Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Mucosal-associated invariant T cells contribute to suppression of inflammatory myeloid cells in immune-mediated kidney disease
Mucosal-associated invariant T cells contribute to suppression of inflammatory myeloid cells in immune-mediated kidney disease
Mucosal associated invariant T (MAIT) cells reside in barrier organs, but their contribution to inflammatory processes in the kidneys is not fully known. Here authors find by single cell RNA sequencing that among the different MAIT cell subtypes found at steady state, a population with MAIT17 signature is expanded in both human crescentic glomerulonephritis and its mouse model, and these cells may play protective role in the disease.
- Ann-Christin Gnirck
- , Marie-Sophie Philipp
- & Jan-Eric Turner
-
Article
| Open Access Dimension-agnostic and granularity-based spatially variable gene identification using BSP
Dimension-agnostic and granularity-based spatially variable gene identification using BSP
Identifying spatially variable genes (SVGs) is essential for linking molecular cell functions with tissue phenotypes. Here, authors introduce a non-parametric model that detects SVGs from two or three-dimensional spatial transcriptomics data by comparing gene expression patterns at granularities.
- Juexin Wang
- , Jinpu Li
- & Dong Xu
-
Article
| Open Access EASTR: Identifying and eliminating systematic alignment errors in multi-exon genes
EASTR: Identifying and eliminating systematic alignment errors in multi-exon genes
The study reveals limitations in widely used RNA-seq aligners, which create 'phantom' introns in reference databases. The authors introduce EASTR, a computational tool that not only enhances alignment accuracy but also uncovers existing annotation errors. This improvement bolsters the dependability of subsequent RNA-seq analyses.
- Ida Shinder
- , Richard Hu
- & Mihaela Pertea
-
Article
| Open Access MePMe-seq: antibody-free simultaneous m6A and m5C mapping in mRNA by metabolic propargyl labeling and sequencing
MePMe-seq: antibody-free simultaneous m6A and m5C mapping in mRNA by metabolic propargyl labeling and sequencing
Methylation is the dominant modification in mRNA and occurs at a variety of sites. Here, Hartstock et al. show that a clickable analogue of the key cosubstrate S-adenosyl-L-methionine (SAM) can be produced in cells, allowing for identification and mapping of different methylated nucleosides in mRNA.
- Katja Hartstock
- , Nadine A. Kueck
- & Andrea Rentmeister
-
Article
| Open Access IL-21R-STAT3 signalling initiates a differentiation program in uterine tissue-resident NK cells to support pregnancy
IL-21R-STAT3 signalling initiates a differentiation program in uterine tissue-resident NK cells to support pregnancy
Uterine natural killer (NK) cells support tissue homeostasis in the uterus during pregnancy, but it is not fully known how they differentiate into potentially cytotoxic effector cells while avoiding tissue damage. Here authors show that Il21 receptor signalling via STAT3 activation governs their differentiation, while an apoptotic cell death program ensures that harm is limited.
- Mengwei Han
- , Luni Hu
- & Chao Zhong
-
Article
| Open Access Systematic analysis of paralogous regions in 41,755 exomes uncovers clinically relevant variation
Systematic analysis of paralogous regions in 41,755 exomes uncovers clinically relevant variation
Chameleolyser enables the accurate identification of genetic variants hidden within complex regions of the genome. Its application uncovers the disease-explanatory variant in 25 previously undiagnosed patients.
- Wouter Steyaert
- , Lonneke Haer-Wigman
- & Christian Gilissen
-
Article
| Open Access Enzymatic synthesis and nanopore sequencing of 12-letter supernumerary DNA
Enzymatic synthesis and nanopore sequencing of 12-letter supernumerary DNA
Unnatural base pairing xenonucleic acids (XNAs) can be used to expand life’s alphabet beyond ATGC. Here, authors show strategies for enzymatic synthesis and next-generation nanopore sequencing of XNA base pairs for reading and writing 12-letter DNA (ATGCBSPZXKJV).
- Hinako Kawabe
- , Christopher A. Thomas
- & Jorge A. Marchand
-
Article
| Open Access Mass production of lumenogenic human embryoid bodies and functional cardiospheres using in-air-generated microcapsules
Mass production of lumenogenic human embryoid bodies and functional cardiospheres using in-air-generated microcapsules
Current methods to generate spheroids are associated with low production throughputs, limiting clinical and industrial translation. Here the authors present a clean ultra-high-throughput in-air microfluidic platform for mass production of lumenogenic embryoid bodies and functional cardiospheres.
