Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Topological superconducting vortex from trivial electronic bands
Topological superconducting vortex from trivial electronic bands
It is widely believed that bulk-state topology is crucial for enabling Majorana zero modes in solid-state systems. Here, the authors predict that superconducting vortices containing Majorana zero modes can arise from topologically-trivial electronic bands, expanding the pool of materials which may host such phenomena.
- Lun-Hui Hu
- & Rui-Xing Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access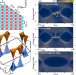 Antiferromagnetism-driven two-dimensional topological nodal-point superconductivity
Antiferromagnetism-driven two-dimensional topological nodal-point superconductivity
Magnet/superconductor hybrids have been explored for the realization of topological superconductivity but have mainly focused on ferromagnets with full gaps. Here, the authors find that the antiferromagnet/superconductor heterostructure of monolayer Mn on a Nb(110) surface is a topological nodal-point superconductor.
- Maciej Bazarnik
- , Roberto Lo Conte
- & Roland Wiesendanger
-
Article
| Open Access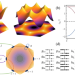 Chiral excitonic order from twofold van Hove singularities in kagome metals
Chiral excitonic order from twofold van Hove singularities in kagome metals
Recent experiments have found a two-fold van Hove singularity (TvHS) in the kagome metal CsV3Sb5. Here, the authors use perturbative renormalization group calculations to find that the leading instability in a model of TvHS is a chiral condensate of electron-hole pairs, breaking time-reversal symmetry.
- Harley D. Scammell
- , Julian Ingham
- & Oleg P. Sushkov
-
Article
| Open Access The scaled-invariant Planckian metal and quantum criticality in Ce1−xNdxCoIn5
The scaled-invariant Planckian metal and quantum criticality in Ce1−xNdxCoIn5
The Planckian metal is a special case of a strange metal, in which the linear-in-temperature scattering rate reaches a universal limit. Here the authors study this state in a heavy-fermion superconductor in magnetic field and propose a microscopic mechanical based on quantum criticality of the Kondo hybridization.
- Yung-Yeh Chang
- , Hechang Lei
- & Chung-Hou Chung
-
Article
| Open Access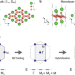 Monolayer Kagome metals AV3Sb5
Monolayer Kagome metals AV3Sb5
Much recent work has focused on the kagome metals AV3Sb5 (A = K, Rb, and Cs), but studies of the monolayer form are only just beginning. Here, the authors theoretically study monolayer kagome metals, and predict modified van Hove singularities that lead to charge-density-wave doublets and d-wave superconductivity.
- Sun-Woo Kim
- , Hanbit Oh
- & Youngkuk Kim
-
Article
| Open Access Tunable unconventional kagome superconductivity in charge ordered RbV3Sb5 and KV3Sb5
Tunable unconventional kagome superconductivity in charge ordered RbV3Sb5 and KV3Sb5
The nature of the superconductivity in the kagome metals AV3Sb5 (A = K, Rb, Cs) remains under debate. Here, using muon spin spectroscopy, the authors find that the superconductivity in RbV3Sb5 and KV3Sb5 evolves from nodal to nodeless with increasing pressure and the superconducting state breaks time-reversal symmetry after suppression of the charge order.
- Z. Guguchia
- , C. Mielke III
- & R. Khasanov
-
Article
| Open Access Unconventional exciton evolution from the pseudogap to superconducting phases in cuprates
Unconventional exciton evolution from the pseudogap to superconducting phases in cuprates
The nature of the excitations in the pseudogap regime and their relation to superconductivity remain core issues in cuprate high-Tc superconductivity. Here, using resonant inelastic x-ray scattering, the authors find that high-energy excitons in optimally-doped Bi2Sr2CaCu2O8+δ are enhanced by the onset of superconductivity, an effect possibly explained in terms of electron fractionalization.
