Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Atomic stiffness for bulk modulus prediction and high-throughput screening of ultraincompressible crystals
Atomic stiffness for bulk modulus prediction and high-throughput screening of ultraincompressible crystals
Fast and accurate prediction of bulk moduli for diverse materials is challenging. Here, the authors introduce the concept of atomic stiffness to accelerate bulk modulus prediction and high-throughput screening of ultra-incompressible crystals.
- Ruihua Jin
- , Xiaoang Yuan
- & Enlai Gao
-
Article
| Open Access Soft corrugated channel with synergistic exclusive discrimination gating for CO2 recognition in gas mixture
Soft corrugated channel with synergistic exclusive discrimination gating for CO2 recognition in gas mixture
Developing porous systems with high molecular recognition performance can be challenging. Here the authors present a corrugated channel system that cooperatively responds to only CO2 molecules over nine other similar gas molecules.
- Yifan Gu
- , Jia-Jia Zheng
- & Susumu Kitagawa
-
Article
| Open Access Mesoporous multimetallic nanospheres with exposed highly entropic alloy sites
Mesoporous multimetallic nanospheres with exposed highly entropic alloy sites
Nanostructured materials made from multimetal alloys are attractive for catalytic applications. Here, the authors propose a soft-templating approach to prepare mesoporous PtPdRhRuCu nanospheres that feature exposed porous structures rich in highly entropic alloy sites.
- Yunqing Kang
- , Ovidiu Cretu
- & Yusuke Yamauchi
-
Article
| Open Access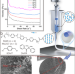 Programmable spatial deformation by controllable off-center freestanding 4D printing of continuous fiber reinforced liquid crystal elastomer composites
Programmable spatial deformation by controllable off-center freestanding 4D printing of continuous fiber reinforced liquid crystal elastomer composites
Liquid crystal elastomer printing methods are often limited to planar structures. In this work, authors integrate 4D printed structures with fully impregnated composite interfaces to enable programmable deformation ability and high bearing capacity by adjusting the off-centre distribution of the fibres.
- Qingrui Wang
- , Xiaoyong Tian
- & Dichen Li
-
Article
| Open Access Radial bimetallic structures via wire arc directed energy deposition-based additive manufacturing
Radial bimetallic structures via wire arc directed energy deposition-based additive manufacturing
Bimetallic wire arc additive manufacturing has traditionally been limited to deposition of planar interfaces. Here, the authors demonstrate deposition of complex radial interfaces with in situ mechanical interlocking, resulting in the prestressed compressive effect in the as-built parts.
- Lile Squires
- , Ethan Roberts
- & Amit Bandyopadhyay
-
Article
| Open Access Substantially enhanced homogeneous plastic flow in hierarchically nanodomained amorphous alloys
Substantially enhanced homogeneous plastic flow in hierarchically nanodomained amorphous alloys
Topological heterostructures are desired in metallic glasses to improve their mechanical properties. Here, the authors present an enthalpy-guided alloy design to introduce nanoscale chemical heterogeneity, producing a metallic glass with a large homogeneous plastic flow at room temperature.
- Ge Wu
- , Sida Liu
- & Zhi-Wei Shan
-
Article
| Open Access Atomic motifs govern the decoration of grain boundaries by interstitial solutes
Atomic motifs govern the decoration of grain boundaries by interstitial solutes
Interplay between structure and composition of grain boundaries remains elusive, particularly at the atomic level. Here, the authors discover the atomic motifs, which is the smallest structural unit, control the most important chemical properties of grain boundaries.
- Xuyang Zhou
- , Ali Ahmadian
- & Dierk Raabe
-
Article
| Open Access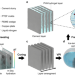 Multi-layered cement-hydrogel composite with high toughness, low thermal conductivity, and self-healing capability
Multi-layered cement-hydrogel composite with high toughness, low thermal conductivity, and self-healing capability
Despite widely used in the construction sector, Portland cement’s high brittleness and low toughness still pose challenges in some applications. Here, authors apply an ice-templating method to fabricate a cement-hydrogel composite with alternating layered microstructure resulting in significantly increased toughness.
