Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access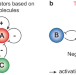 Selenium catalysis enables negative feedback organic oscillators
Selenium catalysis enables negative feedback organic oscillators
Multiple autocatalytic reactions producing thiols are known, but negative feedback loop motifs are unavailable for thiol chemistry. Here, the authors develop a negative feedback loop based on the selenocarbonates, in which thiols induce the release of aromatic selenols that catalyze the oxidation of thiols by organic peroxides.
- Xiuxiu Li
- , Polina Fomitskaya
- & Sergey N. Semenov
-
Article
| Open Access Rapid room-temperature phosphorescence chiral recognition of natural amino acids
Rapid room-temperature phosphorescence chiral recognition of natural amino acids
Chiral recognition of amino acids with luminescence, despite its advantages, is usually slow and lacks generality. Here, the authors demonstrate that L-phenylalanine derived benzamide can manifest the structural difference between the natural, left-handed amino acid and its right-handed counterpart via the difference in room-temperature phosphorescence, irrespective of the specific chemical structure.
- Xiaoyu Chen
- , Renlong Zhu
- & Guoqing Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Orbital hybridization of donor and acceptor to enhance the conductivity of mixed-stack complexes
Orbital hybridization of donor and acceptor to enhance the conductivity of mixed-stack complexes
Mixed-stack complexes consisting of alternating donors and acceptors typically show low electrical conductivity. Here, the authors improved the conductivity by hybridizing the frontier orbitals of the donor and acceptor at the neutral–ionic boundary.
- Tomoko Fujino
- , Ryohei Kameyama
- & Hatsumi Mori
-
Article
| Open Access On the role of asymmetric molecular geometry in high-performance organic solar cells
On the role of asymmetric molecular geometry in high-performance organic solar cells
The correlation between asymmetric molecular geometry of non-fullerene acceptors and their optoelectronic properties was unclear. Here, the authors found asymmetric ones exhibit increased open-circuit voltage compared to their symmetric counterparts due to reduced non-radiative charge recombination.
- Jinfeng Huang
- , Tianyi Chen
- & Lijian Zuo
-
Article
| Open Access Embedding biocatalysts in a redox polymer enhances the performance of dye-sensitized photocathodes in bias-free photoelectrochemical water splitting
Embedding biocatalysts in a redox polymer enhances the performance of dye-sensitized photocathodes in bias-free photoelectrochemical water splitting
A robust and efficient dye-sensitized NiO bio-hybrid photocathode based on a redox polymer and [FeFe]- hydrogenase has been developed to couple with a BiVO4 photoanode for water splitting without applied bias.
- Fangwen Cheng
- , Olha Pavliuk
- & Haining Tian
-
Article
| Open Access Quantum phase synchronization via exciton-vibrational energy dissipation sustains long-lived coherence in photosynthetic antennas
Quantum phase synchronization via exciton-vibrational energy dissipation sustains long-lived coherence in photosynthetic antennas
Photosynthesis in biological systems occurs in a noisy environment that reduces the lifetime of coherences in the excitation energy transfer. Here the author demonstrate that long-lasting coherences are protected by quantum phase synchronization, realized in dimers by exciton-vibrational coupling where energy dissipation occurs predominantly in resonant anti-symmetric collective modes.
- Ruidan Zhu
- , Wenjun Li
- & Yuxiang Weng
-
Article
| Open Access Controlled condensation by liquid contact-induced adaptations of molecular conformations in self-assembled monolayers
Controlled condensation by liquid contact-induced adaptations of molecular conformations in self-assembled monolayers
Surface condensation is predetermined and is typically adjusted by chemical or topographical surface modification. Here, the authors report on a strategy to control the surface condensation behavior by adjusting molecular conformations in self-assembled monolayers.
- Guoying Bai
- , Haiyan Zhang
- & Yufeng Liu
-
Article
| Open Access Spiral packing and chiral selectivity in model membranes probed by phase-resolved sum-frequency generation microscopy
Spiral packing and chiral selectivity in model membranes probed by phase-resolved sum-frequency generation microscopy
The properties of lipid membranes are intimately controlled by their complex heterogeneous structure. Here, the authors use phase-resolved sum-frequency generation microscopy to fully determine the hierarchical lipid packing from the molecular to the mesoscopic scale.
