Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Integrated proteogenomic and metabolomic characterization of papillary thyroid cancer with different recurrence risks
Integrated proteogenomic and metabolomic characterization of papillary thyroid cancer with different recurrence risks
Papillary thyroid cancers (PTC) generally have good prognosis, but their recurrence rate remains high. Here, the authors use proteogenomics and metabolomics to identify molecular features in PTC tumours and determine PTC subtypes that are associated with prognosis and potential targeted therapies.
- Ning Qu
- , Di Chen
- & Rongliang Shi
-
Article
| Open Access Pathogenic mutations of human phosphorylation sites affect protein–protein interactions
Pathogenic mutations of human phosphorylation sites affect protein–protein interactions
Here the authors characterise the impact of phosphorylation site mutations in intrinsically disordered regions (IDRs) on protein-protein interactions, highlighting the critical role of phosphorylation of IDRs in health and disease.
- Trendelina Rrustemi
- , Katrina Meyer
- & Matthias Selbach
-
Article
| Open Access Integrated proteomics reveals autophagy landscape and an autophagy receptor controlling PKA-RI complex homeostasis in neurons
Integrated proteomics reveals autophagy landscape and an autophagy receptor controlling PKA-RI complex homeostasis in neurons
The health of brain cells is known to depend on functional autophagy, but the details are unclear. Here, the authors perform systematic proteomic profiling of human and mouse neurons, delineating the landscape of autophagy degradation in brain.
- Xiaoting Zhou
- , You-Kyung Lee
- & Zhenyu Yue
-
Article
| Open Access Antigen-specific Fab profiling achieves molecular-resolution analysis of human autoantibody repertoires in rheumatoid arthritis
Antigen-specific Fab profiling achieves molecular-resolution analysis of human autoantibody repertoires in rheumatoid arthritis
Although many autoimmune diseases are characterized by the presence of autoantibodies, complete characterisation of autoantibody repertoires is lacking. Here, the authors introduce an autoantigen-specific Fab profiling method to show that the autoantibody repertoire in rheumatoid arthritis is diverse yet dominated only by a few clones.
- Eva Maria Stork
- , Danique M. H. van Rijswijck
- & Albert Bondt
-
Article
| Open Access A chemical proteomics approach for global mapping of functional lysines on cell surface of living cell
A chemical proteomics approach for global mapping of functional lysines on cell surface of living cell
Ligand discovery against membrane proteins has been a major challenge, mainly due to the peculiar nature of their natural habitat. Here, the authors designed a new chemical proteomic probe that targets the lysines exposed on the cell surface and developed a chemical proteomic strategy for global analysis of surface functionality in living cells.
- Ting Wang
- , Shiyun Ma
- & Haojie Lu
-
Article
| Open Access VISTA checkpoint inhibition by pH-selective antibody SNS-101 with optimized safety and pharmacokinetic profiles enhances PD-1 response
VISTA checkpoint inhibition by pH-selective antibody SNS-101 with optimized safety and pharmacokinetic profiles enhances PD-1 response
VISTA is a pH-dependent inhibitory checkpoint for T-cells that is abundant on myeloid lineage cells and antagonists of VISTA may successfully reinvigorate anti-tumour immunity. Here, the authors show that the antibody SNS-101, which is currently being investigated in humans in a clinical trial, is characterized by pH-sensitivity that endows it with favorable pharmacokinetic and safety profiles, and enhanced therapeutic effect when combined with PD-1 checkpoint inhibitors.
- Thomas Thisted
- , F. Donelson Smith
- & Edward H. van der Horst
-
Article
| Open Access ReLo is a simple and rapid colocalization assay to identify and characterize direct protein–protein interactions
ReLo is a simple and rapid colocalization assay to identify and characterize direct protein–protein interactions
Characterising interactions between proteins that are large and poorly soluble remains challenging. Here, the authors describe ReLo, a rapid and versatile eukaryotic cell culture-based method for detecting and studying direct interactions between structurally complex proteins.
- Harpreet Kaur Salgania
- , Jutta Metz
- & Mandy Jeske
-
Article
| Open Access Native-state proteomics of Parvalbumin interneurons identifies unique molecular signatures and vulnerabilities to early Alzheimer’s pathology
Native-state proteomics of Parvalbumin interneurons identifies unique molecular signatures and vulnerabilities to early Alzheimer’s pathology
Native state proteomics of PV interneurons revealed unique molecular features of high translational and metabolic activity, and enrichment of Alzheimer’s risk genes. Early amyloid pathology exerted unique effects on mitochondria, mTOR signaling and neurotransmission in PV neurons.
