Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Enhanced diffusion by binding to the crosslinks of a polymer gel
Enhanced diffusion by binding to the crosslinks of a polymer gel
Gels filtering particles by interactions are a goal of nanotechnology; this is difficult when particles are larger than the mesh of the gel. Here, the authors present an equilibrium mechanism where binding dynamics of crosslinks are affected by interacting particles so that particles experience enhanced diffusion.
- Carl P. Goodrich
- , Michael P. Brenner
- & Katharina Ribbeck
-
Article
| Open Access Nanodiamond autophagy inhibitor allosterically improves the arsenical-based therapy of solid tumors
Nanodiamond autophagy inhibitor allosterically improves the arsenical-based therapy of solid tumors
Arsenic trioxide (ATO) based therapy in solid cancers is limited. Here they repurpose nanodiamonds (NDs) as a safe and potent autophagic inhibitor to improve the efficacy of ATO-based treatment in solid tumors and show the combination therapy to work better in orthotopic liver cancer model.
- Zhifen Cui
- , Yu Zhang
- & Chunhai Fan
-
Article
| Open Access The reaction of hydroxyl and methylperoxy radicals is not a major source of atmospheric methanol
The reaction of hydroxyl and methylperoxy radicals is not a major source of atmospheric methanol
The reaction of hydroxyl and methylperoxy radicals has recently been suggested as the source of missing methanol in the remote troposphere. Here, the authors present direct experimental measurements demonstrating the reaction leads to further underprediction of modelled methanol.
- Rebecca L. Caravan
- , M. Anwar H. Khan
- & Craig A. Taatjes
-
Article
| Open Access Emergence of superconductivity in the cuprates via a universal percolation process
Emergence of superconductivity in the cuprates via a universal percolation process
The emergence of superconductivity from the normal state in the cuprates above the transition temperature (Tc) has been controversial. Here, Pelc et al. report nonlinear conductivity, resulting from superconducting precursors only, vanishing exponentially above Tc both with temperature and with magnetic field.
- Damjan Pelc
- , Marija Vučković
- & Neven Barišić
-
Review Article
| Open Access Metallo-polyelectrolytes as a class of ionic macromolecules for functional materials
Metallo-polyelectrolytes as a class of ionic macromolecules for functional materials
Polyelectrolytes are a class of macromolecules containing charged groups. Here the authors review properties and functions of metallo-polyelectrolytes to shed light on how to harness fundamental physiochemical properties for applications in biomedical sciences and advanced materials.
- Tianyu Zhu
- , Ye Sha
- & Chuanbing Tang
-
Article
| Open Access Narrow bounds for the quantum capacity of thermal attenuators
Narrow bounds for the quantum capacity of thermal attenuators
Bounding the capacity of thermal attenuators would give a powerful instrument to describe decoherence occurring in optical fibres and free space links. Here, the authors improve on the existing upper bounds in the region of small thermal noise, which is of interest for quantum communication.
- Matteo Rosati
- , Andrea Mari
- & Vittorio Giovannetti
-
Article
| Open Access Lewis basicity generated by localised charge imbalance in noble metal nanoparticle-embedded defective metal–organic frameworks
Lewis basicity generated by localised charge imbalance in noble metal nanoparticle-embedded defective metal–organic frameworks
Interactions between metal nanoparticles (NPs) and metal–organic frameworks (MOFs) in their composite forms have proven to exhibit beneficial properties. Here the authors present a unique approach to immobilise Pd NPs and, more importantly, to generate tunable basic sites within an anionic defective MOF.
- Ying Chuan Tan
- & Hua Chun Zeng
-
Article
| Open Access Space-time-coding digital metasurfaces
Space-time-coding digital metasurfaces
Current digital coding metasurfaces are only space-encoded. Here, the authors propose space-time modulated digital coding metasurfaces to obtain simultaneous manipulations of electromagnetic waves and present harmonic beam steering, beam shaping, and scattering-signature control as application examples.
- Lei Zhang
- , Xiao Qing Chen
- & Tie Jun Cui
-
Article
| Open Access A RNA producing DNA hydrogel as a platform for a high performance RNA interference system
A RNA producing DNA hydrogel as a platform for a high performance RNA interference system
Interfering RNA have a range of therapeutic and research based applications, issues with delivery have made systems that make siRNA in situ of interest. Here, the author report on the creation of a DNA hydrogel with improved stability and transcription efficiency over plasmid DNA.
