Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Predictors of the post-COVID condition following mild SARS-CoV-2 infection
Predictors of the post-COVID condition following mild SARS-CoV-2 infection
In this study, the authors investigate the incidence and risk factors for post-COVID condition among people who had a mild initial SARS-CoV-2 infection in Norway. They use national linked registry data including ~215,000 individuals with a positive SARS-CoV-2 test who were not hospitalised and followed them up for 180 days after infection.
- B-A. Reme
- , J. Gjesvik
- & K. Magnusson
-
Article
| Open Access Evidence of a causal and modifiable relationship between kidney function and circulating trimethylamine N-oxide
Evidence of a causal and modifiable relationship between kidney function and circulating trimethylamine N-oxide
TMAO is known to be atherothrombotic. Here the authors show that i) kidney function is the main determinant of serum TMAO, ii) TMAO increases kidney scarring with TGF-β1 signalling and iii) anti-diabetic drugs with reno-protective properties such as GLP1R agonists reduce plasma TMAO.
- Petros Andrikopoulos
- , Judith Aron-Wisnewsky
- & Marc-Emmanuel Dumas
-
Article
| Open Access Quantifying the causal impact of biological risk factors on healthcare costs
Quantifying the causal impact of biological risk factors on healthcare costs
Understanding the causal impact that risk factors have on healthcare cost is critical to evaluate healthcare interventions. Here, authors show that waist circumference, body mass index, and blood pressure have robust causal impact on healthcare cost.
- Jiwoo Lee
- , Sakari Jukarainen
- & Andrea Ganna
-
Article
| Open Access Bacteroides Fragilis in the gut microbiomes of Alzheimer’s disease activates microglia and triggers pathogenesis in neuronal C/EBPβ transgenic mice
Bacteroides Fragilis in the gut microbiomes of Alzheimer’s disease activates microglia and triggers pathogenesis in neuronal C/EBPβ transgenic mice
Gut dysbiosis contributes to Alzheimer’s disease (AD) pathogenesis, and Bacteroides strains are commonly enriched in AD gut microbiota. Here, the authors show that Bacteroides fragilis and its metabolites 12-hydroxy-heptadecatrienoic acid (12-HHTrE) and Prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) can mediate activation of microglia and induce AD pathogenesis in neuronal C/EBPβ transgenic mice.
- Yiyuan Xia
- , Yifan Xiao
- & Keqiang Ye
-
Article
| Open Access Associations of modern initial antiretroviral therapy regimens with all-cause mortality in people living with HIV in resource-limited settings: a retrospective multicenter cohort study in China
Associations of modern initial antiretroviral therapy regimens with all-cause mortality in people living with HIV in resource-limited settings: a retrospective multicenter cohort study in China
First-line integrase strand transfer inhibitors are commonly used for people with HIV. Here, Wu et al. report results from a multicenter cohort study in China observing significant differences in all-cause mortality among patients between various treatment groups.
- Xinsheng Wu
- , Guohui Wu
- & Huachun Zou
-
Article
| Open Access The challenge of population aging for mitigating deaths from PM2.5 air pollution in China
The challenge of population aging for mitigating deaths from PM2.5 air pollution in China
Estimating health burden of air pollution against the background of population aging is of significance for achieving Sustainable Development Goal 3.9. Here, the authors show that population aging is expected to be the leading contributor to increased deaths attributable to PM2.5 in China by 2035, which will counter the positive gains achieved by improvements in air pollution and healthcare.
- Fangjin Xu
- , Qingxu Huang
- & Brett A. Bryan
-
Article
| Open Access SARS-CoV-2 rapid antibody test results and subsequent risk of hospitalisation and death in 361,801 people
SARS-CoV-2 rapid antibody test results and subsequent risk of hospitalisation and death in 361,801 people
The value of SARS-CoV-2 lateral flow immunoassay tests for estimating individual disease risk is unclear. Here, the authors link testing data from the REACT-2 study in England to hospital and death records and show that vaccinated individuals with a negative LFIA test were at a higher risk of hospitalisation and death.
