Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Malaria surveillance reveals parasite relatedness, signatures of selection, and correlates of transmission across Senegal
Malaria surveillance reveals parasite relatedness, signatures of selection, and correlates of transmission across Senegal
Senegal has initiated a national sentinel surveillance program for malaria parasite genetics. Here, the authors report data from the first year of the program and use it to investigate local malaria incidence, patterns of transmission, and genetic loci under selection.
- Stephen F. Schaffner
- , Aida Badiane
- & Sarah K. Volkman
-
Comment
| Open Access The counterintuitive implications of superspreading diseases
The counterintuitive implications of superspreading diseases
The superspreading that characterized SARS and now COVID-19 can be rapidly quantified; however, its implications for outbreak control were never well understood. Recent studies point to its profound impact on outbreak dynamics and prospects for effective control of a future Disease X. These insights necessitate research into the mechanisms, impact and different modes of superspreading more widely.
- Bjarke Frost Nielsen
- , Kim Sneppen
- & Lone Simonsen
-
Comment
| Open AccessLessons for cross-species viral transmission surveillance from highly pathogenic avian influenza Korean cat shelter outbreaks
In this Comment, the authors describe recent outbreaks of highly pathogenic avian influenza in cat shelters in Seoul, South Korea. They discuss potential routes of transmission and describe implications for surveillance of spillover infections in animals in non-agricultural settings.
- Younjung Kim
- , Guillaume Fournié
- & Pierre Nouvellet
-
Article
| Open Access Cumulative effect of PM2.5 components is larger than the effect of PM2.5 mass on child health in India
Cumulative effect of PM2.5 components is larger than the effect of PM2.5 mass on child health in India
Health impact of air pollution is estimated using PM2.5 mass as exposure metric. Here authors show that the impacts on child health is underestimated in India using this metric relative to the cumulative impact of the various PM2.5 components.
- Ekta Chaudhary
- , Franciosalgeo George
- & Unnati Mehta
-
Article
| Open Access Effectiveness of the second COVID-19 booster against Omicron: a large-scale cohort study in Chile
Effectiveness of the second COVID-19 booster against Omicron: a large-scale cohort study in Chile
This study assesses the effectiveness of a second COVID-19 mRNA booster vaccine against severe disease using data from Chile. The authors find that the effectiveness of the second mRNA booster was high with a range of different background vaccination schemes, but there was evidence of waning over time.
- Alejandro Jara
- , Cristobal Cuadrado
- & Rafael Araos
-
Article
| Open Access Using drivers and transmission pathways to identify SARS-like coronavirus spillover risk hotspots
Using drivers and transmission pathways to identify SARS-like coronavirus spillover risk hotspots
Identification of areas with risk factors for spillover of viruses from animals to humans could assist with early detection of emerging infectious diseases. In this study, the authors characterise potential risks for spillover of SARS-like viruses from bats to humans and identify geographical regions in which multiple risk factors cluster together.
- Renata L. Muylaert
- , David A. Wilkinson
- & David T. S. Hayman
-
Article
| Open Access Mortality risks from a spectrum of causes associated with sand and dust storms in China
Mortality risks from a spectrum of causes associated with sand and dust storms in China
Sand and dust storms pose considerable health risks worldwide. Here, the authors conduct a nationwide multicenter time-series study to examine sand and dust storm-associated mortality risks.
- Can Zhang
- , Meilin Yan
- & Tiantian Li
-
Article
| Open Access Long-term health impacts of COVID-19 among 242,712 adults in England
Long-term health impacts of COVID-19 among 242,712 adults in England
The duration of symptomatic COVID-19 and its impacts on health and quality of life are not well understood. In this study, the authors report results from a survey of ~275,000 adults in England and find that persistent COVID-19 is relatively rare but is associated with poorer mental health and health-related quality of life.
- Christina J. Atchison
- , Bethan Davies
- & Paul Elliott
-
Article
| Open Access Individual level analysis of digital proximity tracing for COVID-19 in Belgium highlights major bottlenecks
Individual level analysis of digital proximity tracing for COVID-19 in Belgium highlights major bottlenecks
Digital proximity tracing apps were widely used during the COVID-19 pandemic but have not been thoroughly evaluated. Here, the authors use data from students in Leuven, Belgium and estimate that apps notified only ~4% exposed contacts, had a 1–2 day delay for notification, and identified fewer infected contacts than manual contact tracing.