- Jaejung Song
- , Minhyuk Lee
- & Nokyoung Park
-
Article
| Open Access A discrete organoplatinum(II) metallacage as a multimodality theranostic platform for cancer photochemotherapy
A discrete organoplatinum(II) metallacage as a multimodality theranostic platform for cancer photochemotherapy
It is challenging to design photosensitizers (PS) with high quantum yields generating singlet oxygen due to severe aggregation between the hydrophobic PSs. Here they develop organoplatinum(II) metallatocage-based PS to overcome these challenges and show excellent antitumor effect.
- Guocan Yu
- , Shan Yu
- & Xiaoyuan Chen
-
Article
| Open Access Anisotropic energy transfer in crystalline chromophore assemblies
Anisotropic energy transfer in crystalline chromophore assemblies
Exciton diffusion length and directionality are important parameters in artificial photosynthetic devices. Here, the authors present a way to make crystalline chromophore assemblies with bespoke architecture, fabricating one exhibiting anisotropic exciton transport properties.
- Ritesh Haldar
- , Marius Jakoby
- & Christof Wöll
-
Article
| Open Access Limitation of Fermi level shifts by polaron defect states in hematite photoelectrodes
Limitation of Fermi level shifts by polaron defect states in hematite photoelectrodes
Hematite has been proposed as a suitable photocatalyst for water splitting based on its stability and appealing optical band gap, but its performance has not reached theoretical expectations. Here the authors show that this is due to intra-gap polaronic states that reduce the effective electronic band gap.
- Christian Lohaus
- , Andreas Klein
- & Wolfram Jaegermann
-
Article
| Open Access Photo-induced semimetallic states realised in electron–hole coupled insulators
Photo-induced semimetallic states realised in electron–hole coupled insulators
Ultrafast light pulses can manipulate and probe materials faster than relaxation timescales, leading to new electronic states and insights into equilibrium properties. Okazaki et al. use the properties of photo-induced metallic states to investigate unconventional correlated behaviour in Ta2NiSe5 and Ta2NiS5.
- Kozo Okazaki
- , Yu Ogawa
- & Shik Shin
-
Article
| Open Access Fundamental limits and non-reciprocal approaches in non-Hermitian quantum sensing
Fundamental limits and non-reciprocal approaches in non-Hermitian quantum sensing
Non-Hermitian properties were proposed to be beneficial to sensing but it is not clear if this concept can be extended to the quantum regime. Here, Lau and Clerk self-consistently consider the impact of noise and measurement, and identify that nonreciprocity can improve sensing capabilities.
- Hoi-Kwan Lau
- & Aashish A. Clerk
-
Article
| Open Access Nanoscale metal-organic frameworks for mitochondria-targeted radiotherapy-radiodynamic therapy
Nanoscale metal-organic frameworks for mitochondria-targeted radiotherapy-radiodynamic therapy
Photosensitizers delivered to mitochondria of cancer cells can enhance photodynamic therapy. Here, the authors report mitochondria-targeted radiation therapy and radiodynamic therapy of colorectal cancer models with a cationic nanoscale metal-organic framework to overcome shallow light penetration of Ru-based photosensitizers.
- Kaiyuan Ni
- , Guangxu Lan
- & Wenbin Lin
-
Article
| Open Access A hardware Markov chain algorithm realized in a single device for machine learning
A hardware Markov chain algorithm realized in a single device for machine learning
Despite the need to develop resistive random access memory (RRAM) devices for machine learning, RRAM array-based hardware methods for algorithm require external electronics. Here, the authors realize a Markov chain algorithm in a single 2D multilayer SnSe device without external electronics.
- He Tian
- , Xue-Feng Wang
- & Tian-Ling Ren
-
Article
| Open Access Superresolution mapping of energy landscape for single charge carriers in plastic semiconductors
Superresolution mapping of energy landscape for single charge carriers in plastic semiconductors
To understand the complex nanoscale structure-property relationships in conjugated polymers for device applications, new methods for tracking charge transport are required. Here, the authors employ superresolution mapping to study the charge carrier dynamics in conjugated polymer nanoparticles.