- Yuan Chen
- , Yangzezhi Zheng
- & Changwen Miao
-
Article
| Open Access Three-dimensional printing of silica glass with sub-micrometer resolution
Three-dimensional printing of silica glass with sub-micrometer resolution
Silica glass is a high-performance material used in most branches of society from glassware and windows to optical lenses and fibers. Here, we develop a sintering-free method for 3D printing silica glass with sub-micrometer resolution and successfully demonstrate an optical microtoroid resonator.
- Po-Han Huang
- , Miku Laakso
- & Frank Niklaus
-
Article
| Open Access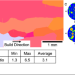 Underlying factors determining grain morphologies in high-strength titanium alloys processed by additive manufacturing
Underlying factors determining grain morphologies in high-strength titanium alloys processed by additive manufacturing
Predictive scheme for Ti alloys with equiaxed microstructures is often limited by the methods based on growth restriction factors, Q. Here, the authors present a predictive solution based on the freezing range of alloys for columnar to equiaxed transition during fusion-based additive manufacturing.
- Mohan S. K. K. Y. Nartu
- , Brian A. Welk
- & Hamish L. Fraser
-
Article
| Open Access Cryogenic characteristics of graphene composites—evolution from thermal conductors to thermal insulators
Cryogenic characteristics of graphene composites—evolution from thermal conductors to thermal insulators
Graphene composites can serve both as efficient thermal insulators at low temperatures and thermal conductors at high temperatures. Here, the authors report the evolution of thermal conductivity of composites with graphene fillers from cryogenic to room temperature.
- Zahra Ebrahim Nataj
- , Youming Xu
- & Alexander A. Balandin
-
Article
| Open Access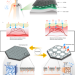 Bidirectional thermo-regulating hydrogel composite for autonomic thermal homeostasis
Bidirectional thermo-regulating hydrogel composite for autonomic thermal homeostasis
Developing materials which mimic thermal homeostasis is limited by complicated fabrication steps or unidirectional temperature transport. Here, the authors develop a homeostatic hydrogel that shows improved heat trapping at low temperatures, and enhanced evaporative cooling at high temperatures.
- Gyeongsuk Park
- , Hyunmin Park
- & Steve Park
-
Article
| Open Access Fabricating strong and tough aramid fibers by small addition of carbon nanotubes
Fabricating strong and tough aramid fibers by small addition of carbon nanotubes
High-performance fibers are promising materials in the impact protection field but fabricating fibers with high strength and high toughness is challenging. Here, the authors polymerize carbon nanotubes into aramid fibers to simultaneously improve strength and toughness.
- Jiajun Luo
- , Yeye Wen
- & Jin Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Compact A15 Frank-Kasper nano-phases at the origin of dislocation loops in face-centred cubic metals
Compact A15 Frank-Kasper nano-phases at the origin of dislocation loops in face-centred cubic metals
It is historically assumed point defects in metals coalesce directly into larger dislocation loops. Here the authors revise the fundamental mechanism, reveal the formation of A15 nano-phase clusters in fcc metals prior to dislocation loops, and highlight the major implications of this discovery.
- Alexandra M. Goryaeva
- , Christophe Domain
- & Mihai-Cosmin Marinica
-
Article
| Open Access Ultra-strong tungsten refractory high-entropy alloy via stepwise controllable coherent nanoprecipitations
Ultra-strong tungsten refractory high-entropy alloy via stepwise controllable coherent nanoprecipitations
Tungsten-based alloys with ultrahigh strength and ductility are in high demand for a wide range of applications, potentially for fusion reactors. Here the authors develop a tungsten refractory high-entropy alloy with high strength (~2.15 GPa) and sufficient ductility (~15%).
- Tong Li
- , Tianwei Liu
- & Lanhong Dai
-
Article
| Open Access Synergy of multiple precipitate/matrix interface structures for a heat resistant high-strength Al alloy
Synergy of multiple precipitate/matrix interface structures for a heat resistant high-strength Al alloy
Coarsening of precipitates in medium and high temperatures causes reduction in strength of Al alloys. Here, the authors design an Al-Cu-Mg-Ag-Si-Sc alloy with multiple interface structures, showing an excellent combination of strength and heat resistance compared to conventional Al alloys.
