Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access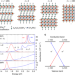 Ultrafast long-range spin-funneling in solution-processed Ruddlesden–Popper halide perovskites
Ultrafast long-range spin-funneling in solution-processed Ruddlesden–Popper halide perovskites
Spin-information transport or transfer is essential for spintronics applications and often relies on high purity and quality materials. Here, the authors report on the defect-tolerant solution-processed Ruddlesden–Popper halide perovskites, where a spin propagation length of 600 nm was achieved via spin funneling.
- David Giovanni
- , Jia Wei Melvin Lim
- & Tze Chien Sum
-
Article
| Open Access Spectroscopic disentanglement of the quantum states of highly excited Cu2
Spectroscopic disentanglement of the quantum states of highly excited Cu2
Transition metals are at the basis of key processes in chemistry and biology but their complex electronic structures make understanding of their properties a challenge. Here the authors resolve individual spectral lines of Cu2 in the deep UV region by two-colour resonant four-wave mixing.
- M. Beck
- , P. Bornhauser
- & P. P. Radi
-
Article
| Open Access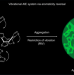 Non-aromatic annulene-based aggregation-induced emission system via aromaticity reversal process
Non-aromatic annulene-based aggregation-induced emission system via aromaticity reversal process
Molecular systems displaying aggregation-induced emission (AIE) have important biomedical and optoelectronic applications. Here the authors report a further mechanism for AIE, through aromaticity reversal from the ground state to the excited state, in the non-aromatic annulene derivative of cyclooctatetrathiophene.
- Zheng Zhao
- , Xiaoyan Zheng
- & Ben Zhong Tang
-
Article
| Open Access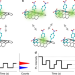 Single-defect spectroscopy in the shortwave infrared
Single-defect spectroscopy in the shortwave infrared
Chemical defects endow materials with unique properties but their investigation is challenging due to their small footprint. Here the authors develop a high throughput shortwave infrared spectroscopy method enabling spectral identification and quantitative counting of fluorescent chemical defects at the single defect level.
- Xiaojian Wu
- , Mijin Kim
- & YuHuang Wang
-
Article
| Open Access High-resolution tip-enhanced Raman scattering probes sub-molecular density changes
High-resolution tip-enhanced Raman scattering probes sub-molecular density changes
Despite recent advances in simulations of tip-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (TERS) under highly confined fields, a simply physical mechanism has remained elusive. Here, the authors show that single molecule TERS images can be explained by local sub-molecular density changes induced by the confined near-field during the Raman process.
- Xing Chen
- , Pengchong Liu
- & Lasse Jensen
-
Article
| Open Access Emerging photoluminescence from the dark-exciton phonon replica in monolayer WSe2
Emerging photoluminescence from the dark-exciton phonon replica in monolayer WSe2
The long lifetime and spin properties of dark excitons in atomically thin transition metal dichalcogenides offer opportunities to explore light-matter interactions beyond electric dipole transitions. Here, the authors demonstrate that the coupling of the dark exciton and an optically silent chiral phonon enables the intrinsic photoluminescence of the dark-exciton replica in monolayer WSe2
- Zhipeng Li
- , Tianmeng Wang
- & Su-Fei Shi
-
Article
| Open Access The valley Zeeman effect in inter- and intra-valley trions in monolayer WSe2
The valley Zeeman effect in inter- and intra-valley trions in monolayer WSe2
The unique valley and spin texture of atomically thin transition metal dichalcogenides (TMDs) allows the observation of the valley Zeeman effect for neutral and charged excitons. Here, the authors unveil the underlying physics of the magneto-optical response and valley Zeeman splitting of trions in tungsten-based TMDs.
- T. P. Lyons
- , S. Dufferwiel
- & A. I. Tartakovskii
-
Article
| Open Access Tracking carrier protein motions with Raman spectroscopy
Tracking carrier protein motions with Raman spectroscopy
Acyl carrier proteins (ACPs), a universal and highly conserved carrier of acyl intermediates during fatty acid and polyketide synthesis, are difficult to visualise. Here, the authors developed a facile, Raman spectroscopy-based method to detect ACP-substrate interactions.