- Yifei Jiang
- & Jason McNeill
-
Article
| Open Access A selenium-catalysed para-amination of phenols
A selenium-catalysed para-amination of phenols
Selenium has emerged as a metalloid for the catalytic construction of C–N bonds; however no functionalisation of aromatic compounds has been developed yet. Here, the authors report the para-amination of phenols via two successive sigmatropic rearrangements of a redox versatile Se–N bond.
- Dingyuan Yan
- , Guoqiang Wang
- & Jing Zhao
-
Article
| Open Access Heat conduction measurements in ballistic 1D phonon waveguides indicate breakdown of the thermal conductance quantization
Heat conduction measurements in ballistic 1D phonon waveguides indicate breakdown of the thermal conductance quantization
At low temperatures and dimensionality it has become possible to probe the quantum limits of heat transport. Tavakoli et al. show that heat transport through a one-dimensional device can be dominated by non-ideal transmission instead of reaching the regime of thermal conductance quantization.
- Adib Tavakoli
- , Kunal Lulla
- & Olivier Bourgeois
-
Article
| Open Access A luminous blue kilonova and an off-axis jet from a compact binary merger at z = 0.1341
A luminous blue kilonova and an off-axis jet from a compact binary merger at z = 0.1341
A faint gamma-ray burst (GRB 170817A) has been recently detected in coincidence with the gravitational wave (GW) event GW 170817. Here, the authors report that another faint short GRB at a cosmological distance (GRB150101B) and its late time emission are analogous to the neutron star merger event GRB 170817A.
- E. Troja
- , G. Ryan
- & S. Veilleux
-
Article
| Open Access Narrow bandgap oxide nanoparticles coupled with graphene for high performance mid-infrared photodetection
Narrow bandgap oxide nanoparticles coupled with graphene for high performance mid-infrared photodetection
Coupling graphene with narrow band-gap Ti2O3 nanoparticles can enable efficient mid-infrared photodetection. Here, the authors report a graphene-Ti2O3 based hybrid photodetector with high responsivity of ~300 A W-1 up to 10 μm by varying the number of graphene layers and size of Ti2O3 nanoparticles.
- Xuechao Yu
- , Yangyang Li
- & Qi Jie Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Tailoring near-field thermal radiation between metallo-dielectric multilayers using coupled surface plasmon polaritons
Tailoring near-field thermal radiation between metallo-dielectric multilayers using coupled surface plasmon polaritons
Here, the authors report on an experimental demonstration of near-field thermal radiation enhancement between metallo-dielectric multilayers separated by submicron gap distances and that near-field thermal radiation can be readily tuned by modifying the resonance condition of coupled surface plasmon polaritons.
- Mikyung Lim
- , Jaeman Song
- & Bong Jae Lee
-
Article
| Open Access Shaping the topology of folding pathways in mechanical systems
Shaping the topology of folding pathways in mechanical systems
Self-folding origami have applications for mechanical metamaterials but one of their pitfalls is that many undesirable folding modes exist. Here the authors propose an algorithm to determine which folding joints to make stiffer in order to ensure that the sheet is folded into the chosen state.
- Menachem Stern
- , Viraaj Jayaram
- & Arvind Murugan
-
Article
| Open Access Cationic nanoparticle as an inhibitor of cell-free DNA-induced inflammation
Cationic nanoparticle as an inhibitor of cell-free DNA-induced inflammation
Cell-free DNA (cfDNA) released from damaged or dead cells can activate DNA sensors that exacerbate the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis (RA). Here the authors use ~40 nm cationic nanoparticles to scavenge cfDNA, and demonstrate the potential for nanomedicine to relieve debilitating RA symptoms.
- Huiyi Liang
- , Bo Peng
- & Yongming Chen
-
Article
| Open Access DNA engineered micromotors powered by metal nanoparticles for motion based cellphone diagnostics
DNA engineered micromotors powered by metal nanoparticles for motion based cellphone diagnostics
Micromotors have a range of potential healthcare applications. Here, the authors describe the development of a metal nanoparticle DNA micromotor which can be used to detect human HIV-1 by a change in the motion of the micromotors, monitored by cell phone camera, triggered by binding of HIV-1 RNA.
