Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Measurement of the cosmic optical background using the long range reconnaissance imager on New Horizons
Measurement of the cosmic optical background using the long range reconnaissance imager on New Horizons
The cosmic optical background is an important cosmological observable. Here the authors show that a direct observation of the background brightness from the outer solar system can be obtained by the LORRI instrument aboard the New Horizons mission, on the basis of data acquired between Jupiter and Uranus.
- Michael Zemcov
- , Poppy Immel
- & Andrew R. Poppe
-
Article
| Open Access Oxidative 1,2-carboamination of alkenes with alkyl nitriles and amines toward γ-amino alkyl nitriles
Oxidative 1,2-carboamination of alkenes with alkyl nitriles and amines toward γ-amino alkyl nitriles
Difunctionalization of readily available alkenes is a powerful method to quickly build molecular complexity. Here the authors report a three-component, oxidative carboamination between alkenes, alkyl nitriles and amines, producingγ-amino alkyl nitriles.
- Yan-Yun Liu
- , Xu-Heng Yang
- & Jin-Heng Li
-
Article
| Open Access Light-assisted delithiation of lithium iron phosphate nanocrystals towards photo-rechargeable lithium ion batteries
Light-assisted delithiation of lithium iron phosphate nanocrystals towards photo-rechargeable lithium ion batteries
Photo-rechargable energy storage cells can provide plug-free power for various applications. Here the authors integrate a photo-absorbing dye complex with LiFePO4nanocrystals as a lithium-ion battery cathode in a two-electrode system demonstrating its photo-charging and galvanostatic discharging.
- Andrea Paolella
- , Cyril Faure
- & Karim Zaghib
-
Article
| Open Access Transient birefringence of liquids induced by terahertz electric-field torque on permanent molecular dipoles
Transient birefringence of liquids induced by terahertz electric-field torque on permanent molecular dipoles
Low-frequency structural dynamics in liquids and their underlying interactions are complex and challenging to resolve. Here, Sajadiet al. use intense terahertz fields to directly interrogate intermolecular modes in polar liquids by coupling the fields to their permanent molecular dipole moments.
- Mohsen Sajadi
- , Martin Wolf
- & Tobias Kampfrath
-
Article
| Open Access Characterizing rare fluctuations in soft particulate flows
Characterizing rare fluctuations in soft particulate flows
Soft particulate flows such as granular media are prone to fluctuations like jamming and avalanches. Here Rahbari et al. consider the statistics of rare fluctuations to identify an effective temperature which, unlike previous ones, is valid for packing fractions both near and far from the jamming point.
- S.H.E. Rahbari
- , A.A. Saberi
- & J. Vollmer
-
Article
| Open Access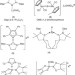 Easy access to nucleophilic boron through diborane to magnesium boryl metathesis
Easy access to nucleophilic boron through diborane to magnesium boryl metathesis
Organoboranes are widely employed in organic synthesis and typically are prepared using electrophilic boron sources. Here the authors report a route to nucleophilic boryl anions via organomagnesium-driven cleavage of boron-boron bonds.
- Anne-Frédérique Pécharman
- , Annie L. Colebatch
- & Catherine Weetman
-
Article
| Open Access Simulation of the NMR response in the pseudogap regime of the cuprates
Simulation of the NMR response in the pseudogap regime of the cuprates
An understanding of nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) in terms of magnetic susceptibility is still lacking. Here, Chenet al. numerically study the temperature and doping dependent Knight shift and spin relaxation time in NMR response, providing insight to understand the pseudogap in cuprates.
- Xi Chen
- , J. P. F. LeBlanc
- & Emanuel Gull
-
Article
| Open Access Chemical labelling for visualizing native AMPA receptors in live neurons
Chemical labelling for visualizing native AMPA receptors in live neurons
Visualizing neurotransmitter receptor traffic is fundamental to understanding brain functions, but the current imaging methods can compromise the process. Here, the authors synthesize small fluorescent probes to label endogenous glutamate receptors in cell cultures and brain tissues, without affecting their function.