- Bas van Loo
- , Simone A. ten Den
- & Jeroen Leijten
-
Article
| Open Access A spatial sequencing atlas of age-induced changes in the lung during influenza infection
A spatial sequencing atlas of age-induced changes in the lung during influenza infection
Ageing is known to impair the immune response against infectious pathogens. Here, Kasmani et al. present a spatial and transcriptomic atlas of immune changes in the lungs of young and aged mice in response to influenza virus infection.
- Moujtaba Y. Kasmani
- , Paytsar Topchyan
- & Weiguo Cui
-
Article
| Open Access mRNA vaccine quality analysis using RNA sequencing
mRNA vaccine quality analysis using RNA sequencing
mRNA vaccines must be rigorously analysed to measure their integrity and detect contaminants, which can be time-consuming and costly. Here, authors describe a method to analyse mRNA vaccine quality using long-read sequencing and a custom bioinformatic pipeline.
- Helen M. Gunter
- , Senel Idrisoglu
- & Tim R. Mercer
-
Article
| Open Access A landscape of complex tandem repeats within individual human genomes
A landscape of complex tandem repeats within individual human genomes
Haplotype-resolved long, complex tandem repeats remain largely hidden despite their potential relevance to disease. Here, the authors reveal and analyze the genome-wide landscape of these repeats using a high-precision algorithm.
- Kazuki Ichikawa
- , Riki Kawahara
- & Shinichi Morishita
-
Article
| Open Access Systematic transcriptional analysis of human cell lines for gene expression landscape and tumor representation
Systematic transcriptional analysis of human cell lines for gene expression landscape and tumor representation
During preclinical drug development, the ability of cancer cell lines to faithfully model human disease is important for identifying potential therapeutic strategies. Here, using transcriptomic datasets of over 1000 cell lines, the authors evaluate how representative each line is of its cancer type and present their cell line selection tool.
- Han Jin
- , Cheng Zhang
- & Adil Mardinoglu
-
Article
| Open Access Metagenomic sequencing of post-mortem tissue samples for the identification of pathogens associated with neonatal deaths
Metagenomic sequencing of post-mortem tissue samples for the identification of pathogens associated with neonatal deaths
Rapid identification of pathogens in neonatal infection, and corresponding antimicrobial susceptibility profiles, would improve patient outcomes and assist in antibiotic stewardship. In this work, the authors utilize metagenomic next-generation sequencing of post-mortem tissue samples to identify pathogens associated with neonatal deaths.
- Vicky L. Baillie
- , Shabir A. Madhi
- & Courtney P. Olwagen
-
Article
| Open Access Barcoded multiple displacement amplification for high coverage sequencing in spatial genomics
Barcoded multiple displacement amplification for high coverage sequencing in spatial genomics
Spatial genomics offers insights into cellular interactions within tissues. Here, the authors develop barcoded multiple displacement amplification, achieving high-coverage sequencing to map complex genomic variations within cellular landscapes.
- Jinhyun Kim
- , Sungsik Kim
- & Sunghoon Kwon
-
Article
| Open Access Projecting RNA measurements onto single cell atlases to extract cell type-specific expression profiles using scProjection
Projecting RNA measurements onto single cell atlases to extract cell type-specific expression profiles using scProjection
Many expression deconvolution approaches have been developed to estimate % RNA contributions of diverse cell types to mixed RNA measurements. Here, the authors have developed a complementary approach called scProjection to recover cell type-specific expression profiles from mixed RNA measurements.
- Nelson Johansen
- , Hongru Hu
- & Gerald Quon
-
Article
| Open Access Long-read whole-genome analysis of human single cells
Long-read whole-genome analysis of human single cells
Here the authors introduce a new method to study DNA in single cells by long-read sequencing. Their method gives a more complete view of the genomic structure of individual cells and allows to study genetic differences at the single-cell level.
