Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Oxygen-evolving photosystem II structures during S1–S2–S3 transitions
Oxygen-evolving photosystem II structures during S1–S2–S3 transitions
Serial femtosecond crystallography reveals the structural dynamics of photosystem II during the S-state transitions that produce dioxygen, providing insight into electron transfer, water insertion, proton release and O–O bond formation on sub-microsecond timescales.
- Hongjie Li
- , Yoshiki Nakajima
- & Jian-Ren Shen
-
Article |
 Tropical forests are approaching critical temperature thresholds
Tropical forests are approaching critical temperature thresholds
Ground truthed thermal data from a new NASA satellite combined with experimental warming data from three continents in an empirical model suggests that tropical forests are closer to a high temperature threshold than previously thought.
- Christopher E. Doughty
- , Jenna M. Keany
- & Joshua B. Fisher
-
Article
| Open Access The electron–proton bottleneck of photosynthetic oxygen evolution
The electron–proton bottleneck of photosynthetic oxygen evolution
Microsecond infrared spectroscopy together with quantum chemistry reveal the rate-determining proton and electron movements and identify an oxygen-radical state of the manganese cluster as the S4 state.
- Paul Greife
- , Matthias Schönborn
- & Holger Dau
-
Article |
 In situ structure of the red algal phycobilisome–PSII–PSI–LHC megacomplex
In situ structure of the red algal phycobilisome–PSII–PSI–LHC megacomplex
In situ structures of PBS–PSII–PSI–LHC megacomplexes from the alga P. purpureum at near-atomic resolution using cryogenic-electron tomography and in situ single-particle analysis are reported, providing interaction details between PBS, PSII and PSI.
- Xin You
- , Xing Zhang
- & Sen-Fang Sui
-
Article |
 Structures of a phycobilisome in light-harvesting and photoprotected states
Structures of a phycobilisome in light-harvesting and photoprotected states
Cryogenic electron microscopy structures of the Synechocystis phycobilisome—alone and bound with orange carotenoid protein—reveal detailed information regarding the biophysical basis of the control of cyanobacterial light harvesting.
- María Agustina Domínguez-Martín
- , Paul V. Sauer
- & Cheryl A. Kerfeld
-
Article |
 Alternative photosynthesis pathways drive the algal CO2-concentrating mechanism
Alternative photosynthesis pathways drive the algal CO2-concentrating mechanism
The CO2-concentrating mechanism of the green alga Chlamydomonas reinhardtii is dependent on pH gradients generated by both cyclic electron flow and O2 photoreduction.
- Adrien Burlacot
- , Ousmane Dao
- & Gilles Peltier
-
Article |
 Architecture of the chloroplast PSI–NDH supercomplex in Hordeum vulgare
Architecture of the chloroplast PSI–NDH supercomplex in Hordeum vulgare
Cryo-electron microscopy structures of the photosystem I–NADH dehydrogenase-like supercomplex in barley provide structural details to elucidate the functions and regulation of photosystem I-dependent cyclic electron transport in chloroplasts.
- Liangliang Shen
- , Kailu Tang
- & Xing Zhang
-
Article |
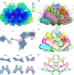 Structural basis of energy transfer in Porphyridium purpureum phycobilisome
Structural basis of energy transfer in Porphyridium purpureum phycobilisome
The cryo-electron microscopy structure of a phycobilisome from the red alga Porphyridium purpureum reveals how aromatic interactions between the linker proteins and the chromophores drive a unidirectional transfer of energy.
- Jianfei Ma
- , Xin You
- & Sen-Fang Sui
-
Article |
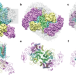 Cryo-EM structure of the spinach cytochrome b6 f complex at 3.6 Å resolution
Cryo-EM structure of the spinach cytochrome b6 f complex at 3.6 Å resolution
A 3.6 Å resolution cryo-electron microscopy structure of the dimeric cytochrome b6f complex from spinach reveals the structural basis for operation of the quinol cycle and its redox-sensing function.
- Lorna A. Malone
- , Pu Qian
- & Matthew P. Johnson
-
Letter |
 A vitamin-C-derived DNA modification catalysed by an algal TET homologue
A vitamin-C-derived DNA modification catalysed by an algal TET homologue
An algal TET dioxygenase homologue, CMD1, uses vitamin C as a glycerol donor to modify 5-methylcytosine and helps to regulate gene transcription in response to high light levels.
- Jian-Huang Xue
- , Guo-Dong Chen
- & Guo-Liang Xu
-
Letter |
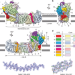 Structure of the complex I-like molecule NDH of oxygenic photosynthesis
Structure of the complex I-like molecule NDH of oxygenic photosynthesis
The structure of NDH, a photosynthetic membrane-protein complex that is related to respiratory complex I, is obtained by single-particle cryo-electron microscopy.
- Thomas G. Laughlin
- , Andrew N. Bayne
- & Karen M. Davies
-
Letter |
 Rubisco condensate formation by CcmM in β-carboxysome biogenesis
Rubisco condensate formation by CcmM in β-carboxysome biogenesis
The structure of a Rubisco–CcmM complex sheds light on the formation of carboxysomes in cyanobacteria.
- H. Wang
- , X. Yan
- & M. Hayer-Hartl
-
Letter |
 Structures of the intermediates of Kok’s photosynthetic water oxidation clock
Structures of the intermediates of Kok’s photosynthetic water oxidation clock
Crystallography and spectroscopy are used to solve high-resolution structures of the intermediates of Kok’s S-state clock in photosystem II.
- Jan Kern
- , Ruchira Chatterjee
- & Vittal K. Yachandra
-
Article |
 Cryo-EM structure of the
Blastochloris viridis LH1–RC complex at 2.9 Å
Cryo-EM structure of the
Blastochloris viridis LH1–RC complex at 2.9 Å
A cryo-electron microscopy structure of the light-harvesting–reaction centre (LH1–RC) complex of the photosynthetic bacterium Blastochloris viridis suggests factors that underlie the large redshift in the absorption spectrum of bacteriochlorophyll in the complex and that promote quinone–quinol translocation across the LH1 ring.
- Pu Qian
- , C. Alistair Siebert
- & C. Neil Hunter
-
Article |
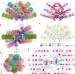 Structure of phycobilisome from the red alga Griffithsia pacifica
Structure of phycobilisome from the red alga Griffithsia pacifica
Single-particle cryo-electron microscopy is used to resolve the structure of the phycobilisome, a 16.8-megadalton light-harvesting megacomplex, from the red alga Griffithsia pacifica at a resolution of 3.5 Å.
- Jun Zhang
- , Jianfei Ma
- & Sen-Fang Sui
-
Letter |
 Global patterns of drought recovery
Global patterns of drought recovery
A global analysis of gross primary productivity reveals that drought recovery is driven by climate and carbon cycling, with recovery longest in the tropics and high northern latitudes, and with impacts increasing over the twentieth century.
- Christopher R. Schwalm
- , William R. L. Anderegg
- & Hanqin Tian
-
Letter |
 Large historical growth in global terrestrial gross primary production
Large historical growth in global terrestrial gross primary production
Long-term records of global carbonyl sulfide levels reveal that terrestrial gross primary production (GPP) increased by around 30% during the twentieth century—a finding that may aid understanding of the connection between GPP growth and climate change.
- J. E. Campbell
- , J. A. Berry
- & M. Laine
-
Letter |
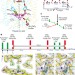 Light-induced structural changes and the site of O=O bond formation in PSII caught by XFEL
Light-induced structural changes and the site of O=O bond formation in PSII caught by XFEL
A new approach, time-resolved serial femtosecond crystallography, is used to view the intermediate states of a photosystem complex following illumination, shedding light on proton transfer and O=O bond formation.
- Michihiro Suga
- , Fusamichi Akita
- & Jian-Ren Shen
-
Letter |
 Structure of photosystem II and substrate binding at room temperature
Structure of photosystem II and substrate binding at room temperature
The structures of three intermediate states of photosystem II, which is crucial for photosynthesis, have been solved at room temperature, shedding new light on this process.
- Iris D. Young
- , Mohamed Ibrahim
- & Junko Yano
-
Letter |
 A blue-light photoreceptor mediates the feedback regulation of photosynthesis
A blue-light photoreceptor mediates the feedback regulation of photosynthesis
Algae rely on blue-light-sensitive phototropin to trigger induction of LHCRS3, allowing it to dissipate energy from excess light that would otherwise compromise the fitness of the organism.
- Dimitris Petroutsos
- , Ryutaro Tokutsu
- & Jun Minagawa
-
Brief Communications Arising |
 No observable conformational changes in PSII
No observable conformational changes in PSII
- Nicholas K. Sauter
- , Nathaniel Echols
- & Vittal K. Yachandra
-
Article |
 Structure of spinach photosystem II–LHCII supercomplex at 3.2 Å resolution
Structure of spinach photosystem II–LHCII supercomplex at 3.2 Å resolution
A high-resolution structural study sheds light on processes of energy transfer within the photosynthetic water-splitting machinery of plants.
- Xuepeng Wei
- , Xiaodong Su
- & Zhenfeng Liu
-
Letter |
 Energetic coupling between plastids and mitochondria drives CO2 assimilation in diatoms
Energetic coupling between plastids and mitochondria drives CO2 assimilation in diatoms
Diatoms optimize their photosynthetic efficiency via extensive energetic exchanges between plastids and mitochondria.
- Benjamin Bailleul
- , Nicolas Berne
- & Giovanni Finazzi
-
Letter |
 Native structure of photosystem II at 1.95 Å resolution viewed by femtosecond X-ray pulses
Native structure of photosystem II at 1.95 Å resolution viewed by femtosecond X-ray pulses
The radiation-damage-free structure of the photosystem II membrane protein complex, which oxidizes water into dioxygen in an oxygen evolving complex, has been determined by an X-ray free electron laser at a resolution of 1.95 Å; one of the substrate oxygen atoms in this reaction is now identified.
- Michihiro Suga
- , Fusamichi Akita
- & Jian-Ren Shen
-
Letter |
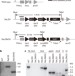 A faster Rubisco with potential to increase photosynthesis in crops
A faster Rubisco with potential to increase photosynthesis in crops
The plant enzyme Rubisco is the main enzyme converting atmospheric carbon dioxide into biological compounds, however, this enzymatic process is inefficient in vascular plants; this study demonstrates that tobacco plants can be engineered to fix carbon with a faster cyanobacterial Rubisco, thus potentially improving plant photosynthesis.
- Myat T. Lin
- , Alessandro Occhialini
- & Maureen R. Hanson
-
Letter |
 Serial time-resolved crystallography of photosystem II using a femtosecond X-ray laser
Serial time-resolved crystallography of photosystem II using a femtosecond X-ray laser
Femtosecond X-ray pulses were used to obtain diffraction data on photosystem II, revealing conformational changes as the complex transitions from the dark S1 state to the double-pumped S3 state; the time-resolved serial femtosecond crystallography technique enables structural determination of protein conformations that are highly prone to traditional radiation damage.
- Christopher Kupitz
- , Shibom Basu
- & Petra Fromme
-
Letter |
 Photosynthetic entrainment of the Arabidopsis thaliana circadian clock
Photosynthetic entrainment of the Arabidopsis thaliana circadian clock
In Arabidopsis thaliana, the rhythm of sugar production by photosynthesis sets the timing of the circadian clock, by regulating the expression of circadian clock genes.
- Michael J. Haydon
- , Olga Mielczarek
- & Alex A. R. Webb
-
Letter |
 Terrestrial water fluxes dominated by transpiration
Terrestrial water fluxes dominated by transpiration
An analysis of the relative effects of transpiration and evaporation, which can be distinguished by how they affect isotope ratios in water, shows that transpiration is by far the largest water flux from Earth’s continents, representing 80 to 90 per cent of terrestrial evapotranspiration and using half of all solar energy absorbed by land surfaces.
- Scott Jasechko
- , Zachary D. Sharp
- & Peter J. Fawcett
-
News |
 Photosynthesis-like process found in insects
Photosynthesis-like process found in insects
Aphids may have a rudimentary sunlight-harvesting system.
- Kathryn Lougheed
-
News |
 How the first plant came to be
How the first plant came to be
A genetic analysis reveals the ancient, complex — and symbiotic — roots of photosynthesis in plants.
- David Biello
-
Article |
 Structure and function of the AAA+ protein CbbX, a red-type Rubisco activase
Structure and function of the AAA+ protein CbbX, a red-type Rubisco activase
- Oliver Mueller-Cajar
- , Mathias Stotz
- & Manajit Hayer-Hartl
-
Letter |
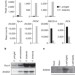 A plastidial sodium-dependent pyruvate transporter
A plastidial sodium-dependent pyruvate transporter
- Tsuyoshi Furumoto
- , Teppei Yamaguchi
- & Katsura Izui
-
News & Views |
 The grass response
The grass response
A three-year study provides insights into how the productivity of a semi-arid rangeland, containing grasses using different photosynthetic pathways, will change in a warmer world with more atmospheric carbon dioxide. See Letter p.202
- Dennis Baldocchi
-
News Feature |
 Physics of life: The dawn of quantum biology
Physics of life: The dawn of quantum biology
The key to practical quantum computing and high-efficiency solar cells may lie in the messy green world outside the physics lab.
- Philip Ball
-
Q&A |
 Turning point: Martin Jonikas
Turning point: Martin Jonikas
A plant biologist has won an international grant for his work using genetic tools to advance understanding of photosynthesis.
- Virginia Gewin
-
Article |
 Crystal structure of oxygen-evolving photosystem II at a resolution of 1.9 Å
Crystal structure of oxygen-evolving photosystem II at a resolution of 1.9 Å
- Yasufumi Umena
- , Keisuke Kawakami
- & Nobuo Kamiya
-
Letter |
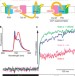 Isolation of the elusive supercomplex that drives cyclic electron flow in photosynthesis
Isolation of the elusive supercomplex that drives cyclic electron flow in photosynthesis
During photosynthesis, light energy is used by photosystems I and II to establish electron flow, which ultimately results in the production of ATP and NADPH. Two modes of electron flow exist, a linear electron flow and a cyclic electron flow (CEF). The latter pathway generates more ATP, but its molecular components have been elusive. Here, a combination of biochemical and spectroscopic techniques has been used to identify the supercomplex that drives CEF in the green alga Chlamydomonas reinhardtii.
- Masakazu Iwai
- , Kenji Takizawa
- & Jun Minagawa
-
News & Views |
 The hidden cost of transpiration
The hidden cost of transpiration
Theoretical analyses reveal how plant investment in the architecture of leaf veins can be shuffled for different conditions, minimizing the construction costs associated with supplying water to leaves.
- David J. Beerling
- & Peter J. Franks
-
Letter |
 Coherently wired light-harvesting in photosynthetic marine algae at ambient temperature
Coherently wired light-harvesting in photosynthetic marine algae at ambient temperature
- Elisabetta Collini
- , Cathy Y. Wong
- & Gregory D. Scholes
-
News & Views |
 Quantum design for a light trap
Quantum design for a light trap
The photosynthetic apparatus of cryptophyte algae is odd — its pigments are farther apart than is expected for efficient functioning. A study into how this apparatus works so well finds quantum effects at play.
- Rienk van Grondelle
- & Vladimir I. Novoderezhkin
-
Article |
 Coupled chaperone action in folding and assembly of hexadecameric Rubisco
Coupled chaperone action in folding and assembly of hexadecameric Rubisco
Form I Rubisco, one of the most abundant proteins in nature, catalyses the fixation of atmospheric CO2 in photosynthesis. The limited catalytic efficiency of Rubisco has sparked extensive efforts to re-engineer the enzyme to enhance agricultural productivity. To bring this goal closer, the formation of cyanobacterial form I Rubisco is now analysed by in vitro reconstitution and cryo-electron microscopy.
- Cuimin Liu
- , Anna L. Young
- & Manajit Hayer-Hartl

 Anoxygenic phototroph of the Chloroflexota uses a type I reaction centre
Anoxygenic phototroph of the Chloroflexota uses a type I reaction centre