- Alexander P. Fellows
- , Ben John
- & Martin Thämer
-
Article
| Open Access A 2D chiral microcavity based on apparent circular dichroism
A 2D chiral microcavity based on apparent circular dichroism
Here the authors induce asymmetric transmission in planar Fabry–Pérot microcavities by embedding organic thin films exhibiting apparent circular dichroism (ACD), an optical phenomenon based on 2D chirality.
- Tzu-Ling Chen
- , Andrew Salij
- & Randall H. Goldsmith
-
Article
| Open Access Universal inter-molecular radical transfer reactions on metal surfaces
Universal inter-molecular radical transfer reactions on metal surfaces
Radicals are expected to be inactive on metal surfaces. Here the authors describe general intermolecular radical transfer reactions on Ag and Cu surfaces and confirm the reaction mechanism by extensive control experiments.
- Junbo Wang
- , Kaifeng Niu
- & Lifeng Chi
-
Article
| Open Access Optically induced charge-transfer in donor-acceptor-substituted p- and m- C2B10H12 carboranes
Optically induced charge-transfer in donor-acceptor-substituted p- and m- C2B10H12 carboranes
Icosahedral carboranes have long been considered to be aromatic but the extent of conjugation between these clusters and their substituents is still being debated. Here the authors demonstrate carboranes as conjugated bridges in optical functional chromophores.
- Lin Wu
- , Marco Holzapfel
- & Lei Ji
-
Article
| Open Access Thermodiffusive desalination
Thermodiffusive desalination
Current desalination technologies are energy intensive and suffer from membrane degradation and fouling. Here, authors propose and explore the potential of thermodiffusion as a means of membrane-free, single-phase thermal desalination. A pathway towards a feasible thermodiffusive desalination is provided.
- Shuqi Xu
- , Alice J. Hutchinson
- & Juan F. Torres
-
Article
| Open Access Emissive brightening in molecular graphene nanoribbons by twilight states
Emissive brightening in molecular graphene nanoribbons by twilight states
The authors demonstrate that the band structure of graphene nanoribbons is modulated by cove edges, brightening the luminescence 4-fold via emission from otherwise dark twilight states. High spectral resolution of the optical response reveals strong vibron-electron coupling
- Bernd K. Sturdza
- , Fanmiao Kong
- & Robin J. Nicholas
-
Article
| Open Access Aluminum corrosion–passivation regulation prolongs aqueous batteries life
Aluminum corrosion–passivation regulation prolongs aqueous batteries life
Aqueous batteries have a short lifespan due to Al current collector corrosion and Li loss from side reactions on the anode. Here, the authors propose a prototype of self-prolonging aqueous Li-ion batteries by introducing hydrolyzation-type anodic additives to regulate Al corrosion-passivation.
- Binghang Liu
- , Tianshi Lv
- & Liumin Suo
-
Article
| Open Access Ultrafast photoinduced C-H bond formation from two small inorganic molecules
Ultrafast photoinduced C-H bond formation from two small inorganic molecules
The formation of C–H bonds via reaction of small inorganic molecules is of great interest for understanding the transition from inorganic to organic matter, but the detailed mechanisms remain elusive. Here, the authors demonstrate real-time visualization and coherent control of the ultrafast C–H bond formation dynamics in a light-induced bimolecular reaction from inorganic species.
- Zhejun Jiang
- , Hao Huang
- & Jian Wu
-
Article
| Open Access Hairpin trimer transition state of amyloid fibril
Hairpin trimer transition state of amyloid fibril
Amyloid fibrils are ordered protein assemblies implicated in neurodegenerative disease. Here the authors show that hairpin trimers can be transition states of fibril nucleation, explaining how different fibril isoforms may arise from alternative nucleation sites.
- Levent Sari
- , Sofia Bali
- & Milo M. Lin
-
Article
| Open Access Large exchange-driven intrinsic circular dichroism of a chiral 2D hybrid perovskite
Large exchange-driven intrinsic circular dichroism of a chiral 2D hybrid perovskite
Li et al. report large circular dichroism in 2D chiral perovskite single crystals, arises from the inorganic sublattice, instead of chiral ligands, driven by electron-hole exchange interactions. This is evidenced by both reflective circular dichroism spectroscopy and ab initio theory.
