Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Mitochondrial injury induced by a Salmonella genotoxin triggers the proinflammatory senescence-associated secretory phenotype
Mitochondrial injury induced by a Salmonella genotoxin triggers the proinflammatory senescence-associated secretory phenotype
Chen et al. probe the role of a genotoxin of Salmonella typhi in triggering a senescence-associated secretory phenotype, via mitochondrial DNA damage.
- Han-Yi Chen
- , Wan-Chen Hsieh
- & Shu-Jung Chang
-
Article
| Open Access Fibrinolytic-deficiencies predispose hosts to septicemia from a catheter-associated UTI
Fibrinolytic-deficiencies predispose hosts to septicemia from a catheter-associated UTI
Catheter-associated urinary tract infections can often lead to secondary bloodstream infections, and catheter-induced bladder inflammation. In this work, authors utilise murine models to probe defective fibrinolysis drives extravascular fibrin formation, potentially predisposing hosts to severe CAUTI.
- Jonathan J. Molina
- , Kurt N. Kohler
- & Ana L. Flores-Mireles
-
Article
| Open Access A fungal core effector exploits the OsPUX8B.2–OsCDC48-6 module to suppress plant immunity
A fungal core effector exploits the OsPUX8B.2–OsCDC48-6 module to suppress plant immunity
Plant ubiquitin regulatory domain-containing proteins (PUX) play vital roles in CDC48-mediated protein quality control processes. Here Shi et al. show that a conserved core Magnaporthe oryzae effector (MoNLE1) can specially target the rice PUX protein OsPUX8B.2 and interfere with host immune responses.
- Xuetao Shi
- , Xin Xie
- & Wende Liu
-
Article
| Open Access Mutations in the efflux pump regulator MexZ shift tissue colonization by Pseudomonas aeruginosa to a state of antibiotic tolerance
Mutations in the efflux pump regulator MexZ shift tissue colonization by Pseudomonas aeruginosa to a state of antibiotic tolerance
Mutations in mexZ, encoding a negative regulator of efflux pump genes, are frequently acquired by Pseudomonas aeruginosa during early lung infection, but do not confer high antibiotic resistance as measured in lab tests. Here, Laborda et al. show that mexZ mutations affect quorum sensing pathways, thus promoting tissue invasiveness and protecting bacteria from the action of antibiotics within tissues.
- Pablo Laborda
- , Signe Lolle
- & Helle Krogh Johansen
-
Article
| Open Access Inter-species gene flow drives ongoing evolution of Streptococcus pyogenes and Streptococcus dysgalactiae subsp. equisimilis
Inter-species gene flow drives ongoing evolution of Streptococcus pyogenes and Streptococcus dysgalactiae subsp. equisimilis
Streptococcus dysgalactiae subsp. equisimilis (SDSE) is an emerging cause of human infection closely related to Streptococcus pyogenes. Here the authors investigate the degree of genomic similarity between the two species and assess implications for development of vaccines.
- Ouli Xie
- , Jacqueline M. Morris
- & Mark R. Davies
-
Article
| Open Access Lipoarabinomannan mediates localized cell wall integrity during division in mycobacteria
Lipoarabinomannan mediates localized cell wall integrity during division in mycobacteria
Mycobacteria have a unique cell envelope that includes characteristic lipoglycans, such as lipoarabinomannan. Here, Sparks et al. show that this lipoglycan plays roles in maintenance of local cell envelope integrity and septal placement during cell division.
- Ian L. Sparks
- , Takehiro Kado
- & Yasu S. Morita
-
Article
| Open Access Dependency on host vitamin B12 has shaped Mycobacterium tuberculosis Complex evolution
Dependency on host vitamin B12 has shaped Mycobacterium tuberculosis Complex evolution
Campos-Pardos et al show that the virulence of Mycobacterium tuberculosis is dependent on sufficient uptake of exogenous vitamin B12 from host serum and this phenotype is not conserved in environmental, opportunistic and ancestral lineages.
- Elena Campos-Pardos
- , Santiago Uranga
- & Jesús Gonzalo-Asensio
-
Article
| Open Access bacLIFE: a user-friendly computational workflow for genome analysis and prediction of lifestyle-associated genes in bacteria
bacLIFE: a user-friendly computational workflow for genome analysis and prediction of lifestyle-associated genes in bacteria
Many bacteria live in close association with eukaryotic hosts, exhibiting detrimental, neutral or beneficial effects on host growth and health. Here, the authors present a streamlined computational workflow for bacterial genome annotation, large-scale comparative genomics, and prediction of genes potentially involved in niche adaptation.
- Guillermo Guerrero-Egido
- , Adrian Pintado
- & Víctor J. Carrión
-
Article
| Open Access Capsules and their traits shape phage susceptibility and plasmid conjugation efficiency
Capsules and their traits shape phage susceptibility and plasmid conjugation efficiency
Bacterial capsules provide protection against the environment, including host immune systems. Authors swap capsule loci in Klebsiella pneumoniae to reveal the role of these sugar coats against plasmid conjugation and phage infection, showing that the serotype is a key player in regulating conjugation rates, and phage susceptibility.
- Matthieu Haudiquet
- , Julie Le Bris
- & Olaya Rendueles
-
Article
| Open Access PsAF5 functions as an essential adapter for PsPHB2-mediated mitophagy under ROS stress in Phytophthora sojae
PsAF5 functions as an essential adapter for PsPHB2-mediated mitophagy under ROS stress in Phytophthora sojae
ROS is an important defense means against pathogens for host. Here the authors show that PsAF5 functions as a mitophagy adapter and regulates mitochondrial homeostasis in Phytophthora sojae under ROS stress, which is crucial for its infection.
- Wenhao Li
- , Hongwei Zhu
- & Xili Liu
-
Article
| Open Access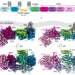 Structure-function analysis of the cyclic β-1,2-glucan synthase from Agrobacterium tumefaciens
Structure-function analysis of the cyclic β-1,2-glucan synthase from Agrobacterium tumefaciens
Here, the authors present the structure of cyclic β-1,2-glucan synthase from Agrobacterium tumefaciens, revealing a distinct mechanism that uses a tyrosine-linked oligosaccharide intermediate in cycles of polymerization and processing of the glucan chain.
- Jaroslaw Sedzicki
- , Dongchun Ni
- & Christoph Dehio
-
Article
| Open Access S-nitrosothiol homeostasis maintained by ADH5 facilitates STING-dependent host defense against pathogens
S-nitrosothiol homeostasis maintained by ADH5 facilitates STING-dependent host defense against pathogens
The generation of reactive oxygen and nitrogen species is an critical part of host defense against microbial infection. Here, Jia et al, characterize the mechanisms by which reactive nitrogen species can modulate innate immunity.
- Mutian Jia
- , Li Chai
- & Wei Zhao
-
Article
| Open Access Implications of the three-dimensional chromatin organization for genome evolution in a fungal plant pathogen
Implications of the three-dimensional chromatin organization for genome evolution in a fungal plant pathogen
The spatial organization of eukaryotic genomes is linked to their biological functions. Here, the authors study the 3D genome organization of the phytopathogenic fungus Verticillium dahliae, revealing links to evolutionary features conserved throughout the Verticillium genus.
- David E. Torres
- , H. Martin Kramer
- & Bart P. H. J. Thomma
-
Article
| Open Access TcrXY is an acid-sensing two-component transcriptional regulator of Mycobacterium tuberculosis required for persistent infection
TcrXY is an acid-sensing two-component transcriptional regulator of Mycobacterium tuberculosis required for persistent infection
Stupar et al. describe a new role for the Mycobacterium tuberculosis two-component system, TcrXY, in the modulation of up to 70 genes, including two effectors, TarA and TarB which mitigate intracellular redox stress.
- Miljan Stupar
- , Lendl Tan
- & Nicholas P. West
-
Article
| Open Access A convergent evolutionary pathway attenuating cellulose production drives enhanced virulence of some bacteria
A convergent evolutionary pathway attenuating cellulose production drives enhanced virulence of some bacteria
Extra-intestinal pathogenic Escherichia coli cause urinary tract and bloodstream infections. Here, the authors show how mutations that disrupt the production of cellulose, a polysaccharide produced by many bacteria, drive enhanced virulence.
- Nguyen Thi Khanh Nhu
- , M. Arifur Rahman
- & Mark A. Schembri
-
Article
| Open Access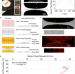 Operando investigation of the synergistic effect of electric field treatment and copper for bacteria inactivation
Operando investigation of the synergistic effect of electric field treatment and copper for bacteria inactivation
The overuse of chemicals in our disinfection processes has warranted the development of alternatives. Here, authors use a lab-on-a-chip device to study and observe the synergistic effects of electric field treatment and copper for inactivation of bacteria with promising applications in many fields.
- Mourin Jarin
- , Ting Wang
- & Xing Xie
-
Article
| Open Access Regulation of TRI5 expression and deoxynivalenol biosynthesis by a long non-coding RNA in Fusarium graminearum
Regulation of TRI5 expression and deoxynivalenol biosynthesis by a long non-coding RNA in Fusarium graminearum
The fungus Fusarium graminearum produces a toxin, deoxynivalenol (DON), that can be found in cereal grains and processed food or feed. Here, Huang et al. study the regulation of DON biosynthesis and show that transcription factors TRI6 and TRI10 regulate each other’s expression and that of a long non-coding RNA which, in turn, downregulates a DON biosynthesis gene.
- Panpan Huang
- , Xiao Yu
- & Cong Jiang
-
Article
| Open Access Hormonal steroids induce multidrug resistance and stress response genes in Neisseria gonorrhoeae by binding to MtrR
Hormonal steroids induce multidrug resistance and stress response genes in Neisseria gonorrhoeae by binding to MtrR
Transcriptional regulator MtrR inhibits the expression of the multidrug efflux pump operon mtrCDE in Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Here, Hooks et al. show that hormonal steroids bind to MtrR and decrease its affinity for cognate promoters, thus leading to increased mtrCDE expression and enhanced antimicrobial resistance.
- Grace M. Hooks
- , Julio C. Ayala
- & Richard G. Brennan
-
Article
| Open Access Microtubules provide force to promote membrane uncoating in vacuolar escape for a cyto-invasive bacterial pathogen
Microtubules provide force to promote membrane uncoating in vacuolar escape for a cyto-invasive bacterial pathogen
Shigella enters human cells in a phagocytic vacuole and then escapes the vacuole to colonize the cytosol. Here, Chang and coworkers show that Shigella uses a bacterial effector to subvert host Rab proteins, microtubules and molecular motors to provide mechanical force to facilitate Shigella escape.
- Yuen-Yan Chang
- , Camila Valenzuela
- & John Rohde
-
Article
| Open Access Isolation and characterization of a pangolin-borne HKU4-related coronavirus that potentially infects human-DPP4-transgenic mice
Isolation and characterization of a pangolin-borne HKU4-related coronavirus that potentially infects human-DPP4-transgenic mice
Pangolins are a potential reservoir for viruses with cross-species infection potential. Here, the authors characterize a HKU4-related coronavirus isolated from pangolin and demonstrate its ability to infect human cell lines as well as its potential to infect transgenic mice expressing the human receptor DPP4.
- Luo-Yuan Xia
- , Zhen-Fei Wang
- & Wu-Chun Cao
-
Article
| Open Access Gestational diabetes augments group B Streptococcus infection by disrupting maternal immunity and the vaginal microbiota
Gestational diabetes augments group B Streptococcus infection by disrupting maternal immunity and the vaginal microbiota
Here, Marcado-Evans et al show that gestational diabetes enhances group B Streptococcus infection through altering host-microbe dynamics, disrupting maternal immunity, and perturbing the vaginal microbiota in a murine pregnancy model.
- Vicki Mercado-Evans
- , Marlyd E. Mejia
- & Kathryn A. Patras
-
Article
| Open Access A two-step activation mechanism enables mast cells to differentiate their response between extracellular and invasive enterobacterial infection
A two-step activation mechanism enables mast cells to differentiate their response between extracellular and invasive enterobacterial infection
Mast cells serve as sentinels for mucosal infection. This study shows how mast cells can differentially detect extracellular and invasive gut bacteria, and in response tune their cytokine production to signal different levels of danger.
- Christopher von Beek
- , Anna Fahlgren
- & Mikael E. Sellin
-
Article
| Open Access Revisiting the Plasmodium sporozoite inoculum and elucidating the efficiency with which malaria parasites progress through the mosquito
Revisiting the Plasmodium sporozoite inoculum and elucidating the efficiency with which malaria parasites progress through the mosquito
Using unique single mosquito data the authors revisit the core quantitative relationships between sequential stages of Plasmodium parasites in their vector host. Their findings demonstrate the importance of mosquito parasite burden in onward transmission success.
- Sachie Kanatani
- , Deborah Stiffler
- & Photini Sinnis
-
Article
| Open Access Natural reversion promotes LPS elongation in an attenuated Coxiella burnetii strain
Natural reversion promotes LPS elongation in an attenuated Coxiella burnetii strain
In vitro propagation of the pathogenic bacterium Coxiella burnetii, the causative agent of Q fever, leads to attenuated virulence and lipopolysaccharide (LPS) truncation. Here, Long et al. show that a strain considered to be avirulent (NMII) can be recovered from infected animals, and these isolates display increased virulence and an elongated LPS due to reversion of a 3-bp mutation in a gene.
- Carrie M. Long
- , Paul A. Beare
- & Robert A. Heinzen
-
Article
| Open Access LOX-1 acts as an N6-methyladenosine-regulated receptor for Helicobacter pylori by binding to the bacterial catalase
LOX-1 acts as an N6-methyladenosine-regulated receptor for Helicobacter pylori by binding to the bacterial catalase
N6-methyladenosine (m6A) modification of mRNA regulates gene expression in eukaryotes. Here, Zeng et al. show that m6A modification of mRNAs contributes to protection against the pathogen Helicobacter pylori by downregulating a host protein that acts as receptor for the pathogen.
- Judeng Zeng
- , Chuan Xie
- & William K. K. Wu
-
Article
| Open Access Quantitative measurement of antibiotic resistance in Mycobacterium tuberculosis reveals genetic determinants of resistance and susceptibility in a target gene approach
Quantitative measurement of antibiotic resistance in Mycobacterium tuberculosis reveals genetic determinants of resistance and susceptibility in a target gene approach
Molecular diagnostics for tuberculosis have focused on predicting drug susceptibilities in a binary manner (i.e., strains are either susceptible or resistant). Here, CRyPTIC Consortium researchers use whole genome sequencing and a quantitative assay to identify associations between genomic mutations and minimum inhibitory concentrations in over 15,000 Mycobacterium tuberculosis clinical isolates.
- Ivan Barilar
- , Simone Battaglia
- & Baoli Zhu
-
Article
| Open Access Effects of plant tissue permeability on invasion and population bottlenecks of a phytopathogen
Effects of plant tissue permeability on invasion and population bottlenecks of a phytopathogen
Bottleneck effects of plant barriers on pathogenic invasions remain unclear. Using a random barcoding approach, this study investigates how plant root permeability limits the invasion and population bottlenecks of a phytopathogenic Ralstonia.
- Gaofei Jiang
- , Yuling Zhang
- & Zhong Wei
-
Article
| Open Access Phage Paride can kill dormant, antibiotic-tolerant cells of Pseudomonas aeruginosa by direct lytic replication
Phage Paride can kill dormant, antibiotic-tolerant cells of Pseudomonas aeruginosa by direct lytic replication
Bacteriophages have primarily been studied using fast-growing laboratory cultures of their bacterial hosts. Here, Maffei et al. show that diverse phages can infect deep-dormant bacteria and suspend their replication until the host resuscitates; however, a particular phage can directly replicate and induce the lysis of deep-dormant hosts.
- Enea Maffei
- , Anne-Kathrin Woischnig
- & Alexander Harms
-
Article
| Open Access Multiplexed multicolor antiviral assay amenable for high-throughput research
Multiplexed multicolor antiviral assay amenable for high-throughput research
Antiviral approaches against entire genera or families of viruses need to be constantly developed and innovated. Focusing on several distantly-related orthoflaviviruses, the authors develop a cell-based multiplex antiviral assay for high-throughput screening against multiple viruses at once.
- Li-Hsin Li
- , Winston Chiu
- & Kai Dallmeier
-
Article
| Open Access Structure and activation mechanism of the Makes caterpillars floppy 1 toxin
Structure and activation mechanism of the Makes caterpillars floppy 1 toxin
The bacterial toxin Makes caterpillars floppy 1 promotes apoptosis in insects. Combining single-particle cryo-EM and biochemistry, the authors determined the molecular architecture of the toxin and revealed its autoproteolytic activation mechanism.
- Alexander Belyy
- , Philipp Heilen
- & Stefan Raunser
-
Article
| Open Access The Helicobacter pylori Genome Project: insights into H. pylori population structure from analysis of a worldwide collection of complete genomes
The Helicobacter pylori Genome Project: insights into H. pylori population structure from analysis of a worldwide collection of complete genomes
The bacterium Helicobacter pylori, often found in the human stomach, can be classified into distinct subpopulations associated with the geographic origin of the host. Here, the authors provide insights into H. pylori population structure by collecting over 1,000 clinical strains from 50 countries and generating and analyzing high-quality bacterial genome sequences.
- Kaisa Thorell
- , Zilia Y. Muñoz-Ramírez
- & Charles S. Rabkin
-
Article
| Open Access Staphylococcus aureus functional amyloids catalyze degradation of β-lactam antibiotics
Staphylococcus aureus functional amyloids catalyze degradation of β-lactam antibiotics
A number of mechanisms are known to mediate bacterial antibiotic resistance. Here, Arad et al show that amyloid fibrils produced by Staphylococcus aureus rapidly degrade common antibiotic molecules.
- Elad Arad
- , Kasper B. Pedersen
- & Raz Jelinek
-
Article
| Open Access Interactions between climate change, urban infrastructure and mobility are driving dengue emergence in Vietnam
Interactions between climate change, urban infrastructure and mobility are driving dengue emergence in Vietnam
The geographic distribution of dengue has been expanding in recent decades, and Vietnam is one of the most severely affected countries. In this study, the authors use Bayesian hierarchical modelling to investigate the socio-environmental and climatic drivers of dengue incidence in Vietnam and how they vary across the country.
- Rory Gibb
- , Felipe J. Colón-González
- & Rachel Lowe
-
Article
| Open Access Geometric constraint-triggered collagen expression mediates bacterial-host adhesion
Geometric constraint-triggered collagen expression mediates bacterial-host adhesion
Cells in the body live in geometrically constrained microenvironments. Here, Feng at al report that these constraints induce collagen IV expression which is responsible for location dependent bacterial adhesion.
- Yuting Feng
- , Shuyi Wang
- & Jianyong Huang
-
Article
| Open Access Functional divergence of a bacterial enzyme promotes healthy or acneic skin
Functional divergence of a bacterial enzyme promotes healthy or acneic skin
Cutibacterium acnes phylotypes can be catalogued based on their association with acneic or healthy skin. Here, Hajam et al show that the functional divergence of a hyaluronidase enzyme expressed by the phylotypes is a major determinant of acne severity.
- Irshad A. Hajam
- , Madhusudhanarao Katiki
- & George Y. Liu
-
Article
| Open Access Machine learning-based motion tracking reveals an inverse correlation between adhesivity and surface motility of the leptospirosis spirochete
Machine learning-based motion tracking reveals an inverse correlation between adhesivity and surface motility of the leptospirosis spirochete
A common approach to study bacterial motility is fluorescent labelling, but this can be hampered by protein expression instability and/or interference with bacterial physiology. Here, Abe et al. describe a machine learning-based method for motion tracking of spirochetes on cultured animal cells, which does not require labelling and might be applied to study motility of other bacterial species.
- Keigo Abe
- , Nobuo Koizumi
- & Shuichi Nakamura
-
Article
| Open Access Diversification of division mechanisms in endospore-forming bacteria revealed by analyses of peptidoglycan synthesis in Clostridioides difficile
Diversification of division mechanisms in endospore-forming bacteria revealed by analyses of peptidoglycan synthesis in Clostridioides difficile
The enzymes FtsW and FtsI are thought to be essential for the synthesis of septal peptidoglycan (PG) during bacterial cell division. Here, Shrestha et al. show that the pathogen Clostridioides difficile lacks a canonical FtsW/FtsI pair, with its homologs fulfilling sporulation-specific roles including the synthesis of septal PG during sporulation-specific cell division.
- Shailab Shrestha
- , Najwa Taib
- & Aimee Shen
-
Article
| Open Access Quorum-sensing synthase mutations re-calibrate autoinducer concentrations in clinical isolates of Pseudomonas aeruginosa to enhance pathogenesis
Quorum-sensing synthase mutations re-calibrate autoinducer concentrations in clinical isolates of Pseudomonas aeruginosa to enhance pathogenesis
Simanek et al. discovered variants that arise in the protein responsible for synthesizing a molecule required for bacterial communication, which mediates the progression of virulence in the pathogen Pseudomonas aeruginosa.
- Kayla A. Simanek
- , Megan L. Schumacher
- & Jon E. Paczkowski
-
Article
| Open Access The protein interactome of the citrus Huanglongbing pathogen Candidatus Liberibacter asiaticus
The protein interactome of the citrus Huanglongbing pathogen Candidatus Liberibacter asiaticus
Research on the biology and pathogenicity of ‘Candidatus Liberibacter asiaticus’ (CLas), the bacterium that causes citrus Huanglongbing disease, is hampered by our inability to cultivate it in artificial media. Here, Carter et al. use a high-throughput yeast-two-hybrid screen to identify thousands of interactions between CLas proteins, thus providing insights into their potential functions.
- Erica W. Carter
- , Orlene Guerra Peraza
- & Nian Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Structural and functional insights into the delivery of a bacterial Rhs pore-forming toxin to the membrane
Structural and functional insights into the delivery of a bacterial Rhs pore-forming toxin to the membrane
Bacterial Rhs proteins constitute a diverse family of secreted toxins. Here, the authors present a cryo-electron microscopy structure of an Rhs protein from Pseudomonas aeruginosa and provide insights into the mechanisms by which the protein delivers its encapsulated pore-forming toxin fragment to the bacterial membrane.
- Amaia González-Magaña
- , Igor Tascón
- & David Albesa-Jové
-
Article
| Open Access RNA is a key component of extracellular DNA networks in Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilms
RNA is a key component of extracellular DNA networks in Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilms
The roles of extracellular RNAs present in bacterial biofilms are poorly understood. Here, Mugunthan et al. show that specific mRNAs associate with extracellular DNA in the matrix of bacterial biofilms, facilitating the formation of viscoelastic networks.
- