Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article |
 Near-room-temperature water-mediated densification of bulk van der Waals materials from their nanosheets
Near-room-temperature water-mediated densification of bulk van der Waals materials from their nanosheets
Strong bulk van der Waals materials are fabricated by the compressive moulding of two-dimensional nanosheets near room temperature through water-mediated densification, providing an energy-efficient way for synthesizing various van der Waals materials and a potential for tailoring compositions.
- Jiuyi Zhu
- , Fei Li
- & Hui-Ming Cheng
-
Article |
 High-density stable glasses formed on soft substrates
High-density stable glasses formed on soft substrates
Controlling substrate elasticity during physical vapour deposition allows access to high-density stable glasses that would otherwise be formed under prohibitively slow deposition conditions on rigid substrates.
- Peng Luo
- , Sarah E. Wolf
- & Zahra Fakhraai
-
Article
| Open Access Unlocking Li superionic conductivity in face-centred cubic oxides via face-sharing configurations
Unlocking Li superionic conductivity in face-centred cubic oxides via face-sharing configurations
Oxides with a face-centred cubic anion sublattice are generally not considered as solid-state electrolytes. Li superionic conductivity in face-centred cubic oxides with face-sharing Li configurations have now been created through cation over-stoichiometry in rocksalt-type lattices via excess Li.
- Yu Chen
- , Zhengyan Lun
- & Gerbrand Ceder
-
Feature |
 Observing deformation in situ
Observing deformation in situ
Marc Legros, Frédéric Mompiou and Daniel Caillard discuss the different aspects that influence the reproducibility and reliability of characterizations performed using in situ mechanical tests in transmission electron microscopes.
- Marc Legros
- , Frédéric Mompiou
- & Daniel Caillard
-
Letter |
 Oxidation-induced superelasticity in metallic glass nanotubes
Oxidation-induced superelasticity in metallic glass nanotubes
Oxidation normally deteriorates the mechanical properties of metals. But it is now shown that the formation of a percolating oxide network in metallic glass nanotubes can result in an unprecedented superelasticity of 14% at room temperature.
- Fucheng Li
- , Zhibo Zhang
- & Yong Yang
-
News & Views |
 Toughening through faint crystallization
Toughening through faint crystallization
Oxide glasses can be intrinsically toughened by forming crystal-like, medium-range order clusters, which transform inversely to the amorphous state under stress, exciting multiple shear bands for plastic deformation.
- Hewei Zhao
- & Lin Guo
-
News & Views |
 Resistance to fatigue
Resistance to fatigue
An additively manufactured AlSi10Mg alloy shows high fatigue strength, even close to its tensile strength, for micro-sized samples. The fine cells in its inherent three-dimensional network are considered as cages to limit damage accumulation.
- Christopher Hutchinson
-
Research Briefing |
 Fractured diamond can heal itself at room temperature
Fractured diamond can heal itself at room temperature
Self-healing behaviour in a nanotwinned diamond composite, at room temperature, has been quantitatively evaluated through tensile testing. The phenomenon is shown to arise from a transition of atomic interactions from repulsion to attraction and the formation of nanoscale diamond ‘osteoblasts’, in analogy to the process of bone healing in living organisms.
-
Article |
 Self-healing of fractured diamond
Self-healing of fractured diamond
The room-temperature self-healing behaviour of a nanotwinned diamond composite is quantitatively evaluated and found to stem from both the formation of nanoscale diamond osteoblasts and the atomic interaction transition from repulsion to attraction.
- Keliang Qiu
- , Jingpeng Hou
- & Lin Guo
-
News & Views |
 Amorphization-mediated plasticity
Amorphization-mediated plasticity
Amorphization can be an additional mechanism to assist plastic deformation in crystalline materials, providing a strategy to improve the load-bearing ability of brittle materials.
