Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access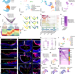 Decoding spatiotemporal transcriptional dynamics and epithelial fibroblast crosstalk during gastroesophageal junction development through single cell analysis
Decoding spatiotemporal transcriptional dynamics and epithelial fibroblast crosstalk during gastroesophageal junction development through single cell analysis
Elucidating the gastroesophageal junction’s development is key to comprehending its disease susceptibility. Here, the authors mapped its development, uncovering cellular diversity and interaction dynamics using advanced spatiotemporal single-cell analysis.
- Naveen Kumar
- , Pon Ganish Prakash
- & Cindrilla Chumduri
-
Article
| Open Access Spatial transcriptomics reveals discrete tumour microenvironments and autocrine loops within ovarian cancer subclones
Spatial transcriptomics reveals discrete tumour microenvironments and autocrine loops within ovarian cancer subclones
Intratumoural heterogeneity in high-grade serous ovarian carcinoma (HGSOC) remains to be explored. Here, the authors perform spatial transcriptomics and reveal a high degree of subclonal heterogeneity in HGSOC.
- Elena Denisenko
- , Leanne de Kock
- & Alistair R. R. Forrest
-
Article
| Open Access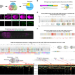 A lineage-resolved cartography of microRNA promoter activity in C. elegans empowers multidimensional developmental analysis
A lineage-resolved cartography of microRNA promoter activity in C. elegans empowers multidimensional developmental analysis
By tracing promoter expression in lineage-mapped single cells, Xu et al. present a whole-body cartography of microRNA transcriptional activities during C. elegans embryogenesis and demonstrate its broad utility in multifaceted functional analyses.
- Weina Xu
- , Jinyi Liu
- & Zhuo Du
-
Perspective
| Open Access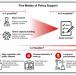 Engineering biology and climate change mitigation: Policy considerations
Engineering biology and climate change mitigation: Policy considerations
Engineering biology is a dynamic field that uses gene editing, synthesis, assembly, and engineering to design new or modified biological systems. Here the authors discuss the policy considerations and interventions needed to support a role for engineering biology in climate change mitigation.
- Jonathan Symons
- , Thomas A. Dixon
- & Isak S. Pretorius
-
Article
| Open Access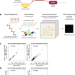 Mutational scanning pinpoints distinct binding sites of key ATGL regulators in lipolysis
Mutational scanning pinpoints distinct binding sites of key ATGL regulators in lipolysis
ATGL is a key enzyme in intracellular lipolysis. Here, the authors use deep mutational scanning to define the determinants of protein interaction between ATGL and its regulatory partners, gaining insights into lipolysis mechanisms in cells.
- Johanna M. Kohlmayr
- , Gernot F. Grabner
- & Ulrich Stelzl
-
Article
| Open Access Engineering intelligent chassis cells via recombinase-based MEMORY circuits
Engineering intelligent chassis cells via recombinase-based MEMORY circuits
The unification of decision-making, communication, and memory would enable the programming of intelligent biotic systems. Here, the authors achieve this goal by engineering E. coli chassis cells with an array of inducible recombinases that mediate diverse genetic programs.
- Brian D. Huang
- , Dowan Kim
- & Corey J. Wilson
-
Article
| Open Access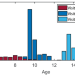 Population-wide cerebellar growth models of children and adolescents
Population-wide cerebellar growth models of children and adolescents
The development of the human cerebellum is not well understood. Here, the authors analyse a large sample of neuroimaging scans from children and adolescents to develop growth models of the cerebellum which mirror age-related developmental trajectories of behaviour and function.
- Carolin Gaiser
- , Rick van der Vliet
- & Ryan L. Muetzel
-
Article
| Open Access A universal system for boosting gene expression in eukaryotic cell-lines
A universal system for boosting gene expression in eukaryotic cell-lines
Production of proteins at scale and affordable cost has been a major need of the biotech sector for the last several decades. Here the authors present a design algorithm called UNILIB for boosting gene expression in eukaryotic cells developed using an oligo-library and machine learning approach, validated in both yeast and mammalian cells using unseen sequences.
- Inbal Vaknin
- , Or Willinger
- & Roee Amit
-
Article
| Open Access SpyMask enables combinatorial assembly of bispecific binders
SpyMask enables combinatorial assembly of bispecific binders
Bispecific antibody architecture is often important for function but rarely optimized. Here, authors present a modular approach to assemble bispecifics in varied formats using a SpyTag/SpyCatcher approach called SpyMask, and build anti-HER2 bispecifics whose activities depend on binder orientation and bispecific geometry.
