Featured
-
-
Article |
 Elementary excitations of single-photon emitters in hexagonal boron nitride
Elementary excitations of single-photon emitters in hexagonal boron nitride
Combining resonant inelastic X-ray scattering and photoluminescence spectroscopy, an elementary excitation in hexagonal-boron-nitride-based single-photon emitters has been demonstrated, giving rise to multiple regular harmonics that can explain the wide frequency range of these emitters.
- Jonathan Pelliciari
- , Enrique Mejia
- & Gabriele Grosso
-
Article |
 Observation of giant non-reciprocal charge transport from quantum Hall states in a topological insulator
Observation of giant non-reciprocal charge transport from quantum Hall states in a topological insulator
The authors report diode-like resistance in a non-magnetic topological insulator in the quantum Hall regime.
- Chunfeng Li
- , Rui Wang
- & Fengqi Song
-
Article |
 Understanding asymmetric switching times in accumulation mode organic electrochemical transistors
Understanding asymmetric switching times in accumulation mode organic electrochemical transistors
The turn-off time is generally faster than the turn-on time in accumulation mode organic electrochemical transistors (OECTs), but the mechanism is less understood. Here the authors find different transient behaviours of turn-on and turn-off in accumulation mode OECTs, and ion transport is the limiting factor of device kinetics.
- Jiajie Guo
- , Shinya E. Chen
- & David S. Ginger
-
Article |
 Uncovering the predictive pathways of lithium and sodium interchange in layered oxides
Uncovering the predictive pathways of lithium and sodium interchange in layered oxides
Ion exchange is a powerful method to access metastable materials for energy storage, but identifying lithium and sodium interchange in layered oxides remains challenging. Using such model materials, vacancy level and corresponding lithium preference are shown to be crucial for ion exchange pathway accessibility.
- Yu Han
- , Weihang Xie
- & Chong Liu
-
Article |
 Manipulating chiral spin transport with ferroelectric polarization
Manipulating chiral spin transport with ferroelectric polarization
The authors report a modulation of the magnon spin current by electric polarization reversal.
- Xiaoxi Huang
- , Xianzhe Chen
- & Ramamoorthy Ramesh
-
Article |
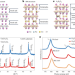 A correlated ferromagnetic polar metal by design
A correlated ferromagnetic polar metal by design
The authors report coexisting ferromagnetism, polar distortion and metallicity in quasi-two-dimensional Ca3Co3O8, providing a platform to exploit magnetoelectric coupling in a metallic system.
- Jianbing Zhang
- , Shengchun Shen
- & Pu Yu
-
Article |
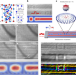 Experimental observation of current-driven antiskyrmion sliding in stripe domains
Experimental observation of current-driven antiskyrmion sliding in stripe domains
Electric current pulses are used to move antiskyrmions, by coupling them with a helical track.
- Zhidong He
- , Zhuolin Li
- & Baogen Shen
-
Article
| Open Access Harnessing instability for work hardening in multi-principal element alloys
Harnessing instability for work hardening in multi-principal element alloys
Harnessing premature necking produces a rapid multiplication of dislocations to interact with local chemical orders for work hardening in VCoNi alloy, achieving ductility of 20% and yield strength of 2 GPa during room-temperature and cryogenic deformation.
- Bowen Xu
- , Huichao Duan
- & Xiaolei Wu
-
Research Briefing |
 Drift-free iontronic sensing enabled by a creep-free polyelectrolyte elastomer
Drift-free iontronic sensing enabled by a creep-free polyelectrolyte elastomer
Soft pressure sensors drift under prolonged high stress because of the creep of soft materials, which causes inaccurate measurements. Now, through molecular-level design, a leakage-free and creep-free polyelectrolyte elastomer is synthesized, and an iontronic sensor using the polyelectrolyte elastomer shows very low signal drift under a high static pressure.
-
Article |
 A DNA origami device spatially controls CD95 signalling to induce immune tolerance in rheumatoid arthritis
A DNA origami device spatially controls CD95 signalling to induce immune tolerance in rheumatoid arthritis
A pH-responsive DNA origami device displays a precise geometric array of CD95 ligands to selectively induce activated immune cell death and elicit localized immune tolerance to alleviate rheumatoid arthritis.