- A. Singh
- , H. Y. Huang
- & D. J. Huang
-
Article
| Open Access Creating superconductivity in WB2 through pressure-induced metastable planar defects
Creating superconductivity in WB2 through pressure-induced metastable planar defects
In 2001 superconductivity with a high critical temperature of 39 K was discovered in MgB2, but efforts since then to identify other diboride-family superconductors have been mostly unsuccessful. Here, the authors report the discovery of superconductivity in pressurized WB2, originating from the formation of metastable stacking faults and twin boundaries that exhibit a local structure resembling MgB2.
- J. Lim
- , A. C. Hire
- & G. R. Stewart
-
Article
| Open Access Unconventional self-similar Hofstadter superconductivity from repulsive interactions
Unconventional self-similar Hofstadter superconductivity from repulsive interactions
Fractal Hofstadter bands have become widely accessible with the advent of moiré superlattices, exemplified by the square-lattice Hubbard-Hofstadter model. Here, the authors predict that, due to a combination of repulsive interactions and Van Hove singularities, this model can realize both nodal and chiral topological superconductivity for different band fillings.
- Daniel Shaffer
- , Jian Wang
- & Luiz H. Santos
-
Article
| Open Access Chern Fermi pocket, topological pair density wave, and charge-4e and charge-6e superconductivity in kagomé superconductors
Chern Fermi pocket, topological pair density wave, and charge-4e and charge-6e superconductivity in kagomé superconductors
The recent discovery of novel charge density wave (CDW) and pair density wave (PDW) in kagome superconductors (SC) AV3Sb5 motivates theoretical study of these phenomena. Here, the authors propose that the CDW state is an orbital Chern metal, leading to a SC state with a chiral PDW, the melting of which leads to vestigial electronic orders including charge-4e and 6e SC.
- Sen Zhou
- & Ziqiang Wang
-
Article
| Open Access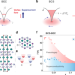 Vortex dynamics in the two-dimensional BCS-BEC crossover
Vortex dynamics in the two-dimensional BCS-BEC crossover
The crossover between the limiting ground states of fermionic systems, the so called BCS-BEC crossover, is of interest to superconductor and ultracold atomic gases communities. The authors study the dynamics of superconducting vortices in the crossover regime via the Hall response in a 2D superconductor LixZrNCl.
- Max Heyl
- , Kyosuke Adachi
- & Yoshihiro Iwasa
-
Article
| Open Access Valence-skipping and quasi-two-dimensionality of superconductivity in a van der Waals insulator
Valence-skipping and quasi-two-dimensionality of superconductivity in a van der Waals insulator
Fluctuation of the cation valence state plays a crucial role in emergent quantum phenomena in correlated electron systems. Here, the authors demonstrate a valence-fluctuation-driven insulator-to-superconductor transition in the van der Waals insulator GeP as a function of hydrostatic pressure.
- Caorong Zhang
- , Junwei Huang
- & Hongtao Yuan
-
Article
| Open Access Strong band renormalization and emergent ferromagnetism induced by electron-antiferromagnetic-magnon coupling
Strong band renormalization and emergent ferromagnetism induced by electron-antiferromagnetic-magnon coupling
The interaction between antiferromagnetic magnons and electrons sits at the heart of many strongly correlated systems, however, investigation has been hampered by a lack of clear-cut examples. Here, Yu et al directly observe a kink in the dispersion, a result of renormalization due to the electron-antiferromagnetic magnon interaction.
- T. L. Yu
- , M. Xu
- & D. L. Feng
-
Article
| Open Access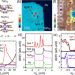 Spin-orbital Yu-Shiba-Rusinov states in single Kondo molecular magnet
Spin-orbital Yu-Shiba-Rusinov states in single Kondo molecular magnet
Yu-Shiba-Rusinov (YSR) states result from the exchange coupling between a localized magnetic moment and a superconductor. Traditionally, the YSR states have been studied for magnetic atoms. For molecular magnets with extended ligand spin, the entanglement of spin and ligand orbital gives rise to new forms of YSR excitations. Here, Xia et al uncovered spin-orbital YSR states in an unpaired ligand spin in the molecular magnet Tb2Pc3 on Pb.
- Hui-Nan Xia
- , Emi Minamitani
- & Ying-Shuang Fu
-
Article
| Open Access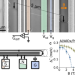 Zero energy states clustering in an elemental nanowire coupled to a superconductor
Zero energy states clustering in an elemental nanowire coupled to a superconductor
Topological superconductivity (TSC) is predicted to exist in nanowires with strong spin-orbit coupling (SOC) when they are in proximity to superconductors, with a key signature being zero-energy states in conductance measurements. Here, using weak-SOC carbon nanotubes as the nanowires, the authors show that similar looking zero-energy states can appear even in nanowires which cannot, in principle, host TSC.
- Lauriane C. Contamin
- , Lucas Jarjat
- & Matthieu R. Delbecq
-
Article
| Open Access Stabilization of three-dimensional charge order through interplanar orbital hybridization in PrxY1−xBa2Cu3O6+δ
Stabilization of three-dimensional charge order through interplanar orbital hybridization in PrxY1−xBa2Cu3O6+δ
External perturbations can induce 3D charge order in cuprates, but the 3D correlation length is limited and the mechanism is not well understood. Ruiz et al. show that Pr substitution in YBa2Cu3O7 enhances interplanar orbital coupling and stabilizes coherent 3D charge order that coexists with superconductivity.
- Alejandro Ruiz
- , Brandon Gunn
- & Alex Frano
-
Article
| Open Access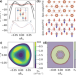 Inter-valley coherent order and isospin fluctuation mediated superconductivity in rhombohedral trilayer graphene
Inter-valley coherent order and isospin fluctuation mediated superconductivity in rhombohedral trilayer graphene
Trilayer graphene was recently shown to exhibit superconductivity without a Moire pattern that had proved important in tuning superconductivity in bilayer graphene. Here, the authors explore correlated metallic phases and the pairing mechanism of superconductivity in trilayer graphene, and show that intervalley coherent fluctuations can act as a pairing glue, giving rise to chiral unconventional superconductivity.
- Shubhayu Chatterjee
- , Taige Wang
- & Michael P. Zaletel
-
Article
| Open Access Giant enhancement of superconducting critical temperature in substitutional alloy (La,Ce)H9
Giant enhancement of superconducting critical temperature in substitutional alloy (La,Ce)H9
Superconductivity was recently discovered in the clathrate hydride CeH9 with superconducting temperature (Tc) of 57 K at pressures below 1 megabar. Here, the authors show that Tc can be increased to 148 K in the substitutional alloy (La,Ce)H9, while maintaining a pressure below 1 megabar.
- Jingkai Bi
- , Yuki Nakamoto
- & Yanming Ma
-
Article
| Open Access Selective control of conductance modes in multi-terminal Josephson junctions
Selective control of conductance modes in multi-terminal Josephson junctions
Multiterminal Josephson junctions may provide a novel way to realize topologically non-trivial band structures in an n-dimensional phase space. Here, the authors experimentally demonstrate the proposed necessary conditions to measure these states.
- Gino V. Graziano
- , Mohit Gupta
- & Vlad S. Pribiag
-
Article
| Open Access Emergent anisotropy in the Fulde–Ferrell–Larkin–Ovchinnikov state
Emergent anisotropy in the Fulde–Ferrell–Larkin–Ovchinnikov state
The famous Fulde–Ferrell–Larkin– Ovchinnikov (FFLO) state is a spatially-modulated superconducting state with a predicted spatial anisotropy, but this anisotropy has never been experimentally verified. Here, the authors present ultrasound evidence for anisotropy of the sound velocity in the FFLO state of a 2D organic superconductor.