- Claudia L. Driscoll
- , Anthony H. Keeble
- & Mark R. Howarth
-
Article
| Open Access CRISPR-powered quantitative keyword search engine in DNA data storage
CRISPR-powered quantitative keyword search engine in DNA data storage
Targeting the files containing content-of-interest is a challenge in DNA data storage. Here, the authors develop a CRISPR-powered search engine to quantitatively identify the keyword in files stored in DNA.
- Jiongyu Zhang
- , Chengyu Hou
- & Changchun Liu
-
Article
| Open Access A citric acid cycle-deficient Escherichia coli as an efficient chassis for aerobic fermentations
A citric acid cycle-deficient Escherichia coli as an efficient chassis for aerobic fermentations
While tricarboxylic acid cycle (TCA cycle) is required for heterotrophic microbes, it reduces carbon yield of industrial products due to the release of excess CO2. Here, the authors construct an E. coli strain without a functional TCA cycle and demonstrate its feasibility as a chassis strain for production of four separate compounds.
- Hang Zhou
- , Yiwen Zhang
- & Baixue Lin
-
Article
| Open Access Advancing the scale of synthetic biology via cross-species transfer of cellular functions enabled by iModulon engraftment
Advancing the scale of synthetic biology via cross-species transfer of cellular functions enabled by iModulon engraftment
Machine learning applied to large compendia of transcriptomic data has enabled the decomposition of bacterial transcriptomes to identify independently modulated sets of genes. Here the authors present iModulon-based engineering for precise identification of genes for cross-species function transfer to streamline synthetic biology for strain development and biomanufacturing.
- Donghui Choe
- , Connor A. Olson
- & Bernhard O. Palsson
-
Article
| Open Access Marine heatwaves disrupt ecosystem structure and function via altered food webs and energy flux
Marine heatwaves disrupt ecosystem structure and function via altered food webs and energy flux
This work leverages a new diet database and six long term monitoring efforts of 361 taxa to build comparable pre- and post-heatwave ecosystem models. The study provides empirical demonstration of changes in ecosystem-wide patterns of energy flux and biomass in response to marine heatwaves.
- Dylan G. E. Gomes
- , James J. Ruzicka
- & Joshua D. Stewart
-
Article
| Open Access An organism-wide atlas of hormonal signaling based on the mouse lemur single-cell transcriptome
An organism-wide atlas of hormonal signaling based on the mouse lemur single-cell transcriptome
Endocrinologists have traditionally focused on studying one hormone or organ system at a time. Here the authors use transcriptomic data from the mouse lemur to globally characterize primate hormonal signaling, describing hormone sources and targets, identifying conserved and primate specific regulation, and elucidating principles of the network.
- Shixuan Liu
- , Camille Ezran
- & James E. Ferrell Jr.
-
Article
| Open Access AlphaPept: a modern and open framework for MS-based proteomics
AlphaPept: a modern and open framework for MS-based proteomics
Mass spectrometry-based proteomics faces the challenge of processing vast data amounts. Here, the authors introduce AlphaPept, an open-source, Python-based framework that offers high speed analysis and easy integration for large-scale proteome analysis.
- Maximilian T. Strauss
- , Isabell Bludau
- & Matthias Mann
-
Article
| Open Access Deep model predictive control of gene expression in thousands of single cells
Deep model predictive control of gene expression in thousands of single cells
Gene expression is inherently dynamic, due to complex regulation and stochastic biochemical events. Here the authors train a deep neural network to predict and dynamically control gene expression in thousands of individual bacteria in real-time which they then apply to control antibiotic resistance and study single-cell survival dynamics.
- Jean-Baptiste Lugagne
- , Caroline M. Blassick
- & Mary J. Dunlop
-
Article
| Open Access ALKBH5-mediated m6A modification of IL-11 drives macrophage-to-myofibroblast transition and pathological cardiac fibrosis in mice
ALKBH5-mediated m6A modification of IL-11 drives macrophage-to-myofibroblast transition and pathological cardiac fibrosis in mice
Cardiac macrophage contributes to the onset of cardiac fibrosis, but the underneath mechanisms remain unclear. Here the authors show that mouse cardiac macrophages from circulating monocytes may trans-differentiate into myofibroblast under hypertensive conditions for fibrosis development, with an AKLBH5/IL11 molecular axis modulating this macrophage-to-myofibroblast transition.
