Featured
-
-
Article |
 RNA regulons in Hox 5′ UTRs confer ribosome specificity to gene regulation
RNA regulons in Hox 5′ UTRs confer ribosome specificity to gene regulation
Specialized ribosomes (with a particular protein composition) carry out translation of specific transcripts; analysis of Hox mRNA translation in mice reveals that unique RNA structural elements within their 5′ UTRs, including internal ribosome entry sites and translation inhibitory elements, are responsible for this specialized mode of translation.
- Shifeng Xue
- , Siqi Tian
- & Maria Barna
-
Letter |
 The complete structure of the large subunit of the mammalian mitochondrial ribosome
The complete structure of the large subunit of the mammalian mitochondrial ribosome
The structure of the 39S large mitoribosome subunit is solved by cryo-electron microscopy at an impressive 3.4 Å resolution, revealing the location of 50 ribosomal proteins, the peptidyl transferase centre, the tRNAs within this active site, and the nascent peptide chain within the exit tunnel.
- Basil J. Greber
- , Daniel Boehringer
- & Nenad Ban
-
Article |
 Structural basis for the inhibition of the eukaryotic ribosome
Structural basis for the inhibition of the eukaryotic ribosome
Whereas previous structural investigation of ribosome inhibitors has been done using the prokaryotic ribosome, this work presents X-ray crystal structures of the yeast ribosome in complex with 16 inhibitors including eukaryotic-specific inhibitors; the inhibitors all bind the mRNA or tRNA binding sites, larger molecules appear to target specifically the first elongation cycle.
- Nicolas Garreau de Loubresse
- , Irina Prokhorova
- & Marat Yusupov
-
Letter |
 Dynamic pathways of −1 translational frameshifting
Dynamic pathways of −1 translational frameshifting
To investigate the mechanism of frameshifting during messenger RNA translation, a technique was developed to monitor translation of single molecules in real time using Förster resonance energy transfer (FRET); ribosomes were revealed to pause tenfold longer than usual during elongation at the frameshifting sites.
- Jin Chen
- , Alexey Petrov
- & Joseph D. Puglisi
-
Article |
 Structural basis of the non-coding RNA RsmZ acting as a protein sponge
Structural basis of the non-coding RNA RsmZ acting as a protein sponge
A novel combined NMR and EPR spectroscopy approach reveals the structure and assembly mechanism of a 70-kDa bacterial ribonucleoprotein complex acting as a protein sponge in translational regulation.
- Olivier Duss
- , Erich Michel
- & Frédéric H.-T. Allain
-
Article |
 Architecture of the large subunit of the mammalian mitochondrial ribosome
Architecture of the large subunit of the mammalian mitochondrial ribosome
Cryo-electron microscopy combined with chemical crosslinking and mass spectrometry is used to determine the structure of the large subunit of the mammalian mitoribosome; this structure provides detailed structural insight, particularly of the molecular architecture of the polypeptide exit site, which has been structurally remodelled during evolution, presumably to help facilitate the membrane insertion of the highly hydrophobic proteins encoded by the mitochondrial genome.
- Basil J. Greber
- , Daniel Boehringer
- & Nenad Ban
-
Letter |
 Coupled GTPase and remodelling ATPase activities form a checkpoint for ribosome export
Coupled GTPase and remodelling ATPase activities form a checkpoint for ribosome export
Two proteins are identified in yeast that regulate the timing of pre-ribosome export from the nucleus; Nug2 binds pre-60S particles until they are ready for export, at which time Nug2 is replaced by the export adaptor Nmd3, enabling the export machinery to recognise the pre-ribosome that is ready to be transferred to the cytoplasm.
- Yoshitaka Matsuo
- , Sander Granneman
- & Ed Hurt
-
Letter |
 Hepatitis-C-virus-like internal ribosome entry sites displace eIF3 to gain access to the 40S subunit
Hepatitis-C-virus-like internal ribosome entry sites displace eIF3 to gain access to the 40S subunit
A sub-nanometre reconstruction of a 40S complex containing eIF3 and a hepatitis C virus (HCV)-like internal ribosome entry site (IRES) shows that the IRES displaces eIF3 from the 40S and sequesters it to gain access to the 40S subunit.
- Yaser Hashem
- , Amedee des Georges
- & Joachim Frank
-
Article |
 The initiation of mammalian protein synthesis and mRNA scanning mechanism
The initiation of mammalian protein synthesis and mRNA scanning mechanism
Three structures of the eukaryotic small ribosomal subunit in complex with initiator tRNA, mRNA and the initiation factors eIF1 and eIF1A have been solved; these structures offer insight into the contributions of the initiation factors, the mechanism by which mRNA is scanned, and the interactions that occur in the ribosome’s P site.
