Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Realization of vertical metal semiconductor heterostructures via solution phase epitaxy
Realization of vertical metal semiconductor heterostructures via solution phase epitaxy
Controlling the composition and crystal phase of layered heterostructures is important. Here, the authors report the liquid-phase epitaxial growth of Sn0.5W0.5S2 nanosheets with 83% metallic phase on SnS2 nanoplates, which are used as 100 ppb level chemiresistive gas sensors at room temperature.
- Xiaoshan Wang
- , Zhiwei Wang
- & Wei Huang
-
Article
| Open Access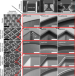 Biomimetic coating-free surfaces for long-term entrapment of air under wetting liquids
Biomimetic coating-free surfaces for long-term entrapment of air under wetting liquids
Trapping air at the solid-liquid interface is a promising strategy for reducing frictional drag but could not be realized without perfluorinated coatings so-far. Here the authors demonstrate a biomimetic coating-free approach for entrapping air for long periods upon immersion in liquids.
- Eddy M. Domingues
- , Sankara Arunachalam
- & Himanshu Mishra
-
Article
| Open Access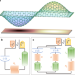 Quantum nondemolition measurement of mechanical motion quanta
Quantum nondemolition measurement of mechanical motion quanta
Although electro-and optomechanics has recently moved towards the quantum regime, the quantized energy spectrum of a mechanical oscillator has not been directly observed. Here Dellantonio et al. propose an electromechanical setup with a membrane resonator that could enable phonon number measurements.
- Luca Dellantonio
- , Oleksandr Kyriienko
- & Anders S. Sørensen
-
Article
| Open Access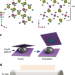 Printing two-dimensional gallium phosphate out of liquid metal
Printing two-dimensional gallium phosphate out of liquid metal
Two-dimensional piezoelectric materials hold promise for nano-electromechanical technologies, yet it is challenging to prepare them in large areas with high sample homogeneity. Syed et al. surface print GaPO4 sheets with unit cell thickness over centimetres using a liquid metal-based synthesis process.
- Nitu Syed
- , Ali Zavabeti
- & Kourosh Kalantar-Zadeh
-
Article
| Open Access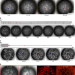 Dynamic capillary assembly of colloids at interfaces with 10,000g accelerations
Dynamic capillary assembly of colloids at interfaces with 10,000g accelerations
The deformation of soft materials under high rates remains challenging to be probed directly and thus understood. Huerre et al. examine the self-assembly of colloids confined at a fluid interface driven by ultrasound and show the formation of string-like microstructures caused by dynamic capillarity.
- Axel Huerre
- , Marco De Corato
- & Valeria Garbin
-
Article
| Open Access Anomalous twin boundaries in two dimensional materials
Anomalous twin boundaries in two dimensional materials
All materials subjected to mechanical deformation form low energy interfaces known as twin boundaries. Here, the authors investigate a variety of structural features that form upon bending atomically thin 2D-crystals, and predict distinct classes of post deformation microstructure based on their atomic arrangement, bend angle and flake thickness.
- A. P. Rooney
- , Z. Li
- & S. J. Haigh
-
Article
| Open Access H-bonded reusable template assisted para-selective ketonisation using soft electrophilic vinyl ethers
H-bonded reusable template assisted para-selective ketonisation using soft electrophilic vinyl ethers
Electrophilic acylation of arenes is largely limited to electron rich systems, non-polar medium and often displays moderate selectivity. Here, the authors show a directed para-selective ketonisation of arenes, overriding electronic bias and structural congestion, and apply it to the synthesis of bioactive compounds.
- Arun Maji
- , Amit Dahiya
- & Debabrata Maiti
-
Article
| Open Access Exploring Peltier effect in organic thermoelectric films
Exploring Peltier effect in organic thermoelectric films
Observing the Peltier effect, e.g. cooling/heating at material junctions due to current flow, in organic thermoelectric films remains a challenge due the inherent properties of these materials. Here, the authors use IR imaging to experimentally observe the Peltier effect in poly(Ni-ett)-based films.
- Wenlong Jin
- , Liyao Liu
- & Daoben Zhu
-
Article
| Open Access Bioinspired ultra-stretchable and anti-freezing conductive hydrogel fibers with ordered and reversible polymer chain alignment
Bioinspired ultra-stretchable and anti-freezing conductive hydrogel fibers with ordered and reversible polymer chain alignment
High-performance stretchable conductive fibers are desired for the development of stretchable electronic devices but preparation of conductive hydrogel fibers is challenging. Inspired by spider silk the authors demonstrate here a spinning method to prepare stretchable conductive hydrogel fibers with ordered polymer chain alignment.
- Xue Zhao
- , Fang Chen
- & Mingming Ma
-
Article
| Open Access Total synthesis and antimicrobial evaluation of natural albomycins against clinical pathogens
Total synthesis and antimicrobial evaluation of natural albomycins against clinical pathogens
Albomycins are promising drug candidates for the treatment of bacterial infections. Here, the authors describe the total syntheses of albomycins δ1, δ2, and ε, and evaluate their antimicrobial activity, identifying albomycin δ2 as a strong agent against S. pneumoniae and S. aureus infections.
- Zihua Lin
- , Xiaobo Xu
- & Yun He
-
Article
| Open Access Non-Abelian adiabatic geometric transformations in a cold strontium gas
Non-Abelian adiabatic geometric transformations in a cold strontium gas
The symmetry group and geometric phase of a system are responsible for many quantum properties related to non-trivial topology. Here the authors show non-Abelian geometric phase in laser-coupled ultracold strontium atoms by using a tripod scheme.
- F. Leroux
- , K. Pandey
- & D. Wilkowski
-
Article
| Open Access Binder driven self-assembly of metal-organic cubes towards functional hydrogels
Binder driven self-assembly of metal-organic cubes towards functional hydrogels
A possible route to producing processable soft materials is by assembling metal organic cubes into hydrogels. Here the authors show charge-assisted H-bond driven self-assembly of Ga3+-based anionic metal organic cubes and suitable molecular binders towards multi-functional hydrogels.
- Papri Sutar
- , Venkata M. Suresh
- & Tapas Kumar Maji
-
Article
| Open Access Atomic force microscopy methodology and AFMech Suite software for nanomechanics on heterogeneous soft materials
Atomic force microscopy methodology and AFMech Suite software for nanomechanics on heterogeneous soft materials
Atomic force microscopy is an indispensable method in characterizing soft materials but the complexity of biological samples makes reproducible measurements difficult. Here the authors use a 3-step method to investigate biological specimens in which vertical and lateral heterogeneity hinders a precise quantitative characterization.
- Massimiliano Galluzzi
- , Guanlin Tang
- & Florian J. Stadler
-
Article
| Open Access Dehydrogenative reagent-free annulation of alkenes with diols for the synthesis of saturated O-heterocycles
Dehydrogenative reagent-free annulation of alkenes with diols for the synthesis of saturated O-heterocycles
Dehydrogenative annulation is a valuable approach to heterocycles, however, stoichiometric oxidants are often required. Here, the authors describe the electrochemical dehydrogenative annulation of diols and alkenes to generate dioxanes and dioxepanes under metal- and oxidant-free conditions.
- Chen-Yan Cai
- & Hai-Chao Xu
-
Article
| Open Access Single crystal toroidal diamond anvils for high pressure experiments beyond 5 megabar
Single crystal toroidal diamond anvils for high pressure experiments beyond 5 megabar
Static pressures exceeding 4 million atmospheres are extremely challenging to achieve, but are necessary for the study of matter that exists under these conditions in natural environments. Here, diamonds anvils with a toroidal design are demonstrated to sustain over 6 million atmospheres in a diamond anvil cell.
- Zs. Jenei
- , E. F. O’Bannon
- & W. J. Evans
-
Article
| Open Access Synthesis of chiral α-trifluoromethyl alcohols and ethers via enantioselective Hiyama cross-couplings of bisfunctionalized electrophiles
Synthesis of chiral α-trifluoromethyl alcohols and ethers via enantioselective Hiyama cross-couplings of bisfunctionalized electrophiles
Compounds containing stereocenters bearing -CF3 groups, especially in proximity of heteroatoms, are of great interest for drug and agrochemicals development. Here, the authors report a nickel-catalyzed Hiyama cross-coupling methodology for the asymmetric synthesis of valuable alpha-trifluoromethyl alcohols and ethers.
- Andrii Varenikov
- & Mark Gandelman
-
Article
| Open Access A hexagon in Saturn’s northern stratosphere surrounding the emerging summertime polar vortex
A hexagon in Saturn’s northern stratosphere surrounding the emerging summertime polar vortex
The Cassini spacecraft has provided an unprecedented characterisation of seasonal changes on Saturn. Here the authors describe the development of a warm polar vortex in Saturn’s northern summer, and show that the hexagon extends hundreds of kilometres from the troposphere into the stratosphere.
- L. N. Fletcher
- , G. S. Orton
- & S. B. Calcutt
-
Article
| Open Access Imaging soliton dynamics in optical microcavities
Imaging soliton dynamics in optical microcavities
In order to study the dynamics of solitons in microresonators, which underlie nonlinear phenomena like Kerr comb generation, both high temporal resolution and long record times are needed. Here, the authors develop a coherent sampling method to directly image the temporal behavior of solitons.
- Xu Yi
- , Qi-Fan Yang
- & Kerry Vahala
-
Article
| Open Access Room-temperature polarized spin-photon interface based on a semiconductor nanodisk-in-nanopillar structure driven by few defects
Room-temperature polarized spin-photon interface based on a semiconductor nanodisk-in-nanopillar structure driven by few defects
Room-temperature spin-generation in 1D systems like semiconductor nanopillars is typically inefficient. Here, the authors demonstrate an approach to achieve efficient spin polarization, even in the absence of a magnetic field, by selectively enhancing the radiative efficiency of one spin direction.
- Shula Chen
- , Yuqing Huang
- & Weimin M. Chen
-
Article
| Open Access A terahertz-driven non-equilibrium phase transition in a room temperature atomic vapour
A terahertz-driven non-equilibrium phase transition in a room temperature atomic vapour
The nonlinear interaction between terahertz frequency electric fields and atoms or molecules can be used to study fundamental and technical problems. Here the authors demonstrate a THz–driven phase transition, with a potential application as a THz sensor, using Rydberg atomic states in a cesium vapor.
- C. G. Wade
- , M. Marcuzzi
- & K. J. Weatherill
-
Article
| Open Access Crystalline TiO2 protective layer with graded oxygen defects for efficient and stable silicon-based photocathode
Crystalline TiO2 protective layer with graded oxygen defects for efficient and stable silicon-based photocathode
While silicon-based materials can convert sunlight directly to fuel and electricity, balancing their stability and efficiency constrains usage. Here, authors protect silicon photocathodes with crystalline titanium dioxide layers with graded oxygen defects to improve both durability and efficiency.
- Jianyun Zheng
- , Yanhong Lyu
- & Shuangyin Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Long-lived polarization memory in the electronic states of lead-halide perovskites from local structural dynamics
Long-lived polarization memory in the electronic states of lead-halide perovskites from local structural dynamics
Anharmonic ultrafast structural dynamics are expected in lead halide perovskites due to their soft nature. Here Rivett et al. show that these dynamics lead to picosecond-long polarization anisotropy of photo-carriers in several halide perovskites, orders of magnitude slower than in conventional semiconductors.
- Jasmine P. H. Rivett
- , Liang Z. Tan
- & Felix Deschler
-
Article
| Open Access Evidence of a turbulent ExB mixing avalanche mechanism of gas breakdown in strongly magnetized systems
Evidence of a turbulent ExB mixing avalanche mechanism of gas breakdown in strongly magnetized systems
Gas breakdown mechanism in plasma under the influence of complex electromagnetic field topology is still debatable. Here the authors present the evidence of the E×B mixing avalanche for gas breakdown in magnetized plasmas in fusion devices as tokamak.
- Min-Gu Yoo
- , Jeongwon Lee
- & Yong-Su Na
-
Article
| Open Access Density-functional fluctuation theory of crowds
Density-functional fluctuation theory of crowds
Tools from statistical physics can be used to investigate a large variety of fields ranging from economics to biology. Here the authors first adapt density-functional theory to predict the distributions of crowds in new environments and then validate their approach using groups of fruit flies.
- J. Felipe Méndez-Valderrama
- , Yunus A. Kinkhabwala
- & T. A. Arias
-
Article
| Open Access Quantitative mappings between symmetry and topology in solids
Quantitative mappings between symmetry and topology in solids
The defining quantities of topological materials—the topological invariants—are often difficult to calculate. Here, Song et al. report a simplified method to calculate both the symmetry data and the topological invariants for arbitrary gapped band structure with time-reversal symmetry.
- Zhida Song
- , Tiantian Zhang
- & Chen Fang
-
Article
| Open Access Color-stable highly luminescent sky-blue perovskite light-emitting diodes
Color-stable highly luminescent sky-blue perovskite light-emitting diodes
Perovskite light-emitting diodes show promising color tunability and device performance but suffer from emission color shift at higher driving voltages. Here Xing et al. report color stable blue light-emitting diodes by drastically increasing the phase purity of the quasi-2D perovskite thin films.
- Jun Xing
- , Yongbiao Zhao
- & Edward H. Sargent
-
Article
| Open Access Luciferase-induced photoreductive uncaging of small-molecule effectors
Luciferase-induced photoreductive uncaging of small-molecule effectors
Bioluminescence resonance energy transfer (BRET) has been mostly employed in imaging applications. Here the authors use BRET to activate a ruthenium-based photocatalyst and perform a bioorthogonal chemical reaction, which can be used to uncage small molecule drugs in a cellular context.
- Eric Lindberg
- , Simona Angerani
- & Nicolas Winssinger
-
Article
| Open Access The photoregulation of a mechanochemical polymer scission
The photoregulation of a mechanochemical polymer scission
Control over mechanochemical polymer scission by external stimuli may offer an avenue to further advance the fields of polymer chemistry, mechanochemistry, and materials science. Here the authors show light regulating the mechanochemical behavior of a diarylethene-conjugated Diels–Alder adduct.
- Jumpei Kida
- , Keiichi Imato
- & Hideyuki Otsuka
-
Article
| Open Access A general deoxygenation approach for synthesis of ketones from aromatic carboxylic acids and alkenes
A general deoxygenation approach for synthesis of ketones from aromatic carboxylic acids and alkenes
Synthesis of aryl ketones can be generally achieved via C–C coupling strategies. Here, the authors show a deoxygenative coupling of carboxylic acids and alkenes enabled by photoredox catalysis and report a wide scope of products, including bioactive and macrocyclic ketones.
- Muliang Zhang
- , Jin Xie
- & Chengjian Zhu
-
Article
| Open Access Role of hydrogen bonding in hysteresis observed in sorption-induced swelling of soft nanoporous polymers
Role of hydrogen bonding in hysteresis observed in sorption-induced swelling of soft nanoporous polymers
Water uptake of natural polymers is accompanied by swelling and changes in the internal structure of the polymeric system but the exact mechanism of water-uptake and swelling remained unknown. Here the authors use atom-scale simulations to identify a molecular mechanism which is responsible for hysteresis in sorption-induced swelling in natural polymers.
- Mingyang Chen
- , Benoit Coasne
- & Jan Carmeliet
-
Article
| Open Access Solution structures of multiple G-quadruplex complexes induced by a platinum(II)-based tripod reveal dynamic binding
Solution structures of multiple G-quadruplex complexes induced by a platinum(II)-based tripod reveal dynamic binding
DNA G-quadruplexes occur in oncologically relevant regions, thus are interesting targets for cancer research and treatment. Here, the authors solved the 1:1 and 4:2 (ligand/DNA) NMR structures of human telomeric DNA in complex with platinum(II)-tripod ligand and show that the binding is dynamic.
- Wenting Liu
- , Yi-Fang Zhong
- & Zong-Wan Mao
-
Article
| Open Access Intermolecular selective carboacylation of alkenes via nickel-catalyzed reductive radical relay
Intermolecular selective carboacylation of alkenes via nickel-catalyzed reductive radical relay
To date the carboacylation of alkenes has been reported only in single- and two-component methodologies. Here, the authors report a three-component nickel-catalyzed carboacylation of olefins which enables the rapid construction of ketones with high levels of complexity and diversity.
- Xian Zhao
- , Hai-Yong Tu
- & Lingling Chu
-
Article
| Open Access Modelling of free-form conformal metasurfaces
Modelling of free-form conformal metasurfaces
Predicting and modelling the responses of free-from photonics devices remain challenging with conventional computational tools. Here, the authors propose an efficient algorithm based on conformal boundary optics and modified finite difference time-domain to calculate the electromagnetic fields across conformal metasurfaces.