- Shunran Li
- , Xian Xu
- & Peijun Guo
-
Article
| Open Access Photoswitchable polyynes for multiplexed stimulated Raman scattering microscopy with reversible light control
Photoswitchable polyynes for multiplexed stimulated Raman scattering microscopy with reversible light control
Bioimaging with photocontrol and multiplexing capability is vital for studying cellular interactions and dynamics, but multiplexed stimulated Raman scattering (SRS) imaging with reversible photocontrol is elusive. Here, the authors report SRS microscopy with Carbow-switch enabling multiplexed SRS imaging and tracking in live cells with reversible photocontrol and high spatiotemporal selectivity.
- Yueli Yang
- , Xueyang Bai
- & Fanghao Hu
-
Article
| Open Access Squeezing formaldehyde into C60 fullerene
Squeezing formaldehyde into C60 fullerene
The interconversion of the two spin isomers of formaldehyd has been studied in the gas phase but has never been observed experimentally in the condensed phase. Here the authors report the encapsulation of formaldehyde inside C60 cages and observe spin-isomer conversion of the formaldehyde guest molecules in the cryogenic solid state.
- Vijyesh K. Vyas
- , George R. Bacanu
- & Richard J. Whitby
-
Article
| Open Access Dynamics of the charge transfer to solvent process in aqueous iodide
Dynamics of the charge transfer to solvent process in aqueous iodide
Solvated electrons can be formed through photo-induced charge-transfer-to-solvent electronic states of halide ions in water. Here, the authors use machine learning accelerated molecular dynamics simulations to follow the evolution of these states for aqueous iodide in detail.
- Jinggang Lan
- , Majed Chergui
- & Alfredo Pasquarello
-
Article
| Open Access Theoretical formulation of chemical equilibrium under vibrational strong coupling
Theoretical formulation of chemical equilibrium under vibrational strong coupling
Strong light-matter interactions in optical microcavities can be used to control molecular kinetic and thermodynamic phenomena. Here, the authors introduce a theory that describes the nonperturbative effects of infrared microcavities on chemical equilibria.
- Kaihong Sun
- & Raphael F. Ribeiro
-
Article
| Open Access Controlled dissolution of a single ion from a salt interface
Controlled dissolution of a single ion from a salt interface
The strong ionic bond in salt is broken by electrostatic interactions with water, but direct observation at the level of a single ion is challenging. Here, the authors have visualized the preferential dissolution of an anion by manipulating a single water molecule.
- Huijun Han
- , Yunjae Park
- & Hyung-Joon Shin
-
Article
| Open Access Mechanistic insight into the competition between interfacial and bulk reactions in microdroplets through N2O5 ammonolysis and hydrolysis
Mechanistic insight into the competition between interfacial and bulk reactions in microdroplets through N2O5 ammonolysis and hydrolysis
The authors report a computational strategy to simulate the hydrolysis and ammonolysis of N2O5 in aerosols using high-level quantum chemical methods. The computational results reveal a complete picture of the reactive uptake of N2O5 by atmospheric aerosols with or without NH3.
- Ye-Guang Fang
- , Bo Tang
- & Wei-Hai Fang
-
Article
| Open Access Understanding of complex spin up-conversion processes in charge-transfer-type organic molecules
Understanding of complex spin up-conversion processes in charge-transfer-type organic molecules
Kim et al. propose a model for the complex spin-flip process in charge-transfer-type thermally activated delayed fluorescence molecules, uncovering the origin of the high-lying triplet state, addressing a pressing issue discussed over the last decade.
- Hyung Suk Kim
- , Sang Hoon Lee
- & Chihaya Adachi
-
Article
| Open Access Stabilization of N6 and N8 anionic units and 2D polynitrogen layers in high-pressure scandium polynitrides
Stabilization of N6 and N8 anionic units and 2D polynitrogen layers in high-pressure scandium polynitrides
The authors discover high-pressure Sc2N6, Sc2N8, and ScN5 polynitrides, synthesized at high pressure and temperature conditions, featuring a unique nitrogen catenation and previously unknown N66− anions, N86− anions and anionic corrugated 2D-polynitrogen layers.