- Tao Zhuang
- , Mei-Hua Chen
- & Cheng-Chao Ruan
-
Article
| Open Access A coarse-grained bacterial cell model for resource-aware analysis and design of synthetic gene circuits
A coarse-grained bacterial cell model for resource-aware analysis and design of synthetic gene circuits
Competition for the host cell’s resources influences synthetic biology circuit behavior. Here the authors present an E. coli cell model that combines insights into bacterial resource allocation with a simplified model of competition, facilitating resource-aware circuit design.
- Kirill Sechkar
- , Harrison Steel
- & Guy-Bart Stan
-
Article
| Open Access Synthetic microbe-to-plant communication channels
Synthetic microbe-to-plant communication channels
The soil microbiome communicates with plant roots using a chemical language. Here, using p-coumaroyl-homoserine lactone as the synthetic communication signal, the authors demonstrate programmable microbe-to-plant communication from the sender in the soil bacteria to a receiver in the plant.
- Alice Boo
- , Tyler Toth
- & Christopher A. Voigt
-
Article
| Open Access Chemoenzymatic indican for light-driven denim dyeing
Chemoenzymatic indican for light-driven denim dyeing
Conventional blue denim dyeing has both environmental and health-related consequences. Here, Bidart et al. use enzyme engineering to develop a viable method for the bulk production of indican and demonstrate dying processes which could significantly reduce the negative consequences of this billion-dollar industry.
- Gonzalo Nahuel Bidart
- , David Teze
- & Ditte Hededam Welner
-
Article
| Open Access Phage-assisted evolution of highly active cytosine base editors with enhanced selectivity and minimal sequence context preference
Phage-assisted evolution of highly active cytosine base editors with enhanced selectivity and minimal sequence context preference
Existing TadA-derived CBEs exhibit residual A•T-to-G•C editing activity and suffer from lower activity at several sequence contexts and with non-SpCas9 targeting domains. Here, the authors use phage-assisted evolution to evolve CBE6 variants that address these limitations.
- Emily Zhang
- , Monica E. Neugebauer
- & David R. Liu
-
Article
| Open Access Protein design using structure-based residue preferences
Protein design using structure-based residue preferences
Recent protein design methods rely on large neural networks, yet it is unclear which dependencies are critical for determining function. Here, authors show that learning the per residue mutation preferences, without considering interactions, enables design of functional and diverse protein variants.
- David Ding
- , Ada Y. Shaw
- & Debora S. Marks
-
Article
| Open Access A hybrid transistor with transcriptionally controlled computation and plasticity
A hybrid transistor with transcriptionally controlled computation and plasticity
Interfacing living systems with electronics for biosensing and biocomputing applications is challenging. Here, Gao et al. present hybrid transistors with electroactive bacteria capable of extracellular electron transfer, enabling transduction of biological computations to electrical readouts.
- Yang Gao
- , Yuchen Zhou
- & Benjamin K. Keitz
-
Article
| Open Access Iterative design of training data to control intricate enzymatic reaction networks
Iterative design of training data to control intricate enzymatic reaction networks
Kinetic modeling of in vitro enzymatic reaction networks (ERNs) is severely hampered by the lack of training data. Here, authors introduce a methodology that combines an active learning-like approach and flow chemistry to create optimized datasets for an intricate ERN.
- Bob van Sluijs
- , Tao Zhou
- & Wilhelm T. S. Huck
-
Article
| Open Access Single-cell and spatial multi-omics highlight effects of anti-integrin therapy across cellular compartments in ulcerative colitis
Single-cell and spatial multi-omics highlight effects of anti-integrin therapy across cellular compartments in ulcerative colitis
Anti-integrin therapy inhibits lymphocyte trafficking in ulcerative colitis. Here Mennillo et al. use single-cell and spatial -omics to show modulation of mononuclear phagocytes and other networks, identifying gene sets related to treatment response.
- Elvira Mennillo
- , Yang Joon Kim
- & Michael G. Kattah
-
Article
| Open Access Time-integrated BMP signaling determines fate in a stem cell model for early human development
Time-integrated BMP signaling determines fate in a stem cell model for early human development
The interpretation of the key developmental signal BMP remains poorly understood. Here, the authors show that the total time-integrated signaling controls differentiation in a stem cell embryo model and provide a possible mechanism.