- Kedi Wu
- , Philippe Coquet
- & Patrice Genevet
-
Article
| Open Access Finite momentum Cooper pairing in three-dimensional topological insulator Josephson junctions
Finite momentum Cooper pairing in three-dimensional topological insulator Josephson junctions
Unconventional superconductivity may emerge from the interplay between strong spin–orbit coupling and magnetism. Here, Chen et al. report an anomalous Fraunhofer pattern in three-dimensional topological insulator Bi2Se3 and attribute it as a signature of finite momentum Cooper pairing.
- Angela Q. Chen
- , Moon Jip Park
- & Nadya Mason
-
Article
| Open Access Dynamical coupling between a nuclear spin ensemble and electromechanical phonons
Dynamical coupling between a nuclear spin ensemble and electromechanical phonons
Nuclear spins in solids can be implemented into quantum devices but their manipulation usually requires microwave irradiation. Here instead the authors show that they can shift the NMR frequency and drive the nuclear spins into the resolved-sideband regime by using the tunable phonon states from an electromechanical resonator.
- Yuma Okazaki
- , Imran Mahboob
- & Hiroshi Yamaguchi
-
Article
| Open Access High-performance artificial nitrogen fixation at ambient conditions using a metal-free electrocatalyst
High-performance artificial nitrogen fixation at ambient conditions using a metal-free electrocatalyst
Electrochemical reduction of nitrogen is a promising route to industrial-scale nitrogen fixation at ambient conditions, but is challenged by activation of inert nitrogen. Here the authors report a metal-free catalyst that selectively reduces nitrogen to ammonia with high efficiency and stability.
- Weibin Qiu
- , Xiao-Ying Xie
- & Xuping Sun
-
Article
| Open Access Solar superstorm of AD 774 recorded subannually by Arctic tree rings
Solar superstorm of AD 774 recorded subannually by Arctic tree rings
Tree rings retain information of sudden variations of ancient radiocarbon (14C) content, however the origin and exact timing of these events often remain uncertain. Here, the authors analyze a set of Arctic tree rings and link a rapid increase in 14C to a solar event that occurred during the spring of AD 774.
- J. Uusitalo
- , L. Arppe
- & M. Oinonen
-
Article
| Open Access Efficient and scalable synthesis of highly aligned and compact two-dimensional nanosheet films with record performances
Efficient and scalable synthesis of highly aligned and compact two-dimensional nanosheet films with record performances
Aligning 2D nanosheets to form a compact layered structure can maximize the in-plane properties. Here the authors report an efficient and scalable continuous centrifugal casting method to produce highly compact and well-aligned films of GO nanosheets that show record performances in some applications.
- Jing Zhong
- , Wei Sun
- & Wencai Ren
-
Article
| Open Access Self-decoupled radiofrequency coils for magnetic resonance imaging
Self-decoupled radiofrequency coils for magnetic resonance imaging
Conventional coil arrays require complex decoupling technologies to reduce electromagnetic coupling between coil elements. Here, the authors report a self-decoupled RF coil design that achieves high inter-coil isolation between adjacent and non-adjacent elements and mixed arrays of loops and dipoles
- Xinqiang Yan
- , John C. Gore
- & William A. Grissom
-
Article
| Open Access Megahertz data collection from protein microcrystals at an X-ray free-electron laser
Megahertz data collection from protein microcrystals at an X-ray free-electron laser
The European X-ray free-electron laser (EuXFEL) in Hamburg is the first megahertz (MHz) repetition rate XFEL. Here the authors use lysozyme crystals and microcrystals from jack bean proteins and demonstrate that damage-free high quality data can be collected at a MHz repetition rate.
- Marie Luise Grünbein
- , Johan Bielecki
- & Ilme Schlichting
-
Article
| Open Access Nanophotonic Pockels modulators on a silicon nitride platform
Nanophotonic Pockels modulators on a silicon nitride platform
Active devices such as modulators made of silicon nitride still lack performance. Here, the authors demonstrate electro-optic modulators based on ferroelectric lead zirconate titanate films on silicon nitride, in both the O- and the C-band with a modulation bandwidth beyond 33 GHz and with data rates of 40 Gbps.