- Joanna Hård
- , Jeff E. Mold
- & Adam Ameur
-
Article
| Open Access Droplet-based high-throughput single microbe RNA sequencing by smRandom-seq
Droplet-based high-throughput single microbe RNA sequencing by smRandom-seq
Population level transcriptomics measurements miss bacterial heterogeneity. Here the authors report smRandom-seq, a droplet-based high-throughput single-microbe RNA-seq assay, using random primers for in situ cDNA generation, droplets for single-microbe barcoding, and CRISPR-based rRNA depletion.
- Ziye Xu
- , Yuting Wang
- & Yongcheng Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Spatial transcriptomics reveal markers of histopathological changes in Duchenne muscular dystrophy mouse models
Spatial transcriptomics reveal markers of histopathological changes in Duchenne muscular dystrophy mouse models
Duchenne muscular dystrophy is a fatal neuromuscular disorder affecting one in 5000 male births. To enrich our understanding of the underlying pathology, the authors apply spatial transcriptomics on dystrophic skeletal muscle to unravel markers related to histopathological changes in Duchenne mouse models.
- L.G.M. Heezen
- , T. Abdelaal
- & P. Spitali
-
Article
| Open Access TEQUILA-seq: a versatile and low-cost method for targeted long-read RNA sequencing
TEQUILA-seq: a versatile and low-cost method for targeted long-read RNA sequencing
The authors report TEQUILA-seq, a versatile, easy-to-implement, and low-cost method for targeted long-read RNA sequencing. TEQUILA-seq uncovers transcript isoforms and RNA mechanisms associated with human health and disease.
- Feng Wang
- , Yang Xu
- & Lan Lin
-
Article
| Open Access spinDrop: a droplet microfluidic platform to maximise single-cell sequencing information content
spinDrop: a droplet microfluidic platform to maximise single-cell sequencing information content
Droplet microfluidics enables high-throughput single-cell sequencing, but often with increased noise. Here the authors report spinDrop (sorting picoinjection inDrop) to increase gene detection and reduce noise; they use this to generate a high-quality molecular atlas of mouse brain development.
- Joachim De Jonghe
- , Tomasz S. Kaminski
- & Florian Hollfelder
-
Article
| Open Access SONAR enables cell type deconvolution with spatially weighted Poisson-Gamma model for spatial transcriptomics
SONAR enables cell type deconvolution with spatially weighted Poisson-Gamma model for spatial transcriptomics
Spatial transcriptomics reveal cellular profiles with spatial context. Here the authors present SONAR, a computational model that utilizes spatial information to decipher cell types in tissues and validate on various spatial patterns and fine-mapped cell types in complex tissues.
- Zhiyuan Liu
- , Dafei Wu
- & Liang Ma
-
Article
| Open Access MAVS signaling is required for preventing persistent chikungunya heart infection and chronic vascular tissue inflammation
MAVS signaling is required for preventing persistent chikungunya heart infection and chronic vascular tissue inflammation
Mosquito-borne viruses are serious global public health threats associated with severe atypical cardiovascular manifestations. Here, the authors dissect how chikungunya virus directly infects cardiac tissue leading to heart disease and define key host pathways involved in viral cardiac persistence and tissue damage.
- Maria G. Noval
- , Sophie N. Spector
- & Kenneth A. Stapleford
-
Article
| Open Access Three-dimensional molecular architecture of mouse organogenesis
Three-dimensional molecular architecture of mouse organogenesis
Qu et al. present a detailed three-dimensional spatial transcriptome atlas of all major organs in the mouse embryo at E13.5, providing a better understanding of organ development and cellular interactions during mammalian development.
- Fangfang Qu
- , Wenjia Li
- & Guangdun Peng
-
Article
| Open Access Guided construction of single cell reference for human and mouse lung
Guided construction of single cell reference for human and mouse lung
Accurate cell-type identification is vital for single-cell analysis. Here, the authors develop a computational pipeline called “LungMAP CellRef” for efficient, automated cell-type annotation of normal and disease human and mouse lung single-cell datasets.
- Minzhe Guo
- , Michael P. Morley
- & Yan Xu
-
Article
| Open Access Increased interregional virus exchange and nucleotide diversity outline the expansion of chikungunya virus in Brazil
Increased interregional virus exchange and nucleotide diversity outline the expansion of chikungunya virus in Brazil
Chikungunya virus is endemic in Brazil and cases have been rapidly increasing in recent years. Here, the authors describe the expansion of a genomic surveillance program across the country allowing them to characterise the emergence and dispersal of two distinct subclades mainly seeded from the north eastern region.