- Qiang Lu
- , Jianchuan Wang
- & Yong Du
-
Article
| Open Access Robust microscale structural superlubricity between graphite and nanostructured surface
Robust microscale structural superlubricity between graphite and nanostructured surface
Structural superlubricity (SSL) is a state of nearly zero friction and no wear between two contacted solid surfaces. Here, authors show that, by preventing edge contact with the substrate, a microscale graphite flake can achieve robust SSL against nanostructured silicon surfaces under ambient condition.
- Xuanyu Huang
- , Tengfei Li
- & Quanshui Zheng
-
Article
| Open Access Wood xerogel for fabrication of high-performance transparent wood
Wood xerogel for fabrication of high-performance transparent wood
Optically transparent wood composites are commonly prepared by delignification of wood and subsequent infiltration of thermo- or photocurable polymer resins but the fabrication is still limited by the intrinsic low mesopore volume of the delignified wood. Here, the authors report a facile approach to fabricate transparent wood using wood xerogel which allows solvent-free infiltration of resin monomers into the wood cell wall under ambient conditions.’
- Shennan Wang
- , Lengwan Li
- & Qi Zhou
-
Article
| Open Access 4D nanoimaging of early age cement hydration
4D nanoimaging of early age cement hydration
In this work, the authors use near-field ptychographic nanotomography to visualize cement hydration in situ. They report hydration features with submicrometer detail including calcium silicate dissolution rates, etch-pit growth rates and water-to-air porosity evolution.
- Shiva Shirani
- , Ana Cuesta
- & Miguel A. G. Aranda
-
Article
| Open Access Theory-guided design of high-entropy alloys with enhanced strength-ductility synergy
Theory-guided design of high-entropy alloys with enhanced strength-ductility synergy
There is a lack of guiding parameters to design metallic materials such as high-entropy alloys with strength-ductility synergy. Here, the authors propose such an effective parameter κ, the ratio of short-ranged interactions between closed-pack planes, experimentally validated by six alloys.
- Zongrui Pei
- , Shiteng Zhao
- & Michael C. Gao
-
Article
| Open Access A quinary WTaCrVHf nanocrystalline refractory high-entropy alloy withholding extreme irradiation environments
A quinary WTaCrVHf nanocrystalline refractory high-entropy alloy withholding extreme irradiation environments
Refractory high entropy alloys (RHEAs) have recently been developed in the context of high-temperature and severe environmental applications. Here the authors, by combining simulation and experiments, develop an irradiation resistant, thermally stable, and strong RHEA for nuclear application.
- O. El Atwani
- , H. T. Vo
- & E. Martinez
-
Article
| Open Access Deconvoluting Cr states in Cr-doped UO2 nuclear fuels via bulk and single crystal spectroscopic studies
Deconvoluting Cr states in Cr-doped UO2 nuclear fuels via bulk and single crystal spectroscopic studies
Additive based UO2 nuclear fuels, which incorporate small amounts of metal oxides such as chromia (Cr2O3), are an important class of accident tolerant fuels. Here authors determine the structural-redox mechanism for Cr lattice incorporation into UO2 nuclear fuels.
- Gabriel L. Murphy
- , Robert Gericke
- & Nina Huittinen
-
Article
| Open Access 3D Printing and processing of miniaturized transducers with near-pristine piezoelectric ceramics for localized cavitation
3D Printing and processing of miniaturized transducers with near-pristine piezoelectric ceramics for localized cavitation
Despite advances in additive manufacturing of piezoceramics, resultant transducers generally suffer from high porosity, weak piezoelectric responses, and limited geometry. Here, authors report the design and printing of fully packaged freeform ultrasonic transducers capable of traveling inside mm-sized channels and deliver localized high ultrasound energy.
- Haotian Lu
- , Huachen Cui
- & Xiaoyu (Rayne) Zheng
-
Article
| Open Access 3D printing of unsupported multi-scale and large-span ceramic via near-infrared assisted direct ink writing
3D printing of unsupported multi-scale and large-span ceramic via near-infrared assisted direct ink writing
In 3D ceramic printing, the need for additional supports can increase processing time and introduce defects during post-processing removal. Here, authors merge direct ink writing and up-conversion particles-assisted photopolymerization under near-infrared irradiation for support-free printing with controlled curing rates reducing material waste, printing time, and post-processing steps.
- Yongqin Zhao
- , Junzhe Zhu
- & Ren Liu
-
Article
| Open Access A non-Newtonian fluid quasi-solid electrolyte designed for long life and high safety Li-O2 batteries
A non-Newtonian fluid quasi-solid electrolyte designed for long life and high safety Li-O2 batteries
Lithium dendrite growth and liquid electrolyte volatilization limit the further development of lithium-oxygen batteries. Here, authors report a non-Newtonian fluid quasi-solid electrolyte to address those issues, which improve the life duration of the lithium-oxygen batteries.
- Guangli Zheng
- , Tong Yan
- & Huiyu Song
-
Article
| Open Access Cell invasion during competitive growth of polycrystalline solidification patterns
Cell invasion during competitive growth of polycrystalline solidification patterns
It is challenging to fully characterize solidification in a well-homogenized conditions owing to the gravity effect. Here the authors perform microgravity experiments and simulations to show interpenetration of spatial domains of different crystal orientations during alloy solidification.
- Younggil Song
- , Fatima L. Mota
- & Alain Karma
-
Article
| Open Access Large piezoelectric response in a Jahn-Teller distorted molecular metal halide
Large piezoelectric response in a Jahn-Teller distorted molecular metal halide
Here, the authors utilise a combination of quasi-spherical theory and Jahn-Teller distortion to enhance the piezoelectric response of molecular metal halides, and the resulting piezoelectric energy harvesters exhibit superior power densities to the best-reported molecular hybrid energy harvesters.
- Sasa Wang
- , Asif Abdullah Khan
- & Edward H. Sargent
-
Article
| Open Access Evanescent field trapping and propulsion of Janus particles along optical nanofibers
Evanescent field trapping and propulsion of Janus particles along optical nanofibers
Manipulation of Janus particles is challenging and has limited precision. Here, the authors propose manipulation of Janus particles by optical forces in the evanescent field of an optical nanofiber, and demonstrate that they exhibit strong transverse localization on the nanofiber and much faster propulsion compared to all-dielectric particles of the same size.
- Georgiy Tkachenko
- , Viet Giang Truong
- & Síle Nic Chormaic
-
Article
| Open Access Multimaterial 3D printed self-locking thick-panel origami metamaterials
Multimaterial 3D printed self-locking thick-panel origami metamaterials
Thick panel origami holds great potential in engineering structures, but conventional fabrication processes limit their design and applications. Here the authors report a multimaterial 3D printing-based design and fabrication strategy for thick-panel origami structures with push-to-pull deformation.
- Haitao Ye
- , Qingjiang Liu
- & Qi Ge
-
Article
| Open Access Trifunctional nanoprecipitates ductilize and toughen a strong laminated metastable titanium alloy
Trifunctional nanoprecipitates ductilize and toughen a strong laminated metastable titanium alloy
Engineering metastability can enhance the ductility of alloys, but it often comes at an expense of relatively low yield strength. Here, the authors fabricate a Ti-based alloy with heterogeneous laminated structures and α-nanoprecipitates that enhance yield strength without sacrificing ductility.
- Chongle Zhang
- , Shuaiyang Liu
- & Jun Sun
-
Article
| Open Access Phase formation capability and compositional design of β-phase multiple rare-earth principal component disilicates
Phase formation capability and compositional design of β-phase multiple rare-earth principal component disilicates
Developing high-entropy environmental barrier coatings is challenged by the intricacy to form stable multicomponent materials. Here the authors report the phases of high-entropy β-RE2Si2O7 could be precisely designed by monitoring the entropy descriptor and the cationic radii on rare earth sites.
- Yixiu Luo
- , Luchao Sun
- & Jingyang Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Engineering zero modes in transformable mechanical metamaterials
Engineering zero modes in transformable mechanical metamaterials
Reconfigurable elastic properties are essential for functional mechanical metamaterials. Here, the authors propose a 3D metamaterial with engineered zero modes, and experimentally demonstrate its transformability covering all seven extremal metamaterial types, leading to programmable wave functions.
- Zhou Hu
- , Zhibo Wei
- & Gengkai Hu
-
Article
| Open Access Robust flexural performance and fracture behavior of TiO2 decorated densified bamboo as sustainable structural materials
Robust flexural performance and fracture behavior of TiO2 decorated densified bamboo as sustainable structural materials
Fast-growing bamboo still need advanced processing before being fabricated into sustainable structural materials. Here, the authors develop high-performance TiO2 reinforced densified bamboo via in situ hydrothermal synthesis and reveal the flexural failure mechanism of the composite.
- Ziyu Ba
- , Hongyun Luo
- & Robert O. Ritchie
-
Article
| Open Access Snake venom-defined fibrin architecture dictates fibroblast survival and differentiation
Snake venom-defined fibrin architecture dictates fibroblast survival and differentiation
A new snake venom-controlled defined fibrin system with stable, reproducible, and independently tuned biophysical properties is established. Employing the system, the authors find fibrin architecture can precisely control fibroblast differentiation.
- Zhao Wang
- , Jan Lauko
- & Alan E. Rowan
-
Article
| Open Access One dimensional wormhole corrosion in metals
One dimensional wormhole corrosion in metals
Corrosion is a ubiquitous failure mode in materials. Here the authors report a percolating 1D wormhole corrosion morphology using advanced electron microscopy and theoretical simulations. The work presents a vacancy mapping method with nm-resolution, identifying the incubation sites of the wormholes.
- Yang Yang
- , Weiyue Zhou
- & Andrew M. Minor
-
Article
| Open Access Manipulating the ordered oxygen complexes to achieve high strength and ductility in medium-entropy alloys
Manipulating the ordered oxygen complexes to achieve high strength and ductility in medium-entropy alloys
Ordered oxygen complexes (OOCs) endow a unique interstitial strengthening mechanism for simultaneously enhancing strength and ductility in HEAs. Here, the authors demonstrate whether such mechanism can be extended to other alloy systems and how the formation of OOCs is tailored.
- Meiyuan Jiao
- , Zhifeng Lei
- & Zhaoping Lu
-
Article
| Open Access Ultrarobust subzero healable materials enabled by polyphenol nano-assemblies
Ultrarobust subzero healable materials enabled by polyphenol nano-assemblies
Self-healing materials hold great promise for applications in wearable electronics, artificial muscles and soft robots but selfhealing at subzero temperatures remains a great challenge. Here, the authors present a robust subzero healable glassy polymer by incorporating polyphenol nano-assemblies with a large number of end groups into polymerizable deep eutectic solvent elastomers.
- Nan Wang
- , Xin Yang
- & Xinxing Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Pt-induced atomic-level tailoring towards paracrystalline high-entropy alloy
Pt-induced atomic-level tailoring towards paracrystalline high-entropy alloy
Paracrystalline state is still challenging to reach in alloy systems in a controlled manner. Here, the authors present an atomic-level tailoring route to create paracrystalline Zr-Nb-Hf-Ta-Mo high-entropy alloy through local amorphization induced by atomic-level Pt with negative mixing enthalpy.
- Xingjia He
- , Yu Zhang
- & Weitao Zheng
-
Article
| Open Access Polymer-dispersed liquid crystal elastomers as moldable shape-programmable material
Polymer-dispersed liquid crystal elastomers as moldable shape-programmable material
Development of Soft shape-memory materials is often limited to the synthesis of two-dimensional specimens and rely on bending mechanisms and scaffolding topology to perform three-dimensional morphing. Here, the authors demonstrate a shape-memory composite material made from main-chain liquid crystal elastomer microparticles dispersed in a silicone polymer matrix which enables molding into full-volume objects of any shape or size.
- Matej Bobnar
- , Nikita Derets
- & Andraž Rešetič
-
Article
| Open Access Grain refinement in titanium prevents low temperature oxygen embrittlement
Grain refinement in titanium prevents low temperature oxygen embrittlement
Oxygen has long been considered as a detrimental impurity in pure titanium since it can severely deteriorate the ductility. Here, the authors propose a simple, yet effective strategy via grain refinement to solve this long-standing issue, while preserving its potential hardening effect.
- Yan Chong
- , Reza Gholizadeh
- & Nobuhiro Tsuji
-
Article
| Open Access Distinct relaxation mechanism at room temperature in metallic glass
Distinct relaxation mechanism at room temperature in metallic glass
The mechanism governing structural relaxation in metallic glasses remains elusive, hampering their stability and engineering applications. Here, the authors reveal a distinct relaxation mechanism with a stretching exponent of 3/7, providing new insight for understanding the nature of glass.