- Seth Teague
- , Gillian Primavera
- & Idse Heemskerk
-
Review Article
| Open Access Choreographing root architecture and rhizosphere interactions through synthetic biology
Choreographing root architecture and rhizosphere interactions through synthetic biology
Engineering the form and function of root systems and their associated microbiota could provide a means to mitigate adverse climate-driven effects. Here, the authors review the recent developments in plant and rhizobacterial synthetic biology and highlight engineering targets for applications in root systems and rhizosphere.
- Carin J. Ragland
- , Kevin Y. Shih
- & José R. Dinneny
-
Article
| Open Access Engineering stringent genetic biocontainment of yeast with a protein stability switch
Engineering stringent genetic biocontainment of yeast with a protein stability switch
Comprehensive safety measures are lacking to employ engineered microorganisms in open-environment applications. Here the authors introduce a genetically encoded biocontainment system for engineered microorganisms based on conditional protein stability.
- Stefan A. Hoffmann
- & Yizhi Cai
-
Article
| Open Access Short-term hypercaloric carbohydrate loading increases surgical stress resilience by inducing FGF21
Short-term hypercaloric carbohydrate loading increases surgical stress resilience by inducing FGF21
Surgery poses significant risks for patients, with attempts to mitigate these risks using multimodal perioperative care pathways. Here, the authors show that preoperative hypercaloric carbohydrate drinks not only alleviate surgical stress but also demonstrates the replicability of this protection using FGF21 treatment alone.
- Thomas Agius
- , Raffaella Emsley
- & Alban Longchamp
-
Article
| Open Access Effect of aging on the human myometrium at single-cell resolution
Effect of aging on the human myometrium at single-cell resolution
Age-associated myometrial dysfunction can cause complications during pregnancy and labor. Here, the authors report that aging myometrium is characterized by diminished contractile capillary cells, altered gene expression, and disrupted cellular communication leading to impaired angiogenesis, increased fibrosis and inflammation.
- Paula Punzon-Jimenez
- , Alba Machado-Lopez
- & Aymara Mas
-
Article
| Open Access A genetic circuit on a single DNA molecule as an autonomous dissipative nanodevice
A genetic circuit on a single DNA molecule as an autonomous dissipative nanodevice
Achieving genetic circuits on single DNA molecules could have varied applications. Here, authors observed proteins emerging from single DNA molecules through coupled transcription-translation complexes, and show that nascent proteins lingered on DNA, regulating cascaded reactions on the same DNA and allowing the design of a pulsatile genetic circuit.
- Ferdinand Greiss
- , Nicolas Lardon
- & Roy Bar-Ziv
-
Article
| Open Access Semi-supervised integration of single-cell transcriptomics data
Semi-supervised integration of single-cell transcriptomics data
Batch effects hinder multi-sample single-cell data analyses. Here, authors present STACAS, a scalable single-cell RNA-seq data integration tool that uses prior cell type knowledge to preserve biological variability, demonstrating robustness to noisy input cell type labels.
- Massimo Andreatta
- , Léonard Hérault
- & Santiago J. Carmona
-
Article
| Open Access i-shaped antibody engineering enables conformational tuning of biotherapeutic receptor agonists
i-shaped antibody engineering enables conformational tuning of biotherapeutic receptor agonists
In contrast to their clinical success as inhibitors and targeting agents, antibodies have generally been ineffective as receptor agonists. Here, Romei et al. leverage a natural homotypic interface to tune antibody geometry, enabling optimization of agonist activity for multiple therapeutic targets.
- Matthew G. Romei
- , Brandon Leonard
- & Greg A. Lazar
-
Article
| Open Access Longevity interventions modulate mechanotransduction and extracellular matrix homeostasis in C. elegans
Longevity interventions modulate mechanotransduction and extracellular matrix homeostasis in C. elegans
Mechanotransduction can be defined as translating physical forces into gene expression, which subsequently drives cell fate. Here, Teuscher et al. showed that mechanotransduction across multiple tissues and extracellular matrices is essential for promoting longevity in vivo.