- Sho Wakayama
- , Shigeki Kiyonaka
- & Itaru Hamachi
-
Article
| Open Access Prediction of intrinsic two-dimensional ferroelectrics in In2Se3 and other III2-VI3 van der Waals materials
Prediction of intrinsic two-dimensional ferroelectrics in In2Se3 and other III2-VI3 van der Waals materials
The development of devices based on 2D materials beyond graphene benefits from identifying compounds with diverse functional properties. Here, the authors predict computationally that 2D In2Se3and related materials are room temperature ferroelectrics with both in- and out-of-plane polarization.
- Wenjun Ding
- , Jianbao Zhu
- & Wenguang Zhu
-
Article
| Open Access Electrical spin injection and detection in molybdenum disulfide multilayer channel
Electrical spin injection and detection in molybdenum disulfide multilayer channel
MoS2 is a promising two-dimensional candidate for opto-electronic and spintronic applications. Here, the authors report electrical spin injection and detection in a few-layered MoS2 channel, demonstrating that the spin diffusion length is at least 235 nm in MoS2conduction band.
- Shiheng Liang
- , Huaiwen Yang
- & Yuan Lu
-
Article
| Open Access Pd-catalysed ligand-enabled carboxylate-directed highly regioselective arylation of aliphatic acids
Pd-catalysed ligand-enabled carboxylate-directed highly regioselective arylation of aliphatic acids
Palladium catalysed C-H functionalization ofsp3carbons typically requires the installation and subsequent removal of a temporary directing group. Here the authors report a method allowing C-H functionalization in carboxylic acids in which the carboxylate acts as a directing group.
- Yan Zhu
- , Xiaolan Chen
- & Yingsheng Zhao
-
Article
| Open Access Naked d-orbital in a centrochiral Ni(II) complex as a catalyst for asymmetric [3+2] cycloaddition
Naked d-orbital in a centrochiral Ni(II) complex as a catalyst for asymmetric [3+2] cycloaddition
Understanding the interplay between electronic structure and performance and how it relates to mechanism is important for catalysis. Here the authors report an asymmetric [3+2] cycloaddition and show the Ni(II) catalyst possesses a weakly bound acetate ligand, leaving thedz2orbital partially vacant.
- Yoshihiro Sohtome
- , Genta Nakamura
- & Mikiko Sodeoka
-
Article
| Open Access Climate variations on Earth-like circumbinary planets
Climate variations on Earth-like circumbinary planets
Large variations in insolation experienced by circumbinary planets raise the question of the habitability of such planets. Here, the authors show that while the changing insolation does not radically affect habitability, it does impact on the planet’s climate and on the interpretation of future observations.
- Max Popp
- & Siegfried Eggl
-
Article
| Open Access Bio-inspired Murray materials for mass transfer and activity
Bio-inspired Murray materials for mass transfer and activity
Plant and animal tissues have evolved to contain hierarchical networks of pores that maximize mass transfer and exchange. Here the authors fabricate bio-inspired materials with multi-scale macro–meso–micropores and show their enhanced performances as photocatalysts, gas sensors and Li-ion battery electrodes.
- Xianfeng Zheng
- , Guofang Shen
- & Bao-Lian Su
-
Article
| Open Access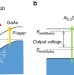 Two-step photon up-conversion solar cells
Two-step photon up-conversion solar cells
Harvesting incident photons with energy below the bandgap may lead to highly efficient solar cells. By introducing InAs quantum dots at the hetero-interface, Asahiet al. achieve efficient two step photon up-conversion resulting in additional photocurrent and very high external quantum efficiency.
- Shigeo Asahi
- , Haruyuki Teranishi
- & Takashi Kita
-
Article
| Open Access DNA origami-based shape IDs for single-molecule nanomechanical genotyping
DNA origami-based shape IDs for single-molecule nanomechanical genotyping
Atomic force microscopy allows for the imaging of molecules at a nanometre resolution. Here the authors combine AFM with self-assembling DNA origami structures to detect single-nucleotide polymorphisms and determine haplotypes.
- Honglu Zhang
- , Jie Chao
- & Chunhai Fan
-
Article
| Open Access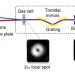 Tunable orbital angular momentum in high-harmonic generation
Tunable orbital angular momentum in high-harmonic generation
The controlled generation of extreme-ultraviolet beams with controllable topological charge has not been demonstrated. Here, Gauthieret al. report on the generation of extreme-ultraviolet optical vortices with femtosecond duration carrying a controllable amount of orbital angular momentum.