- Andrey Aslandukov
- , Alena Aslandukova
- & Leonid Dubrovinsky
-
Article
| Open Access Molecular near-infrared triplet-triplet annihilation upconversion with eigen oxygen immunity
Molecular near-infrared triplet-triplet annihilation upconversion with eigen oxygen immunity
Molecular triplet-triplet upconversion is useful in a wide range of applications, but is limited by significant oxygen quenching. Here the authors report the combination of sensitiser and annihilator that is stable in aerated environments, and suitable for in vivo sensing.
- Xinyu Wang
- , Fangwei Ding
- & Guanying Chen
-
Article
| Open Access Regulating ion affinity and dehydration of metal-organic framework sub-nanochannels for high-precision ion separation
Regulating ion affinity and dehydration of metal-organic framework sub-nanochannels for high-precision ion separation
Understanding ion transport mechanisms in confined environments is key to achieving efficient membrane-based ion separation. Here, the authors regulate the ion affinity and dehydration in metal-organic framework sub-nanochannels and achieve a high-precise mono-/di-valent cation separation.
- Ri-Jian Mo
- , Shuang Chen
- & Zhong-Qiu Li
-
Article
| Open Access Retinal photoisomerization versus counterion protonation in light and dark-adapted bacteriorhodopsin and its primary photoproduct
Retinal photoisomerization versus counterion protonation in light and dark-adapted bacteriorhodopsin and its primary photoproduct
Malakar et al. investigate the photochemical dynamics in the isomerization of bacteriorhodopsin light and dark-adapted forms and in the first photocycle intermediate, K. The results prompt a reevaluation of the counter ion model, revealing that a different protonation then that shown in the classic quadrupole so far considered must be employed to account for the experimental data.
- Partha Malakar
- , Samira Gholami
- & Sanford Ruhman
-
Article
| Open Access Static charge is an ionic molecular fragment
Static charge is an ionic molecular fragment
What is static charge? Analysis of molecularly well-defined surfaces shows that static charge is an ionic molecular fragment. Contact electrification causes the heterolytic cleavage of covalent bonds, generating these fragments.
- Yan Fang
- , Chi Kit Ao
- & Siowling Soh
-
Article
| Open Access A programmable hybrid digital chemical information processor based on the Belousov-Zhabotinsky reaction
A programmable hybrid digital chemical information processor based on the Belousov-Zhabotinsky reaction
Computing platforms based on chemical processes can be an alternative to digital computers in some scenarios but have limited programmability. Here the authors demonstrate a hybrid computing platform combining digital electronics and an oscillatory chemical reaction and demonstrate its computational capabilities.
- Abhishek Sharma
- , Marcus Tze-Kiat Ng
- & Leroy Cronin
-
Article
| Open Access Extensive photochemical restructuring of molecule-metal surfaces under room light
Extensive photochemical restructuring of molecule-metal surfaces under room light
The nature of the molecule-metal interface is crucial for many technological applications. Here, the authors show that the photostability of the material can be sensitive to room light when coated with a single molecular layer, with implications for devices and processes.
- Chenyang Guo
- , Philip Benzie
- & Jeremy J. Baumberg
-
Article
| Open Access Electrofreezing of liquid water at ambient conditions
Electrofreezing of liquid water at ambient conditions
By performing long ab initio molecular dynamics simulations of water under external electric fields, for up to 500 picoseconds, the authors identify a transition to a ferroelectric amorphous phase at ambient conditions.
- Giuseppe Cassone
- & Fausto Martelli
-
Article
| Open Access Disentangling the multiorbital contributions of excitons by photoemission exciton tomography
Disentangling the multiorbital contributions of excitons by photoemission exciton tomography
Understanding excitonic optical excitations is integral to improving optoelectronic and photovoltaic semiconductor devices. Here, Bennecke et al. use photoemission exciton tomography to unravel the multiorbital electron and hole contributions of entangled excitonic states in the prototypical organic semiconductor C60.
- Wiebke Bennecke
- , Andreas Windischbacher
- & Stefan Mathias
-
Article
| Open Access Observation of geometric phase effect through backward angular oscillations in the H + HD → H2 + D reaction
Observation of geometric phase effect through backward angular oscillations in the H + HD → H2 + D reaction
In a combined experimental and theoretical study of the H + HD → H2 + D reaction at low collision energy (1.72 eV), the authors obtain detailed information on the quantum reaction dynamics surrounding a conical intersection.
