Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access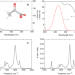 Aqueous pyruvate partly dissociates under deep ultraviolet irradiation but is resilient to near ultraviolet excitation
Aqueous pyruvate partly dissociates under deep ultraviolet irradiation but is resilient to near ultraviolet excitation
The photochemistry of the pyruvate anion plays an important role in the Earth’s atmosphere and aqueous environments. Here, the authors show that excitation of aqueous pyruvate by 200 nm light leads to decarboxylation with a quantum efficiency of 20%, while excitation by 340 nm light does not cause a reaction.
- Jan Thøgersen
- , Fani Madzharova
- & Frank Jensen
-
Article
| Open Access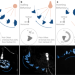 Why flying insects gather at artificial light
Why flying insects gather at artificial light
It is unclear why flying insects congregate around artificial light sources. Here, the authors use high-speed videography and motion-capture, finding that insects fly perpendicular to light sources due to a disruption of the dorsal light response.
- Samuel T. Fabian
- , Yash Sondhi
- & Huai-Ti Lin
-
Article
| Open Access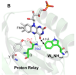 Origin of the multi-phasic quenching dynamics in the BLUF domains across the species
Origin of the multi-phasic quenching dynamics in the BLUF domains across the species
Here the authors combine 19 F NMR and femtosecond transient absorption to characterise the structural origin of the multiphasic quenching dynamics in various species of BLUF domains, highlighting the importance of the heterogeneous active-site H-bond network.
- Yalin Zhou
- , Siwei Tang
- & Dongping Zhong
-
Article
| Open Access Metallopolymer strategy to explore hypoxic active narrow-bandgap photosensitizers for effective cancer photodynamic therapy
Metallopolymer strategy to explore hypoxic active narrow-bandgap photosensitizers for effective cancer photodynamic therapy
Iridium-based photosensitizers exhibit good photocatalytic performance, but the in vivo applications are hindered by conventional O2-dependent Type-II photochemistry and poor absorption. Here, the authors report a general metallopolymerization strategy for engineering iridium complexes exhibiting Type-I photochemistry and enhancing absorption intensity in the blue to near-infrared region.
- Zhao Zhang
- , Zixiang Wei
- & Xuanjun Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access The carbonyl-lock mechanism underlying non-aromatic fluorescence in biological matter
The carbonyl-lock mechanism underlying non-aromatic fluorescence in biological matter
Recent experimental evidence shows a new type of intrinsic fluorescence in biomolecules void of aromatic chemical compounds whose origin is unclear. Here, the authors use non-adiabatic AIMD simulations to show a potential carbonyl-lock mechanism originating this phenomenon.
- Gonzalo Díaz Mirón
- , Jonathan A. Semelak
- & Uriel N. Morzan
-
Article
| Open Access Kinetics of the xanthophyll cycle and its role in photoprotective memory and response
Kinetics of the xanthophyll cycle and its role in photoprotective memory and response
This study explores how the photosynthetic alga Nannochloropsis oceanica, rapidly adapts to changing light conditions, using a short-term “memory" system involving the xanthophyll cycle, which is widespread in photosynthetic organisms.
- Audrey Short
- , Thomas P. Fay
- & Graham R. Fleming
-
Article
| Open Access Two-photon nanoprobes based on bioorganic nanoarchitectonics with a photo-oxidation enhanced emission mechanism
Two-photon nanoprobes based on bioorganic nanoarchitectonics with a photo-oxidation enhanced emission mechanism
Two-photon absorption (TPA) affords unparalleled spatiotemporal resolution for bioimaging, but the photo-oxidation tends to weaken the photoluminescence in vivo, limiting the usefulness of TPA probes. Here, the authors report self-assembling near-infrared cyanine dye-based nanoprobes of enhanced TPA fluorescence imaging capacity based on a photo-oxidation enhanced emission mechanism.
- Shukun Li
- , Rui Chang
- & Xuehai Yan
-
Article
| Open Access Protein control of photochemistry and transient intermediates in phytochromes
Protein control of photochemistry and transient intermediates in phytochromes
Phytochromes are photoreceptors responsible for sensing light in plants, fungi and bacteria. Here the authors use computational simulations to reveal the molecular mechanism of photoactivation and characterize the involved reaction intermediates.
- Giacomo Salvadori
- , Veronica Macaluso
- & Benedetta Mennucci
-
Article
| Open Access Light activation of Orange Carotenoid Protein reveals bicycle-pedal single-bond isomerization
Light activation of Orange Carotenoid Protein reveals bicycle-pedal single-bond isomerization
Orange Carotenoid protein (OCP) is the only photoreceptor with a carotenoid for sensing. Here, the authors report crystal structures of the early OCP photoproduct, suggesting that photo-sensing involves single bond isomerization.
- Volha U. Chukhutsina
- , James M. Baxter
- & Jasper J. van Thor
-
Article
| Open Access On the fluorescence enhancement of arch neuronal optogenetic reporters
On the fluorescence enhancement of arch neuronal optogenetic reporters
Arch-3 rhodopsin variants are common fluorescent reporters of neuronal activity. Here, the authors show with quantum chemical modelling that a set of these proteins reveals a direct proportionality between their observed fluorescence intensity and the stability of an exotic excited-state diradical intermediate.
- Leonardo Barneschi
- , Emanuele Marsili
- & Massimo Olivucci
-
Article
| Open Access Microbial biofilms as living photoconductors due to ultrafast electron transfer in cytochrome OmcS nanowires
Microbial biofilms as living photoconductors due to ultrafast electron transfer in cytochrome OmcS nanowires
Despite enormous potential of solar-driven biocatalysis, most living systems lack photoactive proteins and require toxic and expensive synthetic materials limiting the performance. Here, a class of natural photoconductors is demonstrated through sub-picosecond heme-to-heme electron transfer in bacteria-produced protein nanowires.
- Jens Neu
- , Catharine C. Shipps
- & Nikhil S. Malvankar
-
Article
| Open Access De novo protein design of photochemical reaction centers
De novo protein design of photochemical reaction centers
De novo development of a simplified photosynthetic reaction center protein can clarify practical engineering principles needed to build enzymes for efficient energy conversion. Here, the authors develop an artificial photosynthetic reaction center that functions without the need for sacrificial electron donors or acceptors.
- Nathan M. Ennist
- , Zhenyu Zhao
- & Christopher C. Moser
-
Article
| Open Access N-Heterocyclic carbene-based C-centered Au(I)-Ag(I) clusters with intense phosphorescence and organelle-selective translocation in cells
N-Heterocyclic carbene-based C-centered Au(I)-Ag(I) clusters with intense phosphorescence and organelle-selective translocation in cells
Photoluminescent gold clusters have unique chemical and physical properties based on their perturbed electronic structures. Here, the authors report the synthesis of carbon-centered Au(I)-Ag(I) clusters with high phosphorescence quantum yields using N-heterocyclic carbene ligands.
- Zhen Lei
- , Mizuki Endo
- & Mitsuhiko Shionoya
-
Article
| Open Access Ru(II) photocages enable precise control over enzyme activity with red light
Ru(II) photocages enable precise control over enzyme activity with red light
The cytochrome P450 enzyme CYP1B1 is overexpressed in a variety of tumors, and is correlated with poor treatment outcomes; thus, it is desirable to develop CYP1B1 inhibitors to restore chemotherapy efficacy. Here the authors describe the creation of light-triggered CYP1B1 inhibitors as “prodrugs”, and achieve >6000-fold improvement in potency upon activation with low-energy (660 nm) light.
- Dmytro Havrylyuk
- , Austin C. Hachey
- & Edith C. Glazer
-
Article
| Open Access Signal transduction in light-oxygen-voltage receptors lacking the active-site glutamine
Signal transduction in light-oxygen-voltage receptors lacking the active-site glutamine
Light-oxygen-voltage (LOV) photoreceptors perceive blue light to elicit spatio-temporally defined cellular responses, and their signalling process has been extensively characterized. Here the authors report that the light signal is still transduced in the absence of a conserved Gln residue, thought to be key.
- Julia Dietler
- , Renate Gelfert
- & Andreas Möglich
-
Article
| Open Access Triplet-driven chemical reactivity of β-carotene and its biological implications
Triplet-driven chemical reactivity of β-carotene and its biological implications
The endoperoxides of β-carotene play a key role in signaling of photooxidative stress in plant cells and are regarded as the products of chemical deactivation of singlet oxygen. The authors show that these compounds are instead formed in a reaction between oxygen and β-carotene in their triplet states, revealing the importance of the triplet states in the photoprotection of photosynthetic apparatus.
- Mateusz Zbyradowski
- , Mariusz Duda
- & Leszek Fiedor
-
Article
| Open Access Liquid-microjet photoelectron spectroscopy of the green fluorescent protein chromophore
Liquid-microjet photoelectron spectroscopy of the green fluorescent protein chromophore
The electronic structures of photoactive proteins underlie many natural photoinduced processes. The authors, using UV liquid-microjet photoelectron spectroscopy and quantum chemistry calculations, determine electron detachment energies of the green fluorescent protein chromophore in aqueous solution, approaching conditions of the protein environment.
- Omri Tau
- , Alice Henley
- & Helen H. Fielding
-
Article
| Open Access Dynamics and mechanism of dimer dissociation of photoreceptor UVR8
Dynamics and mechanism of dimer dissociation of photoreceptor UVR8
UVR8 is a plant photoreceptor that dissociates into monomers after sensing UV. Here, via ultrafast spectroscopy and computational calculations, the authors describe the dynamics of charge separation and charge neutralization in UVR8 and describe how these unzip interactions at the dimer interface.
- Xiankun Li
- , Zheyun Liu
- & Dongping Zhong
-
Article
| Open Access Tracking excited state decay mechanisms of pyrimidine nucleosides in real time
Tracking excited state decay mechanisms of pyrimidine nucleosides in real time
The photophysical mechanism by which nucleosides dissipate energy after UV light irradiation is still under debate. Here the authors, using ultrafast time resolved optical spectroscopies and quantum chemical computations, resolve the early steps of such mechanism in uridine and 5-methyluridine in aqueous solution.
- Rocío Borrego-Varillas
- , Artur Nenov
- & Giulio Cerullo
-
Article
| Open Access Ultrafast coherent motion and helix rearrangement of homodimeric hemoglobin visualized with femtosecond X-ray solution scattering
Ultrafast coherent motion and helix rearrangement of homodimeric hemoglobin visualized with femtosecond X-ray solution scattering
Femtosecond time-resolved X-ray solution scattering (fs-TRXSS) measurements provide information on the structural dynamics of proteins in solution. Here, the authors present a structure refinement method for the analysis of fs-TRXSS data and use it to characterise the ultrafast structural changes of homodimeric haemoglobin.
- Yunbeom Lee
- , Jong Goo Kim
- & Hyotcherl Ihee
-
Article
| Open Access 2,6-diaminopurine promotes repair of DNA lesions under prebiotic conditions
2,6-diaminopurine promotes repair of DNA lesions under prebiotic conditions
UV-induced photodamage that likely occurred during the prebiotic synthesis of DNA and RNA is still an untackled issue for their origin on early Earth. Here, the authors show that substitution of 2,6-diaminopurine for adenine enables repair of cyclobutane pyrimidine dimers with high yields, and demonstrate that both 2,6-diaminopurine and adenine nucleosides can be formed under the same prebiotic conditions.
- Rafał Szabla
- , Magdalena Zdrowowicz
- & Janusz Rak
-
Article
| Open Access Photoactivatable metabolic warheads enable precise and safe ablation of target cells in vivo
Photoactivatable metabolic warheads enable precise and safe ablation of target cells in vivo
Metabolites can distinguish pathogenic from healthy cells, but they are hard to couple to current photosensitizers without altering their biological activity. Here the authors design a new family of photosensitizers that retain metabolite function to target pathogenic cells and ablate them by photodynamic therapy.
- Sam Benson
- , Fabio de Moliner
- & Marc Vendrell
-
Article
| Open Access Detection of the thietane precursor in the UVA formation of the DNA 6-4 photoadduct
Detection of the thietane precursor in the UVA formation of the DNA 6-4 photoadduct
The mechanisms of formation of the (6-4) photoproducts in DNA damage by sunlight is still debated. Here the authors show, by optical spectroscopies and computations, the details of the formation of a (6-4) photoadduct via the thietane intermediate in a single-stranded DNA oligonucleotide.
- Luis A. Ortiz-Rodríguez
- , Christian Reichardt
- & Carlos E. Crespo-Hernández
-
Article
| Open Access Photoinduced monooxygenation involving NAD(P)H-FAD sequential single-electron transfer
Photoinduced monooxygenation involving NAD(P)H-FAD sequential single-electron transfer
The number of usable light-responsive enzymes is limited, despite the potential biotechnological applications. Here, the authors report a flavoprotein monooxygenase which is controllable by blue light illumination, and propose a mechanism involving protein-mediated radical photoreduction of FAD via a semiquinone intermediate.