- Joilson Xavier
- , Luiz Carlos Junior Alcantara
- & Marta Giovanetti
-
Article
| Open Access High throughput single cell long-read sequencing analyses of same-cell genotypes and phenotypes in human tumors
High throughput single cell long-read sequencing analyses of same-cell genotypes and phenotypes in human tumors
There is a need for methods that allow the analysis of single-cell long-read sequencing data without depending on known barcode lists or short-read sequencing. Here, the authors develop scNanoGPS, a tool that can independently deconvolute long reads into single cells and single molecules, and apply it on tumour and cell line data.
- Cheng-Kai Shiau
- , Lina Lu
- & Ruli Gao
-
Article
| Open Access Individual bat virome analysis reveals co-infection and spillover among bats and virus zoonotic potential
Individual bat virome analysis reveals co-infection and spillover among bats and virus zoonotic potential
Viral diversity and abundance in bats are incompletely understood. Here, analyzing individual bat viromes, the authors observe a high frequency of co-infection and spillover among the animals and identify viruses with the potential to infect humans or livestock.
- Jing Wang
- , Yuan-fei Pan
- & Mang Shi
-
Article
| Open Access nnSVG for the scalable identification of spatially variable genes using nearest-neighbor Gaussian processes
nnSVG for the scalable identification of spatially variable genes using nearest-neighbor Gaussian processes
The identification of top spatially variable genes is a key step in the analysis of spatially-resolved transcriptomics data. Here, the authors develop a scalable method based on nearest-neighbor Gaussian processes and evaluate performance compared to existing and baseline methods.
- Lukas M. Weber
- , Arkajyoti Saha
- & Stephanie C. Hicks
-
Article
| Open Access Maternal NAT10 orchestrates oocyte meiotic cell-cycle progression and maturation in mice
Maternal NAT10 orchestrates oocyte meiotic cell-cycle progression and maturation in mice
Generation of mature oocytes requires tight regulation of a discontinuous meiotic cell cycle. Here they show that the acetyltransferase Nat10 mediates modification of RNAs targeted for degradation and find that this process is essential for female oocyte meiosis and maturation.
- Xue Jiang
- , Yu Cheng
- & Jianqiang Bao
-
Article
| Open Access Multiplexed ddPCR-amplicon sequencing reveals isolated Plasmodium falciparum populations amenable to local elimination in Zanzibar, Tanzania
Multiplexed ddPCR-amplicon sequencing reveals isolated Plasmodium falciparum populations amenable to local elimination in Zanzibar, Tanzania
Sequencing malaria parasites from low density infections in small amounts of dried blood is important for large-scale genomic surveillance. Here, the authors develop and validate a highly multiplexed droplet digital PCR-based amplicon deep sequencing assay and apply it to data from Zanzibar, Tanzania.
- Aurel Holzschuh
- , Anita Lerch
- & Cristian Koepfli
-
Article
| Open Access Diploid and tetraploid genomes of Acorus and the evolution of monocots
Diploid and tetraploid genomes of Acorus and the evolution of monocots
Acorales is sister to all other monocots and contains only one family with just one genus, Acorus. Here, the authors assemble the genome of the diploid Ac. gramineus and the tetraploid Ac. calamus, reconstruct an ancestral monocot karyotype and gene toolkit, and discuss the origin and evolution of the two species and other monocots.
- Liang Ma
- , Ke-Wei Liu
- & Zhong-Jian Liu
-
Article
| Open Access The genome of Acorus deciphers insights into early monocot evolution
The genome of Acorus deciphers insights into early monocot evolution
Monocots are one of the most diverse and dominant clades of flowering plants. Here, the authors assemble the genome of Acorus gramineus, confirm its phylogenetic position as sister to the rest of monocots and reveal the absence of tau (τ) whole-genome duplication observed in the majority of monocot clades.
- Xing Guo
- , Fang Wang
- & Huan Liu
-
Comment
| Open Access Unravelling the genetic architecture of human complex traits through whole genome sequencing
Unravelling the genetic architecture of human complex traits through whole genome sequencing
Whole genome sequencing has enabled new insights into the genetic architecture of complex traits, especially through access to low-frequency and rare variation. This Comment highlights the key contributions from this technology and discusses considerations for its use and future perspectives.