- Mohamed Shehata Draz
- , Kamyar Mehrabi Kochehbyoki
- & Hadi Shafiee
-
Article
| Open Access Single Particle Automated Raman Trapping Analysis
Single Particle Automated Raman Trapping Analysis
Enabling concurrent, high throughput analysis of single nano particles would greatly increase the capacity to study size, composition and inter and intra particle population variance. Here, the authors present a comprehensive platform for single particle automated Raman trapping analysis without any target modification.
- Jelle Penders
- , Isaac J. Pence
- & Molly M. Stevens
-
Article
| Open Access Definite photon deflections of topological defects in metasurfaces and symmetry-breaking phase transitions with material loss
Definite photon deflections of topological defects in metasurfaces and symmetry-breaking phase transitions with material loss
Photonic structures can be used to simulate fundamental physical phenomena like the optical analog of gravity. Here, the authors use metasurface-engineered waveguides to emulate the optical effects of a topological defect on space-time.
- Chong Sheng
- , Hui Liu
- & Shining Zhu
-
Article
| Open Access Skin-touch-actuated textile-based triboelectric nanogenerator with black phosphorus for durable biomechanical energy harvesting
Skin-touch-actuated textile-based triboelectric nanogenerator with black phosphorus for durable biomechanical energy harvesting
Incorporation of triboelectric nanogenerators into textiles is attractive for self-powered wearable electronics. Here the authors employ black phosphorus with a hydrophobic coating in a durable, washable, and air permeable textile-based device that converts biomechanical motion into electricity.
- Jiaqing Xiong
- , Peng Cui
- & Pooi See Lee
-
Article
| Open Access Energy level tuned indium arsenide colloidal quantum dot films for efficient photovoltaics
Energy level tuned indium arsenide colloidal quantum dot films for efficient photovoltaics
Existing n-type colloidal quantum dot materials easily lose their doping polarity in air. Here Song et al. passivate the reactive covalent surface of indium arsenide quantum dots to gain the energy-level tunability and show p–n junction type solar cells with 7.92% certified efficiency.
- Jung Hoon Song
- , Hyekyoung Choi
- & Sohee Jeong
-
Article
| Open Access Lipopolysaccharide-affinity copolymer senses the rapid motility of swarmer bacteria to trigger antimicrobial drug release
Lipopolysaccharide-affinity copolymer senses the rapid motility of swarmer bacteria to trigger antimicrobial drug release
Urinary tract infections are a common side effect of urethral catheters. Here, the authors report on the development of antibiotic loaded NPs with functional polymer coatings which attach too and are removed by motile bacteria to trigger the release of antibiotic.
- Shengtao Lu
- , Wuguo Bi
- & Edwin K. L. Yeow
-
Article
| Open Access Uncovering the heterogeneity and temporal complexity of neurodegenerative diseases with Subtype and Stage Inference
Uncovering the heterogeneity and temporal complexity of neurodegenerative diseases with Subtype and Stage Inference
Progressive diseases tend to be heterogeneous in their underlying aetiology mechanism, disease manifestation, and disease time course. Here, Young and colleagues devise a computational method to account for both phenotypic heterogeneity and temporal heterogeneity, and demonstrate it using two neurodegenerative disease cohorts.
- Alexandra L Young
- , Razvan V Marinescu
- & Ansgar J Furst
-
Article
| Open Access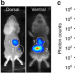 Automated quantification of bioluminescence images
Automated quantification of bioluminescence images
Analysis of bioluminescence images of bacterial distributions in living animals is mostly manual and semiquantitative. Here, the authors present an analysis platform featuring an animal mold, a probabilistic organ atlas, and a mirror gantry to perform automatic in vivo bioluminescence quantification.
- Alexander D. Klose
- & Neal Paragas
-
Article
| Open Access Characterization of a long overlooked copper protein from methane- and ammonia-oxidizing bacteria
Characterization of a long overlooked copper protein from methane- and ammonia-oxidizing bacteria
Methane- and ammonia-oxidizing bacteria use the integral membrane, copper-dependent enzymes particulate methane monooxygenase (pMMO) and ammonia monooxygenase (AMO) to oxidize methane and ammonia. Here the authors structurally characterize the copper-binding protein PmoD, which contains an unusual CuA site and their genetic analyses strongly support a pMMO and AMO related function of PmoD.
- Oriana S. Fisher
- , Grace E. Kenney
- & Amy C. Rosenzweig
-
Article
| Open Access Steering is an essential feature of non-locality in quantum theory
Steering is an essential feature of non-locality in quantum theory
Quantum nonlocality is known to be reducible to quantum uncertainty and steering, but it is unclear whether steering is actually as essential as uncertainty. Here, the authors show that both steering and uncertainty play a role in determining optimal strategies in nonlocal games.
- Ravishankar Ramanathan
- , Dardo Goyeneche
- & Paweł Horodecki
-
Article
| Open Access Photonic thermal management of coloured objects
Photonic thermal management of coloured objects
Understanding the tunable range of radiative thermal load for a given colour is important for thermal management of outdoor structures. Here, the authors theoretically and experimentally highlighted all mechanisms through which one can control the radiative thermal load of coloured objects.
- Wei Li
- , Yu Shi
- & Shanhui Fan
-
Article
| Open Access Fine-tuning the efficiency of para-hydrogen-induced hyperpolarization by rational N-heterocyclic carbene design
Fine-tuning the efficiency of para-hydrogen-induced hyperpolarization by rational N-heterocyclic carbene design
Hyperpolarization methods play a crucial role in the in vivo observation of molecular metabolism by MRI techniques. Here, the authors develop NHC-containing iridium complexes which improve the NMR detectability of 1H, 13C and 15N nuclei via transfer of latent magnetism of para-hydrogen into a substrate.
- Peter J. Rayner
- , Philip Norcott
- & Simon B. Duckett
-
Article
| Open Access Cramming versus threading of long amphiphilic oligomers into a polyaromatic capsule
Cramming versus threading of long amphiphilic oligomers into a polyaromatic capsule
Molecular capsules typically bind only guests with volumes smaller than their cavities. Here, the authors find that a polyaromatic capsule accommodates linear amphiphilic oligomers in a length-dependent manner, whereas short chains are fully crammed into the cavity, long chains can be incorporated into the capsule in a threaded fashion.
- Masahiro Yamashina
- , Shunsuke Kusaba
- & Michito Yoshizawa
-
Article
| Open Access Harnessing copper-palladium alloy tetrapod nanoparticle-induced pro-survival autophagy for optimized photothermal therapy of drug-resistant cancer
Harnessing copper-palladium alloy tetrapod nanoparticle-induced pro-survival autophagy for optimized photothermal therapy of drug-resistant cancer
“Conventional chemotherapy-photothermal therapy combination has limited efficacy in drug resistant cancers. Here they develop Copper-palladium tetrapod nanoparticles to overcome these challenges and show them to work in synergy with autophagy inhibitors to treat drug resistant cancers”
- Yunjiao Zhang
- , Rui Sha
- & Long-ping Wen
-
Article
| Open Access Local generation of hydrogen for enhanced photothermal therapy
Local generation of hydrogen for enhanced photothermal therapy
The tracking and targeted release of multi-agents to cooperatively treat cancer is a developing and evolving field. Here, the authors demonstrate the anticancer effects of cubic Pd hydride nanocrystals with photoacoustic imaging properties that can release hydrogen under an NIR trigger and have photothermal effects.
- Penghe Zhao
- , Zhaokui Jin
- & Qianjun He
-
Article
| Open Access The quantum-confined Stark effect in layered hybrid perovskites mediated by orientational polarizability of confined dipoles
The quantum-confined Stark effect in layered hybrid perovskites mediated by orientational polarizability of confined dipoles
The quantum-confined Stark effect is conventionally observed in inorganic semiconductor multilayer quantum well structures that are expensive to make. Here Walters et al. report large Stark effects in easily made layered hybrid perovskites and exploit the orientational polarizability of dipolar cations.
- G. Walters
- , M. Wei
- & E. Sargent
-
Article
| Open Access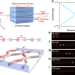 State-recycling and time-resolved imaging in topological photonic lattices
State-recycling and time-resolved imaging in topological photonic lattices
Topological effects can be emulated using photonic lattices where the length of a waveguide represents time, which is often limited by fabrication constraints. Here, Mukherjee et al. exploit a single-photon detector array enabled state-recycling scheme to increase the accessible time scale.
- Sebabrata Mukherjee
- , Harikumar K. Chandrasekharan
- & Robert R. Thomson
-
Article
| Open Access Spatially-resolved fluorescence-detected two-dimensional electronic spectroscopy probes varying excitonic structure in photosynthetic bacteria
Spatially-resolved fluorescence-detected two-dimensional electronic spectroscopy probes varying excitonic structure in photosynthetic bacteria
2D electronic spectroscopy enables a spatially-averaged view of the electronic structure of a heterogeneous system. Here, the authors extend it to sub-micron resolution and ~106 times better sensitivity, to resolve spatially varying excitonic structure in a heterogeneous mixture of photosynthetic cells.
- Vivek Tiwari
- , Yassel Acosta Matutes
- & Jennifer P. Ogilvie
-
Article
| Open Access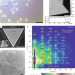 Space- and time-resolved small angle X-ray scattering to probe assembly of silver nanocrystal superlattices
Space- and time-resolved small angle X-ray scattering to probe assembly of silver nanocrystal superlattices
How nanocrystals assemble into superlattices is poorly understood, given the difficulty of probing these processes in real time, in a controlled environment. Here, the authors use space- and time-resolved in situ small angle X-ray scattering to monitor the ordering of nanocrystal superlattices by electric field, which allows them to extract quantitative information about the assembly process.
- Yixuan Yu
- , Dian Yu
- & Christine A. Orme
-
Article
| Open Access Spectral field mapping in plasmonic nanostructures with nanometer resolution
Spectral field mapping in plasmonic nanostructures with nanometer resolution
Characterizing plasmonic coupling has proven elusive. Here, the authors obtain a spectrally resolved deflection map related to a focused electron beam, which has excited a surface plasmon resonance, and relate this deflection to the spectral component of the induced electric and magnetic fields pertaining to the mode.
- J. Krehl
- , G. Guzzinati
- & A. Lubk
-
Article
| Open Access Charging dynamics of an individual nanopore
Charging dynamics of an individual nanopore
Modern energy-storage technologies are based on porous electrodes that store charge within nanometrically-narrow pores or slits. Here the authors show an approach to probe and measure, for the first time, the charging dynamics within an individual nano-slit – the basic element of a porous electrode.
- Ran Tivony
- , Sam Safran
- & Jacob Klein
-
Article
| Open Access Identifying triplet pathways in dilute pentacene films
Identifying triplet pathways in dilute pentacene films
Singlet fission results in the formation of a pair of triplets, known as a quintet. Here, the authors identify long-lived quintets in dilute pentacene films at room temperature, with lifetimes influenced by intermolecular geometry having implications for the design of triplet-harvesting films.
- Daphné Lubert-Perquel
- , Enrico Salvadori
- & Christopher W. M. Kay
-
Article
| Open Access Unbiased biocatalytic solar-to-chemical conversion by FeOOH/BiVO4/perovskite tandem structure
Unbiased biocatalytic solar-to-chemical conversion by FeOOH/BiVO4/perovskite tandem structure
Photoelectrochemical (PEC) cell platforms typically need an electrical bias that drives the electron transfer from the photoanode to the photocathode. Here, the authors report a bias-free PEC tandem device for solar-driven redox biocatalysis.
- Yang Woo Lee
- , Passarut Boonmongkolras
- & Chan Beum Park
-
Article
| Open Access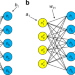 Quantum machine learning for electronic structure calculations
Quantum machine learning for electronic structure calculations
With the rapid development of quantum computers, quantum machine learning approaches are emerging as powerful tools to perform electronic structure calculations. Here, the authors develop a quantum machine learning algorithm, which demonstrates significant improvements in solving quantum many-body problems.
- Rongxin Xia
- & Sabre Kais
-
Article
| Open Access Contact angle measurement of free-standing square-millimeter single-layer graphene
Contact angle measurement of free-standing square-millimeter single-layer graphene
Experimental determination of the contact angle of a two-dimensional film is crucial to understand its wettability characteristics. Here, the authors use the captive bubble method to estimate a contact angle value of 42° ± 3° for a monolayer graphene film.
- Anna V. Prydatko
- , Liubov A. Belyaeva
- & Grégory F. Schneider

 Complex assembly from planar and twisted π-conjugated molecules towards alloy helices and core-shell structures
Complex assembly from planar and twisted π-conjugated molecules towards alloy helices and core-shell structures