- Ivan B. Lomakin
- & Thomas A. Steitz
-
Letter |
 Unusual base pairing during the decoding of a stop codon by the ribosome
Unusual base pairing during the decoding of a stop codon by the ribosome
Here, the structure of the 30S ribosomal subunit and the 70S ribosome in complex with a messenger RNA with pseudouridine in the place of uridine reveals unexpected base pairing.
- Israel S. Fernández
- , Chyan Leong Ng
- & V. Ramakrishnan
-
Article |
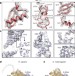 Structures of the human and Drosophila 80S ribosome
Structures of the human and Drosophila 80S ribosome
High-resolution cryo-EM density maps are used to present the structures of Drosophila and human 80S ribosomes in complex with eEF2, E-site transfer RNA and Stm1-like proteins, and reveal the presence of two additional structural layers in the ribosomes of metazoan eukaryotes.
- Andreas M. Anger
- , Jean-Paul Armache
- & Roland Beckmann
-
News & Views |
 All clear for ribosome landing
All clear for ribosome landing
The discovery of a dramatic structural rearrangement that is stabilized by an RNA scaffold helps to explain how nascent proteins are delivered for export from the cell cytoplasm. See Letter p.271
- Harris D. Bernstein
-
Letter |
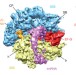 The complex of tmRNA–SmpB and EF-G on translocating ribosomes
The complex of tmRNA–SmpB and EF-G on translocating ribosomes
Stalled bacterial ribosomes can be rescued by interaction with SmpB protein and a highly structured transfer-messenger RNA, and a cryo-electron microscopy map of this complex now shows how EF-G-dependent translocation of this non-canonical ligand is facilitated by conformational changes in the ribosome and the transfer-messenger RNA.
- David J. F. Ramrath
- , Hiroshi Yamamoto
- & Christian M. T. Spahn
-
Letter |
 The anti-Shine–Dalgarno sequence drives translational pausing and codon choice in bacteria
The anti-Shine–Dalgarno sequence drives translational pausing and codon choice in bacteria
Internal Shine–Dalgarno-like sequences in bacterial messenger RNA determine the elongation rate of protein synthesis and synonymous codon usage.
- Gene-Wei Li
- , Eugene Oh
- & Jonathan S. Weissman
-
Letter |
 A new understanding of the decoding principle on the ribosome
A new understanding of the decoding principle on the ribosome
An integrated mechanism for decoding is proposed, based on six X-ray structures of the 70S ribosome determined at 3.1–3.4 Å resolution, modelling cognate or near-cognate states of the decoding centre at the proofreading step.
- Natalia Demeshkina
- , Lasse Jenner
- & Gulnara Yusupova
-
Article |
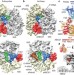 Structural basis of highly conserved ribosome recycling in eukaryotes and archaea
Structural basis of highly conserved ribosome recycling in eukaryotes and archaea
Cryo-electron-microscopy reconstructions of eukaryotic and archaeal ribosomes bound by ABCE1 and Pelota suggest a conserved mechanism for ribosome recycling.
- Thomas Becker
- , Sibylle Franckenberg
- & Roland Beckmann
-
Letter |
 Different substrate-dependent transition states in the active site of the ribosome
Different substrate-dependent transition states in the active site of the ribosome
- Stephan Kuhlenkoetter
- , Wolfgang Wintermeyer
- & Marina V. Rodnina
-
Letter |
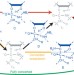 A two-step chemical mechanism for ribosome-catalysed peptide bond formation
A two-step chemical mechanism for ribosome-catalysed peptide bond formation
- David A. Hiller
- , Vipender Singh
- & Scott A. Strobel
-
Letter |
 Head swivel on the ribosome facilitates translocation by means of intra-subunit tRNA hybrid sites
Head swivel on the ribosome facilitates translocation by means of intra-subunit tRNA hybrid sites
During translation, tRNAs enter the ribosome and then move sequentially through three sites, known as A, P and E, as they transfer their attached amino acids onto the growing peptide chain. How the ribosome facilitates tRNA translocation between the sites remains largely unknown. Now a study uses multiparticle cryoelectron microscopy of a ribosome bound to the translation elongation factor, EF-G, to get information about tRNA movement. It identifies two new substates and sees that translocation is linked to unratcheting of the 30S ribosomal subunit.