- Simon Ernst
- , Stefano Rovida
- & Steffen L. Drees
-
Article
| Open Access Three-dimensional view of ultrafast dynamics in photoexcited bacteriorhodopsin
Three-dimensional view of ultrafast dynamics in photoexcited bacteriorhodopsin
Bacteriorhodopsin (bR) is a light-driven proton pump. Here the authors combine time-resolved crystallography at a free-electron laser, ultrafast spectroscopy and quantum chemistry to study the structural changes following multiphoton photoexcitation of bR and find that they occur within 300 fs not only in the light-absorbing chromophore but also in the surrounding protein.
- Gabriela Nass Kovacs
- , Jacques-Philippe Colletier
- & Ilme Schlichting
-
Article
| Open Access Rationally designed azobenzene photoswitches for efficient two-photon neuronal excitation
Rationally designed azobenzene photoswitches for efficient two-photon neuronal excitation
Two-photon absorption capacity of azobenzene photoswitches usually comes with a reduction in thermal stability. Here, the authors developed photoswitches with high two-photon sensitivity and enhanced cis isomer thermal lifetime for the control of glutamate receptors.
- Gisela Cabré
- , Aida Garrido-Charles
- & Ramon Alibés
-
Article
| Open Access Ultrafast carbon monoxide photolysis and heme spin-crossover in myoglobin via nonadiabatic quantum dynamics
Ultrafast carbon monoxide photolysis and heme spin-crossover in myoglobin via nonadiabatic quantum dynamics
Myoglobin bound to carbon monoxide undergoes an ultrafast light-induced reaction, which ends up in a photolyzed carbon monoxide and a spin transition of the iron center. Here, the authors employ quantum wavepacket dynamics to show that photolysis precedes the spin transition, a mechanism dominated by strong electron-nuclear couplings.
- Konstantin Falahati
- , Hiroyuki Tamura
- & Miquel Huix-Rotllant
-
Article
| Open Access A light-regulated host–guest-based nanochannel system inspired by channelrhodopsins protein
A light-regulated host–guest-based nanochannel system inspired by channelrhodopsins protein
Light-controlled gating of ion transport across membranes occurs in nature via channelrhodopsin nanochannels. Here, the authors show facile non-covalent approach towards light-responsive biomimetic nanochannels using host–guest interactions between a negative pillararene host and a positive azobenzene guest.
- Yue Sun
- , Junkai Ma
- & Haibing Li
-
Article
| Open Access Near-infrared uncaging or photosensitizing dictated by oxygen tension
Near-infrared uncaging or photosensitizing dictated by oxygen tension
The generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) in photodynamic cancer treatments is limited by low intraturmoural oxygen availability. Here the authors show that irradiation of a silicon phthalocyanine leads to uncaging of a biologically active molecule or to ROS formation in an oxygen-dependent manner.
- Erin D. Anderson
- , Alexander P. Gorka
- & Martin J. Schnermann
-
Article
| Open Access The origin of efficient triplet state population in sulfur-substituted nucleobases
The origin of efficient triplet state population in sulfur-substituted nucleobases
Sulfur-substituted nucleobases are promising photo- and chemotherapeutic drugs. Here, the authors unravel the electronic and structural aspects that lead to the ultrafast population of triplet states in these molecules, providing an explanation for their efficiency as photosensitizers.
- Sebastian Mai
- , Marvin Pollum
- & Leticia González
-
Article |
 Mechanism of signal transduction of the LOV2-Jα photosensor from Avena sativa
Mechanism of signal transduction of the LOV2-Jα photosensor from Avena sativa
Fusion proteins containing blue-light-activated domains have been used as molecular switches to investigate cell signalling, but molecular understanding of the transduction pathway is lacking. Here, MD simulations are used to elucidate the transduction mechanism in a light oxygen voltage2-Ja photosensor.
- Emanuel Peter
- , Bernhard Dick
- & Stephan A. Baeurle

 Retinal photoisomerization versus counterion protonation in light and dark-adapted bacteriorhodopsin and its primary photoproduct
Retinal photoisomerization versus counterion protonation in light and dark-adapted bacteriorhodopsin and its primary photoproduct