & Xinhui Lu
-
Article
| Open Access Dynamical evolution of CO2 and H2O on garnet electrolyte elucidated by ambient pressure X-ray spectroscopies
Dynamical evolution of CO2 and H2O on garnet electrolyte elucidated by ambient pressure X-ray spectroscopies
Li6.5La3Zr1.5Ta0.5O12 (LLZO) is a promising solid electrolyte but suffers from severe surface degradation in air. Here, authors use mapping of resonant Auger spectroscopy and various ambient pressure X-ray spectroscopies to elucidate the dynamical evolution of CO2 and H2O on clean LLZO surfaces.
- Nian Zhang
- , Guoxi Ren
- & Xiaosong Liu
-
Article
| Open Access Solar-driven sugar production directly from CO2 via a customizable electrocatalytic–biocatalytic flow system
Solar-driven sugar production directly from CO2 via a customizable electrocatalytic–biocatalytic flow system
Solar-driven artificial food synthesis from CO2 provides an approach to overcome the limitations of natural photosynthesis, but it is very challenging. Here, the authors report a hybrid electrocatalytic-biocatalytic flow system, coupling photovoltaics-powered electrocatalysis (CO2 to formate) with a five enzyme cascade platform (formate to sugar), which achieves conversion of CO2 to C6 sugar (L-sorbose) with a solar-to-food energy conversion efficiency of 3.5%.
- Guangyu Liu
- , Yuan Zhong
- & Yujie Xiong
-
Article
| Open Access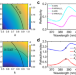 Large exchange-driven intrinsic circular dichroism of a chiral 2D hybrid perovskite
Large exchange-driven intrinsic circular dichroism of a chiral 2D hybrid perovskite
Li et al. report large circular dichroism in 2D chiral perovskite single crystals, arises from the inorganic sublattice, instead of chiral ligands, driven by electron-hole exchange interactions. This is evidenced by both reflective circular dichroism spectroscopy and ab initio theory.
- Shunran Li
- , Xian Xu
- & Peijun Guo
-
Article
| Open Access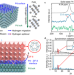 Spectroscopic visualization of reversible hydrogen spillover between palladium and metal–organic frameworks toward catalytic semihydrogenation
Spectroscopic visualization of reversible hydrogen spillover between palladium and metal–organic frameworks toward catalytic semihydrogenation
The authors report an in situ investigation of interfacial hydrogen spillover in Pd/ZIF-8 structures with X-ray and Raman techniques. A mechanistic picture of how Pd/ZIF-8 catalyst mediate alkyne semihydrogenation to alkynes is described.
- Qiaoxi Liu
- , Wenjie Xu
- & Yujie Xiong
-
Article
| Open Access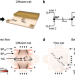 Toward sub-second solution exchange dynamics in flow reactors for liquid-phase transmission electron microscopy
Toward sub-second solution exchange dynamics in flow reactors for liquid-phase transmission electron microscopy
In liquid-phase TEM, microfluidic reactors are used to monitor nanoscale (electro)chemical dynamics in liquid environments. Here, the authors develop a reactor design with accelerated mass transport, facilitating quantitative in-situ and in-operando studies.
- Stefan Merkens
- , Christopher Tollan
- & Andrey Chuvilin
-
Article
| Open Access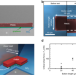 Button shear testing for adhesion measurements of 2D materials
Button shear testing for adhesion measurements of 2D materials
2D materials are being investigated for several applications in micro- and nanoelectronics, but their weak adhesion represents a critical challenge for device integration. Here, the authors propose a button shear testing method to evaluate the adhesion forces of various large-area 2D films on SiO2 and Si3N4 substrates.
- Josef Schätz
- , Navin Nayi
- & Max C. Lemme
-
Article
| Open Access Light and matter co-confined multi-photon lithography
Light and matter co-confined multi-photon lithography
Mask-free multi-photon lithography allows the straightforward fabrication of nanostructures, but high precision and good resolution can be challenging to achieve. Here, the authors report a combination of photo-inhibition and chemical quenchers for improved lithography performance.