- Prateek Kumar
- , Annie M. Goettemoeller
- & Srikant Rangaraju
-
Article
| Open Access Remodeling of the postsynaptic proteome in male mice and marmosets during synapse development
Remodeling of the postsynaptic proteome in male mice and marmosets during synapse development
The proteomic changes that occur during synapse development are not fully understood. In this work, the authors characterise the postsynaptic proteome changes that occur during development in male mice and marmosets.
- Takeshi Kaizuka
- , Takehiro Suzuki
- & Toru Takumi
-
Article
| Open Access Bioorthogonal photocatalytic proximity labeling in primary living samples
Bioorthogonal photocatalytic proximity labeling in primary living samples
Studying subcellular proteomes in primary living cells is crucial for understanding health and disease. Here, the authors introduce CAT-S, a non-genetic method based on photocatalysis, enabling in situ deciphering of mitochondrial proteomes in primary cells from mouse tissues and human blood.
- Ziqi Liu
- , Fuhu Guo
- & Xinyuan Fan
-
Article
| Open Access Mutational scanning pinpoints distinct binding sites of key ATGL regulators in lipolysis
Mutational scanning pinpoints distinct binding sites of key ATGL regulators in lipolysis
ATGL is a key enzyme in intracellular lipolysis. Here, the authors use deep mutational scanning to define the determinants of protein interaction between ATGL and its regulatory partners, gaining insights into lipolysis mechanisms in cells.
- Johanna M. Kohlmayr
- , Gernot F. Grabner
- & Ulrich Stelzl
-
Article
| Open Access A universal molecular control for DNA, mRNA and protein expression
A universal molecular control for DNA, mRNA and protein expression
Multi-omics analyses powerfully combine gene expression and translation, however no available controls can be used across these techniques. Here the authors develop pREF, a universal control construct designed for use in DNA, RNA and protein analyses.
- Helen M. Gunter
- , Scott E. Youlten
- & Tim R. Mercer
-
Article
| Open Access One-Tip enables comprehensive proteome coverage in minimal cells and single zygotes
One-Tip enables comprehensive proteome coverage in minimal cells and single zygotes
Traditional proteomics methods are complex and resource-intensive. Here, the authors develop One-Tip, a highly simplified approach that enables efficient, sensitive, and comprehensive analysis across various sample types, from blood plasma to single cells.
- Zilu Ye
- , Pierre Sabatier
- & Jesper V. Olsen
-
Article
| Open Access Prediction of glycopeptide fragment mass spectra by deep learning
Prediction of glycopeptide fragment mass spectra by deep learning
Deep learning has achieved a notable success in proteomics and is now emerging in glycoproteomics. Here, the authors develop a neural network-based method to predict mass spectra of intact glycopeptides and demonstrate its potential in data-dependent and data-independent acquisition glycoproteomics.
- Yi Yang
- & Qun Fang
-
Article
| Open Access Simultaneous proteome localization and turnover analysis reveals spatiotemporal features of protein homeostasis disruptions
Simultaneous proteome localization and turnover analysis reveals spatiotemporal features of protein homeostasis disruptions
Protein function depends on their subcellular location and turnover rate. Here, the authors report a method to measure spatial and temporal proteome dynamics simultaneously, revealing compartment-specific protein turnover and translocation in cardiac cells under ER stress and carfilzomib treatment.
- Jordan Currie
- , Vyshnavi Manda
- & Edward Lau
-
Article
| Open Access AlphaPept: a modern and open framework for MS-based proteomics
AlphaPept: a modern and open framework for MS-based proteomics
Mass spectrometry-based proteomics faces the challenge of processing vast data amounts. Here, the authors introduce AlphaPept, an open-source, Python-based framework that offers high speed analysis and easy integration for large-scale proteome analysis.
- Maximilian T. Strauss
- , Isabell Bludau
- & Matthias Mann
-
Article
| Open Access OrthoID: profiling dynamic proteomes through time and space using mutually orthogonal chemical tools
OrthoID: profiling dynamic proteomes through time and space using mutually orthogonal chemical tools
Proteomics at the organelle contact site remains challenging due to the spatial and temporal dynamics of proteins. Here, the authors developed OrthoID, a mutually orthogonal dual enzymatic proteomics approach to explore the proteome at the contact site of the endoplasmic reticulum and mitochondria.