- Samuel C. Epstein
- , Adam R. Huff
- & Louise K. Charkoudian
-
Article
| Open Access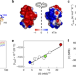 A binding cooperativity switch driven by synergistic structural swelling of an osmo-regulatory protein pair
A binding cooperativity switch driven by synergistic structural swelling of an osmo-regulatory protein pair
The bacterial protein Cnu together with the transcription repressor H-NS regulate expression of virulence factors in an osmo-sensitive manner. Here authors show that the structure of Cnu swells with decreasing ionic strength driving the oligomerization of H-NS and regulating osmo-sensory response.
- Abhishek Narayan
- , Soundhararajan Gopi
- & Athi N. Naganathan
-
Article
| Open Access Femtosecond time synchronization of optical clocks off of a flying quadcopter
Femtosecond time synchronization of optical clocks off of a flying quadcopter
Optical clock networks have many applications from precision time keeping, sensing to fundamental physics. Here the authors demonstrate robust and free-space femtosecond time synchronization of optical clocks via a moving quadcopter.
- Hugo Bergeron
- , Laura C. Sinclair
- & Nathan R. Newbury
-
Article
| Open Access Microscopic insight into non-radiative decay in perovskite semiconductors from temperature-dependent luminescence blinking
Microscopic insight into non-radiative decay in perovskite semiconductors from temperature-dependent luminescence blinking
The mechanism of the non-radiative recombination in halide perovskite nanocrystals has not been fully understood. Here Gerhard et al. resolve the contributions of individual recombination centers by photoluminescence blinking measurements and identify ion migration as the underlying mechanism.
- Marina Gerhard
- , Boris Louis
- & Ivan G. Scheblykin
-
Article
| Open Access Quantitative optical assessment of photonic and electronic properties in halide perovskite
Quantitative optical assessment of photonic and electronic properties in halide perovskite
The electronic and photonic contributions to the power conversion efficiency in solar cell devices are often hard to disentangle. Here Bercegol et al. develop a purely optical method to quantitatively decouple and assess the electronic and photonic processes in halide perovskite solar cells.
- Adrien Bercegol
- , Daniel Ory
- & Laurent Lombez
-
Article
| Open Access Assessment of corneal substrate biomechanics and its effect on epithelial stem cell maintenance and differentiation
Assessment of corneal substrate biomechanics and its effect on epithelial stem cell maintenance and differentiation
The link between how the stiffness of the cornea affects stem cells is unclear. Here, the authors use Brillouin spectro-microscopy to show that mechanical properties of the cornea affect epithelial stem cells and after injury, treating the cornea with collagenase suppresses YAP activation, assisting in regeneration.
- Ricardo M. Gouveia
- , Guillaume Lepert
- & Che J. Connon
-
Article
| Open Access Intramolecular electron-induced proton transfer and its correlation with excited-state intramolecular proton transfer
Intramolecular electron-induced proton transfer and its correlation with excited-state intramolecular proton transfer
Intramolecular electron-induced proton transfer (iEIPT) describes proton motion coupled with the attachment of an electron within a molecule. Here, the authors build a “search engine” for iEIPT-capable molecules that also have the excited-state intramolecular proton transfer property.
- Wei Wang
- , Mary Marshall
- & Xinxing Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Single-molecule trapping and spectroscopy reveals photophysical heterogeneity of phycobilisomes quenched by Orange Carotenoid Protein
Single-molecule trapping and spectroscopy reveals photophysical heterogeneity of phycobilisomes quenched by Orange Carotenoid Protein
Upon photoactivation the Orange Carotenoid Protein (OCP) binds to the phycobilisome and prevents damage by thermally dissipating excess energy. Here authors use an Anti-Brownian ELectrokinetic trap to determine the photophysics of single OCP-quenched phycobilisomes and observe two distinct OCP-quenched states with either one or two OCPs bound.
- Allison H. Squires
- , Peter D. Dahlberg
- & W. E. Moerner
-
Article
| Open Access Protein and RNA dynamical fingerprinting
Protein and RNA dynamical fingerprinting
The characterization of biomacromolecule structural vibrations has been impeded by a broad continuous vibrational density of states obscuring molecule specific vibrations. A terahertz microscopy system using polarization control produces signatures to dynamically fingerprint proteins and a RNA G-quadruplex.
- Katherine A. Niessen
- , Mengyang Xu
- & Andrea G. Markelz
-
Article
| Open Access Both electronic and vibrational coherences are involved in primary electron transfer in bacterial reaction center
Both electronic and vibrational coherences are involved in primary electron transfer in bacterial reaction center
Distinguishing electronic and vibrational coherences helps to clarify the near-unity efficiency of primary electron transfer in reaction centres. Here, the authors report their respective correlation with the electron transfer rate by comparing the 2D electronic spectra of three mutant reaction centres.
- Fei Ma
- , Elisabet Romero
- & Rienk van Grondelle
-
Article
| Open Access Electrochromic semiconductors as colorimetric SERS substrates with high reproducibility and renewability
Electrochromic semiconductors as colorimetric SERS substrates with high reproducibility and renewability
Electrochromic technology has diverse cutting-edge applications, but it has never been used to overcome the critical problems in the field of surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS). Here, the authors demonstrate a generic electrochromic strategy for ensuring the reproducibility and renewability of SERS substrates.
- Shan Cong
- , Zhen Wang
- & Zhigang Zhao
-
Article
| Open Access Infrared-pump electronic-probe of methylammonium lead iodide reveals electronically decoupled organic and inorganic sublattices
Infrared-pump electronic-probe of methylammonium lead iodide reveals electronically decoupled organic and inorganic sublattices
It has been challenging to probe whether dynamically disordered organic cations affect optical properties of CH3NH3PbI3. Here, Guo et al. employ infrared-pump electronic-probe spectroscopy and show that pump-induced atomic motions of the organic cations do not substantially alter optoelectronic properties.
- Peijun Guo
- , Arun Mannodi-Kanakkithodi
- & Richard D. Schaller
-
Article
| Open Access Ice-VII-like molecular structure of ambient water nanomeniscus
Ice-VII-like molecular structure of ambient water nanomeniscus
Ice-VII, the densest phase of ice, has been expected to exist only under extreme conditions, such as in Earth’s deep mantle. Shin et al. show spectroscopic evidence that ice-VII-like structures can also be found in water confined in the nanomeniscus between packed nanoparticles at ambient conditions.
- Dongha Shin
- , Jonggeun Hwang
- & Wonho Jhe
-
Article
| Open Access Controlling the fluorescence and room-temperature phosphorescence behaviour of carbon nanodots with inorganic crystalline nanocomposites
Controlling the fluorescence and room-temperature phosphorescence behaviour of carbon nanodots with inorganic crystalline nanocomposites
Materials exhibiting room temperature phosphorescence (RTP) with short afterglow are desirable for bio-medical applications. Here the authors synthesise a library of compounds with tunable RTP properties, embedding carbon nanodots in non-toxic alkaline-earth carbonate, sulphate and oxalate hosts.
- David C. Green
- , Mark A. Holden
- & Fiona C. Meldrum
-
Article
| Open Access Bioconjugation strategy for cell surface labelling with gold nanostructures designed for highly localized pH measurement
Bioconjugation strategy for cell surface labelling with gold nanostructures designed for highly localized pH measurement
Understanding the pH changes at cell surfaces is important for understanding the mechanisms of different physiological processes. Here, the authors report on the development of a cell membrane anchored gold nanoparticle for surface enhanced Raman spectroscopy determination of pH.
- Leonardo Puppulin
- , Shigekuni Hosogi
- & Yoshinori Marunaka
-
Article
| Open Access Wavepacket insights into the photoprotection mechanism of the UV filter methyl anthranilate
Wavepacket insights into the photoprotection mechanism of the UV filter methyl anthranilate
Here, the authors explore the ultrafast photodynamics of methyl anthranilate. From the quantum beat behavior, the authors find evidence for ultrafast energy redistribution processes which hinder excited state relaxation, making methyl anthranilate a poor choice for a sunscreen chemical filter.
- Natércia d. N. Rodrigues
- , Neil C. Cole-Filipiak
- & Vasilios G. Stavros
-
Article
| Open Access All-optical field-free three-dimensional orientation of asymmetric-top molecules
All-optical field-free three-dimensional orientation of asymmetric-top molecules
Alignment and orientation of the molecules allows studying the photon-molecule interactions in greater detail. Here the authors demonstrate the three-dimensional orientation of SO2 molecules in using COLTRIMS and orthogonally polarized laser pulses but in the absence of DC field.
- Kang Lin
- , Ilia Tutunnikov
- & Jian Wu
-
Article
| Open Access In situ monitoring of molecular aggregation using circular dichroism
In situ monitoring of molecular aggregation using circular dichroism
Molecular aggregation is a widespread and important process in physiological metabolism, but details regarding conformational changes during the process are hard to probe. Here, the authors use circular dichroism to monitor in-situ the conformational changes occurring during molecular aggregation.
- Haoke Zhang
- , Xiaoyan Zheng
- & Ben Zhong Tang
-
Article
| Open Access Valley coherent exciton-polaritons in a monolayer semiconductor
Valley coherent exciton-polaritons in a monolayer semiconductor
The short exciton life time in atomically thin transition metal dichalcogenides poses limitations to efficient control of the valley pseudospin and coherence. Here, the authors manipulate the exciton coherence in a WSe2 monolayer embedded in an optical microcavity in the strong light-matter coupling regime.
- S. Dufferwiel
- , T. P. Lyons
- & A. I. Tartakovskii
-
Article
| Open Access Two-step self-assembly of a spider silk molecular clamp
Two-step self-assembly of a spider silk molecular clamp
Molecular details that underlie mechanical properties of spider silk are of great interest to material scientists. Here, the authors report a previously unknown three-state mechanism of folding and an expanded structure of a spider silk protein that may contribute to elasticity of spider silk.
- Charlotte Rat
- , Julia C. Heiby
- & Hannes Neuweiler
-
Article
| Open Access Vibrational fingerprint of localized excitons in a two-dimensional metal-organic crystal
Vibrational fingerprint of localized excitons in a two-dimensional metal-organic crystal
Long-lived excitons in a two-dimensional metal-organic crystal can be produced by visible light and detected by infrared radiation. Here, the authors show that the excitonic state of a biomimetic macrocycle can be ‘read’ by measuring the vibrations of an adsorbed ligand.
- M. Corva
- , A. Ferrari
- & E. Vesselli
-
Article
| Open Access Seeded X-ray free-electron laser generating radiation with laser statistical properties
Seeded X-ray free-electron laser generating radiation with laser statistical properties
Free electron lasers are emerging as important tools for nonlinear spectroscopy in the X-ray regime. Here the authors demonstrate the second order coherence of a seeded FEL source that may be useful for measurements in quantum optics.
- Oleg Yu. Gorobtsov
- , Giuseppe Mercurio
- & Ivan A. Vartanyants
-
Article
| Open Access Phase-controlled Fourier-transform spectroscopy
Phase-controlled Fourier-transform spectroscopy
Fourier transform spectrometers are generally limited to slow scanning rates at high resolution. Here the authors demonstrate highly efficient Fourier transform spectroscopy using a dynamic phase-control technique that enables fast acquisition without compromising bandwidth or resolution.
- Kazuki Hashimoto
- & Takuro Ideguchi
-
Article
| Open Access High-performance and scalable on-chip digital Fourier transform spectroscopy
High-performance and scalable on-chip digital Fourier transform spectroscopy
On-chip spectrometers typically have limited spectral channels and low signal to noise ratios. Here the authors introduce a digital architecture that uses switches to change the interferometer path lengths, enabling exponentially more spectral channels per circuit element and lower noise by leveraging a machine learning reconstruction algorithm.
- Derek M. Kita
- , Brando Miranda
- & Juejun Hu
-
Article
| Open Access Superresolution mapping of energy landscape for single charge carriers in plastic semiconductors
Superresolution mapping of energy landscape for single charge carriers in plastic semiconductors
To understand the complex nanoscale structure-property relationships in conjugated polymers for device applications, new methods for tracking charge transport are required. Here, the authors employ superresolution mapping to study the charge carrier dynamics in conjugated polymer nanoparticles.
- Yifei Jiang
- & Jason McNeill
-
Article
| Open Access Single Particle Automated Raman Trapping Analysis
Single Particle Automated Raman Trapping Analysis
Enabling concurrent, high throughput analysis of single nano particles would greatly increase the capacity to study size, composition and inter and intra particle population variance. Here, the authors present a comprehensive platform for single particle automated Raman trapping analysis without any target modification.