- Shiteng Zhao
- & Xiaolei Wu
-
Article |
 Achieving ultrahigh fatigue resistance in AlSi10Mg alloy by additive manufacturing
Achieving ultrahigh fatigue resistance in AlSi10Mg alloy by additive manufacturing
An ultrahigh fatigue-resistant AlSi10Mg alloy is achieved by additive manufacturing, with its three-dimensional dual-phase cellular nanostructure acting as a strong volumetric nanocage to inhibit fatigue damage accumulation.
- Chengyi Dan
- , Yuchi Cui
- & Jian Lu
-
Article |
 Multislip-enabled morphing of all-inorganic perovskites
Multislip-enabled morphing of all-inorganic perovskites
In situ tests show that all-inorganic lead halide perovskite micropillars can morph into distinct shapes without affecting their optoelectronic properties and bandgap, which provides insights into the plastic deformation of semiconductors and also shows their potential for manufacturing relevant devices.
- Xiaocui Li
- , You Meng
- & Yang Lu
-
Article |
 Toughening oxide glasses through paracrystallization
Toughening oxide glasses through paracrystallization
Through the approach of paracrystallization under high-pressure and high-temperature conditions, exceptional toughening has been achieved in oxide glasses by enhancing their crystal-like medium-range order structure. This discovery offers possibilities for the design of more resilient glass materials.
- Hu Tang
- , Yong Cheng
- & Tomoo Katsura
-
Comment |
 Extra electron reflections in concentrated alloys do not necessitate short-range order
Extra electron reflections in concentrated alloys do not necessitate short-range order
In many concentrated alloys of current interest, the observation of diffuse superlattice intensities by transmission electron microscopy has been attributed to chemical short-range order. We briefly review these findings and comment on the plausibility of widespread interpretations, noting the absence of expected peaks, conflicts with theoretical predictions, and the possibility of alternative explanations.
- Flynn Walsh
- , Mingwei Zhang
- & Mark Asta
-
Article |
 Amorphous shear bands in crystalline materials as drivers of plasticity
Amorphous shear bands in crystalline materials as drivers of plasticity
Amorphous shear bands in crystalline materials are found to increase the toughness of brittle materials, in contrast to their traditional role as precursors to fracture. Criteria for this toughening have been identified.
- Xuanxin Hu
- , Nuohao Liu
- & Izabela Szlufarska
-
Article |
 Harnessing dislocation motion using an electric field
Harnessing dislocation motion using an electric field
A method to manipulate the dislocation motion via a non-mechanical field alone has remained elusive. Here, using in situ TEM, it is directly observed that dislocation motion can be controlled solely by an external electric field.
- Mingqiang Li
- , Yidi Shen
- & Yu Zou
-
News & Views |
 One dislocation at a time
One dislocation at a time
The direct observation of enhanced dislocation mobility in iron by in situ electron microscopy offers key insights and adds to the ongoing debate on the mechanisms of hydrogen embrittlement.
- Vasily Bulatov
- & Wei Cai
-
News & Views |
 Smoke in the MOF liquid
Smoke in the MOF liquid
An ultra-microporous metal–organic framework glass foam shows outstanding gas sieving properties for challenging gas mixtures.
- Chinmoy Das
- & Sebastian Henke
-
Article |
 Quantitative tests revealing hydrogen-enhanced dislocation motion in α-iron
Quantitative tests revealing hydrogen-enhanced dislocation motion in α-iron
Screw dislocations in α-iron move more easily in the presence of hydrogen, as evidenced by real-time imaging using quantitative transmission electron microscopy.
- Longchao Huang
- , Dengke Chen
- & Zhiwei Shan
-
Article |
 Tailoring planar slip to achieve pure metal-like ductility in body-centred-cubic multi-principal element alloys
Tailoring planar slip to achieve pure metal-like ductility in body-centred-cubic multi-principal element alloys
This work shows that by designing appropriate alloying elements in a body-centred-cubic high-entropy alloy, local chemical order and lattice distortion can be tuned, which influences the evolution of planar-slip bands, realizing pure-metal-like tensile ductility at gigapascal yield strength.