- Ara Lee
- , Gihyun Sung
- & Kimoon Kim
-
Article
| Open Access A transient protein folding response targets aggregation in the early phase of TDP-43-mediated neurodegeneration
A transient protein folding response targets aggregation in the early phase of TDP-43-mediated neurodegeneration
The etiology of TDP-43 proteinopathy in ALS and FTD is complex. Here, the authors show that prior to disease onset in the rNLS8 mouse model, cortex neurons elicit a transient increase in protective chaperones that combat TDP-43 aggregation.
- Rebecca San Gil
- , Dana Pascovici
- & Adam K. Walker
-
Article
| Open Access Spatiotemporal and direct capturing global substrates of lysine-modifying enzymes in living cells
Spatiotemporal and direct capturing global substrates of lysine-modifying enzymes in living cells
Here the authors report a strategy to directly capture substrates of lysine-modifying enzymes via post-translational modification (PTM)-acceptor residue crosslinking in living cells, enabling global profiling of substrates of PTM-enzymes and validation of PTM-sites in a straightforward manner.
- Hao Hu
- , Wei Hu
- & Xiao-Hua Chen
-
Comment
| Open Access Fudging the volcano-plot without dredging the data
Fudging the volcano-plot without dredging the data
Selecting omic biomarkers using both their effect size and their differential status significance (i.e., selecting the “volcano-plot outer spray”) has long been equally biologically relevant and statistically troublesome. However, recent proposals are paving the way to resolving this dilemma.
- Thomas Burger
-
Article
| Open Access Proteomic characterization identifies clinically relevant subgroups of soft tissue sarcoma
Proteomic characterization identifies clinically relevant subgroups of soft tissue sarcoma
The molecular characterisation of soft tissue sarcomas (STSs) across diverse populations remains crucial. Here, the authors perform a proteomics and phosphoproteomics analysis of 272 Chinese STS patients across 12 subtypes, and obtain insights related to progression, metastasis, and immune signatures.
- Shaoshuai Tang
- , Yunzhi Wang
- & Chen Ding
-
Article
| Open Access Proteome-Wide Identification of RNA-dependent proteins and an emerging role for RNAs in Plasmodium falciparum protein complexes
Proteome-Wide Identification of RNA-dependent proteins and an emerging role for RNAs in Plasmodium falciparum protein complexes
Ribonucleoprotein complexes play fundamental roles in many cellular processes. Here, the authors used a proteome-wide approach, R-DeeP, to identify protein complexes associated with RNA in the deadliest human malaria parasite, Plasmodium falciparum.
- Thomas Hollin
- , Steven Abel
- & Karine G. Le Roch
-
Article
| Open Access Pick-up single-cell proteomic analysis for quantifying up to 3000 proteins in a Mammalian cell
Pick-up single-cell proteomic analysis for quantifying up to 3000 proteins in a Mammalian cell
Single-cell proteomics is of fundamental importance to capture biological heterogeneity, while limited in proteome depth. Here, the authors develop a pick-up single-cell proteomic analysis (PiSPA) workflow to achieve a deep coverage of quantifying up to 3000 protein groups in a mammalian cell.
- Yu Wang
- , Zhi-Ying Guan
- & Qun Fang
-
Article
| Open Access Protein degradation by human 20S proteasomes elucidates the interplay between peptide hydrolysis and splicing
Protein degradation by human 20S proteasomes elucidates the interplay between peptide hydrolysis and splicing
Do proteasomes catalyze peptide splicing? Here, the authors develop and apply a method to identify spliced peptides produced from entire proteins, confirm that proteasomes produce a sizeable variety of cis-spliced peptides with well-defined characteristics, and show that non-spliced and spliced peptides are concentrated in hotspots.
- Wai Tuck Soh
- , Hanna P. Roetschke
- & Michele Mishto
-
Article
| Open Access Micropillar arrays, wide window acquisition and AI-based data analysis improve comprehensiveness in multiple proteomic applications
Micropillar arrays, wide window acquisition and AI-based data analysis improve comprehensiveness in multiple proteomic applications
Obtaining a comprehensive proteomic profile for complex samples is still an elusive task. Here, the authors present an LC-MS/MS workflow including micropillar arrays, wide isolation windows and AI-based data analysis to boost proteomic coverage and throughput for multiple proteomic samples.