- Jelle Penders
- , Isaac J. Pence
- & Molly M. Stevens
-
Article
| Open Access Spatially-resolved fluorescence-detected two-dimensional electronic spectroscopy probes varying excitonic structure in photosynthetic bacteria
Spatially-resolved fluorescence-detected two-dimensional electronic spectroscopy probes varying excitonic structure in photosynthetic bacteria
2D electronic spectroscopy enables a spatially-averaged view of the electronic structure of a heterogeneous system. Here, the authors extend it to sub-micron resolution and ~106 times better sensitivity, to resolve spatially varying excitonic structure in a heterogeneous mixture of photosynthetic cells.
- Vivek Tiwari
- , Yassel Acosta Matutes
- & Jennifer P. Ogilvie
-
Article
| Open Access Sounding-rocket microgravity experiments on alumina dust
Sounding-rocket microgravity experiments on alumina dust
Alumina is thought to be the main condensate to form in the gas outflow from oxygen-rich evolved stars. Here, the authors perform a condensation experiment with alumina in a low-gravity environment, and find spectroscopic evidence for a sharp feature at a wavelength of 13.55 μm.
- Shinnosuke Ishizuka
- , Yuki Kimura
- & Yuko Inatomi
-
Article
| Open Access Correct determination of charge transfer state energy from luminescence spectra in organic solar cells
Correct determination of charge transfer state energy from luminescence spectra in organic solar cells
The charge transfer state is the key to understand the open circuit voltage of organic solar cells and is commonly accessed by electroluminescence spectra. Here List et al. show that the reliable spectra can only be obtained by a correction of the device-specific out-coupling effect.
- Mathias List
- , Tanmoy Sarkar
- & Uli Würfel
-
Article
| Open Access Morphology and structure of ZIF-8 during crystallisation measured by dynamic angle-resolved second harmonic scattering
Morphology and structure of ZIF-8 during crystallisation measured by dynamic angle-resolved second harmonic scattering
Angle-resolved monitoring of structure parameters during crystal growth is often slow owing to mechanical movements. Here, the authors use second harmonic scattering and Fourier-plane imaging to dynamically monitor size, shape and concentration of ZIF-8 in situ during the growth process.
- Stijn Van Cleuvenbergen
- , Zachary J. Smith
- & Monique A. van der Veen
-
Article
| Open Access Exploiting the tunability of stimulated emission depletion microscopy for super-resolution imaging of nuclear structures
Exploiting the tunability of stimulated emission depletion microscopy for super-resolution imaging of nuclear structures
A known limitation of super-resolution STED microscopy is the need of high laser power which can cause photobleaching and phototoxicity. Here the authors further optimize this method and show that modulating STED intensity during acquisition results in an enhanced resolution and reduced background.
- Maria J. Sarmento
- , Michele Oneto
- & Luca Lanzanò
-
Article
| Open Access Measurement of complex optical susceptibility for individual carbon nanotubes by elliptically polarized light excitation
Measurement of complex optical susceptibility for individual carbon nanotubes by elliptically polarized light excitation
One-dimensional materials such as carbon nanotubes have many applications, but not all of their properties can be described in the same way as for conventional media. Here, the authors devise a method to measure the complex optical susceptibility in a 1D nanomaterial and demonstrate it for carbon nanotubes.
- Fengrui Yao
- , Can Liu
- & Kaihui Liu
-
Article
| Open Access Optical imaging of metabolic dynamics in animals
Optical imaging of metabolic dynamics in animals
Non-destructive methods to image metabolism in situ in living tissues are limited. Here the authors combine deuterium oxide probing and stimulated Raman scattering microscopy to image lipid metabolic dynamics and protein synthesis in cells and in vivo in mice, C. elegans, and zebrafish.
- Lingyan Shi
- , Chaogu Zheng
- & Wei Min
-
Article
| Open Access A phase-stable dual-comb interferometer
A phase-stable dual-comb interferometer
Dual-comb interferometry promises to be a high-precision metrology technique, but is hindered by short coherence times that limit the maximum number of averages. Here, Chen et al. achieve mutual coherence times of almost 2000 s by feed-forward stabilization of the carrier-envelope offsets.