- Shihao Li
- , Jiayu Huang
- & Xueming Yang
-
Article
| Open Access Transient chemical and structural changes in graphene oxide during ripening
Transient chemical and structural changes in graphene oxide during ripening
Graphene oxide is in demand for various applications - however, this is complicated by changing physicochemical properties over time. Here, the authors show the intrinsic, metastable, and transient states of graphene oxide colloids upon ripening.
- Hayato Otsuka
- , Koki Urita
- & Katsumi Kaneko
-
Article
| Open Access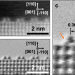 Direct in-situ insights into the asymmetric surface reconstruction of rutile TiO2 (110)
Direct in-situ insights into the asymmetric surface reconstruction of rutile TiO2 (110)
The reconstruction of rutile TiO2 (110) impacts its surface chemistry and catalytic properties. Here, the authors offer a detailed understanding of the asymmetric surface reconstruction of TiO2 (110)-(1×2) through a combination of STEM and DFT calculations.
- Wentao Yuan
- , Bingwei Chen
- & Yong Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Large dynamics of a phase separating arginine-glycine-rich domain revealed via nuclear and electron spins
Large dynamics of a phase separating arginine-glycine-rich domain revealed via nuclear and electron spins
The authors show the RNA-induced droplet formation by a component of Cajal bodies and reveal the large nanoseconds mobility of glycine residues inside droplets as a molecular factor potentially contributing to the large dynamics of Cajal bodies.
- Giuseppe Sicoli
- , Daniel Sieme
- & Nasrollah Rezaei-Ghaleh
-
Article
| Open Access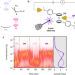 Photooxidation driven formation of Fe-Au linked ferrocene-based single-molecule junctions
Photooxidation driven formation of Fe-Au linked ferrocene-based single-molecule junctions
Metal-metal interfaces hold promise as contacting moieties for single-molecule devices with tunable functionality, yet the direct bonding has remained a challenge. Here, Lee et al. report the formation of Fe-Au bond without chemical ligand support in ferrocene-based molecular junctions.
- Woojung Lee
- , Liang Li
- & Latha Venkataraman
-
Article
| Open Access Unified picture of vibrational relaxation of OH stretch at the air/water interface
Unified picture of vibrational relaxation of OH stretch at the air/water interface
Using femtosecond time-resolved heterodyne-detected vibrational sum-frequency generation spectroscopy the authors determine the vibrational relaxation (T1) time of the O-H stretch at the air/water interface by observing the decay of excited-state OH signals, providing a comprehensive picture of the interfacial vibrational relaxation process of water.
- Woongmo Sung
- , Ken-ichi Inoue
- & Tahei Tahara
-
Article
| Open Access Twofold rigidity activates ultralong organic high-temperature phosphorescence
Twofold rigidity activates ultralong organic high-temperature phosphorescence
Obtaining high-temperature phosphorescence in organic materials can potentially lead to broader applications, but can be challenging to achieve. Here, the authors report the use of rigid molecules as both host and guest to give temperature resistance and therefore high-temperature phosphorescence.
- Kaijun Chen
- , Yongfeng Zhang
- & Xiang Ma
-
Article
| Open Access Visualization-enhanced under-oil open microfluidic system for in situ characterization of multi-phase chemical reactions
Visualization-enhanced under-oil open microfluidic system for in situ characterization of multi-phase chemical reactions
Under-oil open microfluidic systems have potential for studying multi-phase chemical reactions but have so far demonstrated largely only for biological applications. Here, the authors report the development of a system for in situ characterization of gas-liquid reactions by Raman spectroscopy.
- Qiyuan Chen
- , Hang Zhai
- & Bu Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Multicompartmental coacervate-based protocell by spontaneous droplet evaporation
Multicompartmental coacervate-based protocell by spontaneous droplet evaporation
Coacervate-based compartments are attractive as potential protocells, but formation and control of the compartments can be challenging. Here, the authors report the spontaneous formation of core-shell, cell-sized coacervate compartments driven by droplet evaporation.
- Cheng Qi
- , Xudong Ma
- & Zhou Liu
-
Article
| Open Access Imaging the state-to-state charge-transfer dynamics between the spin-orbit excited Ar+(2P1/2) ion and N2
Imaging the state-to-state charge-transfer dynamics between the spin-orbit excited Ar+(2P1/2) ion and N2
The charge-transfer reaction Ar++N2 → Ar+N2+ has been largely studied as a model gas-phase reaction but many aspects remain to be understood. Here, differential cross sections of the reaction are measured and calculated with Ar+ prepared in 2P1/2 state, showing that the charge-transfer dynamics differs significantly for Ar+(2P1/2) compared to Ar+(2P3/2) when colliding with N2.
- Guodong Zhang
- , Dandan Lu
- & Hong Gao
-
Article
| Open Access Ag3PO4 enables the generation of long-lived radical cations for visible light-driven [2 + 2] and [4 + 2] pericyclic reactions
Ag3PO4 enables the generation of long-lived radical cations for visible light-driven [2 + 2] and [4 + 2] pericyclic reactions
Photoredox catalysis is an important approach for synthesizing fine chemicals from olefins, but the limited lifetime of radical cation intermediates severely restricts the efficiency. Here, the authors report that Ag3PO4 can efficiently catalyze intramolecular and intermolecular [2 + 2] and Diels–Alder cycloadditions under visible-light irradiation.
- Lirong Guo
- , Rongchen Chu
- & Yifeng Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Observing growth and interfacial dynamics of nanocrystalline ice in thin amorphous ice films
Observing growth and interfacial dynamics of nanocrystalline ice in thin amorphous ice films
In-situ cryo-electron microscopy in thin amorphous ice films and ice-dynamics simulations reveal polymorph-dependent growth kinetics of nanoscale ice crystals. Hetero-crystalline ice exhibits anisotropic growth: fast-growing facets are associated with low-density interfaces, driving tetrahedral ordering of interfacial H2O molecules and accelerating ice growth.
- Minyoung Lee
- , Sang Yup Lee
- & Dong June Ahn
-
Article
| Open Access Anisotropic carrier dynamics and laser-fabricated luminescent patterns on oriented single-crystal perovskite wafers
Anisotropic carrier dynamics and laser-fabricated luminescent patterns on oriented single-crystal perovskite wafers
Based on differently-oriented MAPbBr3 single-crystal wafers, the authors revealed anisotropic carrier dynamics by using angle-resolved pump-probe technique, and the microstructural mechanism of the femtosecond laser-induced emission enhancement
- Chao Ge
- , Yachao Li
- & Yang Liu
-
Article
| Open Access Bioinspired light-driven chloride pump with helical porphyrin channels
Bioinspired light-driven chloride pump with helical porphyrin channels
Artificial ion channels have potential in a range of applications, but achieving performance comparable to biological channels has been challenging. Here, the authors report an artificial, light-driven chloride pump, inspired by halorhodopsin, with a helical porphyrin channel array.
- Chao Li
- , Yi Zhai
- & Lei Jiang
-
Article
| Open Access Origin of the multi-phasic quenching dynamics in the BLUF domains across the species
Origin of the multi-phasic quenching dynamics in the BLUF domains across the species
Here the authors combine 19 F NMR and femtosecond transient absorption to characterise the structural origin of the multiphasic quenching dynamics in various species of BLUF domains, highlighting the importance of the heterogeneous active-site H-bond network.
- Yalin Zhou
- , Siwei Tang
- & Dongping Zhong
-
Article
| Open Access Site-specific metal-support interaction to switch the activity of Ir single atoms for oxygen evolution reaction
Site-specific metal-support interaction to switch the activity of Ir single atoms for oxygen evolution reaction
Common methods for regulating metal-support interactions for single-atom catalysts usually suffer from interference of the variation of supports or sacrificing the stability of catalysts. Here, the authors report a facile electrochemical deposition strategy to design highly active oxygen evolution catalysts with site-specific metal-support interactions via selective anchoring of single atoms.
- Jie Wei
- , Hua Tang
- & Jie Zeng

 Redefined ion association constants have consequences for calcium phosphate nucleation and biomineralization
Redefined ion association constants have consequences for calcium phosphate nucleation and biomineralization