- Liang Wang
- , Jun Ding
- & En Ma
-
Article |
 Scalable manufacturing of high-index atomic layer–polymer hybrid metasurfaces for metaphotonics in the visible
Scalable manufacturing of high-index atomic layer–polymer hybrid metasurfaces for metaphotonics in the visible
The authors propose a method for the scalable manufacturing of metalenses using deep-ultraviolet argon fluoride immersion lithography and wafer-scale nanoimprint lithography, opening a route towards their low-cost, high-throughput mass production.
- Joohoon Kim
- , Junhwa Seong
- & Junsuk Rho
-
Research Briefing |
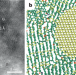 Combining the properties of nanodiamond and disordered multilayer graphene
Combining the properties of nanodiamond and disordered multilayer graphene
An ultrastrong and superhard conductive carbon composite has been synthesized, which consists of ultrafine nanodiamond homogeneously dispersed in disordered multilayer graphene with incoherent interfaces. The microstructures of the composite suggest that the transition from amorphous carbon to diamond involves the extensive nucleation and diffusion-driven growth of nanodiamond.
-
News & Views |
 Heat-resistant aluminium alloys
Heat-resistant aluminium alloys
Scandium added to Al–Cu–Mg–Ag alloys leads to an in situ phase transformation of coherent Cu-rich nanoprecipitates at elevated temperature, with Sc atoms diffusing and occupying their interstitial sites. The transformed nanoprecipitates have enhanced thermal stability while maintaining a large volume fraction and these two microstructural features enable high tensile strength of the Al alloy with creep resistance up to 400 °C.
- Amit Shyam
- & Sumit Bahl
-
Article |
 Highly stable coherent nanoprecipitates via diffusion-dominated solute uptake and interstitial ordering
Highly stable coherent nanoprecipitates via diffusion-dominated solute uptake and interstitial ordering
High-density, highly stable coherent nanoprecipitates are created in Al alloys that enable high strength and creep resistance at 400 °C. This is realized via a growth-ledge-triggered in situ phase transformation assembling slow-diffusing solutes with high-solubility solutes into nanoprecipitates.
- Hang Xue
- , Chong Yang
- & Jun Sun
-
Article
| Open Access Ultrastrong conductive in situ composite composed of nanodiamond incoherently embedded in disordered multilayer graphene
Ultrastrong conductive in situ composite composed of nanodiamond incoherently embedded in disordered multilayer graphene
In situ composites consisting of nanodiamond homogeneously dispersed in disordered multilayer graphene with incoherent interfaces and complex bonding are synthesized that exhibit an ultrahigh hardness and compressive strength, and excellent electrical conductivity.
- Zihe Li
- , Yujia Wang
- & Xiaoyan Li
-
Review Article |
 Hierarchically structured bioinspired nanocomposites
Hierarchically structured bioinspired nanocomposites
This Review discusses recent progress in bioinspired nanocomposite design, emphasizing the role of hierarchical structuring at distinct length scales to create multifunctional, lightweight and robust structural materials for diverse technological applications.
- Dhriti Nepal
- , Saewon Kang
- & Hendrik Heinz
-
News & Views |
 Unusual microstructures by 3D printing
Unusual microstructures by 3D printing
Additive manufacturing imparts defects in as-built titanium alloy microstructures, which form internally twinned nanoprecipitates with heat treatment to yield attractive mechanical properties.
- Amy J. Clarke
-
Comment |
 Carbon neutrality orientates the reform of the steel industry
Carbon neutrality orientates the reform of the steel industry
The steel industry in China has an important role in reducing national and global carbon emissions, demanding integrated actions and efforts across policies, industry and science to achieve the goal of carbon neutrality.
- Zhuo Kang
- , Qingliang Liao
- & Yue Zhang
-
Article |
 Ultrastrong nanotwinned titanium alloys through additive manufacturing
Ultrastrong nanotwinned titanium alloys through additive manufacturing
Laser additive manufacturing can be exploited to generate unique internally twinned nanoprecipitates in commercial titanium alloys, paving the way to fabricate ultrastrong metallic materials with intricate shapes for broad applications.
- Yuman Zhu
- , Kun Zhang
- & Aijun Huang
-
Article |
 Low-oxygen rare earth steels
Low-oxygen rare earth steels
The variation in the properties of rare earth (RE) steels is shown to stem from the presence of oxygen-based inclusions, and only under very-low-oxygen conditions can RE elements perform a vital role in purifying, modifying and micro-alloying steels.
- Dianzhong Li
- , Pei Wang
- & Yiyi Li
-
Comment |
 Growing designability in structural materials
Growing designability in structural materials
Structural materials are critical components for our daily lives and industries. This Comment highlights the emerging concepts in structural materials over the past two decades, particularly the multi-principal element alloys, heterostructured materials and additive manufacturing that enables the fabrication of complex architectures.
- Robert O. Ritchie
- & Xiaoyu Rayne Zheng
-
Letter |
 Liquid-like atoms in dense-packed solid glasses
Liquid-like atoms in dense-packed solid glasses
The existence of fast dynamics in glass solids at low temperatures is attributed to liquid-like atoms that are inherited from high-temperature liquids and exhibit behaviour similar to that of atoms in liquid states.
- C. Chang
- , H. P. Zhang
- & H. Y. Bai
-
Article |
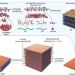 Graphene oxide bulk material reinforced by heterophase platelets with multiscale interface crosslinking
Graphene oxide bulk material reinforced by heterophase platelets with multiscale interface crosslinking
A nacre-inspired, centimetre-sized bulk material is prepared by assembling graphene oxide and microscale amorphous/crystalline heterophase reinforcing platelets adhered together with polymer-based crosslinkers, which shows high flexural strength and fracture toughness.
- Ke Chen
- , Xuke Tang
- & Lin Guo
-
Letter |
 A lightweight strain glass alloy showing nearly temperature-independent low modulus and high strength
A lightweight strain glass alloy showing nearly temperature-independent low modulus and high strength
Temperature-independent (Elinvar) soft elasticity with high strength, which is technologically desired but scientifically challenging, is achieved in a lightweight strain glass Mg alloy.
- Chang Liu
- , Yuanchao Ji
- & Xiaobing Ren
-
News & Views |
 Nanotwinning-assisted recrystallization
Nanotwinning-assisted recrystallization
Dynamic recrystallization helps to refine grain structures in metals and tune their properties. Confining recrystallization within prior nanoscale twinning provides a path for reaching exceptional grain refinement.
- Roland E. Logé
-
Article
| Open Access Programmable gear-based mechanical metamaterials
Programmable gear-based mechanical metamaterials
A design paradigm to create robust robotic metamaterials using versatile gear clusters is demonstrated. It enables intriguing programmability of elastic properties and shape while preserving stability for intelligent machines.
- Xin Fang
- , Jihong Wen
- & Peter Gumbsch
-
Article |
 High-entropy enhanced capacitive energy storage
High-entropy enhanced capacitive energy storage
Electrostatic capacitors can enable ultrafast energy storage and release, but advances in energy density and efficiency need to be made. Here, by doping equimolar Zr, Hf and Sn into Bi4Ti3O12 thin films, a high-entropy stabilized Bi2Ti2O7 pyrochlore phase forms with an energy density of 182 J cm−3 and 78% efficiency.
- Bingbing Yang
- , Yang Zhang
- & Yuan-Hua Lin
-
News & Views |
 Reassembled nanoprecipitates resisting radiation
Reassembled nanoprecipitates resisting radiation
Outstanding resistance to destructive radiation damage in structural alloys is realized by ultra-high-density reversible nanoprecipitate inclusions, and the improvement is attributed to the reordering process of low-misfit superlattices in highly supersaturated matrices.
- Yanwen Zhang
-
Article |
 Superior radiation tolerance via reversible disordering–ordering transition of coherent superlattices
Superior radiation tolerance via reversible disordering–ordering transition of coherent superlattices
The cycling disordering–ordering transition of low-misfit superlattice nanoprecipitates in metallic materials continuously annihilates radiation defects via a short-range atom-reshuffling process, giving rise to high radiation tolerance.