- Zaijun Chen
- , Ming Yan
- & Nathalie Picqué
-
Article
| Open Access Operando and three-dimensional visualization of anion depletion and lithium growth by stimulated Raman scattering microscopy
Operando and three-dimensional visualization of anion depletion and lithium growth by stimulated Raman scattering microscopy
The relationship between Li-ion concentration and Li deposition remains an issue to be addressed. Here the authors show that stimulated Raman scattering microscopy offers insight into the concentration evolution and its impact on the dendrite growth, which is not possible by existing techniques.
- Qian Cheng
- , Lu Wei
- & Yuan Yang
-
Article
| Open Access In situ topographical chemical and electrical imaging of carboxyl graphene oxide at the nanoscale
In situ topographical chemical and electrical imaging of carboxyl graphene oxide at the nanoscale
Mapping the distribution of functional groups on 2D materials with high resolution remains challenging. Here, the authors combine tip-enhanced Raman spectroscopy and Kelvin probe force microscopy to simultaneously examine the topography, chemical composition and electronic nature of graphene oxide surfaces with nanoscale spatial resolution.
- Weitao Su
- , Naresh Kumar
- & Marc Chaigneau
-
Article
| Open Access Slow thermal equilibration in methylammonium lead iodide revealed by transient mid-infrared spectroscopy
Slow thermal equilibration in methylammonium lead iodide revealed by transient mid-infrared spectroscopy
Hybrid organic-inorganic perovskites are emerging materials for efficient photovoltaics; however understanding how charge/heat dissipates inside the material remains a challenge. Here, the authors use a spectroscopic approach to observe unusually slow thermal equilibration between the organic and inorganic components.
- Peijun Guo
- , Jue Gong
- & Richard D. Schaller
-
Article
| Open Access Domino-like multi-emissions across red and near infrared from solid-state 2-/2,6-aryl substituted BODIPY dyes
Domino-like multi-emissions across red and near infrared from solid-state 2-/2,6-aryl substituted BODIPY dyes
The class of BODIPY dyes has high solubility and high quantum yields and is widely used in imaging applications. Here Tian et al. synthesize new dye molecules and demonstrate extended emission properties and application scope controllable both by the excitation wavelength and aggregation states.
- Dan Tian
- , Fen Qi
- & Wei Huang
-
Article
| Open Access Spin–phonon couplings in transition metal complexes with slow magnetic relaxation
Spin–phonon couplings in transition metal complexes with slow magnetic relaxation
Transition metal complexes that display slow magnetic relaxation show promise for information storage, but our mechanistic understanding of the magnetic relaxation of such compounds remains limited. Here, the authors spectroscopically and computationally characterize the strength of spin–phonon couplings, which play an important role in the relaxation process.
- Duncan H. Moseley
- , Shelby E. Stavretis
- & Zi-Ling Xue
-
Article
| Open Access Coherent two-dimensional electronic mass spectrometry
Coherent two-dimensional electronic mass spectrometry
Multidimensional spectroscopy is a powerful tool in exploring photo-induced dynamics and electron coupling processes in molecules. Here the authors demonstrate coherent two-dimensional electronic mass spectrometry on molecular beams and its application to photoionization studies of the NO2 molecule.
- Sebastian Roeding
- & Tobias Brixner
-
Article
| Open Access Direct observation of exciton–exciton interactions
Direct observation of exciton–exciton interactions
Some photo-physical processes in multichromophore systems might get triggered only if two excitations are present. Here, the authors introduce exciton–exciton-interaction 2D spectroscopy, which is a non-linear optical method that can selectively track the time evolution of such effects.
- Jakub Dostál
- , Franziska Fennel
- & Tobias Brixner
-
Article
| Open Access Selective manipulation of electronically excited states through strong light–matter interactions
Selective manipulation of electronically excited states through strong light–matter interactions
Manipulating energy levels in molecules could allow applications such as improving organic LEDs. Here, the authors show evidence that reversed intersystem crossing can be enhanced in Erythrosine B coupled to a cavity by selectively manipulating the energy of the singlet state.
- Kati Stranius
- , Manuel Hertzog
- & Karl Börjesson

 An alternative framework for fluorescence correlation spectroscopy
An alternative framework for fluorescence correlation spectroscopy