- Shusaku Imajo
- , Toshihiro Nomura
- & Koichi Kindo
-
Article
| Open Access Self-heating hotspots in superconducting nanowires cooled by phonon black-body radiation
Self-heating hotspots in superconducting nanowires cooled by phonon black-body radiation
Unlocking the ultimate potential of superconducting nanowire single photon detectors requires engineering their thermal properties. Here, the authors improve our understanding of heat flow in these devices and suggest routes to improved performance.
- Andrew Dane
- , Jason Allmaras
- & Karl K. Berggren
-
Article
| Open Access Record high Tc element superconductivity achieved in titanium
Record high Tc element superconductivity achieved in titanium
Superconductivity at megabar pressures has recently attracted interest in the context of hydrides. Here, the authors demonstrate superconductivity up to 26 K at high pressure in elemental titanium, and further suggest that electron correlations contribute to the high Tc.
- Changling Zhang
- , Xin He
- & Changqing Jin
-
Article
| Open Access Anomalous transverse resistance in the topological superconductor β-Bi2Pd
Anomalous transverse resistance in the topological superconductor β-Bi2Pd
Centrosymmetric β-Bi2Pd is a candidate topological superconductor. Here, the authors observe a transverse voltage in β-Bi2Pd thin films and propose that this voltage is a result of chiral topological surface states.
- Xiaoying Xu
- , Yufan Li
- & C. L. Chien
-
Article
| Open Access Superfluid stiffness of a KTaO3-based two-dimensional electron gas
Superfluid stiffness of a KTaO3-based two-dimensional electron gas
Heterostructures based on (111)-oriented KTaO3crystals are a new platform for studying oxide interfaces. Gate-tunable superconductivity in 2D electron gases at the surface of (111)-oriented KTaO3is now reported, with the superconducting transition being of the Berezinskii-Kosterlitz-Thouless type.
- S. Mallik
- , G. C. Ménard
- & N. Bergeal
-
Article
| Open Access Superconductivity from energy fluctuations in dilute quantum critical polar metals
Superconductivity from energy fluctuations in dilute quantum critical polar metals
Superconductivity in low-carrier-density polar metals, such as SrTiO3, challenges the conventional electron-phonon theory due to the absence of retardation required to overcome Coulomb repulsion. Here, the authors propose that energy fluctuations of quantum-critical phonons could account for the superconductivity of SrTiO3.
- Pavel A. Volkov
- , Premala Chandra
- & Piers Coleman
-
Article
| Open Access The superconductivity of Sr2RuO4 under c-axis uniaxial stress
The superconductivity of Sr2RuO4 under c-axis uniaxial stress
In the superconductor Sr2RuO4, in-plane strain is known to enhance both the superconducting transition temperature Tc and upper critical field Hc2, but the effect of out-of-plane strain has not been studied. Here, the authors find that Hc2 is enhanced under out-of-plane strain, but Tc unexpectedly decreases.
- Fabian Jerzembeck
- , Henrik S. Røising
- & Clifford W. Hicks
-
Article
| Open Access An electronic nematic liquid in BaNi2As2
An electronic nematic liquid in BaNi2As2
Electronic nematicity is typically associated with the breaking of rotational symmetry. Here the authors report unusual nematicity in BaNi2As2, manifested in a large splitting of the optical phonon mode above the structural transition temperature, and link it to the coupling between the lattice and nematic fluctuations.
- Yi Yao
- , Roland Willa
- & Matthieu Le Tacon
-
Article
| Open Access Tuning lower dimensional superconductivity with hybridization at a superconducting-semiconducting interface
Tuning lower dimensional superconductivity with hybridization at a superconducting-semiconducting interface
Lower-dimensional superconductors are typically synthesized on insulating substrates. Here, the authors find that the hybrid electronic structure formed at the interface between a lead film and a semiconducting black phosphorus substrate significantly renormalizes the superconductivity in the lead film.
- Anand Kamlapure
- , Manuel Simonato
- & Alexander Ako Khajetoorians
-
Article
| Open Access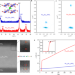 Pressure-induced monotonic enhancement of Tc to over 30 K in superconducting Pr0.82Sr0.18NiO2 thin films
Pressure-induced monotonic enhancement of Tc to over 30 K in superconducting Pr0.82Sr0.18NiO2 thin films
Despite much recent effort, the highest reported Tc of the infinite-layer nickelates remains lower than 15 K. Here, the authors apply pressure to Pr0.82Sr0.18NiO2 thin films and observe a monotonic increase of Tc to 31 K at 12.1 GPa, an increase that does not level off with increasing pressure.
- N. N. Wang
- , M. W. Yang
- & J.-G. Cheng
-
Article
| Open Access Supercurrent diode effect and magnetochiral anisotropy in few-layer NbSe2
Supercurrent diode effect and magnetochiral anisotropy in few-layer NbSe2
The supercurrent diode effect was recently observed in a Nb/V/Ta superlattice thin film with Rashba-type spin-orbit coupling. Here, the authors observe this effect in few-layer NbSe2 crystals driven by valley-Zeeman-type spin-orbit coupling and find that the effect is proportional to out-of-plane magnetic field.
- Lorenz Bauriedl
- , Christian Bäuml
- & Nicola Paradiso
-
Article
| Open Access Demonstration of a superconducting diode-with-memory, operational at zero magnetic field with switchable nonreciprocity
Demonstration of a superconducting diode-with-memory, operational at zero magnetic field with switchable nonreciprocity
Superconducting diodes, operational at zero magnetic field, can be used in supercomputers. Here, the authors demonstrate prototypes of diodes-with-memory, based on Nb Josephson junctions, with a large and switchable nonreciprocity at zero field.
- Taras Golod
- & Vladimir M. Krasnov
-
Article
| Open Access High critical current density and high-tolerance superconductivity in high-entropy alloy thin films
High critical current density and high-tolerance superconductivity in high-entropy alloy thin films
Thin-film high-entropy alloy (HEA) superconductors have recently attracted a lot of attention, but their critical current density and potential usefulness in engineering applications has remained unclear. Here, the authors fabricate HEA films with remarkably high critical current density and resistance to radiation damage.
- Soon-Gil Jung
- , Yoonseok Han
- & Tuson Park
-
Article
| Open Access Magnetic field screening in hydrogen-rich high-temperature superconductors
Magnetic field screening in hydrogen-rich high-temperature superconductors
Superconductivity in hydrides has been primarily explored by electrical transport measurements. Here, the authors perform SQUID magnetometry under extreme high-pressure and report characteristic superconducting parameters for Im-3m-H3S and Fm-3m- LaH10—the representative members of two families of high-temperature superconducting hydrides.
- V. S. Minkov
- , S. L. Bud’ko
- & M. I. Eremets
-
Article
| Open Access Paramagnons and high-temperature superconductivity in a model family of cuprates
Paramagnons and high-temperature superconductivity in a model family of cuprates
Finding a parameter that limits the critical temperature of cuprate superconductors can provide crucial insight on the superconducting mechanism. Here, the authors use inelastic photon scattering on two Ruddlesden-Popper members of the model Hg-family of cuprates to reveal that the energy of magnetic fluctuations may play such a role, and suggest that the Cooper pairing is mediated by paramagnons.
- Lichen Wang
- , Guanhong He
- & Yuan Li
-
Article
| Open Access Pressured-induced superconducting phase with large upper critical field and concomitant enhancement of antiferromagnetic transition in EuTe2
Pressured-induced superconducting phase with large upper critical field and concomitant enhancement of antiferromagnetic transition in EuTe2
Here, the authors report pressure-induced superconductivity with concomitant enhancement of antiferromagnetic transition in layered EuTe2. The superconductivity is distinctly characterized by the high upper critical fields exceeding the Pauli limit among binary tellurides, a prerequisite of the coexistence of ferromagnetism with superconductivity.
- P. T. Yang
- , Z. Y. Liu
- & J.-G. Cheng
-
Article
| Open Access Superconductivity above 200 K discovered in superhydrides of calcium
Superconductivity above 200 K discovered in superhydrides of calcium
The discovery of superconductivity in hydrides at critical temperature (Tc) near room temperature receives intensive attentions. Here the authors report experimental synthesis and discovery of superconductivity with Tc above 210 K in calcium superhydrides at 160–190 GPa.
- Zhiwen Li
- , Xin He
- & Changqing Jin
-
Article
| Open Access A new class of bilayer kagome lattice compounds with Dirac nodal lines and pressure-induced superconductivity
A new class of bilayer kagome lattice compounds with Dirac nodal lines and pressure-induced superconductivity
Kagome lattices composed of transition-metal ions have recently attracted great interest. Here, the authors report a new class of vanadium-based compounds with kagome bilayers which show lines of Dirac nodes in reciprocal space and superconductivity under pressure.
- Mengzhu Shi
- , Fanghang Yu
- & Xianhui Chen
-
Article
| Open Access Monte Carlo study of the pseudogap and superconductivity emerging from quantum magnetic fluctuations
Monte Carlo study of the pseudogap and superconductivity emerging from quantum magnetic fluctuations
The origin of pseudogap in high-Tc superconductors remains a big puzzle. Here, the authors report numerical evidence of pseudogap behavior employing Quantum Monte Carlo algorithm emerging from pairing fluctuations in a quantum-critical non-Fermi liquid, similar to the pseudogap phase observed in cuprate superconductors.
- Weilun Jiang
- , Yuzhi Liu
- & Zi Yang Meng
-
Article
| Open Access Transmon platform for quantum computing challenged by chaotic fluctuations
Transmon platform for quantum computing challenged by chaotic fluctuations
Superconducting quantum processors need to balance intentional disorder (to protect qubits) and nonlinear resonator coupling (to manipulate qubits), while avoiding chaotic instabilities. Berke et al. use the techniques of many-body localization theory to study the stability of current platforms against quantum chaos.
- Christoph Berke
- , Evangelos Varvelis
- & David P. DiVincenzo
-
Article
| Open Access Effect of alloying in monolayer niobium dichalcogenide superconductors
Effect of alloying in monolayer niobium dichalcogenide superconductors
The non-monotonic behaviour of the superconducting transition temperature in NbSe2-xSx monolayer alloys has been linked to fractal superconductivity. Here, using first-principles calculations, the authors provide an alternative explanation for this behavior based on the effects of alloying and defects on the electronic structure and magnetism.
- Darshana Wickramaratne
- & I. I. Mazin
-
Article
| Open Access Excitations in a superconducting Coulombic energy gap
Excitations in a superconducting Coulombic energy gap
The fate of Yu-Shiba-Rusinov states in the presence of a strong Coulomb repulsion in a superconductor remains unknown. Here, the authors couple a quantum dot to a superconducting island with a tunable Coulomb repulsion, where they find a singlet many-body state which, by a strong Coulomb repulsion, changes to a two-body state.
- Juan Carlos Estrada Saldaña
- , Alexandros Vekris
- & Jesper Nygård
-
Article
| Open Access Rich nature of Van Hove singularities in Kagome superconductor CsV3Sb5
Rich nature of Van Hove singularities in Kagome superconductor CsV3Sb5
Predictions suggest enhanced correlation effect due to multiple van Hove singularities (VHS) in the vicinity of the Fermi level in the recently discovered AV3Sb5 kagome metals. Here the authors identify three VHSs close to the Fermi level with diverse sublattice characters in CsV3Sb5, and one of them shows flat dispersion suggesting the higher-order nature.
- Yong Hu
- , Xianxin Wu
- & Ming Shi
-
Article
| Open Access Quantum spins and hybridization in artificially-constructed chains of magnetic adatoms on a superconductor
Quantum spins and hybridization in artificially-constructed chains of magnetic adatoms on a superconductor
Previous studies of magnetic adatom chains on superconducting substrates have mostly focused on the regime of dense chains and classical spins. Here, using scanning tunnelling microscopy, the authors study the excitation spectra of Fe chains on a NbSe2 surface, adatom by adatom, in the regime of quantum spins.
- Eva Liebhaber
- , Lisa M. Rütten
- & Katharina J. Franke
-
Article
| Open Access Uniaxial pressure induced stripe order rotation in La1.88Sr0.12CuO4
Uniaxial pressure induced stripe order rotation in La1.88Sr0.12CuO4
Transverse stripe order fluctuations may promote superconductivity, but experimental verifications remain difficult. Here, the authors report that a mild uniaxial pressure changes the ordering pattern and pins the stripe order to the crystal axis in La1.88Sr0.12CuO4.
- Qisi Wang
- , K. von Arx
- & J. Chang
-
Article
| Open Access Fusion of Majorana bound states with mini-gate control in two-dimensional systems
Fusion of Majorana bound states with mini-gate control in two-dimensional systems
The current efforts to look for Majorana bound states (MBS) still cannot probe the hallmark property, the non-Abelian statistics. Here, the authors propose to realize non-Abelian statistics through MBS fusion in mini-gate controlled planar Josephson junctions.
- Tong Zhou
- , Matthieu C. Dartiailh
- & Igor Žutić
-
Article
| Open Access Giant second harmonic transport under time-reversal symmetry in a trigonal superconductor
Giant second harmonic transport under time-reversal symmetry in a trigonal superconductor
Even-order nonlinear transport is a powerful probe of quantum materials, but such studies in superconductors have been limited to those which break time-reversal symmetry. Here, the authors observe second-order nonlinear transport in time-reversal-symmetric PbTaSe2, where the nonlinearity is enhanced in the superconducting state.
- Yuki M. Itahashi
- , Toshiya Ideue
- & Yoshihiro Iwasa
-
Article
| Open Access Magnetotransport signatures of antiferromagnetism coexisting with charge order in the trilayer cuprate HgBa2Ca2Cu3O8+δ
Magnetotransport signatures of antiferromagnetism coexisting with charge order in the trilayer cuprate HgBa2Ca2Cu3O8+δ
The interplay between superconductivity and competing orders in multi-layered cuprates can shed light on the nature of the superconducting pairing. Here, the authors report on the coexistence of antiferromagnetic and charge orders in different CuO2 planes in a tri-layer cuprate, pointing to a magnetically-mediated mechanism.
- V. Oliviero
- , S. Benhabib
- & C. Proust
-
Article
| Open Access Topotactic fluorination of intermetallics as an efficient route towards quantum materials
Topotactic fluorination of intermetallics as an efficient route towards quantum materials
Insertion of light elements in intermetallics has been explored to synthesize functional materials. Here the authors report topotactic intercalation of fluorine atoms into intermetallics using a perfluorocarbon reactant with covalent C-F bonds to obtain quantum materials.
- Jean-Baptiste Vaney
- , Baptiste Vignolle
- & Sophie Tencé
-
Article
| Open Access Little-Parks like oscillations in lightly doped cuprate superconductors
Little-Parks like oscillations in lightly doped cuprate superconductors
Understanding the rich electronic orders in cuprate superconductors provide insights into the mechanism of high-temperature superconductivity. Here, the authors report a distinct charge order with Little-Parks like resistance oscillations at magnetic fields up to 10 T and around Tc in lightly doped Bi2Sr2CaCu2O8+x.
- Menghan Liao
- , Yuying Zhu
- & Qi-Kun Xue

 Bulk evidence of anisotropic s-wave pairing with no sign change in the kagome superconductor CsV3Sb5
Bulk evidence of anisotropic s-wave pairing with no sign change in the kagome superconductor CsV3Sb5