- Jinlong Du
- , Suihe Jiang
- & Zhaoping Lu
-
News & Views |
 Uncovering the flow of metallic glass
Uncovering the flow of metallic glass
Plastic yielding of metallic glasses is mediated by strain softening, which promotes localized failure and impairs engineering predictability. Unravelling the mechanisms associated with this plastic flow behaviour lays the groundwork for reliable engineering design of this elusive material.
- Marios D. Demetriou
-
Article |
 Tough and stretchable ionogels by in situ phase separation
Tough and stretchable ionogels by in situ phase separation
Two monomers with distinct solubility of their corresponding polymers in an ionic liquid enable tuning of the microstructure of the copolymers during their polymerization. Thus, energy dissipative and elastic molecular domains are created, resulting in highly tough and stretchable ionogels.
- Meixiang Wang
- , Pengyao Zhang
- & Michael D. Dickey
-
Article |
 The toughness of mechanical metamaterials
The toughness of mechanical metamaterials
Microscale architecting enables metamaterials to achieve mechanical properties not accessible to bulk materials. Here the authors show that established design protocols for the fracture of materials need to be revised to predict the failure of these materials.
- Angkur Jyoti Dipanka Shaikeea
- , Huachen Cui
- & Vikram Sudhir Deshpande
-
News & Views |
 Efficient glassy alloy screening
Efficient glassy alloy screening
Glass-forming ability in metallic systems is related to the diversity of atomic packing schemes quenched into the glassy state, which manifests itself in the width of the first broad X-ray diffraction peak. This provides a swift way for screening libraries of deposited alloy films and searching for good glass formers.
- Simon Pauly
-
Article |
 Universal scaling law of glass rheology
Universal scaling law of glass rheology
The liquid nature of hard glasses is demonstrated by broadband stress relaxation experiments. The rheology and dynamic transition of various glass systems can be unified by a universal scaling law in the time–stress–temperature–volume domain.
- Shuangxi Song
- , Fan Zhu
- & Mingwei Chen
-
Article |
 Atomic-scale observation of non-classical nucleation-mediated phase transformation in a titanium alloy
Atomic-scale observation of non-classical nucleation-mediated phase transformation in a titanium alloy
A full kinetic pathway of a non-classical nucleation-induced phase transformation through metastable states is elucidated at sub-ångström resolution in a technologically important titanium alloy.
- Xiaoqian Fu
- , Xu-Dong Wang
- & En Ma
-
Article |
 Data-driven discovery of a universal indicator for metallic glass forming ability
Data-driven discovery of a universal indicator for metallic glass forming ability
The glass forming ability of alloys is found to be strongly correlated with the full-width at half-maximum of the first diffraction peak in the X-ray diffraction pattern, which facilitates the discovery of bulk metallic glass compositions.
- Ming-Xing Li
- , Yi-Tao Sun
- & Yan-Hui Liu
-
News & Views |
 Built from connected nested tubes
Built from connected nested tubes
Nanoarchitected carbon composed of intricate tube-in-tube beams connected with nanostruts has been fabricated, achieving both ultralightweight and ultrahigh modulus.
- Yujia Wang
- & Xiaoyan Li
-
News & Views |
 Nano goes the distance
Nano goes the distance
Centimetre-scale crack-free metal nanolattices are realized, enabling outstanding high tensile strength in low-density materials.
- Andreas Stein
- & Nathan A. Mara
-
Article |
 Ultra-low-density digitally architected carbon with a strutted tube-in-tube structure
Ultra-low-density digitally architected carbon with a strutted tube-in-tube structure
A nanoscale tube-in-tube sandwich structure is generated by a two-step templating-pyrolysis process, which strengthens the log-pile carbon architecture and slows down the decrease of stiffness with decreasing density.
- Jianchao Ye
- , Ling Liu
- & Juergen Biener

 Harnessing instability for work hardening in multi-principal element alloys
Harnessing instability for work hardening in multi-principal element alloys