- Ozvan Bocher
- , Cristen J. Willer
- & Eleftheria Zeggini
-
Article
| Open Access A global genomic analysis of Salmonella Concord reveals lineages with high antimicrobial resistance in Ethiopia
A global genomic analysis of Salmonella Concord reveals lineages with high antimicrobial resistance in Ethiopia
Authors carry out a longitudinal genomic analysis of Salmonella enterica serovar Concord isolates from various geographical locations, to reconstruct population diversity, evolution and antimicrobial resistance distribution.
- Wim L. Cuypers
- , Pieter Meysman
- & Sandra Van Puyvelde
-
Article
| Open Access Rare genetic variants impact muscle strength
Rare genetic variants impact muscle strength
Here, the authors provide an exome study of hand grip strength, a proxy of generalized muscle strength. They identify six exome-wide significant genes, with links to disease, and additivity of rare and common genetic variant effects on muscle strength.
- Yunfeng Huang
- , Dora Bodnar
- & Heiko Runz
-
Article
| Open Access Co-translational binding of importins to nascent proteins
Co-translational binding of importins to nascent proteins
Importins are known to facilitate nucleocytoplasmic transport and cytoplasmic chaperoning of some proteins. Here, the authors uncover that these proteins also act as co-translational chaperones for specific sets of proteins, for example ribonucleic acid binding factors.
- Maximilian Seidel
- , Natalie Romanov
- & Martin Beck
-
Article
| Open Access Systematic detection of tertiary structural modules in large RNAs and RNP interfaces by Tb-seq
Systematic detection of tertiary structural modules in large RNAs and RNP interfaces by Tb-seq
Compact RNA structural motifs control many aspects of gene expression, but methods for their identification are lacking. Here the authors present a sequencing-based terbium probing approach to detect complex 3D structural elements, which can be used to pinpoint potential riboregulatory elements.
- Shivali Patel
- , Alec N. Sexton
- & Anna Marie Pyle
-
Article
| Open Access A village in a dish model system for population-scale hiPSC studies
A village in a dish model system for population-scale hiPSC studies
Village cultures, where multiple stem cell lines are cultured in a single dish, provide an elegant solution for population-scale studies. Here, authors show the utility of village models – showing that expression heterogeneity is largely a result of line-specific effects and not village cultures.
- Drew R. Neavin
- , Angela M. Steinmann
- & Joseph E. Powell
-
Article
| Open Access PIE-seq: identifying RNA-binding protein targets by dual RNA-deaminase editing and sequencing
PIE-seq: identifying RNA-binding protein targets by dual RNA-deaminase editing and sequencing
Tracking protein-RNA interaction across cell types is challenging. Here, Ruan et al develop a dual-deaminase method called PIE-Seq, where protein targets are marked by both C-to-U and A-to-I RNA base editors, and apply it to 25 human RNA-binding proteins.
- Xiangbin Ruan
- , Kaining Hu
- & Xiaochang Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access MoS2 nanopore identifies single amino acids with sub-1 Dalton resolution
MoS2 nanopore identifies single amino acids with sub-1 Dalton resolution
Protein sequencing is one of the key aims of the nanopore field. Working toward this goal, here the authors report the direct identification of single amino acids in MoS2 nanopores with sub-1 Dalton resolution, as well as the discrimination of the amino acid isomers and amino acid phosphorylation.
- Fushi Wang
- , Chunxiao Zhao
- & Jiandong Feng
-
Article
| Open Access Single cell transcriptomics clarifies the basophil differentiation trajectory and identifies pre-basophils upstream of mature basophils
Single cell transcriptomics clarifies the basophil differentiation trajectory and identifies pre-basophils upstream of mature basophils
Single cell sequencing can be used to better characterize immune cell progenitors. Here the authors characterize CLEC12Ahi pre-basophils downstream of pre-basophil and mast cell progenitors (pre-BMPs) but upstream of mature basophils and this population includes basophil progenitors (BaPs).
- Kensuke Miyake
- , Junya Ito
- & Hajime Karasuyama
-
Article
| Open Access Cellular population dynamics shape the route to human pluripotency
Cellular population dynamics shape the route to human pluripotency
The contribution of cell-extrinsic factors during cellular reprogramming to human induced pluripotent stem cells has long been overlooked. Here, the authors show functional protein communication between reprogramming intermediates and the re-shaping of a permissive extracellular environment.
