Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access A quantitative model predicts how m6A reshapes the kinetic landscape of nucleic acid hybridization and conformational transitions
A quantitative model predicts how m6A reshapes the kinetic landscape of nucleic acid hybridization and conformational transitions
m6A RNA post-transcriptional modification changes RNA hybridization kinetics. Here the authors show that the methylamino group can adopt syn-conformation pairing with uridine with a mismatch-like conformation in RNA duplex. They also develop a quantitative model that predicts how m6A affects the kinetics of hybridization.
- Bei Liu
- , Honglue Shi
- & Hashim M. Al-Hashimi
-
Article
| Open Access PD-L1 degradation is regulated by electrostatic membrane association of its cytoplasmic domain
PD-L1 degradation is regulated by electrostatic membrane association of its cytoplasmic domain
The cytoplasmic domain of PD-L1 (PD-L1-CD) is involved in regulating PD-L1 stability and degradation. Here the authors show that membrane binding of PD-L1-CD mediates the cellular levels of PD-L1, while metformin can disrupt the interaction between PD-L1-CD and the membrane to reduce PD-L1 levels.
- Maorong Wen
- , Yunlei Cao
- & Bo OuYang
-
Article
| Open Access Switching at the ribosome: riboswitches need rProteins as modulators to regulate translation
Switching at the ribosome: riboswitches need rProteins as modulators to regulate translation
Translational regulation by riboswitches is an important mechanism for the modulation of gene expression in bacteria. Here the authors show that the ligand-induced allosteric switch in the adenine-sensing riboswitch from V. vulnificus is insufficient and leads only to a partial opening of the ribosome binding site and requires interaction with 30S-bound ribosomal protein S1, which acts as an RNA chaperone.
- Vanessa de Jesus
- , Nusrat S. Qureshi
- & Boris Fürtig
-
Article
| Open Access Porous functionalized polymers enable generating and transporting hyperpolarized mixtures of metabolites
Porous functionalized polymers enable generating and transporting hyperpolarized mixtures of metabolites
Hyperpolarization by dissolution dynamic nuclear polarization has brought highly sensitive magnetic resonance to reality but there still remains severe limitations. Here the authors show an approach relying on the generation of hyperpolarizing polymers that bear a dual function.
- Théo El Daraï
- , Samuel F. Cousin
- & Sami Jannin
-
Article
| Open Access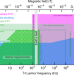 Fast-field-cycling ultralow-field nuclear magnetic relaxation dispersion
Fast-field-cycling ultralow-field nuclear magnetic relaxation dispersion
Nuclear spin polarization and relaxation can be studied using nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR). Here the authors demonstrate a combination of fast-field cycling and optical magnetometry techniques, to realize a NMR sensor that operates in the region of very low frequency and high relaxation rate.
- Sven Bodenstedt
- , Morgan W. Mitchell
- & Michael C. D. Tayler
-
Article
| Open Access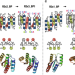 Role of backbone strain in de novo design of complex α/β protein structures
Role of backbone strain in de novo design of complex α/β protein structures
The authors show that consideration of global backbone strain enables successful de novo design of larger αβ-proteins with five- and six- stranded β-sheets flanked by α-helices.
- Nobuyasu Koga
- , Rie Koga
- & David Baker
-
Article
| Open Access Proline/arginine dipeptide repeat polymers derail protein folding in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis
Proline/arginine dipeptide repeat polymers derail protein folding in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis
The most frequent cause of familial Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS) and Frontotemporal Dementia (FTD) are hexanucleotide repeat expansions in the non-coding region of the C9ORF72 gene that are translated into five dipeptide repeat (DPR) proteins. Here, the authors show that proline/arginine (PR) DPRs inhibit the prolyl isomerase PPIA and reveal the molecular mechanism of the impaired protein folding activity of PPIA by performing NMR measurements and determining a PR DPR bound PPIA crystal structure.
- Maria Babu
- , Filippo Favretto
- & Markus Zweckstetter
-
Article
| Open Access Distinct EH domains of the endocytic TPLATE complex confer lipid and protein binding
Distinct EH domains of the endocytic TPLATE complex confer lipid and protein binding
AtEH/Pan1 proteins contain two N-terminal Eps15 homology (EH) domains and are subunits of the endocytic TPLATE complex present in plants. Here, the authors combine X-ray crystallography, NMR and MD simulations with biochemical and in planta analysis to characterize the two AtEH1/Pan1 EH domains and reveal their structural differences and complementary functional roles.