- Matthew Whitaker
- , Bethan Davies
- & Helen Ward
-
Article
| Open Access Effects of COVID-19 vaccination and previous infection on Omicron SARS-CoV-2 infection and relation with serology
Effects of COVID-19 vaccination and previous infection on Omicron SARS-CoV-2 infection and relation with serology
The relative protection against Omicron SARS-CoV-2 infection conferred by vaccination and previous infection are not fully understood. Here, the authors use data from a prospective cohort study in the Netherlands and show that hybrid immunity (vaccination plus previous infection) conferred strongest protection.
- Brechje de Gier
- , Anne J. Huiberts
- & Mirjam J. Knol
-
Article
| Open Access Genetic insights into resting heart rate and its role in cardiovascular disease
Genetic insights into resting heart rate and its role in cardiovascular disease
The genetics and clinical consequences of resting heart rate (RHR) remain incompletely understood. Here, the authors discover new genetic variants associated with RHR and find that higher genetically predicted RHR decreases risk of atrial fibrillation and ischemic stroke.
- Yordi J. van de Vegte
- , Ruben N. Eppinga
- & Pim van der Harst
-
Article
| Open Access Increasing number of long-lived ancestors marks a decade of healthspan extension and healthier metabolomics profiles
Increasing number of long-lived ancestors marks a decade of healthspan extension and healthier metabolomics profiles
Although human life expectancy has been increasing, time spent in good physical and cognitive health has not been rising at similar rate. Here, the authors show that both lifespan and healthspan are quantitatively linked to ancestral longevity, and that those from the longest-lived families have a healthier metabolomics profile before the onset of disease, highlighting the important role of the family in healthy survival.
- Niels van den Berg
- , Mar Rodríguez-Girondo
- & Marian Beekman
-
Article
| Open Access Circulating trans fatty acids are associated with prostate cancer in Ghanaian and American men
Circulating trans fatty acids are associated with prostate cancer in Ghanaian and American men
Analyses of the association between fatty acids and prostate cancer have often neglected African patients. Here, the authors analyse 24 circulating fatty acids in Ghanaian, African American, and European American men, and explore the associations with socio-demographic factors, diet, FADS1/2 locus, and prostate cancer.
- Tsion Zewdu Minas
- , Brittany D. Lord
- & Stefan Ambs
-
Article
| Open Access Nutritional redundancy in the human diet and its application in phenotype association studies
Nutritional redundancy in the human diet and its application in phenotype association studies
Studying human diet may help us identify measures to treat or prevent chronic diseases. Here, the authors discover the nutritional redundancy phenomenon in human diet and demonstrate its association with cardiovascular disease and type 2 diabetes.
- Xu-Wen Wang
- , Yang Hu
- & Yang-Yu Liu
-
Article
| Open Access Causal associations between cardiorespiratory fitness and type 2 diabetes
Causal associations between cardiorespiratory fitness and type 2 diabetes
Being fit has been linked to a lower risk of type 2 diabetes, but it is unclear whether this relationship is causal. Using large scale studies with genetic data and measurements of cardiorespiratory fitness, the authors show evidence that higher genetically predicted fitness is causally associated with lower risk of type 2 diabetes independent of adiposity.
- Lina Cai
- , Tomas Gonzales
- & Nicholas J. Wareham
-
Article
| Open Access Longitudinal body mass index and cancer risk: a cohort study of 2.6 million Catalan adults
Longitudinal body mass index and cancer risk: a cohort study of 2.6 million Catalan adults
Here, the authors show that longer duration and greater degree of overweight and obesity during early adulthood as well as younger age of onset of a high body mass index are associated with a higher risk of 18 cancer types.
- Martina Recalde
- , Andrea Pistillo
- & Talita Duarte-Salles
-
Article
| Open Access UBAP2 plays a role in bone homeostasis through the regulation of osteoblastogenesis and osteoclastogenesis
UBAP2 plays a role in bone homeostasis through the regulation of osteoblastogenesis and osteoclastogenesis
The authors identify UBAP2 as a novel osteoporosis susceptibility gene by performing association studies focusing on coding regions of the genome, and report that it plays a role in bone homeostasis through the regulation of bone remodelling.
- Jeonghyun Kim
- , Bo-Young Kim
- & Seon-Yong Jeong
-
Article
| Open Access Leveraging football accelerometer data to quantify associations between repetitive head impacts and chronic traumatic encephalopathy in males
Leveraging football accelerometer data to quantify associations between repetitive head impacts and chronic traumatic encephalopathy in males
The relationship between the components of repetitive head impacts and chronic traumatic encephalopathy (CTE) remains unclear. Here, the authors use American football helmet sensor data to show that duration of play, cumulative head impacts and linear and rotational accelerations are significantly associated with CTE pathology.