- Koen Alexander
- , John P. George
- & Jeroen Beeckman
-
Article
| Open Access Selective conversion of CO2 and H2 into aromatics
Selective conversion of CO2 and H2 into aromatics
Selective conversion of CO2 and H2 into aromatics remains challenging due to the high unsaturation degree and complex structure of aromatics. Here the authors report a composite catalyst of ZnAlOx and H-ZSM-5 which promotes the formation of aromatics with high selectivity while inhibiting CO and CH4 formation in CO2 hydrogenation reactions.
- Youming Ni
- , Zhiyang Chen
- & Zhongmin Liu
-
Article
| Open Access Controlling electric potential to inhibit solid-electrolyte interphase formation on nanowire anodes for ultrafast lithium-ion batteries
Controlling electric potential to inhibit solid-electrolyte interphase formation on nanowire anodes for ultrafast lithium-ion batteries
Lithium-based rechargeable batteries suffer from unstable evolution of solid-electrolyte interphase on the electrode surface. Here, the authors provide an approach to inhibiting SEI formation by controlling electric potential distribution across electrolyte and electrode.
- Won Jun Chang
- , Su Han Kim
- & Won Il Park
-
Article
| Open Access Single photon emission from graphene quantum dots at room temperature
Single photon emission from graphene quantum dots at room temperature
The optical properties of nanographenes can be engineered by designing their size, shape, and edges. Here, the authors show that graphene quantum dots are single photon emitters at room temperature, and their emission wavelength can be controlled by edge functionalization.
- Shen Zhao
- , Julien Lavie
- & Jean-Sébastien Lauret
-
Article
| Open Access Transformation from crystalline precursor to perovskite in PbCl2-derived MAPbI3
Transformation from crystalline precursor to perovskite in PbCl2-derived MAPbI3
The existence of a crystalline precursor is key to perovskite film formation, but the precise chemistry of the precursor and its transformation into perovskite are poorly understood. Here, the authors identify the crystal structure and conversion chemistry of the precursor for PbCl2-derived methylammonium lead iodide perovskites.
- Kevin H. Stone
- , Aryeh Gold-Parker
- & Christopher J. Tassone
-
Article
| Open Access Near-infrared-triggered photon upconversion tuning in all-inorganic cesium lead halide perovskite quantum dots
Near-infrared-triggered photon upconversion tuning in all-inorganic cesium lead halide perovskite quantum dots
Optimizing luminescence from quantum dots benefits various optoelectronic and photovoltaic applications. Here the authors drive high-efficiency, tunable upconversion luminescence in perovskite quantum dots by energy transfer from lanthanide-doped nanoparticles excited by near-infrared light, to produce full-color emission with low driving power.
- Wei Zheng
- , Ping Huang
- & Xueyuan Chen
-
Article
| Open Access Experimental implementation of fully controlled dephasing dynamics and synthetic spectral densities
Experimental implementation of fully controlled dephasing dynamics and synthetic spectral densities
The study of dephasing dynamics have wide implications for understanding open systems evolutions and in particular decoherence of qubits. Here, the authors implement arbitrary qubit decoherence dynamics in a photonic simulator, also capable of implementing non-positive dynamical maps.
- Zhao-Di Liu
- , Henri Lyyra
- & Jyrki Piilo
-
Article
| Open Access Hyperfine-phonon spin relaxation in a single-electron GaAs quantum dot
Hyperfine-phonon spin relaxation in a single-electron GaAs quantum dot
The application of spin based qubits requests understanding and control of spin relaxation time T1 which remains challenging. Here the authors experimentally demonstrate the spin relaxation mechanism via hyper fine interaction and long spin-relaxation time T1 ~ 57 s for a single electron spin in GaAs quantum dot.
- Leon C. Camenzind
- , Liuqi Yu
- & Dominik M. Zumbühl
-
Article
| Open Access A molecular overlayer with the Fibonacci square grid structure
A molecular overlayer with the Fibonacci square grid structure
Quasicrystals possess long range order but no translational symmetry, and rotational symmetries that are forbidden in periodic crystals. Here, a fullerene overlayer deposited on a surface of an icosahedral intermetallic quasicrystal achieves a Fibonacci square grid structure, by selective adsorption at specific sites.
- Sam Coates
- , Joseph A. Smerdon
- & Hem Raj Sharma

 Unexpected stability of aqueous dispersions of raspberry-like colloids
Unexpected stability of aqueous dispersions of raspberry-like colloids