- Klaas Yperman
- , Anna C. Papageorgiou
- & Daniel Van Damme
-
Article
| Open Access Molecular basis for the allosteric activation mechanism of the heterodimeric imidazole glycerol phosphate synthase complex
Molecular basis for the allosteric activation mechanism of the heterodimeric imidazole glycerol phosphate synthase complex
The allosteric regulation of the bienzyme complex imidazole glycerol phosphate synthase (HisFH) remains to be elucidated. Here, the authors provide structural insights into the dynamic allosteric mechanism by which ligand binding to the cyclase and glutaminase active sites of HisFH regulate enzyme activation.
- Jan Philip Wurm
- , Sihyun Sung
- & Remco Sprangers
-
Article
| Open Access Design of buried charged networks in artificial proteins
Design of buried charged networks in artificial proteins
Buried charged networks in proteins are often important for their biological functionality and are believed to destabilise the protein fold. Here, the authors combine computational design, MD simulations, biophysical experiments, NMR and X-ray crystallography to design and characterise artificial 4α-helical proteins with buried charged elements. They analyse their conformational landscapes and observe that the ion-pairs are stabilised by amphiphilic residues that electrostatically shield the charged motif, which increases structural stability.
- Mona Baumgart
- , Michael Röpke
- & Ville R. I. Kaila
-
Article
| Open Access Phosphorylation regulates the binding of autophagy receptors to FIP200 Claw domain for selective autophagy initiation
Phosphorylation regulates the binding of autophagy receptors to FIP200 Claw domain for selective autophagy initiation
Cooperation between the ULK complex and autophagy receptors mediates targeting cargoes to autophagosomes. Here, the authors show that interactions of ULK subunit FIP200 with autophagy receptors CCPG1 and Optineurin can be regulated by phosphorylation, suggesting a general binding mode shared by autophagy receptors.
- Zixuan Zhou
- , Jianping Liu
- & Lifeng Pan
-
Article
| Open Access Structural elements in the flexible tail of the co-chaperone p23 coordinate client binding and progression of the Hsp90 chaperone cycle
Structural elements in the flexible tail of the co-chaperone p23 coordinate client binding and progression of the Hsp90 chaperone cycle
p23 is a co-chaperone of Hsp90 but its mode of action is mechanistically not well understood. Here, the authors combine in vitro and yeast in vivo assays, biochemical measurements and NMR experiments to characterize p23 and identify two conserved helical elements in the intrinsically disordered C-terminal tail of p23 that together with the folded domain of p23 regulate the Hsp90 ATPase activity and affect the binding and maturation of Hsp90 clients.
- Maximilian M. Biebl
- , Abraham Lopez
- & Johannes Buchner
-
Article
| Open Access Backbone-independent NMR resonance assignments of methyl probes in large proteins
Backbone-independent NMR resonance assignments of methyl probes in large proteins
Here, the authors present Methyl Assignments Using Satisfiability (MAUS), a method for the assignment of methyl groups using raw NOE data. They use eight proteins in the 10–45 kDa size range as test cases and show that MAUS yields 100% accurate assignments at high completeness levels.
- Santrupti Nerli
- , Viviane S. De Paula
- & Nikolaos G. Sgourakis
-
Article
| Open Access An N-terminal conserved region in human Atg3 couples membrane curvature sensitivity to conjugase activity during autophagy
An N-terminal conserved region in human Atg3 couples membrane curvature sensitivity to conjugase activity during autophagy
The E2-like enzyme human Atg3 catalyses the transfer of ubiquitin-like mammalian LC3 to the lipid phosphatidylethanolamine during autophagosome formation. Here, the authors combine NMR measurements with in vitro biochemical and in vivo cellular assays and show that the N-terminal conserved region of human Atg3 communicates information from the curvature-sensing domain to its active site.
- Yansheng Ye
- , Erin R. Tyndall
- & Fang Tian
-
Article
| Open Access A method for validating the accuracy of NMR protein structures
A method for validating the accuracy of NMR protein structures
The authors present a method for calculating the accuracy of an NMR structure, where flexibility from backbone chemical shifts is compared to structural flexibility predicted using rigidity theory. The authors validate their method and use it to compare the accuracy of NMR and X-ray structures.