- Andreas H. Ratje
- , Justus Loerke
- & Christian M. T. Spahn
-
News |
 Elusive protein factory mapped at last
Elusive protein factory mapped at last
Victory claimed in race to determine structure of eukaryotic ribosome.
- Daniel Cressey
-
Letter |
 Role of a ribosome-associated E3 ubiquitin ligase in protein quality control
Role of a ribosome-associated E3 ubiquitin ligase in protein quality control
The translation of messenger RNA that lacks stop codons results in the production of aberrant proteins, which may have harmful effects on the cell. It is unclear how eukaryotic cells eliminate these 'non-stop' proteins. Here it is shown that, in Saccharomyces cerevisiae, an E3 ubiquitin ligase called Ltn1 acts in the quality-control pathway. It associates with ribosomes and marks non-stop proteins with ubiquitin, which targets the proteins for degradation.
- Mario H. Bengtson
- & Claudio A. P. Joazeiro
-
Letter |
 A ribosome-associating factor chaperones tail-anchored membrane proteins
A ribosome-associating factor chaperones tail-anchored membrane proteins
Tail-anchored proteins have a single transmembrane domain at their carboxy termini and are post-translationally targeted to the endoplasmic reticulum via the cytosolic ATPase TRC40. These authors identify a conserved protein complex called Bat3 complex that is recruited to ribosomes, interacts with the transmembrane domain of newly released tail-anchored proteins and transfers them to TRC40 for subsequent targeting to the endoplasmic reticulum.
- Malaiyalam Mariappan
- , Xingzhe Li
- & Ramanujan S. Hegde
-
Article |
 Ribosome dynamics and tRNA movement by time-resolved electron cryomicroscopy
Ribosome dynamics and tRNA movement by time-resolved electron cryomicroscopy
During protein synthesis within the ribosome, transfer RNAs (tRNAs) move sequentially through different sites as their attached amino acids are transferred onto the growing protein chain. Large conformational movements accompany this process. Here, a staggering 1.9 million electron cryomicroscopy images of the ribosome have been processed to visualize these changes. The results reveal that the ribosome functions as a Brownian machine that couples spontaneous changes driven by thermal energy to directed movement.
- Niels Fischer
- , Andrey L. Konevega
- & Holger Stark
-
Letter |
 Principles of stop-codon reading on the ribosome
Principles of stop-codon reading on the ribosome
Stop codons in messenger RNA define when a protein sequence has been completely synthesized; such codons bind release factors (RFs), which cause the newly made protein to be released. Structures of RFs alone and in combination with the ribosome have been reported, but the energetics of the reaction in the presence of codons had not been determined. Here, molecular dynamics simulations of 14 termination complexes are used to define how termination is achieved and how the RFs distinguish different sequences.
- Johan Sund
- , Martin Andér
- & Johan Åqvist
-
Article |
 Real-time tRNA transit on single translating ribosomes at codon resolution
Real-time tRNA transit on single translating ribosomes at codon resolution
Single-molecule studies allow biological processes to be examined one molecule at a time, as they occur. Here, zero-mode waveguides have been used to concentrate reactions in zeptolitre-sized volumes, making it possible to study real-time translocation by the ribosome. The binding of transfer RNAs (tRNAs) to the ribosome could be followed; the results show that tRNA release from the exit site is uncoupled from tRNA binding to the aminoacyl-tRNA site.
- Sotaro Uemura
- , Colin Echeverría Aitken
- & Joseph D. Puglisi
-
News & Views |
 A ribosome in action
A ribosome in action
The manufacture of proteins by ribosomes involves complex interactions of diverse nucleic-acid and protein ligands. Single-molecule studies allow us, for the first time, to follow the synthesis of full-length proteins in real time.
- Susanne Brakmann
-
Letter |
 Encoding multiple unnatural amino acids via evolution of a quadruplet-decoding ribosome
Encoding multiple unnatural amino acids via evolution of a quadruplet-decoding ribosome
Although new amino acids with desirable properties can be devised, only a few have been successfully introduced into proteins by the cellular machinery. Even then, only one type of unnatural amino acid can be added to a given protein. Here, a new system has been designed that could allow the incorporation of up to 200 novel amino acids. The system involves an orthogonal ribosome that uses quadruplet — rather than triplet — codons, as well as orthogonal tRNA synthetase–tRNA pairs.
- Heinz Neumann
- , Kaihang Wang
- & Jason W. Chin

 Initiation of translation in bacteria by a structured eukaryotic IRES RNA
Initiation of translation in bacteria by a structured eukaryotic IRES RNA