- Caspar Geenen
- , Joren Raymenants
- & Emmanuel André
-
Article
| Open Access Epidemiology of Plasmodium malariae and Plasmodium ovale spp. in Kinshasa Province, Democratic Republic of Congo
Epidemiology of Plasmodium malariae and Plasmodium ovale spp. in Kinshasa Province, Democratic Republic of Congo
Non-falciparum malaria may cause a significant disease burden in highly endemic regions, but epidemiological data is limited. In this study, the authors estimate the incidence and prevalence of P. malariae, P. ovale spp., in Kinshasa, Democratic Republic of Congo and compare to P. falciparum, which known to be common in the region.
- Rachel Sendor
- , Kristin Banek
- & Jonathan B. Parr
-
Article
| Open Access Metabolic fingerprinting on retinal pigment epithelium thickness for individualized risk stratification of type 2 diabetes mellitus
Metabolic fingerprinting on retinal pigment epithelium thickness for individualized risk stratification of type 2 diabetes mellitus
The retina’s role in type 2 diabetes is not well understood. Here, the authors show that retinal pigment epithelium thickness, with its metabolic fingerprints, might offer improved predictability and clinical utility beyond traditional indicators.
- Shaopeng Yang
- , Zhuoting Zhu
- & Wei Wang
-
Article
| Open Access SARS-CoV-2 genomic surveillance in wastewater as a model for monitoring evolution of endemic viruses
SARS-CoV-2 genomic surveillance in wastewater as a model for monitoring evolution of endemic viruses
SARS-CoV-2 wastewater surveillance could provide an important means of monitoring population trends as clinical testing decreases. Here, the authors demonstrate the use of wastewater to track variants of concern through a sentinel wastewater surveillance system in South Africa.
- Mukhlid Yousif
- , Said Rachida
- & Kerrigan McCarthy
-
Article
| Open Access Viral kinetics of sequential SARS-CoV-2 infections
Viral kinetics of sequential SARS-CoV-2 infections
In this study, the authors compare the viral kinetics of first and second SARS-CoV-2 infections using data from an occupational surveillance scheme in the National Basketball League. They find that second infections tend to have a faster clearance time, and that clearance times in first and second infections were positively correlated.
- Stephen M. Kissler
- , James A. Hay
- & Yonatan H. Grad
-
Article
| Open Access Disentangling age, gender, and racial/ethnic disparities in multiple myeloma burden: a modeling study
Disentangling age, gender, and racial/ethnic disparities in multiple myeloma burden: a modeling study
Multiple myeloma (MM) is a haematological malignancy that is preceded by monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance (MGUS). Here, the authors use a mechanistic model fitted to surveillance data from the United States to investigate whether variation in MM is best explained by incidence of MGUS or rate of progression to MM.
- John H. Huber
- , Mengmeng Ji
- & Su-Hsin Chang
-
Article
| Open Access mRNA-1273 bivalent (original and Omicron) COVID-19 vaccine effectiveness against COVID-19 outcomes in the United States
mRNA-1273 bivalent (original and Omicron) COVID-19 vaccine effectiveness against COVID-19 outcomes in the United States
Bivalent mRNA COVID-19 vaccines have been developed to provide broader protection against SARS-CoV-2 variants. In this cohort study based on electronic health records from the United States, the authors estimate the effectiveness of bivalent, compared to monovalent, vaccines and no vaccination against a range of COVID-19-related outcomes.
- Hung Fu Tseng
- , Bradley K. Ackerson
- & Lei Qian
-
Article
| Open Access Breastfeeding and impact on childhood hospital admissions: a nationwide birth cohort in South Korea
Breastfeeding and impact on childhood hospital admissions: a nationwide birth cohort in South Korea
Benefits of breastfeeding are well established, but a comprehensive study about its impacts on hospitalizations is lacking. Here, the authors use Korean nationwide birth cohort data (n = 1,608,540) and find that breastfeeding for at least 6 months was associated with a lower risk for subsequent hospital admissions.
- Jeong-Seon Lee
- , Jae Il Shin
- & Dong Keon Yon
-
Comment
| Open AccessZoonotic malaria requires new policy approaches to malaria elimination
WHO guidelines for classification of malaria elimination in a country require that the risk of human infection from zoonotic, as well as nonzoonotic, malaria parasites is negligible. In this Comment, the authors discuss the implications of this policy for countries, such as Malaysia, with no recent reported nonzoonotic cases but ongoing zoonotic transmission.