- Nicholas J. Fowler
- , Adnan Sljoka
- & Mike P. Williamson
-
Article
| Open Access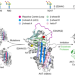 High-resolution ex vivo NMR spectroscopy of human Z α1-antitrypsin
High-resolution ex vivo NMR spectroscopy of human Z α1-antitrypsin
α1-Antitrypsin (AAT) is a 52 kDa serum glycoprotein, the misfolding and polymerisation of which is associated with COPD and liver disease. Here the authors demonstrate the use of high-resolution multidimensional solution-state NMR spectroscopy to characterise the structure and dynamics in solution of Z AAT purified directly from clinical patients.
- Alistair M. Jagger
- , Christopher A. Waudby
- & David A. Lomas
-
Article
| Open Access Catalysis of proline isomerization and molecular chaperone activity in a tug-of-war
Catalysis of proline isomerization and molecular chaperone activity in a tug-of-war
Cyclophilin A (CypA) is a peptidylprolyl isomerase that also has chaperone activity and interacts with the intrinsically disordered protein α-Synuclein (aSyn). Here, the authors combine NMR measurements and biochemical experiments to characterise the interplay between the catalysis of proline isomerization and molecular chaperone activity of CypA and find that both activities have opposing effects on aSyn and further show that the that cis/trans isomerization outpowers the holding activity of CypA.
- Filippo Favretto
- , David Flores
- & Markus Zweckstetter
-
Article
| Open Access Nucleocapsid protein of SARS-CoV-2 phase separates into RNA-rich polymerase-containing condensates
Nucleocapsid protein of SARS-CoV-2 phase separates into RNA-rich polymerase-containing condensates
The SARS-CoV-2 viral genome is encapsulated by the nucleocapsid protein (NSARS-CoV-2) that is essential for viral replication. Here, the authors show that RNA induces liquid-liquid phase separation of NSARS-CoV-2 and how NSARS-CoV-2 phosphorylation modulates RNA-binding and phase separation and that these RNA/NSARS-CoV-2-droplets recruit and concentrate the SARS-CoV-2 RNA-dependent RNA polymerase complex in vitro, which would enable high initiation and elongation rates during viral transcription.
- Adriana Savastano
- , Alain Ibáñez de Opakua
- & Markus Zweckstetter
-
Article
| Open Access Cysteine oxidation and disulfide formation in the ribosomal exit tunnel
Cysteine oxidation and disulfide formation in the ribosomal exit tunnel
As protein synthesis takes place, newly synthesized polypeptide chain passes through the ribosomal exit tunnel, which can accommodate up to 70 residues in the case of a helical peptide. Here the authors show that oxidation of cysteine residues in the nascent chain can occur within the ribosome exit tunnel, where sufficient space exists for the formation of disulfide bonds.
- Linda Schulte
- , Jiafei Mao
- & Harald Schwalbe
-
Article
| Open Access Nearest-neighbor NMR spectroscopy: categorizing spectral peaks by their adjacent nuclei
Nearest-neighbor NMR spectroscopy: categorizing spectral peaks by their adjacent nuclei
The structure and dynamics of large proteins and complexes can be studied by methyl-NMR but resonance assignment is still challenging. Here, the authors present a NMR method that leverages optimal control pulse design to unambiguously distinguish between Leu and Val using a simple 2D HMQC experiment and they apply it to several proteins including Cas9, interleukin, and human translation initiation factor eIF4a.
- Soumya P. Behera
- , Abhinav Dubey
- & Haribabu Arthanari
-
Article
| Open Access Allomorphy as a mechanism of post-translational control of enzyme activity
Allomorphy as a mechanism of post-translational control of enzyme activity
β-phosphoglucomutase (βPGM) from Lactococcus lactis is a phosphoryl transfer enzyme required for catabolism of trehalose and maltose. Coupled analyses of multiple βPGM structures and enzymatic activity lead to the proposal of allomorphy — a post-translational mechanism controlling enzyme activity.