- Manuel Matzinger
- , Anna Schmücker
- & Rupert L. Mayer
-
Article
| Open Access Nuclear and cytoplasmic specific RNA binding proteome enrichment and its changes upon ferroptosis induction
Nuclear and cytoplasmic specific RNA binding proteome enrichment and its changes upon ferroptosis induction
The reported assay shows a subcellular-specific RNA labeling method for efficient enrichment and deep profiling of nuclear and cytoplasmic RBPs, the authors apply this to investigate changes of subcellular-specific RBP-RNA interactions in ferroptosis.
- Haofan Sun
- , Bin Fu
- & Weijie Qin
-
Article
| Open Access Proteomic screens of SEL1L-HRD1 ER-associated degradation substrates reveal its role in glycosylphosphatidylinositol-anchored protein biogenesis
Proteomic screens of SEL1L-HRD1 ER-associated degradation substrates reveal its role in glycosylphosphatidylinositol-anchored protein biogenesis
The nature of SEL1L-HRD1 ERAD substrates remains unclear. Here, the authors identified ~100 endogenous substrates, and showed that SEL1L-HRD1 ERAD is indispensable for the activity of GPI transamidase complex and the biogenesis of GPI-anchored proteins.
- Xiaoqiong Wei
- , You Lu
- & Ling Qi
-
Article
| Open Access From interaction networks to interfaces, scanning intrinsically disordered regions using AlphaFold2
From interaction networks to interfaces, scanning intrinsically disordered regions using AlphaFold2
Here, the authors show that AlphaFold2 accurately predicts protein interfaces involving disordered regions. Combining different delimitations and sequence alignments increases the success rate, while scanning short overlapping fragments identifies binding sites.
- Hélène Bret
- , Jinmei Gao
- & Raphaël Guerois
-
Article
| Open Access Targeted treatment of injured nestmates with antimicrobial compounds in an ant society
Targeted treatment of injured nestmates with antimicrobial compounds in an ant society
Infected wounds pose a major mortality risk in animals and are common in predatory ants. Here, the authors show that M. analis ants apply antimicrobial compounds produced in the metapleural glands to treat infected wounds and reduce nestmate mortality.
- Erik. T. Frank
- , Lucie Kesner
- & Laurent Keller
-
Article
| Open Access Structure and dynamics of endogenous cardiac troponin complex in human heart tissue captured by native nanoproteomics
Structure and dynamics of endogenous cardiac troponin complex in human heart tissue captured by native nanoproteomics
The heterogenous nature and dynamics of endogenous protein complexes pose challenges for conventional structural biology techniques. Here, the authors develop a native nanoproteomics strategy for the enrichment and subsequent native top-down mass spectrometry (nTDMS) analysis of endogenous cardiac troponin (cTn) complex directly from human heart tissue.
- Emily A. Chapman
- , David S. Roberts
- & Ying Ge
-
Article
| Open Access Mapping protein states and interactions across the tree of life with co-fractionation mass spectrometry
Mapping protein states and interactions across the tree of life with co-fractionation mass spectrometry
Co-fractionation mass spectrometry (CF-MS) is a powerful technique for mapping protein interactions under physiological conditions. Here, the authors uniformly re-process 411 CF-MS experiments and carry out meta-analyses of protein abundance, protein-protein interactions, and phosphorylation sites in the resulting resource.
- Michael A. Skinnider
- , Mopelola O. Akinlaja
- & Leonard J. Foster
-
Article
| Open Access Profiling ubiquitin signalling with UBIMAX reveals DNA damage- and SCFβ-Trcp1-dependent ubiquitylation of the actin-organizing protein Dbn1
Profiling ubiquitin signalling with UBIMAX reveals DNA damage- and SCFβ-Trcp1-dependent ubiquitylation of the actin-organizing protein Dbn1
Using Xenopus egg extracts, the authors developed a mass spectrometry method (UBIMAX) to identify proteins ubiquitylated in response to defined DNA lesions. Highlighting UBIMAX’s versatility, they describe the ubiquitylation of the actin regulator Dbn1 in response to DNA double-strand breaks.
- Camilla S. Colding-Christensen
- , Ellen S. Kakulidis
- & Michael L. Nielsen
-
Article
| Open Access Proximity extracellular protein-protein interaction analysis of EGFR using AirID-conjugated fragment of antigen binding
Proximity extracellular protein-protein interaction analysis of EGFR using AirID-conjugated fragment of antigen binding
Extracellular protein-protein interactions (exPPIs) are essential for understanding the biological function of membrane receptor proteins. Here, the authors demonstrate the FabID technology as a new proximity biotinylation approach that can analyse exPPIs dynamically modulated by drugs and ligands.