- Yi-Tao Sun
- , Rui Zhao
- & Wei-Hua Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Untangling competition between epitaxial strain and growth stress through examination of variations in local oxidation
Untangling competition between epitaxial strain and growth stress through examination of variations in local oxidation
The corrosion properties of engineering alloys are strongly influenced by local variations seen at the micro level. Here, the authors demonstrate how the metal grain orientation can influence the protectiveness of the oxide, which provides a possible route for improving corrosion performance.
- Maria S. Yankova
- , Alistair Garner
- & Philipp Frankel
-
Article
| Open Access Bio-inspired magnetic-driven folded diaphragm for biomimetic robot
Bio-inspired magnetic-driven folded diaphragm for biomimetic robot
Soft robotics holds promise for realizing easy control over complex locomotion and deformation. Lin et al. report an earthworm-inspired untethered magnetic robot that consists one-piece-mold folded diaphragm to achieve large three-dimensional deformation with inside-volume change capability.
- Dezhao Lin
- , Fan Yang
- & Ruihong Li
-
Article
| Open Access Doubled strength and ductility via maraging effect and dynamic precipitate transformation in ultrastrong medium-entropy alloy
Doubled strength and ductility via maraging effect and dynamic precipitate transformation in ultrastrong medium-entropy alloy
Commercial maraging alloys provide high strength and toughness by traditional precipitation strengthening mechanism. Here, the authors demonstrate a new strategy involving deformable precipitates and their dynamic phase transformation resulting in a twofold enhancement of strength and ductility.
- Hyun Chung
- , Won Seok Choi
- & Seok Su Sohn
-
Article
| Open Access Vascular smooth muscle-inspired architecture enables soft yet tough self-healing materials for durable capacitive strain-sensor
Vascular smooth muscle-inspired architecture enables soft yet tough self-healing materials for durable capacitive strain-sensor
Catastrophically mechanical failure, of soft self-healing materials often stems from its poor resistance to crack, propagation. Here, the authors present a strategy of surpassing trade-off, between soft self-healing and high fracture toughness, enabling the, conversion of soft and weak into soft yet tough self-healing materials.
- FuYao Sun
- , LongFei Liu
- & JiaJun Fu
-
Article
| Open Access Toward the design of ultrahigh-entropy alloys via mining six million texts
Toward the design of ultrahigh-entropy alloys via mining six million texts
The avalanche of publications challenges the norm that researchers extract knowledge from literature to design materials. Here the authors present a text-mining method that is implemented based on the abstracts of 6.4 million papers to enable the design of new high entropy alloys.
- Zongrui Pei
- , Junqi Yin
- & Dierk Raabe
-
Article
| Open Access Revealing the relationship between liquid fragility and medium-range order in silicate glasses
Revealing the relationship between liquid fragility and medium-range order in silicate glasses
Fragility describes the sharpness of dynamical arrest of a melt at its glass transition, yet its structural origin remains elusive. Shi et al. show that fragility inversely correlates with the medium-range order structure characterized by a measurable parameter named the average medium-range distance.
- Ying Shi
- , Binghui Deng
- & Douglas C. Allan
-
Article
| Open Access Self-growing photonic composites with programmable colors and mechanical properties
Self-growing photonic composites with programmable colors and mechanical properties
Structural coloration - i.e. colors arising from light interference in microstructures - is a good resource for several applications but usually involves elaborate fabrication techniques. Here, the authors achieve controllable coloration using silica particles embedded in a rearrangeable polymer network.
- Juan Xue
- , Xuewu Yin
- & Jiaxi Cui
-
Article
| Open Access Self-rolling of vanadium dioxide nanomembranes for enhanced multi-level solar modulation
Self-rolling of vanadium dioxide nanomembranes for enhanced multi-level solar modulation
In this work, authors demonstrate a smart window combining mechanochromism with thermochromism by self-rolling of VO2 nanomembranes to modulate in-door temperature self-adapted to seasons and climate with high efficiency.
- Xing Li
- , Cuicui Cao
- & Yongfeng Mei

 3D printing of ultra-high viscosity resin by a linear scan-based vat photopolymerization system
3D printing of ultra-high viscosity resin by a linear scan-based vat photopolymerization system