- Henry P. Wood
- , F. Aaron Cruz-Navarrete
- & Jonathan P. Waltho
-
Article
| Open Access Rapid and accurate determination of atomistic RNA dynamic ensemble models using NMR and structure prediction
Rapid and accurate determination of atomistic RNA dynamic ensemble models using NMR and structure prediction
Determining dynamic ensembles of biomolecules is still challenging. Here the authors present an approach for rapid RNA ensemble determination that combines RNA structure prediction tools and NMR residual dipolar coupling data and use it to determine atomistic ensemble models for a variety of RNAs.
- Honglue Shi
- , Atul Rangadurai
- & Hashim M. Al-Hashimi
-
Article
| Open Access Sensitivity enhancement of homonuclear multidimensional NMR correlations for labile sites in proteins, polysaccharides, and nucleic acids
Sensitivity enhancement of homonuclear multidimensional NMR correlations for labile sites in proteins, polysaccharides, and nucleic acids
Here, the authors present an approach that enhances the sensitivity of basic 2D biomolecular NMR experiments like NOESY and TOCSY, when carried out in polysaccharides, proteins and nucleic acids. This method combines principles associated to quantum Anti-Zeno Effects and advanced data acquisition methods based on Hadamard multiplexing.
- Mihajlo Novakovic
- , Ēriks Kupče
- & Lucio Frydman
-
Article
| Open Access Conformational equilibrium shift underlies altered K+ channel gating as revealed by NMR
Conformational equilibrium shift underlies altered K+ channel gating as revealed by NMR
Potassium ion channels control K+ permeation across cell membranes and mutations that cause cardiovascular and neural diseases are known. Here, the authors perform NMR measurements with the prototypical K+ channel from Streptomyces lividans, KcsA and characterise the effects of disease causing mutations on the conformational dynamics of K+ channels in a physiological solution environment.
- Yuta Iwahashi
- , Yuki Toyama
- & Ichio Shimada
-
Article
| Open Access Mechanism and evolution of the Zn-fingernail required for interaction of VARP with VPS29
Mechanism and evolution of the Zn-fingernail required for interaction of VARP with VPS29
VARP is bound to endosomes and functions as a protein:protein interaction platform. Here, the authors present the NMR structure of the complex between the retromer subunit VPS29 and a VARP Zn-fingernail microdomain that is structurally distinct from Zn-fingers and further show that mutations, which abolish VPS29:VARP binding, inhibit trafficking from endosomes to the cell surface.
- Harriet Crawley-Snowdon
- , Ji-Chun Yang
- & David J. Owen
-
Article
| Open Access Structural and mechanistic basis of capsule O-acetylation in Neisseria meningitidis serogroup A
Structural and mechanistic basis of capsule O-acetylation in Neisseria meningitidis serogroup A
Neisseria meningitidis capsular polysaccharide (CPS) is a major virulence factor and vaccine formulations against Neisseria meningitidis serogroup A (NmA) contain O-acetylated CPS. Here, the authors provide mechanistic insights into CPS O-acetylation in NmA by determining the crystal structure of the O-acetyltransferase CsaC and NMR measurements further reveal that the CsaC-mediated reaction is regioselective for O3 and that the O4 modification results from spontaneous O-acetyl migration.
- Timm Fiebig
- , Johannes T. Cramer
- & Martina Mühlenhoff
-
Article
| Open Access Relative configuration of micrograms of natural compounds using proton residual chemical shift anisotropy
Relative configuration of micrograms of natural compounds using proton residual chemical shift anisotropy
Determination of 3D molecular structures remains challenging for natural products or organic compounds available in minute amounts. Here, the authors determine the structure of complex molecules, including few micrograms of briarane B-3 isolated from Briareum asbestinums, through measurement of 1H residual chemical shift anisotropy.
- Nilamoni Nath
- , Juan Carlos Fuentes-Monteverde
- & Christian Griesinger
-
Article
| Open Access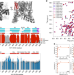 Evidence that the TRPV1 S1-S4 membrane domain contributes to thermosensing
Evidence that the TRPV1 S1-S4 membrane domain contributes to thermosensing
The TRPV1 ion channel is a heat-sensing receptor that is also activated by vanilloid compounds, but the molecular underpinnings of thermosensing have remained elusive. Here authors use in solution NMR on the isolated human TRPV1 S1-S4 domain and show that this domain undergoes a non-denaturing temperature-dependent transition with a high thermosensitivity.