- Kohdai Yamada
- , Ryouhei Shioya
- & Tatsuya Sawasaki
-
Article
| Open Access Selenium-based metabolic oligosaccharide engineering strategy for quantitative glycan detection
Selenium-based metabolic oligosaccharide engineering strategy for quantitative glycan detection
Metabolic oligosaccharide engineering (MOE) is a classical strategy for carbohydrate perception but suffers from glycan quantification. Here the authors develop a selenium-based metabolic oligosaccharide engineering strategy (SeMOE), based on elemental analysis, to quantitatively detect and visualize glycans both in vitro and in vivo.
- Xiao Tian
- , Lingna Zheng
- & Ran Xie
-
Article
| Open Access An integrated workflow for quantitative analysis of the newly synthesized proteome
An integrated workflow for quantitative analysis of the newly synthesized proteome
Analysis of newly synthesized proteins upon perturbation can provide detailed insights into immediate proteome remodeling, which drives cellular responses. Here, the authors report an optimized semi-automated workflow for the quantitative analysis of the newly synthesized proteome.
- Toman Borteçen
- , Torsten Müller
- & Jeroen Krijgsveld
-
Article
| Open Access Immunoproximity biotinylation reveals the axon initial segment proteome
Immunoproximity biotinylation reveals the axon initial segment proteome
The molecular composition of the axon initial segment (AIS) is not well defined. Here, the authors used a ratiometric immunoproximity labeling strategy on fixed wild-type rat neurons to identify the AIS proteome, including the scaffolding protein SCRIB.
- Wei Zhang
- , Yu Fu
- & Peng Zou
-
Article
| Open Access Quantitative proteomics defines mechanisms of antiviral defence and cell death during modified vaccinia Ankara infection
Quantitative proteomics defines mechanisms of antiviral defence and cell death during modified vaccinia Ankara infection
Modified vaccinia Ankara (MVA) virus is the vaccine deployed to curb mpox. Here the authors conduct a multiplexed proteomic analysis to quantify cellular and viral proteins throughout MVA virus infection of human fibroblasts and macrophages and see substantial remodelling of the host proteome.
- Jonas D. Albarnaz
- , Joanne Kite
- & Michael P. Weekes
-
Article
| Open Access A biotin targeting chimera (BioTAC) system to map small molecule interactomes in situ
A biotin targeting chimera (BioTAC) system to map small molecule interactomes in situ
Unbiased chemical biology strategies for direct readout of small molecule protein interactomes provide advantages over target-focused approaches. Here, the authors describe the BioTAC system, a network-scale small molecule guided proximity labeling platform, to rapidly identify ligand-target interactomes.
- Andrew J. Tao
- , Jiewei Jiang
- & Fleur M. Ferguson
-
Article
| Open Access Accurate de novo peptide sequencing using fully convolutional neural networks
Accurate de novo peptide sequencing using fully convolutional neural networks
De novo peptide sequencing allows the identification of peptides without requiring target databases. Here, the authors present PepNet, a convolutional neural network model for accurate de novo peptide sequencing that is capable of analysing large-scale proteomics data.
- Kaiyuan Liu
- , Yuzhen Ye
- & Haixu Tang
-
Article
| Open Access Bile proteome reveals biliary regeneration during normothermic preservation of human donor livers
Bile proteome reveals biliary regeneration during normothermic preservation of human donor livers
Normothermic machine perfusion (NMP) is increasingly used for preserving and evaluating donor livers before transplantation. Here, the authors demonstrate increased regenerative protein profiles in the bile of perfused livers considered suitable for transplantation, providing insight into the mechanisms linked to recovery of the biliary tree following ischemia-reperfusion injury.
- Adam M. Thorne
- , Justina C. Wolters
- & Vincent E. de Meijer
-
Article
| Open Access The SPOC proteins DIDO3 and PHF3 co-regulate gene expression and neuronal differentiation
The SPOC proteins DIDO3 and PHF3 co-regulate gene expression and neuronal differentiation
Death-inducer obliterator 3 (DIDO3) and PHD finger protein 3 (PHF3) are paralogue proteins that regulate transcription elongation by docking onto phosphorylated serine-2 in the C-terminal domain (CTD) of Pol II through their SPOC domains. Here the authors characterize the interplay of these proteins and show that they coregulate neuronal target genes.