- Francesco Panariello
- , Onelia Gagliano
- & Nicola Elvassore
-
Article
| Open Access High-throughput single nucleus total RNA sequencing of formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded tissues by snRandom-seq
High-throughput single nucleus total RNA sequencing of formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded tissues by snRandom-seq
Formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded (FFPE) tissues constitute a vast and valuable patient material bank, but single nucleus RNAseq using such tissues is challenging. Here the authors develop a droplet-based method called snRandom-seq for high-throughput and sensitive single nucleus RNA-seq of FFPE samples.
- Ziye Xu
- , Tianyu Zhang
- & Yongcheng Wang
-
Article
| Open Access High-throughput and high-accuracy single-cell RNA isoform analysis using PacBio circular consensus sequencing
High-throughput and high-accuracy single-cell RNA isoform analysis using PacBio circular consensus sequencing
Long-read single-cell RNA isoform sequencing can elucidate the intricate landscape of alternative RNA splicing in individual cells, but it suffers from a low read throughput. Here, the authors develop circular consensus sequencing methods to allow high-throughput and high-accuracy single-cell RNA isoform sequencing.
- Zhuo-Xing Shi
- , Zhi-Chao Chen
- & Yi-Zhi Liu
-
Article
| Open Access Single-cell analysis reveals inflammatory interactions driving macular degeneration
Single-cell analysis reveals inflammatory interactions driving macular degeneration
Single-nucleus RNA-seq was used to profile 11 retinas with varying stages of age-related macular degeneration and 6 control retinas. The authors identified shared glial states across neurodegeneration, indicating that the retina provides a human system for investigating therapeutic approaches in neurodegeneration.
- Manik Kuchroo
- , Marcello DiStasio
- & Brian P. Hafler
-
Article
| Open Access Reconstruction of the cell pseudo-space from single-cell RNA sequencing data with scSpace
Reconstruction of the cell pseudo-space from single-cell RNA sequencing data with scSpace
Methods to reanalyze scRNA-seq data in a spatial perspective are vital but lacking. Here, the authors develop scSpace, an integrative method that uses ST data as spatial reference to reconstruct the pseudo-space of scRNA-seq data and identify spatially variable cell subpopulations, providing insights into spatial heterogeneity from scRNA-seq data.
- Jingyang Qian
- , Jie Liao
- & Xiaohui Fan
-
Article
| Open Access A massively parallel screening platform for converting aptamers into molecular switches
A massively parallel screening platform for converting aptamers into molecular switches
Efforts to convert aptamers into molecular switches using rational design are often unsuccessful. Here the authors describe a massively parallel screening-based strategy whereby millions of potential aptamer switches are synthesised, sequenced and screened directly on a flow-cell.
- Alex M. Yoshikawa
- , Alexandra E. Rangel
- & H. Tom Soh
-
Article
| Open Access The small and large intestine contain related mesenchymal subsets that derive from embryonic Gli1+ precursors
The small and large intestine contain related mesenchymal subsets that derive from embryonic Gli1+ precursors
Stromal cells are essential for intestinal homeostasis. Here the authors describe the phenotype, transcriptional profile and location of stromal cell subsets in the adult murine small intestine and colon lamina propria and demonstrate that these cells derive from Gli1+ precursors present in embryonic day 12.5 intestine.
- Simone Isling Pærregaard
- , Line Wulff
- & William W. Agace
-
Article
| Open Access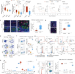 Targeting CXCL16 and STAT1 augments immune checkpoint blockade therapy in triple-negative breast cancer
Targeting CXCL16 and STAT1 augments immune checkpoint blockade therapy in triple-negative breast cancer
Chemotherapy priming sensitizes triple-negative breast cancers to immune checkpoint blockade. However, immune suppressive myeloid cells may impede its optimal effect. Here authors characterise the immune suppressive myeloid cells via single-cell analyses of immune cells from low dose chemotherapy treated breast tumours and identify STAT1 signalling as a regulator for immune suppressive state.
- Bhavana Palakurthi
- , Shaneann R. Fross
- & Siyuan Zhang

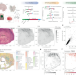 High-sensitive spatially resolved T cell receptor sequencing with SPTCR-seq
High-sensitive spatially resolved T cell receptor sequencing with SPTCR-seq