- Minjoo Kim
- , Nicholas J. Sisco
- & Wade D. Van Horn
-
Article
| Open Access A distal regulatory region of a class I human histone deacetylase
A distal regulatory region of a class I human histone deacetylase
Human Histone Deacetylases (HDACs) regulate gene expression and are important drug targets. Here, the authors combine NMR measurements, enzymatic assays and molecular dynamics simulations and show that HDAC8 samples a catalytically active and an inactive state and further demonstrate that mutations and ligand binding alter the populations of the two states, which is of interest for inhibitor design.
- Nicolas D. Werbeck
- , Vaibhav Kumar Shukla
- & D. Flemming Hansen
-
Article
| Open Access Functional 3D architecture in an intrinsically disordered E3 ligase domain facilitates ubiquitin transfer
Functional 3D architecture in an intrinsically disordered E3 ligase domain facilitates ubiquitin transfer
RNF4 is a prototypical single-subunit E3 enzyme that can bind both substrate and ubiquitin-loaded E2. Here, the authors show that the RNF4 N-terminal region, although lacking a defined secondary structure, maintains a compact global conformation to facilitate ubiquitin transfer to the substrate.
- Paul Murphy
- , Yingqi Xu
- & Ronald T. Hay
-
Article
| Open Access Molecular basis of host-adaptation interactions between influenza virus polymerase PB2 subunit and ANP32A
Molecular basis of host-adaptation interactions between influenza virus polymerase PB2 subunit and ANP32A
Avian influenza polymerase undergoes host adaptation in order to efficiently replicate in human cells. Here, the authors use NMR spectroscopy and quantitative ensemble modelling to describe the highly dynamic assemblies formed by the human-adapted or avian-adapted C-terminal domains with the respective ANP32A host proteins.
- Aldo R. Camacho-Zarco
- , Sissy Kalayil
- & Martin Blackledge
-
Article
| Open Access Characterization of an alternative BAK-binding site for BH3 peptides
Characterization of an alternative BAK-binding site for BH3 peptides
Mitochondrial apoptosis is controlled by BCL2 family proteins, and the BH3-only proteins often act as sensors that transmit apoptotic signals. Here the authors show how the BH3-only proteins BMF and HRK can directly activate the BCL2 protein BAK and interact with BAK through an alternative binding groove.
- Kaiqin Ye
- , Wei X. Meng
- & Haiming Dai
-
Article
| Open Access Ultrafast diffusion exchange nuclear magnetic resonance
Ultrafast diffusion exchange nuclear magnetic resonance
Analysis of exchange processes is time consuming by two-dimensional exchange NMR spectroscopy. Here the authors demonstrate a single-scan ultrafast Laplace NMR approach based on spatial encoding to measure molecular diffusion, with an increase by a factor six in the sensitivity per unit time.
- Otto Mankinen
- , Vladimir V. Zhivonitko
- & Ville-Veikko Telkki
-
Article
| Open Access Non-cooperative 4E-BP2 folding with exchange between eIF4E-binding and binding-incompatible states tunes cap-dependent translation inhibition
Non-cooperative 4E-BP2 folding with exchange between eIF4E-binding and binding-incompatible states tunes cap-dependent translation inhibition
Phosphorylation of eIF4E binding proteins (4E-BPs) controls their folding and regulates cap-dependent translation. Here, the authors show that phosphorylation of the C-terminal disordered region stabilizes the non-cooperatively folded 4E-BP domain to an eIF4E binding-incompatible state to control translation.
- Jennifer E. Dawson
- , Alaji Bah
- & Julie D. Forman-Kay
-
Article
| Open Access Aβ(1-42) tetramer and octamer structures reveal edge conductivity pores as a mechanism for membrane damage
Aβ(1-42) tetramer and octamer structures reveal edge conductivity pores as a mechanism for membrane damage
Formation of amyloid-beta (Aβ) oligomer pores in the membrane of neurons has been proposed to explain neurotoxicity in Alzheimer´s disease. Here authors present the 3D- structure of an Aβ oligomer formed in a membrane mimicking environment and observe that Aβ tetramers and octamers inserted into lipid bilayers as well-defined pores.