- Kimberly M. Fornace
- , Chris J. Drakeley
- & Kamruddin Ahmed
-
Article
| Open Access Food inflation and child undernutrition in low and middle income countries
Food inflation and child undernutrition in low and middle income countries
The 21st Century has witnessed a series of global food crises, though little is known about how rising food prices affect child nutrition. The authors show that increases in the real price of food elevate the risk of a child being wasted, which in turn poses a serious risk for their survival.
- Derek Headey
- & Marie Ruel
-
Article
| Open Access Quantifying the causal impact of biological risk factors on healthcare costs
Quantifying the causal impact of biological risk factors on healthcare costs
Understanding the causal impact that risk factors have on healthcare cost is critical to evaluate healthcare interventions. Here, authors show that waist circumference, body mass index, and blood pressure have robust causal impact on healthcare cost.
- Jiwoo Lee
- , Sakari Jukarainen
- & Andrea Ganna
-
Article
| Open Access Previous immunity shapes immune responses to SARS-CoV-2 booster vaccination and Omicron breakthrough infection risk
Previous immunity shapes immune responses to SARS-CoV-2 booster vaccination and Omicron breakthrough infection risk
In this study, the authors investigate immune responses following a third (booster) SARS-CoV-2 vaccination dose in a cohort of healthcare professionals in Denmark. They find stronger immune responses among those with a prior infection, and correlation between lower antibody responses and higher risk of subsequent breakthrough infection.
- Laura Pérez-Alós
- , Cecilie Bo Hansen
- & Peter Garred
-
Article
| Open Access Benefit-cost analysis of coordinated strategies for control of rabies in Africa
Benefit-cost analysis of coordinated strategies for control of rabies in Africa
Control of rabies in Africa through mass vaccination of dogs may be compromised by cross-border transmission. Here, the authors use mathematical modelling and a benefit-cost analysis to demonstrate that coordinating rabies control measures across borders could lead to the elimination of dog rabies in Africa.
- A. Bucher
- , A. Dimov
- & J. Zinsstag
-
Article
| Open Access Highly pathogenic avian influenza A (H5N1) in marine mammals and seabirds in Peru
Highly pathogenic avian influenza A (H5N1) in marine mammals and seabirds in Peru
Highly pathogenic avian influenza (HPAI) A/H5N1 has recently emerged in the Americas and has been implicated in mass die-off events of pelicans and sea lions. Here, the authors report sampling and characterisation of HPAI A/H5N1 genomes from five marine mammal and seabird species in Peru.
- Mariana Leguia
- , Alejandra Garcia-Glaessner
- & Jesus Lescano
-
Article
| Open Access Effect of SARS-CoV-2 prior infection and mRNA vaccination on contagiousness and susceptibility to infection
Effect of SARS-CoV-2 prior infection and mRNA vaccination on contagiousness and susceptibility to infection
It is unclear whether SARS-CoV-2 immunity decreases transmission through reduction in contagiousness of cases or susceptibility of contacts. Here, the authors use testing and contact data from Geneva, Switzerland and find that increased protection of contacts was the main driver of reduced transmission.
- Denis Mongin
- , Nils Bürgisser
- & Delphine Sophie Courvoisier
-
Article
| Open Access Effects of public-health measures for zeroing out different SARS-CoV-2 variants
Effects of public-health measures for zeroing out different SARS-CoV-2 variants
China maintained a ‘zero-COVID’ policy from early in the pandemic until late 2022 that employed various public health interventions with the aim of COVID-19 containment. Here, the authors use data from 131 outbreaks in China to estimate the effects of a range of interventions against different SARS-CoV-2 variants in diverse settings.
- Yong Ge
- , Xilin Wu
- & Shengjie Lai
-
Article
| Open Access Accelerated evolution of SARS-CoV-2 in free-ranging white-tailed deer
Accelerated evolution of SARS-CoV-2 in free-ranging white-tailed deer
White-tailed deer are an important reservoir of SARS-CoV-2 in the USA and continued monitoring of the virus in deer populations is needed. In this genomic epidemiology study from Ohio, the authors show that the virus has been introduced multiple times to deer from humans, and that it has evolved faster in deer.