- Ling Li
- , Jue Yin
- & Xiaoyuan Chen
-
Article |
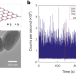 Solution-phase sample-averaged single-particle spectroscopy of quantum emitters with femtosecond resolution
Solution-phase sample-averaged single-particle spectroscopy of quantum emitters with femtosecond resolution
Combining fluorescence correlation spectroscopy and ultrafast spectroscopy, the sample-averaged dynamics of defects are studied with single-particle sensitivity in two-dimensional hexagonal boron nitride heterogeneous emitters.
- Jiaojian Shi
- , Yuejun Shen
- & Aaron M. Lindenberg
-
Article |
 1T′-transition metal dichalcogenide monolayers stabilized on 4H-Au nanowires for ultrasensitive SERS detection
1T′-transition metal dichalcogenide monolayers stabilized on 4H-Au nanowires for ultrasensitive SERS detection
High-phase-purity and stable 1T′-transition metal dichalcogenide monolayers are grown on 4H-Au nanowires by a facile and rapid wet-chemical method, enabling ultrasensitive surface-enhanced Raman scattering detection.
- Zijian Li
- , Li Zhai
- & Hua Zhang
-
Article |
 Ferroelastically protected reversible orthorhombic to monoclinic-like phase transition in ZrO2 nanocrystals
Ferroelastically protected reversible orthorhombic to monoclinic-like phase transition in ZrO2 nanocrystals
Ferroelectric phase stability is a pivotal challenge for fluorite-structure ferroelectrics. Using electron microscopy, a ferroelastically protected reversible polar-to-non-polar phase transition in ZrO2 is observed and the critical strain state to break the reversibility is measured.
- Xinyan Li
- , Zhuohui Liu
- & Lin Gu
-
News & Views |
 Goosebumps drive microstructures
Goosebumps drive microstructures
Light-driven artificial goosebumps enable the simple yet precise actuation of microstructures.
- Jaeil Kim
- & Hoon Eui Jeong
-
News & Views |
 “The unreasonable effectiveness of mathematics” in evading polaritonic losses
“The unreasonable effectiveness of mathematics” in evading polaritonic losses
Polaritonic losses, a root impediment to the many bounties of nanophotonics, may be evaded by resorting to the mathematics of synthetic frequencies offering ‘virtual’ gain.
- Dmitri N. Basov
- & Michael M. Fogler
-
News & Views |
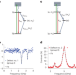 Identifying single spin defects in gallium nitride
Identifying single spin defects in gallium nitride
Single spin defects are identified in gallium nitride at room temperature, exhibiting a spin readout contrast of up to 30%.
- Jin-Shi Xu
- & Chuan-Feng Li
-
News & Views |
 Efficient blue emitter with a hoop
Efficient blue emitter with a hoop
Highly efficient matrix-free hyperfluorescent organic light-emitting diodes are constructed with remarkably supressed Dexter transfer utilizing narrowband blue emitters encapsulated with hopped alkyl chains.
- Yuewei Zhang
- & Lian Duan
-
News & Views |
 A soft crystalline packing with no metallic analogue
A soft crystalline packing with no metallic analogue
Pentagonal polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxane (POSS)-based giant atoms self-assemble into Frank–Kasper phases that have not been previously observed in soft-matter systems.
- Pengyu Chen
- & Kevin D. Dorfman
-
News & Views |
 A noticeable absence
A noticeable absence
Better control over the quality of materials dissipates doubts about charge order in infinite-layer nickelates and indicates that a previously observed superstructure is probably a spurious effect related to other crystalline phases. This finding strengthens the similarities between nickelates and cuprates.
- Giacomo Ghiringhelli
-
Review Article |
 Heterostructures coupling ultrathin metal carbides and chalcogenides
Heterostructures coupling ultrathin metal carbides and chalcogenides
Non-layered transition metal carbides (TMCs) and layered transition metal dichalcogenides (TMDs) can form various heterostructure configurations through chemical conversion. This Review highlights the progress in the fabrication and control of TMC/TMD heterostructures and the exotic properties arising from these interfaces.
- Alexander J. Sredenschek
- , David Emanuel Sanchez
- & Mauricio Terrones
-
Article |
 Light-induced electronic polarization in antiferromagnetic Cr2O3
Light-induced electronic polarization in antiferromagnetic Cr2O3
A light-induced polar electronic state is generated in Cr2O3; the symmetry reduction occurs on an ultrafast timescale, ruling out contributions from the lattice or spins.