- Sonia Ciudad
- , Eduard Puig
- & Natàlia Carulla
-
Article
| Open Access Structural basis of transmembrane coupling of the HIV-1 envelope glycoprotein
Structural basis of transmembrane coupling of the HIV-1 envelope glycoprotein
HIV-1 envelope glycoprotein (Env) mediates the fusion of viral and target cell membranes and is a major target for HIV vaccine development. Here, the authors determine the NMR structure of a bicelle incorporated Env segment comprising the transmembrane domain (TMD) and a portion of the cytoplasmic tail (CT), and show that the CT folds into membrane attached amphipathic helices that wrap around the TMD thereby forming a support baseplate for the rest of Env, and they also provide insights into the dynamic coupling across the TMD between the ectodomain and CT.
- Alessandro Piai
- , Qingshan Fu
- & James J. Chou
-
Article
| Open Access Different regions of synaptic vesicle membrane regulate VAMP2 conformation for the SNARE assembly
Different regions of synaptic vesicle membrane regulate VAMP2 conformation for the SNARE assembly
Vesicle associated membrane protein 2 (VAMP2) contains a conserved SNARE motif that interacts with syntaxin-1 and SNAP25 for SNARE complex assembly. Here authors use in-cell NMR spectroscopy to describe the dynamic membrane association of VAMP2 SNARE motif in mammalian cells at the atomic resolution.
- Chuchu Wang
- , Jia Tu
- & Cong Liu
-
Article
| Open Access Liquid-liquid phase separation and extracellular multivalent interactions in the tale of galectin-3
Liquid-liquid phase separation and extracellular multivalent interactions in the tale of galectin-3
Galectin-3 consists of an unstructured N-terminal domain (NTD) and a structured carbohydrate-recognition domain and agglutinates neutrophils and glycosylated molecules in the extracellular milieu. Here the authors combine biophysical and biochemical experiments with NMR measurements and show that the galectin-3 NTD undergoes liquid-liquid phase separation (LLPS) and agglutinates other molecules through this process.
- Yi-Ping Chiu
- , Yung-Chen Sun
- & Jie-rong Huang
-
Article
| Open Access Structural basis for two-way communication between dynein and microtubules
Structural basis for two-way communication between dynein and microtubules
The movement of cytoplasmic dynein on microtubule tracks is coordinated by the microtubule-binding domain (MTBD) and the ATPase domain via a coiled-coil stalk. Here authors use NMR and cryo-EM and suggest that the communication between the ATPase-domain and MTBD is achieved by sliding of the stalk α-helix by a half-turn or one-turn.
- Noritaka Nishida
- , Yuta Komori
- & Masahide Kikkawa
-
Article
| Open Access A molecular switch regulating transcriptional repression and activation of PPARγ
A molecular switch regulating transcriptional repression and activation of PPARγ
Structural studies of nuclear receptor transcription factors revealed that nearly all nuclear receptors share a conserved helix 12 dependent transcriptional activation mechanism. Here the authors present two crystal structures of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPARγ) in an inverse agonist/corepressor-bound transcriptionally repressive conformation, where helix 12 is located within the orthosteric ligand-binding pocket instead, and discuss mechanistic implications.
- Jinsai Shang
- , Sarah A. Mosure
- & Douglas J. Kojetin
-
Article
| Open Access Tripartite phase separation of two signal effectors with vesicles priming B cell responsiveness
Tripartite phase separation of two signal effectors with vesicles priming B cell responsiveness
Antibody-mediated immune responses rely on antigen recognition by the B cell antigen receptor (BCR) and SLP65 is a key scaffold protein mediating BCR signaling. Here authors show that effective B cell activation requires tripartite phase separation of SLP65, CIN85, and lipid vesicles.
- Leo E. Wong
- , Arshiya Bhatt
- & Christian Griesinger
-
Article
| Open Access Conformational plasticity of ligand-bound and ternary GPCR complexes studied by 19F NMR of the β1-adrenergic receptor
Conformational plasticity of ligand-bound and ternary GPCR complexes studied by 19F NMR of the β1-adrenergic receptor
The β1-adrenergic receptor (β1AR) is a G-protein-coupled receptor (GPCRs) that binds catecholamine ligands. Here the authors employ site-specific labelling and 19F NMR measurements to characterise the structural changes and dynamics in the cytoplasmic region of β1AR upon agonist stimulation and coupling to a Gs-protein-mimetic nanobody.
