Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Visualizing the disordered nuclear transport machinery in situ
Visualizing the disordered nuclear transport machinery in situ
Previously shown as a 60-nm hole in the nuclear pore complex, the transport machinery by FG-nucleoporins is mapped.
- Miao Yu
- , Maziar Heidari
- & Edward A. Lemke
-
Article
| Open Access Nonlinear mechanics of human mitotic chromosomes
Nonlinear mechanics of human mitotic chromosomes
A method that uses a combination of optical trapping, fluorescence microscopy and microfluidics to analyse the internal structure of chromosomes shows that there is a distinct nonlinear stiffening of the chromosome in response to tension.
- Anna E. C. Meijering
- , Kata Sarlós
- & Gijs J. L. Wuite
-
Article |
 Structural architecture of the human NALCN channelosome
Structural architecture of the human NALCN channelosome
The structure of the human NALCN channelosome and a model of the gating mechanism are determined.
- Marc Kschonsak
- , Han Chow Chua
- & Jian Payandeh
-
Article |
 Structure and assembly of the mammalian mitochondrial supercomplex CIII2CIV
Structure and assembly of the mammalian mitochondrial supercomplex CIII2CIV
SCAF1 is solely required for supercomplex CIII2CIV assembly and is not involved in the formation of the respirasome (supercomplex CICIII2CIV)
- Irene Vercellino
- & Leonid A. Sazanov
-
Article |
 Cryo-EM structure of SWI/SNF complex bound to a nucleosome
Cryo-EM structure of SWI/SNF complex bound to a nucleosome
The cryo-electron microscopy structure of the yeast SWI/SNF complex bound to a nucleosome substrate provides insights into the chromatin-remodelling function of this family of protein complexes and suggests mechanisms by which the mutated proteins may cause cancer.
- Yan Han
- , Alexis A Reyes
- & Yuan He
-
Letter |
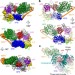 The cryo-electron microscopy structure of human transcription factor IIH
The cryo-electron microscopy structure of human transcription factor IIH
The cryo-electron microscopy structure of the ten-subunit human transcription factor IIH, revealing the molecular architecture of the TFIIH core complex, the detailed structures of its constituent XPB and XPD ATPases, and how the core and kinase subcomplexes of TFIIH are connected.
- Basil J. Greber
- , Thi Hoang Duong Nguyen
- & Eva Nogales
-
Article |
 Structure of the T4 baseplate and its function in triggering sheath contraction
Structure of the T4 baseplate and its function in triggering sheath contraction
A tour-de-force of structural biology solves the structure of the macromolecular injection machinery used to deliver a phage genome into a bacterium.
- Nicholas M. I. Taylor
- , Nikolai S. Prokhorov
- & Petr G. Leiman
-
Article |
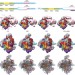 Near-atomic resolution visualization of human transcription promoter opening
Near-atomic resolution visualization of human transcription promoter opening
Cryo-electron microscopy structural models of the human pre-initiation complex at all major steps of transcription initiation at near atomic-level resolution are presented, providing new mechanistic insights into the processes of promoter melting and transcription-bubble formation, as well as an almost complete proposed structural model of all of the pre-initiation complex components and their interactions with DNA.
- Yuan He
- , Chunli Yan
- & Eva Nogales
-
Article |
 Transcription initiation complex structures elucidate DNA opening
Transcription initiation complex structures elucidate DNA opening
The cryo-electron microscopy structures of yeast initiation complexes containing the transcription factors TBP, TFIIA, TFIIB, TFIIE, and TFIIF and containing either closed or open promoter DNA are reported, providing mechanistic insights into DNA opening and template-strand loading.
- C. Plaschka
- , M. Hantsche
- & P. Cramer
-
Letter |
 A Ctf4 trimer couples the CMG helicase to DNA polymerase α in the eukaryotic replisome
A Ctf4 trimer couples the CMG helicase to DNA polymerase α in the eukaryotic replisome
This study shows how the yeast Ctf4 protein couples the DNA helicase, Cdc45–MCM–GINS, to DNA polymerase α — the GINS subunit of the helicase and the polymerase use a similar interaction to bind Ctf4, suggesting that, as Ctf4 is a trimer, two polymerases could be simultaneously coupled to a single helicase during lagging-strand synthesis.
- Aline C. Simon
- , Jin C. Zhou
- & Luca Pellegrini
-
Letter |
 Co-crystal structure of a T-box riboswitch stem I domain in complex with its cognate tRNA
Co-crystal structure of a T-box riboswitch stem I domain in complex with its cognate tRNA
The co-crystal structure of the T-box tRNA-binding region, stem I, bound to tRNA is solved, showing that this region not only binds the anticodon, but also cradles the entire tRNA, forming an extended interface; the two T-loop motifs of stem I mediate interactions similar to those of RNase P and the large ribosomal subunit, even though the three species do not share a common evolutionary ancestor.
- Jinwei Zhang
- & Adrian R. Ferré-D’Amaré
-
Article |
 Structural basis for the subunit assembly of the anaphase-promoting complex
Structural basis for the subunit assembly of the anaphase-promoting complex
The APC/C is a large multiprotein complex that functions as an E3 ubiquitin ligase to regulate the cell cycle. Here, the entire APC/C complex is reconstituted, and in combination with structural studies a pseudo-atomic model for 70% of the complex is provided. These results contribute towards a molecular understanding of the roles of individual subunits in APC/C assembly and their interactions with co-activators, substrates and regulatory proteins.
- Anne Schreiber
- , Florian Stengel
- & David Barford

 The structure and physical properties of a packaged bacteriophage particle
The structure and physical properties of a packaged bacteriophage particle