- Xinshu Zhang
- , Tyler Carbin
- & Anshul Kogar
-
Perspective |
 Potential and challenges of computing with molecular materials
Potential and challenges of computing with molecular materials
Molecular materials for computing progress intensively but the performance and reliability still lag behind. Here the authors assess the current state of computing with molecular-based materials and describe two issues as the basis of a new computing technology: continued exploration of molecular electronic properties and process development for on-chip integration.
- R. Stanley Williams
- , Sreebrata Goswami
- & Sreetosh Goswami
-
News & Views |
 Diving into interlayer confinement
Diving into interlayer confinement
Noble gas atoms sandwiched in bilayer graphene are directly visualized with scanning transmission electron microscopy, revealing solid and liquid-like dynamics of two-dimensional cluster structures at room temperature under encapsulation.
- Tao Xu
- & Litao Sun
-
Article |
 Phase patterning of liquid crystal elastomers by laser-induced dynamic crosslinking
Phase patterning of liquid crystal elastomers by laser-induced dynamic crosslinking
Lack of local phase patterning in liquid crystal elastomers has hindered their broad implementation. The authors report a laser-induced dynamic crosslinking approach with allyl sulfide groups to achieve reconfigurable high-resolution patterning of multiple liquid crystalline phases in a single film.
- Seok Hwan Choi
- , Ju Hee Kim
- & Seung Hwan Ko
-
Research Briefing |
 Electrocaloric effects at a phase transition created by strain
Electrocaloric effects at a phase transition created by strain
Electrocaloric effects have not hitherto been experimentally studied at a phase transition created by strain. It is now shown that the continuous transition created by epitaxial strain in strontium titanate films greatly enhances electrocaloric effects over a wide range of temperatures, including room temperature.
-
Article |
 Effect of pre-intercalation on Li-ion diffusion mapped by topochemical single-crystal transformation and operando investigation
Effect of pre-intercalation on Li-ion diffusion mapped by topochemical single-crystal transformation and operando investigation
Pre-intercalation with alkali-metal ions is attractive for accessing higher reversible capacity and improved rate performance in Li-ion batteries. Topochemical single-crystal transformations in a tunnel-structured positive electrode are used to clarify the effect of pre-intercalation in modifying the host lattice and altering diffusion pathways.
- Yuting Luo
- , Joseph V. Handy
- & Sarbajit Banerjee
-
Article
| Open Access Highly reversible extrinsic electrocaloric effects over a wide temperature range in epitaxially strained SrTiO3 films
Highly reversible extrinsic electrocaloric effects over a wide temperature range in epitaxially strained SrTiO3 films
Electrocaloric effects are large in a limited set of materials that display hysteretic first-order phase transitions. Here epitaxial SrTiO3 thin films are strain engineered to achieve anhysteretic second-order phase transitions, with electrocaloric effects enhanced by one order of magnitude over bulk.
- S. Zhang
- , J. Deliyore-Ramírez
- & N. D. Mathur
-
Article |
 Creep-free polyelectrolyte elastomer for drift-free iontronic sensing
Creep-free polyelectrolyte elastomer for drift-free iontronic sensing
Conventional iontronic pressure sensors suffer from signal drift and inaccuracy owing to creep of soft materials and ion leakage. Here the authors report a leakage-free and creep-free polyelectrolyte-elastomer-based iontronic sensor that achieves a drift rate two to three orders of magnitude lower than those of conventional iontronic sensors.
- Yunfeng He
- , Yu Cheng
- & Chuan Fei Guo
-
Research Briefing |
 Semiconducting black phosphorus nanoribbons grown on insulating substrates
Semiconducting black phosphorus nanoribbons grown on insulating substrates
Single-crystal black phosphorus nanoribbons have been grown through chemical vapour transport, using black phosphorus nanoparticles as seeds. The nanoribbons orient exclusively along the zigzag direction and have good semiconductor properties that render them suitable for use as channel material in field-effect transistors.
-
Article |
 Inverse chirality-induced spin selectivity effect in chiral assemblies of π-conjugated polymers
Inverse chirality-induced spin selectivity effect in chiral assemblies of π-conjugated polymers
The authors report the inverse effect of chiral-induced spin selectivity in an organic material.