- J. Niclas Frei
- , Richard W. Broadhurst
- & Daniel Nietlispach
-
Article
| Open Access Definition of functionally and structurally distinct repressive states in the nuclear receptor PPARγ
Definition of functionally and structurally distinct repressive states in the nuclear receptor PPARγ
The repressive states of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ (PPARγ) are ill-defined, despite nuclear receptors being a major drug target. Here authors demonstrate multiple structurally distinct repressive states, providing a structural rationale for ligand bias in a nuclear receptor.
- Zahra Heidari
- , Ian M. Chrisman
- & Travis S. Hughes
-
Article
| Open Access Structural basis for Fullerene geometry in a human endogenous retrovirus capsid
Structural basis for Fullerene geometry in a human endogenous retrovirus capsid
In retroviruses, the capsid protein (CA) forms a shell surrounding the viral core. Here the authors combine cryo-electron microscopy with NMR and X-ray crystallography to examine the CA structure from the human endogenous retrovirus HML2 (HERV-K) and determine the structures of four Fullerene CA closed shells that reveal the molecular basis of capsid assembly.
- Oliver Acton
- , Tim Grant
- & Peter B. Rosenthal
-
Article
| Open Access Solution structure of human myeloid-derived growth factor suggests a conserved function in the endoplasmic reticulum
Solution structure of human myeloid-derived growth factor suggests a conserved function in the endoplasmic reticulum
Myeloid-derived growth factor (MYDGF) is an endoplasmic reticulum protein of therapeutic interest because it promotes tissue repair in a murine model of myocardial infarction. Here the authors present the NMR structure of human MYDGF and attribute function to a set of residues conserved in MYDGFs but not the vanin base domain, which has a similar fold.
- Valeriu Bortnov
- , Marco Tonelli
- & Deane F. Mosher
-
Article
| Open Access Structural heterogeneity of α-synuclein fibrils amplified from patient brain extracts
Structural heterogeneity of α-synuclein fibrils amplified from patient brain extracts
Parkinson’s disease (PD) and Multiple System Atrophy (MSA) are characterized by the pathological accumulation of α-synuclein. Here the authors employ fluorescent probes, electron microscopy and NMR spectroscopy to study the properties of α-synuclein aggregates that were amplified from patient brain extracts and observe a greater structural diversity among PD patients compared to MSA patients.
- Timo Strohäker
- , Byung Chul Jung
- & Markus Zweckstetter
-
Article
| Open Access Structural determinants of microtubule minus end preference in CAMSAP CKK domains
Structural determinants of microtubule minus end preference in CAMSAP CKK domains
CKK domain containing CAMSAP/Patronins recognise and regulate microtubule (MT) minus end dynamics. Here the authors compare cryo-EM structures of MT-bound human CKK and Naegleria gruberi CKK which lacks minus-end binding preference, finding NgCKK has a different interaction with, and inability to remodel, its MT binding site, shedding light on the CAMSAP/Patronin end binding mechanism.
- Joseph Atherton
- , Yanzhang Luo
- & Carolyn A. Moores
-
Article
| Open Access Concerted dynamics of metallo-base pairs in an A/B-form helical transition
Concerted dynamics of metallo-base pairs in an A/B-form helical transition
Metal-mediated base pairs expand the repertoire of nucleic acid structures and dynamics. Here, the authors prepared a metallo-DNA duplex including two C-Hg(II)-T base pairs separated by six normal Watson-Crick base pairs and investigated its solution structure and dynamics using NMR spectroscopy.
- Olivia P. Schmidt
- , Simon Jurt
- & Nathan W. Luedtke
-
Article
| Open Access Evaluation of integrin αvβ6 cystine knot PET tracers to detect cancer and idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis
Evaluation of integrin αvβ6 cystine knot PET tracers to detect cancer and idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis
Knottin is a cystine knot peptide. Here, the authors develop a knottin-based tracer for positron emission tomography and demonstrate its ability to detect cancer and idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis through selective binding to integrin αvβ6.
- Richard H. Kimura
- , Ling Wang
- & Sanjiv S. Gambhir

 Structural and functional consequences of NEDD8 phosphorylation
Structural and functional consequences of NEDD8 phosphorylation