- Daniel H. Daneshvar
- , Evan S. Nair
- & Jesse Mez
-
Article
| Open Access Natural history of long-COVID in a nationwide, population cohort study
Natural history of long-COVID in a nationwide, population cohort study
The long-term natural history of long-COVID is not well understood. In this population-based cohort study from Scotland, the authors describe symptom prevalence and health-related quality of life up to 18 months after a positive SARS-CoV-2 test and compare with matched test-negative controls.
- Claire E. Hastie
- , David J. Lowe
- & Jill P. Pell
-
Article
| Open Access Immune resilience despite inflammatory stress promotes longevity and favorable health outcomes including resistance to infection
Immune resilience despite inflammatory stress promotes longevity and favorable health outcomes including resistance to infection
The response to infectious and inflammatory challenges differs among people but the reasons for this are poorly understood. Here the authors explore the impact of variables such as age, sex, and the capacity for controlling inflammation and maintaining immunocompetence, linking this capacity to favourable health outcomes and lifespan.
- Sunil K. Ahuja
- , Muthu Saravanan Manoharan
- & Weijing He
-
Article
| Open Access Identification of BRCA1/2 mutation female carriers using circulating microRNA profiles
Identification of BRCA1/2 mutation female carriers using circulating microRNA profiles
BRCA1/2 mutations are known to increase risk of breast and ovarian cancer but carrier status in healthy individuals is unknown without genetic testing. Here, the authors created a circulating miRNA signature to predict BRCA1/2 carrier status in healthy individuals to aid the decision process on genetic testing.
- Kevin Elias
- , Urszula Smyczynska
- & Dipanjan Chowdhury
-
Article
| Open Access Elevated plasma complement factor H related 5 protein is associated with venous thromboembolism
Elevated plasma complement factor H related 5 protein is associated with venous thromboembolism
Improved biomarker-based tools for diagnosis and risk prediction of venous thromboembolism (VTE) are needed. Here, the authors show that Complement Factor H Related 5 protein, a regulator of the alternative pathway of complement activation, is a VTE-associated plasma biomarker in 5 independent cohorts.
- Maria Jesus Iglesias
- , Laura Sanchez-Rivera
- & Jacob Odeberg
-
Article
| Open Access Evaluating the use of blood pressure polygenic risk scores across race/ethnic background groups
Evaluating the use of blood pressure polygenic risk scores across race/ethnic background groups
Here, the authors assess performance and limitations to polygenic risk scores in different race/ethnic groups. They find that polygenic risk score performance improves with diverse training data, and a better understanding of varying genetic backgrounds, social and environmental factors, and gene-environment interactions, is needed to enhance PRS performance for all groups.
- Nuzulul Kurniansyah
- , Matthew O. Goodman
- & Tamar Sofer
-
Article
| Open Access The contributions of mitochondrial and nuclear mitochondrial genetic variation to neuroticism
The contributions of mitochondrial and nuclear mitochondrial genetic variation to neuroticism
Genetic variation in mitochondrial DNA can influence human traits, but it is not as well studied in association with complex traits. Here, the authors find associations between mitochondrial haplogroups and genetic variation and neuroticism.
- Charley Xia
- , Sarah J. Pickett
- & W. David Hill
-
Article
| Open Access Comparative mRNA booster effectiveness against death or hospitalization with COVID-19 pneumonia across at-risk US Veteran populations
Comparative mRNA booster effectiveness against death or hospitalization with COVID-19 pneumonia across at-risk US Veteran populations
mRNA boosters have been shown to be effective against severe COVID-19 illness. In this work, the authors show that in high-risk populations, three doses of mRNA-1273 vaccine instead of BNT162b2 vaccine conferred a small benefit against death or hospitalization with COVID-19 pneumonia.