- Johannes Benedum
- , Vedran Franke
- & Dea Slade
-
Article
| Open Access The protein interactome of the citrus Huanglongbing pathogen Candidatus Liberibacter asiaticus
The protein interactome of the citrus Huanglongbing pathogen Candidatus Liberibacter asiaticus
Research on the biology and pathogenicity of ‘Candidatus Liberibacter asiaticus’ (CLas), the bacterium that causes citrus Huanglongbing disease, is hampered by our inability to cultivate it in artificial media. Here, Carter et al. use a high-throughput yeast-two-hybrid screen to identify thousands of interactions between CLas proteins, thus providing insights into their potential functions.
- Erica W. Carter
- , Orlene Guerra Peraza
- & Nian Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Proteomic characterization of epithelial ovarian cancer delineates molecular signatures and therapeutic targets in distinct histological subtypes
Proteomic characterization of epithelial ovarian cancer delineates molecular signatures and therapeutic targets in distinct histological subtypes
The molecular phenotypic features of epithelial ovarian cancer (EOC) remain elusive. Here, the authors perform mass spectrometry-based proteomic profiling for 269 EOC patients and reveal molecularly distinct features and potential therapeutic targets among the histological subtypes of EOC.
- Ting-Ting Gong
- , Shuang Guo
- & Qi-Jun Wu
-
Article
| Open Access Plasma proteomic profiles predict individual future health risk
Plasma proteomic profiles predict individual future health risk
The predictive capability of future health risk using plasma proteomic profiles remains largely unexplored. Using 1461 proteins collected from 50k individuals, authors show proteins can derive much better or equivalent performance than established clinical indicators for more than 40 endpoints.
- Jia You
- , Yu Guo
- & Jin-Tai Yu
-
Article
| Open Access Time-resolved proteomic profiling reveals compositional and functional transitions across the stress granule life cycle
Time-resolved proteomic profiling reveals compositional and functional transitions across the stress granule life cycle
Stress granules (SGs) are dynamic compartments with a poorly characterized transition in composition and function during prolonged stress. In this study, the authors investigated the dynamic changes in SG constituents during acute to prolonged heat shock using time-resolved proteomic profiling.
- Shuyao Hu
- , Yufeng Zhang
- & Yun Bai
-
Article
| Open Access Evaluation of circulating plasma proteins in breast cancer using Mendelian randomisation
Evaluation of circulating plasma proteins in breast cancer using Mendelian randomisation
Proteomics of blood samples is a promising avenue for cancer diagnosis. Here, the authors conduct Mendelian randomisation analysis of protein levels across multiple cohorts, and identify 5 proteins that show promise as biomarkers for the long-term risk of breast cancer, and as potential drug targets.
- Anders Mälarstig
- , Felix Grassmann
- & Åsa K. Hedman
-
Article
| Open Access Improved in situ characterization of protein complex dynamics at scale with thermal proximity co-aggregation
Improved in situ characterization of protein complex dynamics at scale with thermal proximity co-aggregation
Vast majority of cellular activities are carried out by protein complexes that assembled dynamically in response to cellular needs and environmental cues. Here, the authors present Slim-TPCA, an effective and readily deployable strategy to unravel the functional roles of protein complexes en masse across various cellular processes.
- Siyuan Sun
- , Zhenxiang Zheng
- & Chris Soon Heng Tan
-
Article
| Open Access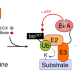 BioE3 identifies specific substrates of ubiquitin E3 ligases
BioE3 identifies specific substrates of ubiquitin E3 ligases
Here, the authors describe BioE3, a biotin-based method to discriminate direct substrates of ubiquitin E3 ligases of interest from mere interactors using proximity proteomics. BioE3 responds to chemical treatments, and works with RING- and HECT-type E3s, as well as ubiquitin-likes (e.g., SUMO).
- Orhi Barroso-Gomila
- , Laura Merino-Cacho
- & James D. Sutherland
-
Article
| Open Access Targetable lesions and proteomes predict therapy sensitivity through disease evolution in pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia
Targetable lesions and proteomes predict therapy sensitivity through disease evolution in pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia
The role of clonal evolution on the actionable proteome and response to therapy in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) remains unknown. Here, targeted sequencing and proteomic analysis of paired ALL diagnosis and relapsed samples revealed PARP1 as a potential therapeutic target.
- Amanda C. Lorentzian
- , Jenna Rever
- & Philipp F. Lange

 Cross-link assisted spatial proteomics to map sub-organelle proteomes and membrane protein topologies
Cross-link assisted spatial proteomics to map sub-organelle proteomes and membrane protein topologies