- Alina C. Teuscher
- , Cyril Statzer
- & Collin Y. Ewald
-
Article
| Open Access De novo biosynthesis of the hops bioactive flavonoid xanthohumol in yeast
De novo biosynthesis of the hops bioactive flavonoid xanthohumol in yeast
Xanthohumol is a prenylated flavonoid produced by hops and is an important flavor substance in beer. Here, the authors engineer brewing yeast for the de novo biosynthesis of xanthohumol from glucose by balancing the three parallel biosynthetic pathways.
- Shan Yang
- , Ruibing Chen
- & Yongjin J. Zhou
-
Article
| Open Access Modular assembly of an artificially concise biocatalytic cascade for the manufacture of phenethylisoquinoline alkaloids
Modular assembly of an artificially concise biocatalytic cascade for the manufacture of phenethylisoquinoline alkaloids
Plant alkaloids – an important class of pharmaceuticals - are still largely acquired through phytoextraction. Here, the authors develop an artificial and concise four-enzyme biocatalytic cascade for synthesizing various phenethylisoquinoline alkaloids from readily available starting materials.
- Yue Gao
- , Fei Li
- & Yijian Rao
-
Article
| Open Access MAPS: pathologist-level cell type annotation from tissue images through machine learning
MAPS: pathologist-level cell type annotation from tissue images through machine learning
Current cell annotation methods using high-plex spatial proteomics data are resource intensive and demand iterative expert input. Here, the authors present MAPS (Machine learning for Analysis of Proteomics in Spatial biology), an approach that facilitates rapid and precise cell type identification with human-level accuracy from spatial proteomics data.
- Muhammad Shaban
- , Yunhao Bai
- & Faisal Mahmood
-
Article
| Open Access Mammalian cell growth characterisation by a non-invasive plate reader assay
Mammalian cell growth characterisation by a non-invasive plate reader assay
Automated and non-invasive mammalian cell analysis is currently lagging behind due to a lack of methods suitable for a variety of cell lines and applications. Here the authors develop a high throughput non-invasive method for tracking suspension and adhesion mammalian cell growth based on plate reader measures to characterize engineered cell lines.
- Alice Grob
- , Chiara Enrico Bena
- & Francesca Ceroni
-
Article
| Open Access Microbial interactions shape cheese flavour formation
Microbial interactions shape cheese flavour formation
Cheese fermentation and flavour formation are the result of complex biochemical reactions driven by the activity of multiple microorganisms. Here, the authors identify microbial interactions as a mechanism underlying flavour formation in Cheddar cheese.
- Chrats Melkonian
- , Francisco Zorrilla
- & Ahmad A. Zeidan
-
Article
| Open Access Deciphering driver regulators of cell fate decisions from single-cell transcriptomics data with CEFCON
Deciphering driver regulators of cell fate decisions from single-cell transcriptomics data with CEFCON
Deciphering the roles of gene regulation in cell fate decisions is crucial. Here, authors present CEFCON, a network-based framework that reveals cell-lineage-specific gene regulatory networks and identifies driver regulators controlling cell fate decisions from single-cell transcriptomics data.
- Peizhuo Wang
- , Xiao Wen
- & Jianyang Zeng
-
Review Article
| Open Access Customizing cellular signal processing by synthetic multi-level regulatory circuits
Customizing cellular signal processing by synthetic multi-level regulatory circuits
As synthetic biology permeates society, the signal processing circuits in engineered living systems must be customized to meet practical demands. In this review, the authors outline design strategies for the DNA, RNA, and protein-level circuits and the hybrid “multi-level” circuits.
- Yuanli Gao
- , Lei Wang
- & Baojun Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Mapping protein states and interactions across the tree of life with co-fractionation mass spectrometry
Mapping protein states and interactions across the tree of life with co-fractionation mass spectrometry
Co-fractionation mass spectrometry (CF-MS) is a powerful technique for mapping protein interactions under physiological conditions. Here, the authors uniformly re-process 411 CF-MS experiments and carry out meta-analyses of protein abundance, protein-protein interactions, and phosphorylation sites in the resulting resource.
- Michael A. Skinnider
- , Mopelola O. Akinlaja
- & Leonard J. Foster
-
Article
| Open Access Evolutionary modelling indicates that mosquito metabolism shapes the life-history strategies of Plasmodium parasites
Evolutionary modelling indicates that mosquito metabolism shapes the life-history strategies of Plasmodium parasites
Little is known about how malaria parasites adapt the speed of their development to their mosquito vectors. Using an evolutionary modelling framework, this study predicts that the metabolic status of mosquitoes shapes the parasites’ life-history strategies and transmission dynamics.