- D. Gauthier
- , P. Rebernik Ribič
- & G. De Ninno
-
Article
| Open Access Controlling the orbital angular momentum of high harmonic vortices
Controlling the orbital angular momentum of high harmonic vortices
Few methods can produce orbital angular momentum beams in the extreme ultraviolet or X-ray, and controlling orbital angular momentum on these beams remains challenging. Here the authors apply wave mixing to a tabletop high-harmonic source and control the topological charge of extreme ultraviolet beams.
- Fanqi Kong
- , Chunmei Zhang
- & P. B. Corkum
-
Article
| Open Access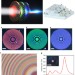 Composite functional metasurfaces for multispectral achromatic optics
Composite functional metasurfaces for multispectral achromatic optics
Metasurfaces promise the possibility of thin optical elements, like lenses, but these mostly suffer from chromatic aberrations. Here, the authors demonstrate a multilayer fabrication approach with multiple materials to realise achromatic lenses and multispectral functional optical elements.
- Ori Avayu
- , Euclides Almeida
- & Tal Ellenbogen
-
Article
| Open Access Precise through-space control of an abiotic electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction
Precise through-space control of an abiotic electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction
Regioselectivity during electrophilic aromatic substitution is typically controlled by substituents on the aryl group. Here the authors report an electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction, wherein remote chiral ester groups direct the electrophile to a precise location on the molecule.
- Kyle E. Murphy
- , Jessica L. Bocanegra
- & Severin T. Schneebeli
-
Article
| Open Access Optimal free descriptions of many-body theories
Optimal free descriptions of many-body theories
Physicists’ understanding of interacting many-body systems often depends on finding an approximate description in terms of non-interacting particles. Here, the authors propose a systematic approach to identify the closest free particle description of a given model.
- Christopher J. Turner
- , Konstantinos Meichanetzidis
- & Jiannis K. Pachos
-
Article
| Open Access Formation of the first three gravitational-wave observations through isolated binary evolution
Formation of the first three gravitational-wave observations through isolated binary evolution
Advanced LIGO has detected gravitational waves from two binary black hole mergers, plus a merger candidate. Here the authors use the COMPAS code to show that all three events can be explained by a single evolutionary channel via a common envelope phase, and characterize the progenitor metallicity and masses.
- Simon Stevenson
- , Alejandro Vigna-Gómez
- & Selma E. de Mink
-
Article
| Open Access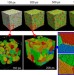 Heterogeneity in homogeneous nucleation from billion-atom molecular dynamics simulation of solidification of pure metal
Heterogeneity in homogeneous nucleation from billion-atom molecular dynamics simulation of solidification of pure metal
Nucleation is a fundamental physical process, however it is a long-standing issue whether completely homogeneous nucleation can occur. Here the authors reveal, via a billion-atom molecular dynamics simulation, that local heterogeneity exists during homogeneous nucleation in an undercooled iron melt.
- Yasushi Shibuta
- , Shinji Sakane
- & Munekazu Ohno
-
Article
| Open Access Biomimetic catalytic transformation of toxic α-oxoaldehydes to high-value chiral α-hydroxythioesters using artificial glyoxalase I
Biomimetic catalytic transformation of toxic α-oxoaldehydes to high-value chiral α-hydroxythioesters using artificial glyoxalase I
Glyoxalase I converts toxic methylglyoxal to a thioester. Here the authors report a synthetic analogue capable of enantioselectively converting alpha-keto aldehydes to thioesters via formation of a hemithioacetal, giving access to both enantiomers of a range of alpha-hydroxy thioesters.
- Sang Yeon Park
- , In-Soo Hwang
- & Choong Eui Song
-
Article
| Open Access Remarkable catalytic activity of dinitrogen-bridged dimolybdenum complexes bearing NHC-based PCP-pincer ligands toward nitrogen fixation
Remarkable catalytic activity of dinitrogen-bridged dimolybdenum complexes bearing NHC-based PCP-pincer ligands toward nitrogen fixation
Catalytic nitrogen fixation is a very active research area, given the need to develop mild routes for ammonia production. Here the authors report a PCP-pincer molybdenum complex allowing for highly efficient ammonia generation under ambient conditions.
- Aya Eizawa
- , Kazuya Arashiba
- & Yoshiaki Nishibayashi
-
Article
| Open Access Quinuclidinium salt ferroelectric thin-film with duodecuple-rotational polarization-directions
Quinuclidinium salt ferroelectric thin-film with duodecuple-rotational polarization-directions
Molecular ferroelectric crystals hold promise in data storage applications, yet their preparations by maximizing molecular polarization are challenging. Here, Youet al. report quinuclidinium periodate with six rotation axes and grow them in macroscopic ferroelectric thin films via a solution process.
- Yu-Meng You
- , Yuan-Yuan Tang
- & Ren-Gen Xiong
-
Article
| Open Access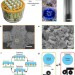 Mechano-regulated surface for manipulating liquid droplets
Mechano-regulated surface for manipulating liquid droplets
Droplet manipulation is an essential task for designing microfluidic platforms such as lab-on-chip devices. Here Tanget al. develop a non-wettable mesh with reversible liquid adhesion controlled by mechanically inserting wettable pillars which allows for effective and rapid droplet manoeuvring.
- Xin Tang
- , Pingan Zhu
- & Liqiu Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Human seizures couple across spatial scales through travelling wave dynamics
Human seizures couple across spatial scales through travelling wave dynamics
The authors record both local and long-range neural activity during human epileptic seizures to study the underlying multi-scale dynamics. They find that coupling of activity across spatial scales increases during seizures through propagating waves that are fit by a model that combines neural activity and potassium concentration dynamics.
- L-E Martinet
- , G. Fiddyment
- & M. A. Kramer
-
Article
| Open Access On-surface synthesis of aligned functional nanoribbons monitored by scanning tunnelling microscopy and vibrational spectroscopy
On-surface synthesis of aligned functional nanoribbons monitored by scanning tunnelling microscopy and vibrational spectroscopy
On-surface synthesis, in which molecular units assemble and couple on a defined surface, can access rare reaction pathways and products. Here, the authors synthesize functionalized organic nanoribbons on the Ag(110) surface, and monitor the evolution of the covalent reactions by an unorthodox vibrational spectroscopy approach.
- Nataliya Kalashnyk
- , Kawtar Mouhat
- & Sylvain Clair
-
Article
| Open Access Enabling valley selective exciton scattering in monolayer WSe2 through upconversion
Enabling valley selective exciton scattering in monolayer WSe2 through upconversion
Monolayer transition metal dichalcogenides host excitons, bound electron-hole pairs that play a pivotal role in optoelectronic applications relying on strong light-matter interaction. Here, the authors unveil the spectroscopic signature of boson scattering of two-dimensional excitons in monolayer WSe2.
- M. Manca
- , M. M. Glazov
- & B. Urbaszek
-
Article
| Open Access Learning through ferroelectric domain dynamics in solid-state synapses
Learning through ferroelectric domain dynamics in solid-state synapses
Accurate modelling of memristor dynamics is essential for the development of autonomous learning in artificial neural networks. Through a combined theoretical and experimental study of the polarization switching process in ferroelectric memristors, Boynet al. establish a model that enables learning and retrieving patterns in a neural system.
- Sören Boyn
- , Julie Grollier
- & Vincent Garcia
-
Article
| Open Access A bright triggered twin-photon source in the solid state
A bright triggered twin-photon source in the solid state
Photon twins are important for interdisciplinary research fields using non-classical light, such as quantum biology. Here, Heindelet al. demonstrate that a single semiconductor quantum dot integrated into a microlens operates as an efficient photon-pair source.
- T. Heindel
- , A. Thoma
- & S. Reitzenstein
-
Article
| Open Access Enzyme catalysed Pictet-Spengler formation of chiral 1,1’-disubstituted- and spiro-tetrahydroisoquinolines
Enzyme catalysed Pictet-Spengler formation of chiral 1,1’-disubstituted- and spiro-tetrahydroisoquinolines
The Pictet-Spengler condensation of β-arylethylamine and carbonyl compounds is an important step in the synthesis of bioactive alkaloids. Here, the authors report a Pictet-Spengler reaction between dopamine and unactivated ketones catalysed by norcoclaurine synthase and its engineered variants.
