Comment
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Modulation of peroxisomal import by the PEX13 SH3 domain and a proximal FxxxF binding motif
Modulation of peroxisomal import by the PEX13 SH3 domain and a proximal FxxxF binding motif
Import of proteins into peroxisomes depends on PEX5, PEX13 and PEX14. Here the authors obtain crystal structures and NMR data to show the recognition of diaromatic peptide motifs on a noncanonical surface of the PEX13 SH3 domain, revealing a dynamic network which modulates peroxisomal matrix import.
- Stefan Gaussmann
- , Rebecca Peschel
- & Michael Sattler
-
Article
| Open Access Structural basis for antiepileptic drugs and botulinum neurotoxin recognition of SV2A
Structural basis for antiepileptic drugs and botulinum neurotoxin recognition of SV2A
SV2A is a receptor for botulinum neurotoxin (BoNT) and new generation antiepileptic drugs (AEDs). Here the authors report cryo-EM structures of SV2A in complex with BoNT receptor binding domain and AEDs highlighting the difference in the binding affinity between AEDs.
- Atsushi Yamagata
- , Kaori Ito
- & Mikako Shirouzu
-
Article
| Open Access RNA targeting and cleavage by the type III-Dv CRISPR effector complex
RNA targeting and cleavage by the type III-Dv CRISPR effector complex
Here, Schwartz, Bravo, and Ahsan et al. show how multi-subunit fusion proteins are arranged around a crRNA in a type III CRISPR-Cas effector to cleave target RNA. Structures and molecular dynamics of this complex show three distinct active sites that can be used for programmable RNA cleavage.
- Evan A. Schwartz
- , Jack P. K. Bravo
- & David W. Taylor
-
Article
| Open Access The DEAD-box ATPase Dbp10/DDX54 initiates peptidyl transferase center formation during 60S ribosome biogenesis
The DEAD-box ATPase Dbp10/DDX54 initiates peptidyl transferase center formation during 60S ribosome biogenesis
Cruz et al. describe the role of Dbp10/DDX54 in remodeling rRNA structure within the immature eukaryotic peptidyl transferase center of the ribosome, coupling energy-dependent catalysis to a post-catalytic role in factor exchange during 60S ribosomal subunit assembly.
- Victor E. Cruz
- , Christine S. Weirich
- & Jan P. Erzberger
-
Article
| Open Access Exposing the molecular heterogeneity of glycosylated biotherapeutics
Exposing the molecular heterogeneity of glycosylated biotherapeutics
The molecular heterogeneity of glycosylated biotherapeutics often complicates analysis by intact mass spectrometry. Here, the authors propose a simplified procedure for characterization that employs proton transfer charge reduction. Integration with glycomic and glycopeptide datasets can further provide glycoform-level information.
- Luis F. Schachner
- , Christopher Mullen
- & Wendy Sandoval
-
Article
| Open Access Insights into the inhibition of protospacer integration via direct interaction between Cas2 and AcrVA5
Insights into the inhibition of protospacer integration via direct interaction between Cas2 and AcrVA5
Here, the authors characterize an anti-CRISPR protein that prevents protospacer integration by Cas1-Cas2, providing structural insights that may benefit CRISPR-Cas systems research.
- Mingfang Bi
- , Wenjing Su
- & Xiaobing Mo
-
Article
| Open Access Emerging variants develop total escape from potent monoclonal antibodies induced by BA.4/5 infection
Emerging variants develop total escape from potent monoclonal antibodies induced by BA.4/5 infection
Many emerging SARS-CoV-2 variants partially escape the humoral immune response. Here, Liu et al. characterize 28 antibodies from BA.4/5 breakthrough infections and find attrition of neutralization and complete loss of function for variants with Spike mutations at positions 455 and 456.
- Chang Liu
- , Raksha Das
- & Gavin R. Screaton
-
Article
| Open Access Mechanism and structural dynamics of sulfur transfer during de novo [2Fe-2S] cluster assembly on ISCU2
Mechanism and structural dynamics of sulfur transfer during de novo [2Fe-2S] cluster assembly on ISCU2
The biogenesis of iron-sulfur proteins in eukaryotes is initiated by the mitochondrial core ISC complex. Here, the authors provide structural, biochemical and spectroscopic data to characterize sulfur transfer intermediates in the core ISC complex.
- Vinzent Schulz
- , Ralf Steinhilper
- & Roland Lill
-
Article
| Open Access Cryo-EM structures of adenosine receptor A3AR bound to selective agonists
Cryo-EM structures of adenosine receptor A3AR bound to selective agonists
Adenosine A3 receptor (A3AR) holds promise for treating inflammatory and cancer conditions. Here, Cai et al. present cryo-EM structures of A3AR bound to agonists CF101 and CF102, offering insights into its activation and ligand interaction, crucial for developing targeted therapies.
- Hongmin Cai
- , Shimeng Guo
- & H. Eric Xu
-
Article
| Open Access Sm-like protein Rof inhibits transcription termination factor ρ by binding site obstruction and conformational insulation
Sm-like protein Rof inhibits transcription termination factor ρ by binding site obstruction and conformational insulation
Said et al. used cryoEM, biochemistry and bioinformatics to uncover how the Sm-like protein Rof regulates transcription termination. Rof binds termination factor ρ, inhibiting ρ ring closure and its association with RNA or transcription complexes.
- Nelly Said
- , Mark Finazzo
- & Markus C. Wahl
-
Article
| Open Access A widely conserved protein Rof inhibits transcription termination factor Rho and promotes Salmonella virulence program
A widely conserved protein Rof inhibits transcription termination factor Rho and promotes Salmonella virulence program
Bacterial protein Rof (Rho-off) directly interacts with bacterial factor Rho and inhibits Rho-dependent transcription termination. Here, authors report cryo-EM structure of Rho-Rof antitermination complex and reveal their role in bacterial pathogenesis.
- Jing Zhang
- , Shuo Zhang
- & Chengyuan Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Dynamic inter-domain transformations mediate the allosteric regulation of human 5, 10-methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase
Dynamic inter-domain transformations mediate the allosteric regulation of human 5, 10-methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase
Here the authors present the cryo-EM structure of active and inhibited human MTHFR, revealing a dynamic inhibitory mechanism dependent on dual SAM binding. The resulting closed conformation features an autoinhibitory element effectively blocking enzymatic activity.
- Linnea K. M. Blomgren
- , Melanie Huber
- & Thomas J. McCorvie
-
Article
| Open Access One substrate many enzymes virtual screening uncovers missing genes of carnitine biosynthesis in human and mouse
One substrate many enzymes virtual screening uncovers missing genes of carnitine biosynthesis in human and mouse
With structural models now available on a proteome scale, Malatesta et al. show that structure-based screening can help identify proteins catalyzing orphan reactions in metabolic pathways, offering functional insights beyond sequence-based approaches.
- Marco Malatesta
- , Emanuele Fornasier
- & Riccardo Percudani
-
Article
| Open Access A hemoprotein with a zinc-mirror heme site ties heme availability to carbon metabolism in cyanobacteria
A hemoprotein with a zinc-mirror heme site ties heme availability to carbon metabolism in cyanobacteria
Heme is an abundant cofactor required by nearly all known organisms. Here, authors discover a cyanobacterial protein with a distinct Zn-mirror heme site, which may function to sense heme and regulate energy metabolism.
- Nicolas Grosjean
- , Estella F. Yee
- & Crysten E. Blaby-Haas
-
Article
| Open Access Regulation by the RNA-binding protein Unkempt at its effector interface
Regulation by the RNA-binding protein Unkempt at its effector interface
How RNA-binding proteins (RBPs) regulate gene expression via effectors of RNA processing is unclear. Here, the authors dissect the effector interface of an essential RBP, Unkempt, and investigate its contribution to translational control in cells.
- Kriti Shah
- , Shiyang He
- & Jernej Murn
-
Article
| Open Access Structural basis for dimerization of a paramyxovirus polymerase complex
Structural basis for dimerization of a paramyxovirus polymerase complex
The structure and function of polymerase dimers of non-segmented, negative-strand RNA viruses are poorly understood. Here, this study presents the structural basis for dimerization of a paramyxovirus L–P polymerase and its role in genome replication.
- Jin Xie
- , Mohamed Ouizougun-Oubari
- & Shuai Chen
-
Article
| Open Access A subgroup of light-driven sodium pumps with an additional Schiff base counterion
A subgroup of light-driven sodium pumps with an additional Schiff base counterion
Light-driven sodium-pumping rhodopsins are unique ion transporters. Here, authors present a characterization of such rhodopsins with a modified active center allowing for efficient sodium transport under various environmental conditions.
- E. Podoliak
- , G. H. U. Lamm
- & K. Kovalev
-
Article
| Open Access Fuzzy recognition by the prokaryotic transcription factor HigA2 from Vibrio cholerae
Fuzzy recognition by the prokaryotic transcription factor HigA2 from Vibrio cholerae
Here, the authors dissect the fuzzy interaction between the prokaryote transcription factor HigA2 and its DNA target and show that specific, transient interactions drive specificity despite HigA2 remaining mostly disordered.
- San Hadži
- , Zala Živič
- & Remy Loris
-
Article
| Open Access Structure-guided functional suppression of AML-associated DNMT3A hotspot mutations
Structure-guided functional suppression of AML-associated DNMT3A hotspot mutations
DNMT3A R882H and R882C are mutation hotspots in acute myeloid leukemia. This study describes the structural and functional consequences of the DNMT3A R882H/R882C mutations which can provide a strategy for therapy of the disease mutations.
- Jiuwei Lu
- , Yiran Guo
- & Jikui Song
-
Article
| Open Access The assembly platform FimD is required to obtain the most stable quaternary structure of type 1 pili
The assembly platform FimD is required to obtain the most stable quaternary structure of type 1 pili
Type 1 pili are crucial cell surface bacterial virulence factors. Here, the authors show that FimD is required to assemble the most stable quaternary pilus structure by ensuring that the resulting protein polymer is free of structural defects.
- Dawid S. Zyla
- , Thomas Wiegand
- & Rudi Glockshuber
-
Article
| Open Access Concerted transformation of a hyper-paused transcription complex and its reinforcing protein
Concerted transformation of a hyper-paused transcription complex and its reinforcing protein
Here, authors use cryoEM, biochemistry and molecular dynamics simulations to delineate a functional cycle of RfaH, a universally conserved transcription factor that undergoes a fold-switch during recruitment to the transcribing RNA polymerase.
- Philipp K. Zuber
- , Nelly Said
- & Stefan H. Knauer
-
Article
| Open Access Cryo-EM structure of the human Asc-1 transporter complex
Cryo-EM structure of the human Asc-1 transporter complex
The human Asc-1-4F2hc complex plays an important role in the neural development and stability. Here, authors determine the cryo-EM structures of Asc-1-4F2hc complex in three states, revealing its substrate recognition and transport mechanism.
- Yaning Li
- , Yingying Guo
- & Renhong Yan
-
Article
| Open Access Structure and mechanisms of transport of human Asc1/CD98hc amino acid transporter
Structure and mechanisms of transport of human Asc1/CD98hc amino acid transporter
Asc1/CD98hc is a key regulator of small neutral amino acid transport in the brain and adipose tissue. Here, authors report the structure of semi-occluded hAsc1/CD98hc and provide a model for Asc1 exchange and facilitated diffusion modes of transport.
- Josep Rullo-Tubau
- , Maria Martinez-Molledo
- & Oscar Llorca
-
Article
| Open Access Probing altered receptor specificities of antigenically drifting human H3N2 viruses by chemoenzymatic synthesis, NMR, and modeling
Probing altered receptor specificities of antigenically drifting human H3N2 viruses by chemoenzymatic synthesis, NMR, and modeling
Binding modes of antigenically drifted hemagglutinins of human influenza A viruses have been determined by NMR using synthetic N-glycans having 13C-labeled monosaccharides to pinpoint which monosaccharides of extended LacNAc chains engage with the HAs.
- Luca Unione
- , Augustinus N. A. Ammerlaan
- & Geert-Jan Boons
-
Article
| Open Access Cryo-EM structures of prokaryotic ligand-gated ion channel GLIC provide insights into gating in a lipid environment
Cryo-EM structures of prokaryotic ligand-gated ion channel GLIC provide insights into gating in a lipid environment
Gloeobacter proton-gated ion channel (GLIC) is a convenient model of pentameric ligand-gated ion channels. Here, Bharambe & Li et al. report structures and simulations of GLIC with insights into the role of lipids in GLIC gating mechanism.
- Nikhil Bharambe
- , Zhuowen Li
- & Sandip Basak
-
Article
| Open Access Cryo-EM structures of pannexin 1 and 3 reveal differences among pannexin isoforms
Cryo-EM structures of pannexin 1 and 3 reveal differences among pannexin isoforms
Pannexins are large pore channels involved in ion and ATP release. Here the authors use cryo-EM structures of Pannexins 1 and 3 to demonstrate the effects of distinct residue substitutions on channel structure and function.
- Nazia Hussain
- , Ashish Apotikar
- & Aravind Penmatsa
-
Article
| Open Access Discovery of a small-molecule inhibitor that traps Polθ on DNA and synergizes with PARP inhibitors
Discovery of a small-molecule inhibitor that traps Polθ on DNA and synergizes with PARP inhibitors
Here the authors discover a small-molecule that inhibits DNA polymerase theta by trapping the enzyme on DNA in the closed conformation. The inhibitor selectively kills BRCA-mutant cells and exhibits strong synergistic activity with PARP inhibitors.
- William Fried
- , Mrityunjay Tyagi
- & Richard T. Pomerantz
-
Article
| Open Access Architecture and regulation of filamentous human cystathionine beta-synthase
Architecture and regulation of filamentous human cystathionine beta-synthase
Cystathionine beta-synthase is a conserved essential enzyme of one-carbon metabolism. Here, the authors show that the enzyme oligomerises to form filaments that undergo conformational and morphological changes in response to its activator S-adenosyl-L-methionine, the global methyl donor.
- Thomas J. McCorvie
- , Douglas Adamoski
- & Wyatt W. Yue
-
Article
| Open Access Structural basis for phage-mediated activation and repression of bacterial DSR2 anti-phage defense system
Structural basis for phage-mediated activation and repression of bacterial DSR2 anti-phage defense system
The bacterial DSR2 defense system counters phage invasion by depleting NAD+. Here, Zhang et al. reveal molecular mechanisms underlying phage-mediated activation and repression of DSR2, enhancing our understanding of the bacterial-phage arms race.
- Jun-Tao Zhang
- , Xiao-Yu Liu
- & Ning Jia
-
Article
| Open Access Structural bases of inhibitory mechanism of CaV1.2 channel inhibitors
Structural bases of inhibitory mechanism of CaV1.2 channel inhibitors
CaV1.2 is crucial in cardiac, vascular and neuronal function, serving as a target for many drugs. Here, authors identify the binding site of herb-derived drug tetrandrine, and explore inhibitory mechanism of L/T-type selective DHP drug benidipine.
- Yiqing Wei
- , Zhuoya Yu
- & Yan Zhao
-
Article
| Open Access Development and crystal structures of a potent second-generation dual degrader of BCL-2 and BCL-xL
Development and crystal structures of a potent second-generation dual degrader of BCL-2 and BCL-xL
Here, the authors have determined structures of 753b PROTAC, BCL-xL/BCL-2 and VHL E3 ligase ternary complexes which reveal the basis for the dual degrader activity of 753b. The structures and subsequent functional analyses facilitated design of WH244 PROTAC, with enhanced degrader activity in cells.
- Digant Nayak
- , Dongwen Lv
- & Shaun K. Olsen
-
Article
| Open Access Structural basis of Acinetobacter type IV pili targeting by an RNA virus
Structural basis of Acinetobacter type IV pili targeting by an RNA virus
Here, the authors structurally characterise the interaction between Acinetobacter phage AP205 and the type IV Acinetobacter pili using cryo-electron microscopy, uncovering the mechanistic determinants of this interaction.
- Ran Meng
- , Zhongliang Xing
- & Junjie Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Correlating fluorescence microscopy, optical and magnetic tweezers to study single chiral biopolymers such as DNA
Correlating fluorescence microscopy, optical and magnetic tweezers to study single chiral biopolymers such as DNA
It is hard to correlate force, torque and localization information. The authors report Combined Optical and Magnetic BIomolecule TWEEZers, COMBI-Tweez, that integrates optical trapping, time-resolved electromagnetic tweezers, and fluorescence microscopy: they demonstrate visualisation of higher order structural motifs in DNA.
- Jack W. Shepherd
- , Sebastien Guilbaud
- & Mark C. Leake
-
Article
| Open Access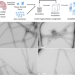 Structure of alpha-synuclein fibrils derived from human Lewy body dementia tissue
Structure of alpha-synuclein fibrils derived from human Lewy body dementia tissue
The accumulation of alpha-synuclein fibrils within neurons is the defining feature of Lewy body dementia (LBD). Here the authors report a method to produce large quantities of alpha-synuclein fibrils that reproduce the complex structure of the fibrils that accumulate in LBD brain tissue.
- Dhruva D. Dhavale
- , Alexander M. Barclay
- & Paul T. Kotzbauer
-
Article
| Open Access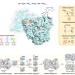 Identifying a key spot for electron mediator-interaction to tailor CO dehydrogenase’s affinity
Identifying a key spot for electron mediator-interaction to tailor CO dehydrogenase’s affinity
Carbon monoxide dehydrogenases (CODH) employ artificial electron mediators like viologens for biocatalysis, but little is known about the interaction between the mediators and the enzyme. Here, the authors discover the critical site for viologen interactions at the D-cluster of Carboxydothermus hydrogenoformans CODH2 via alanine mutations and crystallography, and report variants with increased ethyl viologen affinity.
- Suk Min Kim
- , Sung Heuck Kang
- & Yong Hwan Kim
-
Article
| Open Access Structure and function of Semaphorin-5A glycosaminoglycan interactions
Structure and function of Semaphorin-5A glycosaminoglycan interactions
Semaphorin 5A (Sema5A) forms complexes with heparan and chondroitin sulfate proteoglycans to regulate neuronal migration. Here, the authors show that the thrombospondin-like repeat 4 (TSR4) of Sema5A enables glycosaminoglycan association, multimerization, and neural progenitor cell distribution.
- Gergely N. Nagy
- , Xiao-Feng Zhao
- & E. Yvonne Jones
-
Article
| Open Access Architecture and activation of human muscle phosphorylase kinase
Architecture and activation of human muscle phosphorylase kinase
High-resolution cryo-EM study of human muscle phosphorylase kinase reveals its complex structure and how calcium ions activate it, offering insights into glycogen metabolism and kinase regulation.
- Xiaoke Yang
- , Mingqi Zhu
- & Junyu Xiao
-
Article
| Open Access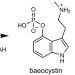 Methyl transfer in psilocybin biosynthesis
Methyl transfer in psilocybin biosynthesis
The natural hallucinogen psilocybin — produced by so-called magic mushrooms — holds promise for the treatment of depression and other mental health conditions. Here, the authors provide a structural and biochemical analysis of the Psilocybe methyl transferase PsiM that provides mechanistic insight into the last step of psilocybin biosynthesis.
- Jesse Hudspeth
- , Kai Rogge
- & Sebastiaan Werten
-
Article
| Open Access Photocobilins integrate B12 and bilin photochemistry for enzyme control
Photocobilins integrate B12 and bilin photochemistry for enzyme control
Photoreceptor proteins utilise biological chromophores to regulate a large range of cellular processes in response to light. Here the authors identify and characterise a sub-family of multi-centre photoreceptors, termed photocobilins, that not only utilise B12 but also contain biliverdin (BV) as an additional chromophore.
- Shaowei Zhang
- , Laura N. Jeffreys
- & Nigel S. Scrutton
-
Article
| Open Access Diverse roles of the metal binding domains and transport mechanism of copper transporting P-type ATPases
Diverse roles of the metal binding domains and transport mechanism of copper transporting P-type ATPases
Controlling copper levels is essential for life, causing disease when impaired. Here, structures of a copper transporter sheds light on the function of its metal binding domains and unifies previous theories on the details of copper transport.
- Zongxin Guo
- , Fredrik Orädd
- & Pontus Gourdon
-
Article
| Open Access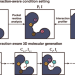 3D molecular generative framework for interaction-guided drug design
3D molecular generative framework for interaction-guided drug design
Designing a molecule that favorably binds to a protein pocket is a keystone of drug discovery. Zhung et al. devise DeepICL, which leverages the generalizable features of non-covalent protein-ligand interactions on a 3D molecular generative model, improving the quality of AI-designed molecules.