- Paola Carrillo-Bustamante
- , Giulia Costa
- & Elena A. Levashina
-
Article
| Open Access Competition and evolutionary selection among core regulatory motifs in gene expression control
Competition and evolutionary selection among core regulatory motifs in gene expression control
Regulators represent a bioenergetic cost in gene expression control. Here, the author shows how functionally equivalent regulatory motifs have fundamentally different impacts on population structure, growth dynamics, and evolutionary outcomes.
- Andras Gyorgy
-
Article
| Open Access Single-cell spatial metabolomics with cell-type specific protein profiling for tissue systems biology
Single-cell spatial metabolomics with cell-type specific protein profiling for tissue systems biology
The authors developed a framework for joint protein-metabolite profiling at the single-cell level in human tissue combining targeted multiplexed protein imaging and untargeted spatial metabolomics in a single pipeline.
- Thomas Hu
- , Mayar Allam
- & Ahmet F. Coskun
-
Article
| Open Access GNTD: reconstructing spatial transcriptomes with graph-guided neural tensor decomposition informed by spatial and functional relations
GNTD: reconstructing spatial transcriptomes with graph-guided neural tensor decomposition informed by spatial and functional relations
Reconstructing transcriptome-wide spatially-resolved gene expressions requires modelling nonlinear patterns and spatial structures in RNA profiling data. Here, authors introduce a graph-guided neural hierarchical tensor decomposition model that incorporates spatial and functional relations for the task.
- Tianci Song
- , Charles Broadbent
- & Rui Kuang
-
Article
| Open Access An integrated workflow for quantitative analysis of the newly synthesized proteome
An integrated workflow for quantitative analysis of the newly synthesized proteome
Analysis of newly synthesized proteins upon perturbation can provide detailed insights into immediate proteome remodeling, which drives cellular responses. Here, the authors report an optimized semi-automated workflow for the quantitative analysis of the newly synthesized proteome.
- Toman Borteçen
- , Torsten Müller
- & Jeroen Krijgsveld
-
Article
| Open Access In vivo RNA interactome profiling reveals 3’UTR-processed small RNA targeting a central regulatory hub
In vivo RNA interactome profiling reveals 3’UTR-processed small RNA targeting a central regulatory hub
Here the authors report a new approach to profile RNA-RNA interactions in live bacterial cells. The charted RNA interaction networks unveil a key mRNA regulatory hub targeted by twelve small RNAs, including a novel RNA involved in fatty acid metabolism.
- Fang Liu
- , Ziying Chen
- & Yanjie Chao
-
Article
| Open Access Environmental modulation of global epistasis in a drug resistance fitness landscape
Environmental modulation of global epistasis in a drug resistance fitness landscape
Global epistasis can be used to reconstruct fitness landscapes and infer adaptive trajectories. Here, the authors investigate how environmental variation impacts patterns of global epistasis, finding that global epistasis in the malaria parasite P. falciparum can be modulated by drug concentration in the environment.
- Juan Diaz-Colunga
- , Alvaro Sanchez
- & C. Brandon Ogbunugafor
Browse broader subjects
Browse narrower subjects
- Bayesian inference
- Biobricks
- Biochemical networks
- Bioenergetics
- Cellular noise
- Complexity
- Computer modelling
- Computer science
- Control theory
- Criticality
- Differential equations
- DNA computing and cryptography
- Dynamic networks
- Dynamical systems
- Emergence
- Evolvability
- Genetic circuit engineering
- Genetic interaction
- Genomic engineering
- Information theory
- Logic gates
- Metabolic engineering
- Modularity
- Molecular engineering
- Molecular fluctuations
- Multicellular systems
- Multistability
- Nonlinear dynamics
- Numerical simulations
- Oscillators
- Population dynamics
- Programming language
- Protein engineering
- Regulatory networks
- Reverse engineering
- Robustness
- Signal processing
- Single-cell imaging
- Software
- Standardization
- Stochastic modelling
- Stochastic networks
- Synthetic biology
- Systems analysis
- Time series

 Cell-type-specific mRNA transcription and degradation kinetics in zebrafish embryogenesis from metabolically labeled single-cell RNA-seq
Cell-type-specific mRNA transcription and degradation kinetics in zebrafish embryogenesis from metabolically labeled single-cell RNA-seq