- Rui Sun
- , Kyung Sun Park
- & Dali Sun
-
Article |
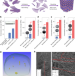 Near-room-temperature water-mediated densification of bulk van der Waals materials from their nanosheets
Near-room-temperature water-mediated densification of bulk van der Waals materials from their nanosheets
Strong bulk van der Waals materials are fabricated by the compressive moulding of two-dimensional nanosheets near room temperature through water-mediated densification, providing an energy-efficient way for synthesizing various van der Waals materials and a potential for tailoring compositions.
- Jiuyi Zhu
- , Fei Li
- & Hui-Ming Cheng
-
Article |
 Prediction of DNA origami shape using graph neural network
Prediction of DNA origami shape using graph neural network
Limited datasets hinder the accurate prediction of DNA origami structures. A data-driven and physics-informed approach for model training is presented using a graph neural network to facilitate the rapid virtual prototyping of DNA-based nanostructures.
- Chien Truong-Quoc
- , Jae Young Lee
- & Do-Nyun Kim
-
Article
| Open Access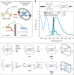 Suppression of Dexter transfer by covalent encapsulation for efficient matrix-free narrowband deep blue hyperfluorescent OLEDs
Suppression of Dexter transfer by covalent encapsulation for efficient matrix-free narrowband deep blue hyperfluorescent OLEDs
Suppressed Dexter transfer is needed to achieve efficient and stable hyperfluorescence, but complex matrices must be involved. A molecular design strategy has been proposed where Dexter transfer can be substantially reduced by an encapsulated terminal emitter, leading to ‘matrix-free’ hyperfluorescence.
- Hwan-Hee Cho
- , Daniel G. Congrave
- & Hugo Bronstein
-
News & Views |
 Mobile ion confinement for better thermoelectrics
Mobile ion confinement for better thermoelectrics
Restricting the directional segregation of mobile ions via strategic local ion confinement allows remarkable thermoelectric performance with better stability.
- Animesh Bhui
- & Kanishka Biswas
-
Article |
 Highly stabilized and efficient thermoelectric copper selenide
Highly stabilized and efficient thermoelectric copper selenide
Cu2Se is of interest for thermoelectrics as it is environmentally sustainable and has a high figure of merit ZT; however, copper ion migration impacts device stability. Here a co-doping strategy that combines steric and electrostatic effects is shown to improve device stability as well as improving ZT to 3.
- Haihua Hu
- , Yiwei Ju
- & Jing-Feng Li
-
Article |
 Lyophilized lymph nodes for improved delivery of chimeric antigen receptor T cells
Lyophilized lymph nodes for improved delivery of chimeric antigen receptor T cells
Implants made from patient-derived lyophilized lymph nodes loaded with chimeric antigen receptor T cells improve T cell delivery and inhibit tumour recurrence.
- Jiaqi Shi
- , Wei Wu
- & Zhen Gu
-
Article |
 An intelligent DNA nanodevice for precision thrombolysis
An intelligent DNA nanodevice for precision thrombolysis
An intelligent DNA nanodevice, composed of DNA origami nanosheets and a thrombin-responsive DNA fastener, accurately delivers the appropriate dose of tissue plasminogen activator following activation by distinct thrombosis events.
- Jue Yin
- , Siyu Wang
- & Lianhui Wang
-
News & Views |
 Unveiling the intricate moiré of moiré texture
Unveiling the intricate moiré of moiré texture
The atomic reconstruction and stacking arrangement in twisted trilayer graphene with a range of varying twist angles are elucidated by four-dimensional scanning transmission electron microscopy, revealing the hierarchical moiré of moiré superstructures that govern the structural symmetry at different length scales.
- Ruichun Luo
- & Wu Zhou
-
News & Views |
 A thicker skin for better immune evasion
A thicker skin for better immune evasion
Cancer cells adjust the composition of their glycocalyx to increase its thickness and create a physical barrier that shields them from immune recognition and engagement.
- Edward N. Schmidt
- & Matthew S. Macauley
-
Article
| Open Access Discovery of orbital ordering in Bi2Sr2CaCu2O8+x
Discovery of orbital ordering in Bi2Sr2CaCu2O8+x
An orbitally ordered state in Bi2Sr2CaCu2O8+x is revealed, which splits the energy levels of oxygen orbitals by ~50 meV.