- Lingling Guan
- , Chun Cao
- & Xu Liu
-
Article
| Open Access Lanthanide luminescence nanothermometer with working wavelength beyond 1500 nm for cerebrovascular temperature imaging in vivo
Lanthanide luminescence nanothermometer with working wavelength beyond 1500 nm for cerebrovascular temperature imaging in vivo
The strong scattering of biological tissue causes challenges when monitoring temperature changes at the microscale. Here, the authors propose a nanothermometer based on lanthanide luminescence, enabling minimally invasive imaging of the cerebrovascular system of mice at nearly 200 μm resolution.
- Yukai Wu
- , Fang Li
- & Xingjun Zhu
-
Article
| Open Access Atomically precise engineering of spin–orbit polarons in a kagome magnetic Weyl semimetal
Atomically precise engineering of spin–orbit polarons in a kagome magnetic Weyl semimetal
Defect engineering in topological materials is a frontier that promises tunable physical properties with rich applications. Here, the authors demonstrate the atomically precise engineering of vacancies in a topological semimetal, which locally tunes the magnetic properties.
- Hui Chen
- , Yuqing Xing
- & Hong-Jun Gao
-
Article
| Open Access Monolithic thin-film lithium niobate broadband spectrometer with one nanometre resolution
Monolithic thin-film lithium niobate broadband spectrometer with one nanometre resolution
A framework to break the inherent trade-off barrier between spectral resolution and operational bandwidth of integrated optical spectrometers is developed and demonstrated on thin-film lithium niobate without sacrificing the compact footprint.
- Giovanni Finco
- , Gaoyuan Li
- & Rachel Grange
-
Article
| Open Access Subwavelength dielectric waveguide for efficient travelling-wave magnetic resonance imaging
Subwavelength dielectric waveguide for efficient travelling-wave magnetic resonance imaging
Achieving uniform spin excitation, crucial for MRI, is challenging in the electrically large human body at UHF. Here, authors introduce an innovative dielectric waveguide specifically designed for traveling-wave MRI, which enhances homogeneity and efficiency through effective wave manipulation.
- Yang Gao
- , Tong Liu
- & Xiaotong Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Time-of-flight detection of terahertz phonon-polariton
Time-of-flight detection of terahertz phonon-polariton
Polaritons, light-matter hybridized quasiparticles, are the fundamental excitation of strong coupling systems and are widely applicable in information technologies. Here the authors applied the concept of time-of-flight measurement in terahertz induced second harmonic generation experiments in various systems to comprehensively study the dispersion relation of phonon-polaritons and reveal potential spin-lattice couplings.
- Tianchuang Luo
- , Batyr Ilyas
- & Nuh Gedik
-
Article
| Open Access 3D printing by stereolithography using thermal initiators
3D printing by stereolithography using thermal initiators
Common stereolithography-based 3D printing relies on photopolymerization using photoinitiators. Here, the authors replace the conventional photoinitiators with low-cost, widely used thermal initiators to achieve 3D-printed objects.
- Doron Kam
- , Omri Rulf
- & Shlomo Magdassi
-
Article
| Open Access The first demonstration of entirely roll-to-roll fabricated perovskite solar cell modules under ambient room conditions
The first demonstration of entirely roll-to-roll fabricated perovskite solar cell modules under ambient room conditions
The translation of perovskite solar cells to large-area devices fabricated by industry-relevant manufacturing methods remains a critical challenge. Here, authors report solar modules with serially-interconnected cells produced entirely by industrial roll-to-roll printing under ambient conditions.
- Hasitha C. Weerasinghe
- , Nasiruddin Macadam
- & Doojin Vak
-
Article
| Open Access Area-selective atomic layer deposition on 2D monolayer lateral superlattices
Area-selective atomic layer deposition on 2D monolayer lateral superlattices
Area selective atomic layer deposition (AS-ALD) has been recently proposed as a controlled growth method, but the patterning resolution and selectivity require improvements. Here, the authors report a superlattice-based AS-ALD method to deposit various materials onto 2D MoS2-MoSe2 lateral superlattices, with a minimum half-pitch size of ~ 10 nm.
- Jeongwon Park
- , Seung Jae Kwak
- & Kibum Kang
-
Article
| Open Access Effect of inorganic material surface chemistry on structures and fracture behaviours of epoxy resin
Effect of inorganic material surface chemistry on structures and fracture behaviours of epoxy resin
The mechanisms of adhesion between polymers and inorganic materials are not fully understood. Here, authors demonstrate the clear evidence that the surface chemistry impacts the crosslinked structures of resins near the interfaces, resulting in different fracture behaviours and adhesive strengths.
- Tomohiro Miyata
- , Yohei K. Sato
- & Hiroshi Jinnai
-
Article
| Open Access Fast topographic optical imaging using encoded search focal scan
Fast topographic optical imaging using encoded search focal scan
Quickly acquiring topographical information from a sample remains a challenge in optics. Here, the authors introduce encoded search focal scan, a technique for sub-micrometric imaging of tens of topographies per second based on collecting a reduced set of images.
- Narcís Vilar
- , Roger Artigas
- & Guillem Carles
-
Article
| Open Access Interrogating site dependent kinetics over SiO2-supported Pt nanoparticles
Interrogating site dependent kinetics over SiO2-supported Pt nanoparticles
Kim and co-workers introduce a new ‘kinetic site deconvolution’ method to identify active sites on heterogeneous catalysts by linking reaction rates to specific adsorption environments.
- Taek-Seung Kim
- , Christopher R. O’Connor
- & Christian Reece
-
Article
| Open Access In situ electrochemical regeneration of nanogap hotspots for continuously reusable ultrathin SERS sensors
In situ electrochemical regeneration of nanogap hotspots for continuously reusable ultrathin SERS sensors
SERS is a powerful analytical technique, but achieving reproducibility for continuous analysis a challenge. Here, the authors report a SERS substrate recycling method that enables direct analysis of complex samples without substrate contamination.
- Sarah May Sibug-Torres
- , David-Benjamin Grys
- & Jeremy J. Baumberg
-
Article
| Open Access High-density volumetric super-resolution microscopy
High-density volumetric super-resolution microscopy
Current approaches for volumetric super-resolution microscopy can yield large and complex PSF spatial footprints. Here, the authors show a super-resolution microscopy approach using a hexagonal microlens array, which offers speed improvements in volumetric imaging compared to other single-molecule methods.
- Sam Daly
- , João Ferreira Fernandes
- & Steven F. Lee
-
Article
| Open Access Scalable production of structurally colored composite films by shearing supramolecular composites of polymers and colloids
Scalable production of structurally colored composite films by shearing supramolecular composites of polymers and colloids
Structurally coloured composite films are flexible optical materials with potential in a range of applications, but their production is impacted by long time-frames and limited materials. Here, the authors report a method for the production of large scale films by shearing supramolecular composites.
- Miaomiao Li
- , Bolun Peng
- & Jintao Zhu
-
Article
| Open Access Crystallization of piezoceramic films on glass via flash lamp annealing
Crystallization of piezoceramic films on glass via flash lamp annealing
Direct growth of piezoelectric oxides on glass is difficult due to high processing temperatures. Here, the authors demonstrate a flash lamp process for the growth of films on various glasses in a few seconds only. The films have piezoelectric e33,f of −5 C m−2 and can be used in haptic devices.
- Longfei Song
- , Juliette Cardoletti
- & Sebastjan Glinšek
-
Article
| Open Access High-strength and crack-free welding of 2024 aluminium alloy via Zr-core-Al-shell wire
High-strength and crack-free welding of 2024 aluminium alloy via Zr-core-Al-shell wire
Solidification cracking during fusion welding of high-strength aluminum alloys has been a long-standing issue. Here, the authors achieve reliable and crack-free welding of 2024 aluminum alloy using a Zr-core-Al-shell wire and the oscillating laser-arc hybrid welding technique.
- Jun Jin
- , Shaoning Geng
- & Xiangqi Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Energy transfer driven brightening of MoS2 by ultrafast polariton relaxation in microcavity MoS2/hBN/WS2 heterostructures
Energy transfer driven brightening of MoS2 by ultrafast polariton relaxation in microcavity MoS2/hBN/WS2 heterostructures
Here, the authors design a microcavity-confined 2D heterojunction to realize the strong coupling among donor exciton, acceptor exciton, and cavity photon mode, leading to an unconventional energy transfer via polariton relaxation with an enhancement factor of ~440.
- Zehua Hu
- , Tanjung Krisnanda
- & Qihua Xiong
-
Article
| Open Access Pore evolution mechanisms during directed energy deposition additive manufacturing
Pore evolution mechanisms during directed energy deposition additive manufacturing
Porosity is a key issue in additive manufacturing (AM). Here, the authors reveal the bubble evolution mechanisms including formation, coalescence, pushing, growth, entrainment, escape, and entrapment during directed energy deposition AM using in situ X-ray imaging and multiphysics modelling.
- Kai Zhang
- , Yunhui Chen
- & Peter D. Lee
-
Article
| Open Access Insights into structural defect formation in individual InP/ZnSe/ZnS quantum dots under UV oxidation
Insights into structural defect formation in individual InP/ZnSe/ZnS quantum dots under UV oxidation
InP/ZnSe/ZnS quantum dots (QDs) are promising candidates for advanced light-emitting diodes, but low emission efficiency due to oxidation hampers applications. Here, the authors provide insight into the structural defects that form on individual QDs during UV-facilitated oxidation.
- Hayeon Baek
- , Sungsu Kang
- & Jungwon Park
-
Article
| Open Access In situ modulating coordination fields of single-atom cobalt catalyst for enhanced oxygen reduction reaction
In situ modulating coordination fields of single-atom cobalt catalyst for enhanced oxygen reduction reaction
The electrochemical oxygen reduction reaction plays an important role in new energy technologies such as fuel cells and metal-air batteries. Here the authors present a cobalt catalyst with a symmetry-broken Cl−Co−N4 moiety capable of dynamically modulating electron occupancy at active sites during practical reaction conditions to optimize oxygen reduction performance.
- Meihuan Liu
- , Jing Zhang
- & Qinghua Liu
-
Article
| Open Access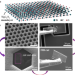 Elastic properties and tensile strength of 2D Ti3C2Tx MXene monolayers
Elastic properties and tensile strength of 2D Ti3C2Tx MXene monolayers
The Young’s modulus of the MXene Ti3C2Tx, theoretically predicted to be 0.502 TPa, has not yet been experimentally confirmed. This work supplants previous reports using nanoindentation with the correctly measured Young’s modulus of 0.484 ± 0.013 TPa.
- Chao Rong
- , Ting Su
- & Fu-Zhen Xuan
-
Article
| Open Access Harmonic amide bond density as a game-changer for deciphering the crosslinking puzzle of polyamide
Harmonic amide bond density as a game-changer for deciphering the crosslinking puzzle of polyamide
Relating the degree of network crosslinking as a descriptor to the desalination performance of crosslinked polymer membranes remains challenging. Here, the authors introduce a parameter based on distinct amide bonds per unit mass of polyamide, to unravel the relationship between the crosslinked networks of polyamide membranes and their desalination performance.
- Yu-Ren Xue
- , Chang Liu
- & Zhi-Kang Xu
-
Article
| Open Access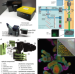 Open-source microscope add-on for structured illumination microscopy
Open-source microscope add-on for structured illumination microscopy
Researchers developed an open-hardware structured illumination microscopy add-on. This affordable upgrade provides super-resolution capabilities for normal optical microscopes. Detailed instructions enable easy reproduction to help democratize advanced microscopy.