- Benjamin R. Lichman
- , Jianxiong Zhao
- & John M. Ward
-
Article
| Open Access Tight cohesion between glycolipid membranes results from balanced water–headgroup interactions
Tight cohesion between glycolipid membranes results from balanced water–headgroup interactions
Glycolipids are commonly found in densely stacked biological membranes, which show unusually strong self-cohesion compared to phospholipid membranes. Here, the authors attribute this phenomenon to the lack of long-range repulsion between glycolipid membranes, a consequence of the headgroup architecture.
- Matej Kanduč
- , Alexander Schlaich
- & Emanuel Schneck
-
Article
| Open Access Improved ethanol electrooxidation performance by shortening Pd–Ni active site distance in Pd–Ni–P nanocatalysts
Improved ethanol electrooxidation performance by shortening Pd–Ni active site distance in Pd–Ni–P nanocatalysts
Incorporating oxophilic metals into noble metal catalysts can improve electrocatalytic performance; however, the influence of the distance between noble metal and oxophilic metal active site is not well understood. Here the authors make Pd–Ni–P nanocatalysts for ethanol oxidation, with improved performance achieved by shortening the Pd–Ni distance.
- Lin Chen
- , Lilin Lu
- & Leyu Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Graphene-like nanoribbons periodically embedded with four- and eight-membered rings
Graphene-like nanoribbons periodically embedded with four- and eight-membered rings
Graphene nanoribbons consist of carbon atoms arranged in a hexagonal lattice. Despite non-hexagonal rings generally being more unstable, the authors demonstrate the successful synthesis of graphene-like nanoribbons with periodically embedded four- and eight-membered carbon rings, with tailored electronic properties.
- Meizhuang Liu
- , Mengxi Liu
- & Dingyong Zhong
-
Article
| Open Access Integrated arrays of air-dielectric graphene transistors as transparent active-matrix pressure sensors for wide pressure ranges
Integrated arrays of air-dielectric graphene transistors as transparent active-matrix pressure sensors for wide pressure ranges
Electronic skins and health monitoring devices rely on integrated tactile sensors, which often require tailored degrees of sensitivity in specific pressure ranges. Here, the authors fabricate a versatile matrix array of pressure-sensitive graphene transistors operating in the wide 250 Pa to 3 MPa pressure range.
- Sung-Ho Shin
- , Sangyoon Ji
- & Jang-Ung Park
-
Article
| Open Access Synthesizing topological structures containing RNA
Synthesizing topological structures containing RNA
In vivo, complex topologies have been identified in proteins and DNA, while their existence in RNA is still unclear. Here, the authors design synthetic topological structures containing single stranded RNA, offering tools for investigating biologically relevant questions about RNA topology.
- Di Liu
- , Yaming Shao
- & Yossi Weizmann
-
Article
| Open Access Wave-particle energy exchange directly observed in a kinetic Alfvén-branch wave
Wave-particle energy exchange directly observed in a kinetic Alfvén-branch wave
Alfvén waves are fundamental plasma modes that provide a mechanism for the transfer of energy between particles and fields. Here the authors confirm experimentally the conservative energy exchange between Alfvén wave fields and plasma particles via high-resolution MMS observations of Earth’s magnetosphere.
- Daniel J. Gershman
- , Adolfo F-Viñas
- & James L. Burch
-
Article
| Open Access Rapid electron transfer by the carbon matrix in natural pyrogenic carbon
Rapid electron transfer by the carbon matrix in natural pyrogenic carbon
Electron transfer reactions govern most biogeochemical processes, yet we have a limited knowledge of the electrochemistry of pyrogenic carbon, a major component of organic matter. Here, the authors quantify electron transfers between pyrogenic carbon and mineral phases under different pyrolysis temperatures.
- Tianran Sun
- , Barnaby D. A. Levin
- & Johannes Lehmann
-
Article
| Open Access Chasing the thermodynamical noise limit in whispering-gallery-mode resonators for ultrastable laser frequency stabilization
Chasing the thermodynamical noise limit in whispering-gallery-mode resonators for ultrastable laser frequency stabilization
High-quality optical resonators have the potential to provide a miniaturized frequency reference for metrology and sensing but they often lack stability. Here, Lim et al. experimentally characterize the stability of whispering-gallery resonators at their fundamental noise limits.