- Shuqiu Wang
- , Niall Kennedy
- & Shane M. O’Mahony
-
Article
| Open Access Trapped O2 and the origin of voltage fade in layered Li-rich cathodes
Trapped O2 and the origin of voltage fade in layered Li-rich cathodes
Oxygen redox cathodes deliver higher energy densities than those based on transition metal redox but commonly exhibit voltage fade on extended cycling. The loss of O-redox capacity and voltage fade is shown to arise from a reduction in O2−/O2 redox process reversibility and O2 loss.
- John-Joseph Marie
- , Robert A. House
- & Peter G. Bruce
-
Article |
 Fibration of powdery materials
Fibration of powdery materials
A universal and non-destructive technique is developed to process diverse types of powder into micro- or nanofibres, providing flexibility for material design and applications based on functional particles.
- Hanwei Wang
- , Cheng Zeng
- & Huiqiao Li
-
Article |
 Seeded growth of single-crystal black phosphorus nanoribbons
Seeded growth of single-crystal black phosphorus nanoribbons
Single-crystal black phosphorus nanoribbons are grown uniformly on insulating substrates by chemical vapour transport growth with black phosphorus nanoparticles as seeds, demonstrating potential for application in nanoelectronic devices and the exploration of the exotic physics in black phosphorus.
- Hongya Wang
- , Yichen Song
- & Yuanbo Zhang
-
Article |
 Nanosecond solvation dynamics in a polymer electrolyte for lithium batteries
Nanosecond solvation dynamics in a polymer electrolyte for lithium batteries
Solvation dynamics at picosecond timescales critically affect charge transport in aqueous systems, but conflicting values have been reported for organic electrolytes. Lifetimes on the order of 1 ns for mixtures of organic polymer and lithium salt exhibiting ultraslow dynamics of solvation shell break-up are now reported.
- Neel J. Shah
- , Chao Fang
- & Nitash P. Balsara
-
Article |
 Nanofeather ruthenium nitride electrodes for electrochemical capacitors
Nanofeather ruthenium nitride electrodes for electrochemical capacitors
Fast charging is driving extensive research on enhanced electrodes for high-performance electrochemical capacitors and micro-supercapacitors. Thick ruthenium nitride pseudocapacitive films are shown to exhibit enhanced capacitance with a time constant of less than 6 s.
- Huy Dinh Khac
- , Grace Whang
- & Christophe Lethien
-
Article |
 High-density stable glasses formed on soft substrates
High-density stable glasses formed on soft substrates
Controlling substrate elasticity during physical vapour deposition allows access to high-density stable glasses that would otherwise be formed under prohibitively slow deposition conditions on rigid substrates.
- Peng Luo
- , Sarah E. Wolf
- & Zahra Fakhraai
-
Article
| Open Access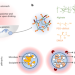 Drinkable in situ-forming tough hydrogels for gastrointestinal therapeutics
Drinkable in situ-forming tough hydrogels for gastrointestinal therapeutics
Sequential drinks of crosslinker and polymer solutions form a tough hydrogel in the stomach, enabling delivery of drugs and biologics in this harsh chemical environment.
- Gary W. Liu
- , Matthew J. Pickett
- & Giovanni Traverso
-
Article |
 Bridging length scales in organic mixed ionic–electronic conductors through internal strain and mesoscale dynamics
Bridging length scales in organic mixed ionic–electronic conductors through internal strain and mesoscale dynamics
Understanding mesoscale structure and dynamics in organic mixed ionic–electronic conductors is crucial. Mesoscale strain kinetics and structural hysteresis have been studied, and they uncover the coupling between charge carrier dynamics and mesoscale order in organic mixed ionic–electronic conductors.
- Ruiheng Wu
- , Dilara Meli
- & Christopher J. Takacs
-
Perspective |
 Creating chirality in the nearly two dimensions
Creating chirality in the nearly two dimensions
Two-dimensional (2D) materials, despite their small thickness, can display chirality that enables prominent asymmetric optical, electrical transport, and magnetic properties. This Perspective discusses the intriguing physics enabled by the structural chirality and the possible ways to create and control chirality in 2D materials.
- Hanyu Zhu
- & Boris I. Yakobson

 Evolution of the flat band and the role of lattice relaxations in twisted bilayer graphene
Evolution of the flat band and the role of lattice relaxations in twisted bilayer graphene