- Wonho Zhung
- , Hyeongwoo Kim
- & Woo Youn Kim
-
Article
| Open Access Phosphorylation and O-GlcNAcylation at the same α-synuclein site generate distinct fibril structures
Phosphorylation and O-GlcNAcylation at the same α-synuclein site generate distinct fibril structures
Here, the authors use cryo-EM to show that phosphorylating or O-GlcNAcylating α-synuclein on serine 87 leads to the formation of two distinct fibril structures. Both structures display reduced neurotoxicity and propagation activity.
- Jinjian Hu
- , Wencheng Xia
- & Yan-Mei Li
-
Article
| Open Access Insights into the modulation of bacterial NADase activity by phage proteins
Insights into the modulation of bacterial NADase activity by phage proteins
The defense-associated sirtuin 2 (DSR2) effector protects bacteria from phage infection by depleting NAD+. Here, the authors employ biochemical and structural approaches to reveal the inhibition and activation mechanisms of DSR2 by the phage anti-DSR2 protein (DSAD1) and tail tube protein (TTP).
- Hang Yin
- , Xuzichao Li
- & Heng Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Structure of the intact tail machine of Anabaena myophage A-1(L)
Structure of the intact tail machine of Anabaena myophage A-1(L)
The Myoviridae cyanophage A-1(L) specifically infects the model cyanobacteria Anabaena sp. PCC 7120. Here, authors present the high-resolution cryo-EM structure of its intact tail machine, and identify multiple hydrolytic and binding modules.
- Rong-Cheng Yu
- , Feng Yang
- & Cong-Zhao Zhou
-
Article
| Open Access Ultrastructure of human brain tissue vitrified from autopsy revealed by cryo-ET with cryo-plasma FIB milling
Ultrastructure of human brain tissue vitrified from autopsy revealed by cryo-ET with cryo-plasma FIB milling
Here the authors report a method for cryogenic electron microscopy imaging of human brain tissue samples directly obtained from autopsy, offering insights into cellular ultrastructure and a tool to study potential pathologic features.
- Benjamin C. Creekmore
- , Kathryn Kixmoeller
- & Yi-Wei Chang
-
Article
| Open Access Activation of the insulin receptor by insulin-like growth factor 2
Activation of the insulin receptor by insulin-like growth factor 2
IGF2 has a distinct binding affinity for two insulin receptor (IR) isoforms and mimics insulin’s function. Here, the authors present the activation mechanism of IR by IGF2 and reveal the molecular basis for IGF2’s different affinity for two IR isoforms.
- Weidong An
- , Catherine Hall
- & Eunhee Choi
-
Article
| Open Access Myosin-binding protein C regulates the sarcomere lattice and stabilizes the OFF states of myosin heads
Myosin-binding protein C regulates the sarcomere lattice and stabilizes the OFF states of myosin heads
Myosin-binding protein C (MyBP-C) resides and interacts with the myosin filaments in striated muscle and regulates contraction via an unclear mechanism. Here, the authors demonstrate that MyBP-C regulates the performance of myosin heads.
- Anthony L. Hessel
- , Nichlas M. Engels
- & Samantha P. Harris
-
Article
| Open Access Structure of the human Bre1 complex bound to the nucleosome
Structure of the human Bre1 complex bound to the nucleosome
The structure of the nucleosome-bound human Bre1 complex reveals that its two RING domains bind the acidic patch and nucleosomal DNA, directing the E2 enzyme and ubiquitin for H2BK120-specific ubiquitination. The binding mode suggests a possible regulatory mechanism through nucleosomal DNA flexibility.
- Shuhei Onishi
- , Kotone Uchiyama
- & Toru Sengoku
-
Article
| Open Access Structural basis for peroxidase encapsulation inside the encapsulin from the Gram-negative pathogen Klebsiella pneumoniae
Structural basis for peroxidase encapsulation inside the encapsulin from the Gram-negative pathogen Klebsiella pneumoniae
Peroxidase encapsulins are self-assembling protein compartments involved in oxidative stress response found in many pathogens. Here, the authors characterize the structural basis of peroxidase encapsulation inside the Klebsiella pneumoniae encapsulin.
- Jesse A. Jones
- , Michael P. Andreas
- & Tobias W. Giessen

 Shining light on dinoflagellate photosystem I
Shining light on dinoflagellate photosystem I