- J. Daniel Kelly
- , Samuel Leonard
- & Salomeh Keyhani
-
Comment
| Open AccessStakeholder alliances are essential to reduce the scourge of plastic pollution
Progress to reduce plastic pollution has been painfully slow and the consequent damage to the natural environment and to human health is likely to increase further. This has been because the views and ways of working of four distinct stakeholder communities are not sufficiently well integrated. (1) Scientists, (2) industry, (3) society at large and (4) those making policy and legislation must in future find ways to work together.
- Richard S. Lampitt
- , Stephen Fletcher
- & Adrian Whyle
-
Article
| Open Access Deep learning to estimate lung disease mortality from chest radiographs
Deep learning to estimate lung disease mortality from chest radiographs
Risk assessment of lung disease mortality is currently limited. Here, authors show that deep learning can estimate lung disease mortality from a chest x-ray beyond risk factors, which may help to identify individuals at risk in screening and cancer populations.
- Jakob Weiss
- , Vineet K. Raghu
- & Hugo J.W.L. Aerts
-
Article
| Open Access Prioritization of potential causative genes for schizophrenia in placenta
Prioritization of potential causative genes for schizophrenia in placenta
The placenta has been proposed to be potentially relevant to schizophrenia risk. Here, the authors use the genetically predicted transcriptome to identify genes expressed in the placenta that could be involved in schizophrenia.
- Gianluca Ursini
- , Pasquale Di Carlo
- & Daniel R. Weinberger
-
Article
| Open Access Germline modifiers of the tumor immune microenvironment implicate drivers of cancer risk and immunotherapy response
Germline modifiers of the tumor immune microenvironment implicate drivers of cancer risk and immunotherapy response
The contribution of genetic factors to the tumour immune microenvironment (TIME) remains to be investigated. Here, the authors suggest the role of TIME eQTLs for target genes involved in reversing immune suppressive features.
- Meghana Pagadala
- , Timothy J. Sears
- & Hannah Carter
-
Article
| Open Access State-level macro-economic factors moderate the association of low income with brain structure and mental health in U.S. children
State-level macro-economic factors moderate the association of low income with brain structure and mental health in U.S. children
Lower income is associated with smaller hippocampal volume and mental health problems. Here, the authors show that this association is weaker in areas of the United States that are less expensive or that have a stronger social safety net.
- David G. Weissman
- , Mark L. Hatzenbuehler
- & Katie A. McLaughlin
-
Article
| Open Access Spatiotemporal distribution of power outages with climate events and social vulnerability in the USA
Spatiotemporal distribution of power outages with climate events and social vulnerability in the USA
The authors find within-day, seasonal, and regional differences in county-level power outages from 2018–2020. Outages commonly co-occur with climate events. Counties in the south and Michigan faced high social and medical vulnerabilities and outages.
- Vivian Do
- , Heather McBrien
- & Joan A. Casey
-
Perspective
| Open Access A precision environmental health approach to prevention of human disease
A precision environmental health approach to prevention of human disease
Precision environmental health leverages environmental and system-level data to understand underlying environmental causes of disease, identify biomarkers of exposure, and develop new prevention and intervention strategies. In this Perspective, the authors provide real-life illustrations of the utility of precision environmental health approaches and identify current challenges in the field.
- Andrea Baccarelli
- , Dana C. Dolinoy
- & Cheryl Lyn Walker
-
Article
| Open Access Health disparities among older adults following tropical cyclone exposure in Florida
Health disparities among older adults following tropical cyclone exposure in Florida
Tropical cyclones pose a significant threat to human health. Here, authors show associations between tropical cyclones and risk of cause-specific hospitalizations, with elevated risks according to neighborhood-level poverty, homeownership and urbanicity.
- K. Burrows
- , G. B. Anderson
- & M. L. Bell
-
Article
| Open Access Antimicrobial exposure is associated with decreased survival in triple-negative breast cancer
Antimicrobial exposure is associated with decreased survival in triple-negative breast cancer
Here, in a cohort of 772 women undergoing triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) therapy, the authors show that antimicrobial prescription during TNBC treatment associates with inferior overall and breast cancer-specific survival, in turn related to peripheral lymphocyte count and gut microbiome dysbiosis.