- Mélanie T. M. Hannebelle
- , Esther Raeth
- & Georg E. Fantner
-
Article
| Open Access Liquid Madelung energy accounts for the huge potential shift in electrochemical systems
Liquid Madelung energy accounts for the huge potential shift in electrochemical systems
Electrode potential in any electrochemical systems has long been discussed by classical Debye-Hückel theory which holds only under extremely dilute concentrations. Here, the authors establish the concept ‘liquid Madelung potential’ to comprehensively describe the potential shift at practical concentrations.
- Norio Takenaka
- , Seongjae Ko
- & Atsuo Yamada
-
Article
| Open Access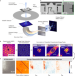 Rejuvenation as the origin of planar defects in the CrCoNi medium entropy alloy
Rejuvenation as the origin of planar defects in the CrCoNi medium entropy alloy
High and medium-entropy alloys have shown excellent mechanical performance, yet the role of short-range order (SRO) on these properties has been unclear. Here, the authors demonstrate that the reduction of SRO by deformation leads to rejuvenation, explaining their remarkable damage tolerance.
- Yang Yang
- , Sheng Yin
- & Andrew M. Minor
-
Perspective
| Open Access Performance metrics to unleash the power of self-driving labs in chemistry and materials science
Performance metrics to unleash the power of self-driving labs in chemistry and materials science
Assessing the performance of self-driving labs (SDLs) is challenging due to the specificities of each experiment. In this Perspective, the authors review recent literature of SDLs for materials science and chemistry and suggest how to report SDL performance more effectively.
- Amanda A. Volk
- & Milad Abolhasani
-
Article
| Open Access Three dimensional classification of dislocations from single projections
Three dimensional classification of dislocations from single projections
Many material properties are governed by the internal dislocation network within the material. Here, the authors describe a method to determine the three dimensional position and type of dislocations from a measurement along only a single direction within a scanning transmission electron microscope.
- Tore Niermann
- , Laura Niermann
- & Michael Lehmann
-
Article
| Open Access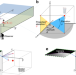 Two-edge-resolved three-dimensional non-line-of-sight imaging with an ordinary camera
Two-edge-resolved three-dimensional non-line-of-sight imaging with an ordinary camera
Ordinary cameras cannot directly see objects hidden around corners. Here, from an ordinary indirect 2D photograph, the authors compute a 3D image of a scene hidden behind a doorway by exploiting two perpendicular edges of the doorway.
- Robinson Czajkowski
- & John Murray-Bruce
-
Article
| Open Access Ultracompact mirror device for forming 20-nm achromatic soft-X-ray focus toward multimodal and multicolor nanoanalyses
Ultracompact mirror device for forming 20-nm achromatic soft-X-ray focus toward multimodal and multicolor nanoanalyses
Optics used for X-ray focusing suffer from wavelength dependent effects like chromatic aberration. Here the authors demonstrate fabrication of a ultracompact Kirkpatrick-Baez mirror and use it for achromatic focusing to 20 nm spot for the soft X-ray at 2-keV photon energy.
- Takenori Shimamura
- , Yoko Takeo
- & Hidekazu Mimura
-
Article
| Open Access Development of multifunctional membranes via plasma-assisted nonsolvent induced phase separation
Development of multifunctional membranes via plasma-assisted nonsolvent induced phase separation
The structures and properties of membranes depend strongly on their preparation methods. Here, the authors present a plasma-assisted nonsolvent-induced phase separation method that allows to tailor the physicochemical and electrical characteristics of PVDF membranes for various applications.
- Yueh-Han Huang
- , Meng-Jiy Wang
- & Tai-Shung Chung
-
Article
| Open Access 3D atomic structure from a single X-ray free electron laser pulse
3D atomic structure from a single X-ray free electron laser pulse
X-ray Free Electron Lasers allow fast structure determination. Here, the authors push the temporal limit of atomic level structure determination to 25 fs, the length of a single pulse, paving the way to the study of fast, non-repeatable processes.
- Gábor Bortel
- , Miklós Tegze
- & Gyula Faigel

 Dynamic acoustic optimization of pulse tube refrigerators for rapid cooldown
Dynamic acoustic optimization of pulse tube refrigerators for rapid cooldown