- Jinkang Lim
- , Anatoliy A. Savchenkov
- & Chee Wei Wong
-
Article
| Open Access Sequence-selective encapsulation and protection of long peptides by a self-assembled FeII8L6 cubic cage
Sequence-selective encapsulation and protection of long peptides by a self-assembled FeII8L6 cubic cage
One of the challenges of synthetic self-assembled capsules is achieving selective recognition of specific cargoes. Here, authors synthesize a self-assembled porphyrin cubic cage that is capable of sequestering imidazole and thiazole-containing small molecules and peptides, protecting them from proteolysis.
- Jesús Mosquera
- , Bartosz Szyszko
- & Jonathan R. Nitschke
-
Article
| Open Access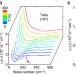 Temperature-tunable Fano resonance induced by strong coupling between Weyl fermions and phonons in TaAs
Temperature-tunable Fano resonance induced by strong coupling between Weyl fermions and phonons in TaAs
The study of lattice vibrations coupled to electronic excitations may provide an avenue for exploring exotic physical phenomena. Here, Xuet al. observe a Fano resonance in the Weyl semimetal TaAs, revealing evidence for a strong coupling between phonons and Weyl fermions.
- B. Xu
- , Y. M. Dai
- & X. G. Qiu
-
Article
| Open Access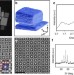 Structure and vacancy distribution in copper telluride nanoparticles influence plasmonic activity in the near-infrared
Structure and vacancy distribution in copper telluride nanoparticles influence plasmonic activity in the near-infrared
CuTe nanocrystals may be used as an alternative to noble metals for plasmonics but requires understanding of the atomic structure and the influence of defects. Here Willhammaret al. use electron tomography to reveal the distribution of vacancies in the nanocrystals and their effect on the optical properties.
- Tom Willhammar
- , Kadir Sentosun
- & Gustaaf Van Tendeloo
-
Article
| Open Access Allosteric cross-talk in chromatin can mediate drug-drug synergy
Allosteric cross-talk in chromatin can mediate drug-drug synergy
Allostery and drug-drug synergism can yield potential novel therapies with existing molecules. Here, the authors provide evidence that two unrelated drugs have increased cytotoxicity in cancer cells, which coincides with increased formation of chromatin adducts.
- Zenita Adhireksan
- , Giulia Palermo
- & Curt A. Davey
-
Article
| Open Access Stable and solubilized active Au atom clusters for selective epoxidation of cis-cyclooctene with molecular oxygen
Stable and solubilized active Au atom clusters for selective epoxidation of cis-cyclooctene with molecular oxygen
Gold catalysts have previously been reported for the epoxidation of alkenes with molecular oxygen. Here the authors show that, rather than the gold nanoparticles, the active species for this reaction are actually small, soluble gold species stabilized by the oxidised organic products.
- Linping Qian
- , Zhen Wang
- & Harold H. Kung
-
Review Article
| Open Access Regioregular narrow-bandgap-conjugated polymers for plastic electronics
Regioregular narrow-bandgap-conjugated polymers for plastic electronics
The continued search of high-performance semiconductors for organic electronics calls for smart molecular designs. Here, Yinget al. review the recent development of synthesizing regioregular narrow bandgap conjugated polymers and the effect of regioregularity on transistor and photovoltaic performance.
- Lei Ying
- , Fei Huang
- & Guillermo C. Bazan
-
Article
| Open Access One-step fabrication of crystalline metal nanostructures by direct nanoimprinting below melting temperatures
One-step fabrication of crystalline metal nanostructures by direct nanoimprinting below melting temperatures
Rapid fabrication of well-controlled metallic nanostructures remains a challenge. Here, the authors directly nanoimprint several different crystalline metals by superplastic forming well below their melting temperatures, obtaining uniform nanostructures with small features and high aspect ratios in one step.
- Ze Liu
-
Article
| Open Access Plasmonic hot electron transport drives nano-localized chemistry
Plasmonic hot electron transport drives nano-localized chemistry
Quantitative understanding of the spatial localization of hot carriers has been elusive. Here Corteset al. spatially map hot-electron-driven reduction chemistry with 15 nm resolution as a function of time and electromagnetic field polarization for different plasmonic nanostructures.
- Emiliano Cortés
- , Wei Xie
- & Stefan A. Maier

 Topological superconductivity in monolayer transition metal dichalcogenides
Topological superconductivity in monolayer transition metal dichalcogenides