- Julia D. Ransohoff
- , Victor Ritter
- & Allison W. Kurian
-
Article
| Open Access Next-Generation Morphometry for pathomics-data mining in histopathology
Next-Generation Morphometry for pathomics-data mining in histopathology
Pathology diagnostics still rely on tissue morphology assessment by trained experts. Here, the authors perform deep-learning-based segmentation followed by large-scale feature extraction of histological images, i.e., next-generation morphometry, to enable outcome-relevant and disease-specific pathomics analysis of non-tumor kidney pathology.
- David L. Hölscher
- , Nassim Bouteldja
- & Peter Boor
-
Article
| Open Access Rapidly shifting immunologic landscape and severity of SARS-CoV-2 in the Omicron era in South Africa
Rapidly shifting immunologic landscape and severity of SARS-CoV-2 in the Omicron era in South Africa
Emergence of the Omicron BA.1/2 SARS-CoV-2 subvariants led to a wave of infection South Africa. Here, the authors use serological data from a prospective household study to characterise infection rates in the context of diverse immune histories following vaccination and exposure to different variants.
- Kaiyuan Sun
- , Stefano Tempia
- & Floidy Wafawanaka
-
Article
| Open Access Temperature-related mortality in China from specific injury
Temperature-related mortality in China from specific injury
Injury poses heavy burden on public health, but little evidence on the potential role of climate change on injury exists. Here, the authors collect data during 2013-2019 in six provinces of China to estimate the associations between temperature and injury mortality, and to project future mortality burden attributable to temperature change driven by climate change.
- Jianxiong Hu
- , Guanhao He
- & Wenjun Ma
-
Article
| Open Access Multi-organ imaging demonstrates the heart-brain-liver axis in UK Biobank participants
Multi-organ imaging demonstrates the heart-brain-liver axis in UK Biobank participants
While heart disease, dementia and liver disease often co-occur, multi-organ imaging is needed for deeper elucidation of these cross-organ links. Here, the authors use image-derived phenotypes to describe underlying associations between heart, brain and liver health in a large population cohort.
- Celeste McCracken
- , Zahra Raisi-Estabragh
- & Stefan Neubauer
-
Article
| Open Access Short-term exposure to wildfire-related PM2.5 increases mortality risks and burdens in Brazil
Short-term exposure to wildfire-related PM2.5 increases mortality risks and burdens in Brazil
To assess mortality risks and burdens associated with short-term exposure to wildfire-related PM2.5, the authors collect daily mortality data from 2000 to 2016 for 510 immediate regions in Brazil, the most wildfire-prone area.
- Tingting Ye
- , Rongbin Xu
- & Shanshan Li
-
Article
| Open AccessFood abundance in men before puberty predicts a range of cancers in grandsons
Nutritional conditions experienced early in life may influence the disease risk of future children and grandchildren. Here the authors report that food abundance among boys before puberty associates with the relative risk of a range of cancers in grandsons, but not in granddaughters.
- Denny Vågerö
- , Agneta Cederström
- & Gerard J. van den Berg
-
Article
| Open Access Genome-wide association study of REM sleep behavior disorder identifies polygenic risk and brain expression effects
Genome-wide association study of REM sleep behavior disorder identifies polygenic risk and brain expression effects
REM-sleep behavior disorder often precedes Parkinson’s disease or dementia. Here, the authors perform a genome-wide association study for REM-sleep behavior disorder, and discover how it potentially affects gene expression in the brain.
- Lynne Krohn
- , Karl Heilbron
- & Ziv Gan-Or
-
Article
| Open Access Nationwide geospatial analysis of county racial and ethnic composition and public drinking water arsenic and uranium
Nationwide geospatial analysis of county racial and ethnic composition and public drinking water arsenic and uranium
Environmental justice and drinking water in the US: Higher proportions of Hispanic/Latino, American Indian/Alaskan Native, and non-Hispanic Black residents were associated with higher public water arsenic and uranium at the county-level, findings differed by region.
- Irene Martinez-Morata
- , Benjamin C. Bostick
- & Anne E. Nigra
-
Article
| Open Access HTLV-1 infection of donor-derived T cells might promote acute graft-versus-host disease following liver transplantation
HTLV-1 infection of donor-derived T cells might promote acute graft-versus-host disease following liver transplantation
Acute graft versus host disease is a rare but deadly complication following liver transplantation. Author show here, upon screening a large cohort of liver transplanted patients and detailed immune phenotyping of samples from the 7 affected individuals and appropriate controls, that human T cell lymphotropic virus type I infection of donor immune cells appear to correlate with the occurrence of acute graft versus host disease.
- Chuan Shen
- , Yiyang Li
- & Qiang Xia
-
Article
| Open Access A population-based serological study of post-COVID syndrome prevalence and risk factors in children and adolescents
A population-based serological study of post-COVID syndrome prevalence and risk factors in children and adolescents
The post-acute impacts of COVID-19 in children and adolescents are not well understood. In this population-based study in Geneva, the authors find evidence of COVID-19-related symptom persistence beyond 12 weeks in adolescents, and identify chronic conditions and lower socioeconomic status as risk factors.
- Roxane Dumont
- , Viviane Richard
- & Idris Guessous
-
Article
| Open Access Validation of Food Compass with a healthy diet, cardiometabolic health, and mortality among U.S. adults, 1999–2018
Validation of Food Compass with a healthy diet, cardiometabolic health, and mortality among U.S. adults, 1999–2018
The Food Compass is a nutrient profiling system to characterize the healthfulness of diverse foods, beverages and meals. In a nationally representative cohort of 47,999 U.S. adults, the authors validate a person’s individual Food Compass Score against health outcomes.
- Meghan O’Hearn
- , Joshua Erndt-Marino
- & Dariush Mozaffarian
-
Article
| Open Access Multi-omics signatures of the human early life exposome
Multi-omics signatures of the human early life exposome
Environmental exposures in early life can have lasting health effects, but the molecular mechanisms are not well understood. Here, the authors discover >1000 associations between exposure factors and child multi-omics profiles, revealing signatures for diet, toxic chemical compounds, essential trace elements, and weather conditions.
- Léa Maitre
- , Mariona Bustamante
- & Martine Vrijheid
-
Article
| Open Access Disparate impacts on online information access during the Covid-19 pandemic
Disparate impacts on online information access during the Covid-19 pandemic
The COVID-19 pandemic has stimulated an important changes in online information access. Here, the authors analyse everyday web search interactions across 25,150 US ZIP codes revealing significant differences in how digital informational resources are mobilized by different communities.
- Jina Suh
- , Eric Horvitz
- & Tim Althoff
-
Article
| Open Access Variant-specific symptoms of COVID-19 in a study of 1,542,510 adults in England
Variant-specific symptoms of COVID-19 in a study of 1,542,510 adults in England
In this study, the authors assess changing symptom profiles associated with different SARS-CoV-2 variants from May 2020 to March 2022 in England. Using data from the REACT-1 study, they find that Omicron infection is more often associated with cold and influenza-like symptoms, and less with loss of taste and smell.
- Matthew Whitaker
- , Joshua Elliott
- & Paul Elliott
-
Article
| Open Access Associations of hurricane exposure and forecasting with impaired birth outcomes
Associations of hurricane exposure and forecasting with impaired birth outcomes
Early forecasts give people in a storm’s path time to prepare, but less is known about the cost to society when forecasts are incorrect. In this observational study, the authors examine over 700,000 births in the path of Hurricane Irene and find exposure was associated with impaired birth outcomes.
- Jacob Hochard
- , Yuanhao Li
- & Nino Abashidze
-
Article
| Open Access Amino acid variability, tradeoffs and optimality in human diet
Amino acid variability, tradeoffs and optimality in human diet
Amino acids are important components in a variety of human foods and diets. Here, the authors show trade-offs linking dietary intake of amino acids to human health and develop amino acid intake guidelines based on them.
- Ziwei Dai
- , Weiyan Zheng
- & Jason W. Locasale
-
Article
| Open Access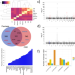 Shared genetic risk factors and causal association between psoriasis and coronary artery disease
Shared genetic risk factors and causal association between psoriasis and coronary artery disease
Coronary artery disease (CAD) and psoriasis are established comorbidities, however their molecular relationship remains unclear. Here, the authors performed trans-disease meta-analysis, highlighting four genetic loci with evidence of colocalization, and prioritized genes based on multiomic data integration.
- Matthew T. Patrick
- , Qinmengge Li
- & Lam C. Tsoi

 Analysis of 72,469 UK Biobank exomes links rare variants to male-pattern hair loss
Analysis of 72,469 UK Biobank exomes links rare variants to male-pattern hair loss