- Dillon S. McBride
- , Sofya K. Garushyants
- & Andrew S. Bowman
-
Article
| Open Access The challenge of population aging for mitigating deaths from PM2.5 air pollution in China
The challenge of population aging for mitigating deaths from PM2.5 air pollution in China
Estimating health burden of air pollution against the background of population aging is of significance for achieving Sustainable Development Goal 3.9. Here, the authors show that population aging is expected to be the leading contributor to increased deaths attributable to PM2.5 in China by 2035, which will counter the positive gains achieved by improvements in air pollution and healthcare.
- Fangjin Xu
- , Qingxu Huang
- & Brett A. Bryan
-
Article
| Open Access Gabapentinoid consumption in 65 countries and regions from 2008 to 2018: a longitudinal trend study
Gabapentinoid consumption in 65 countries and regions from 2008 to 2018: a longitudinal trend study
With their misuse potential, there is a need to understand the global consumption of gabapentinoids. Here, authors show a + 17.20% worldwide average annual increase in consumption of gabapentinoids from 2008 to 2018.
- Adrienne Y. L. Chan
- , Andrew S. C. Yuen
- & Kenneth K. C. Man
-
Editorial
| Open AccessPromoting the science of One Health
One Health refers to the interconnectedness of the health of humans, animals, and the environment. It recognises that coordination across sectors is needed for effective prevention, detection, and management of infectious disease threats. Although the concept of One Health is not new, it has gained increased prominence following the COVID-19 pandemic, prompting national and international institutions to adopt One Health policies aimed at preventing disease spillover
1 –4 . At Nature Communications, we have launched a Collection and call for papers in recognition of the need for better scientific evidence to support One Health policy ambitions. -
Article
| Open Access Preventing antimalarial drug resistance with triple artemisinin-based combination therapies
Preventing antimalarial drug resistance with triple artemisinin-based combination therapies
Triple artemisinin-based combination therapies have shown high efficacy for treatment of malaria in preliminary studies. Here, the authors use mathematical modelling to assess whether these therapies could also delay the emergence and spread of antimalarial drug resistance when compared against frontline therapies.
- Tran Dang Nguyen
- , Bo Gao
- & Ricardo Aguas
-
Article
| Open Access A small area model to assess temporal trends and sub-national disparities in healthcare quality
A small area model to assess temporal trends and sub-national disparities in healthcare quality
Here, authors present an approach to assess subnational healthcare quality, leveraging health facility survey data. The method jointly estimates indicators over space and time, and may provide insights to decision-makers and health service program managers.
- Adrien Allorant
- , Nancy Fullman
- & Robert C. Reiner Jr
-
Article
| Open Access Wastewater-based epidemiology predicts COVID-19-induced weekly new hospital admissions in over 150 USA counties
Wastewater-based epidemiology predicts COVID-19-induced weekly new hospital admissions in over 150 USA counties
Wastewater-based epidemiology is increasingly used to predict disease occurrence. Here, the authors use SARS-CoV-2 RNA concentrations in wastewater in machine learning models to predict COVID-19 related hospitalisation in the United States.
- Xuan Li
- , Huan Liu
- & Qilin Wang
-
Article
| Open Access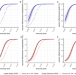 Estimating long-term vaccine effectiveness against SARS-CoV-2 variants: a model-based approach
Estimating long-term vaccine effectiveness against SARS-CoV-2 variants: a model-based approach
Evaluation of the effectiveness of COVID-19 vaccines is increasingly challenging due to high levels of exposure to infection and vaccination. Here, the authors use a model-based approach incorporating these factors and estimate that using a variant-matched rather than ancestral booster could prevent nearly twice as many hospitalisations and deaths over one year.
- Alexandra B. Hogan
- , Patrick Doohan
- & Azra C. Ghani
-
Article
| Open Access Herpes zoster vaccine safety in the Aotearoa New Zealand population: a self-controlled case series study
Herpes zoster vaccine safety in the Aotearoa New Zealand population: a self-controlled case series study
The herpes zoster vaccine live was approved in New Zealand in 2018 for use in older adults. This self-controlled case-series study uses whole-country electronic health record data to assess the risk of serious adverse events associated with the vaccine, with results supporting its safety.
- James F. Mbinta
- , Alex X. Wang
- & Colin R. Simpson
-
Article
| Open AccessPrevalence of diabetic retinopathy and vision-threatening diabetic retinopathy in adults with diabetes in China
Current data on the national distribution of diabetic retinopathy (DR) is lacking. Here, the authors show the national distribution, associated multi-level factors, and visual impairment of DR and vision-threatening DR in Chinese adults with diabetes.
- Xuhong Hou
- , Limin Wang
- & Weiping Jia
-
Article
| Open Access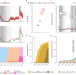 Epidemiological drivers of transmissibility and severity of SARS-CoV-2 in England
Epidemiological drivers of transmissibility and severity of SARS-CoV-2 in England
The COVID-19 pandemic has been characterised by periods of dominance of different SARS-CoV-2 variants. In this mathematical modelling study, the authors investigate the epidemiological properties of successive variants in England until early 2022 and quantify the impacts of control measures.
- Pablo N. Perez-Guzman
- , Edward Knock
- & Marc Baguelin
-
Article
| Open Access The role of vaccination and public awareness in forecasts of Mpox incidence in the United Kingdom
The role of vaccination and public awareness in forecasts of Mpox incidence in the United Kingdom
An outbreak of Mpox in the UK began in May 2022 and peaked in July. In this modelling study, the authors show that the decline in cases was likely due to behavioural changes among high-risk populations, whilst vaccination could prevent a rebound.
- Samuel P. C. Brand
- , Massimo Cavallaro
- & Matt J. Keeling
-
Article
| Open Access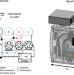 Real-time environmental surveillance of SARS-CoV-2 aerosols
Real-time environmental surveillance of SARS-CoV-2 aerosols
Rapid detection of respiratory pathogens circulating in indoor environments could facilitate improved infection prevention responses. In this proof-of-concept study, the authors develop a pathogen air quality monitor for real-time direct detection of SARS-CoV-2 aerosols and demonstrate its application in rooms of people with SARS-CoV-2 infections.
- Joseph V. Puthussery
- , Dishit P. Ghumra
- & Rajan K. Chakrabarty
-
Article
| Open Access Detecting temporal and spatial malaria patterns from first antenatal care visits
Detecting temporal and spatial malaria patterns from first antenatal care visits
Pregnant people visiting antenatal clinics may represent a useful sentinel surveillance population for monitoring infections such as malaria. Here, the authors investigate the potential of this approach by comparing malaria prevalence in pregnant people and children living in the same area of southern Mozambique.
- Arnau Pujol
- , Nanna Brokhattingen
- & Alfredo Mayor
-
Article
| Open Access Longitudinal body mass index and cancer risk: a cohort study of 2.6 million Catalan adults
Longitudinal body mass index and cancer risk: a cohort study of 2.6 million Catalan adults
Here, the authors show that longer duration and greater degree of overweight and obesity during early adulthood as well as younger age of onset of a high body mass index are associated with a higher risk of 18 cancer types.
- Martina Recalde
- , Andrea Pistillo
- & Talita Duarte-Salles
-
Article
| Open Access Genomic epidemiology of Vibrio cholerae during a mass vaccination campaign of displaced communities in Bangladesh
Genomic epidemiology of Vibrio cholerae during a mass vaccination campaign of displaced communities in Bangladesh
The Cox’s Bazar area of Bangladesh has received a large number of Forcibly Displaced Myanmar Nationals. Cholera outbreaks have been detected in the area, and here, the authors perform genomic surveillance of cholera in the refugee and non-refugee population to infer the risk of epidemic spread.
- Alyce Taylor-Brown
- , Mokibul Hassan Afrad
- & Firdausi Qadri
-
Article
| Open Access Practical intelligent diagnostic algorithm for wearable 12-lead ECG via self-supervised learning on large-scale dataset
Practical intelligent diagnostic algorithm for wearable 12-lead ECG via self-supervised learning on large-scale dataset
Intelligent diagnostic algorithms for ECG are becoming increasingly important to reduce the workload of cardiologists, enable telemedicine and real-time monitoring. Here, the authors show a model based on self-supervised learning that can classify 60 diagnostic terms for ECG.
- Jiewei Lai
- , Huixin Tan
- & Wei Yang
-
Article
| Open Access Multiplexed ddPCR-amplicon sequencing reveals isolated Plasmodium falciparum populations amenable to local elimination in Zanzibar, Tanzania
Multiplexed ddPCR-amplicon sequencing reveals isolated Plasmodium falciparum populations amenable to local elimination in Zanzibar, Tanzania
Sequencing malaria parasites from low density infections in small amounts of dried blood is important for large-scale genomic surveillance. Here, the authors develop and validate a highly multiplexed droplet digital PCR-based amplicon deep sequencing assay and apply it to data from Zanzibar, Tanzania.
- Aurel Holzschuh
- , Anita Lerch
- & Cristian Koepfli
-
Article
| Open Access Natural history of long-COVID in a nationwide, population cohort study
Natural history of long-COVID in a nationwide, population cohort study
The long-term natural history of long-COVID is not well understood. In this population-based cohort study from Scotland, the authors describe symptom prevalence and health-related quality of life up to 18 months after a positive SARS-CoV-2 test and compare with matched test-negative controls.
- Claire E. Hastie
- , David J. Lowe
- & Jill P. Pell
-
Article
| Open Access Predicting the antigenic evolution of SARS-COV-2 with deep learning
Predicting the antigenic evolution of SARS-COV-2 with deep learning
SARS-CoV-2’s rapid evolution threatens public health. Here, authors present a deep learning approach to forecast high-risk mutations that may appear in the future, aiding vaccine development and enhancing preparedness against future variants.
- Wenkai Han
- , Ningning Chen
- & Xin Gao
-
Article
| Open Access Augmented temperature fluctuation aggravates muscular atrophy through the gut microbiota
Augmented temperature fluctuation aggravates muscular atrophy through the gut microbiota
Higher diurnal temperature range in humans correlates with the prevalence of sarcopenia. Here, the authors show that fluctuated temperature exposure accelerates muscle atrophy and dampens exercise performance via altering microbiota composition in aged mice.
- Ya Liu
- , Yifan Guo
- & Yan Huang
-
Article
| Open Access No evidence of sustained nonzoonotic Plasmodium knowlesi transmission in Malaysia from modelling malaria case data
No evidence of sustained nonzoonotic Plasmodium knowlesi transmission in Malaysia from modelling malaria case data
Plasmodium knowlesi is a zoonotic malaria parasite that can infect humans, but whether human-mosquito-human transmission occurs is not known. Here, the authors use data from Malaysia and show, through mathematical modelling, that sustained non-zoonotic transmission is unlikely to be occurring in this setting.
- Kimberly M. Fornace
- , Hillary M. Topazian
- & Chris Drakeley
-
Article
| Open Access Newborn metabolomic signatures of maternal per- and polyfluoroalkyl substance exposure and reduced length of gestation
Newborn metabolomic signatures of maternal per- and polyfluoroalkyl substance exposure and reduced length of gestation
Mechanisms of the impact of PFAS (also known as forever chemicals) on adverse birth outcomes remain largely unknown. Here, authors identified tissue neogenesis, neuroendocrine function, and redox homeostasis as imprints of prenatal PFAS exposures and reduced gestational age in the newborn metabolome.
- Kaitlin R. Taibl
- , Anne L. Dunlop
- & Donghai Liang
-
Article
| Open Access Evidence-driven spatiotemporal COVID-19 hospitalization prediction with Ising dynamics
Evidence-driven spatiotemporal COVID-19 hospitalization prediction with Ising dynamics
Amid the COVID-19 pandemic, accurate hospitalization predictions are vital. Here, the authors show that a deep learning model based on statistical mechanics is able to forecast hospitalizations, supporting targeted vaccination efforts.
- Junyi Gao
- , Joerg Heintz
- & Jimeng Sun
-
Article
| Open Access Comparative mRNA booster effectiveness against death or hospitalization with COVID-19 pneumonia across at-risk US Veteran populations
Comparative mRNA booster effectiveness against death or hospitalization with COVID-19 pneumonia across at-risk US Veteran populations
mRNA boosters have been shown to be effective against severe COVID-19 illness. In this work, the authors show that in high-risk populations, three doses of mRNA-1273 vaccine instead of BNT162b2 vaccine conferred a small benefit against death or hospitalization with COVID-19 pneumonia.
- J. Daniel Kelly
- , Samuel Leonard
- & Salomeh Keyhani

 Impact of vaccinations, boosters and lockdowns on COVID-19 waves in French Polynesia
Impact of vaccinations, boosters and lockdowns on COVID-19 waves in French Polynesia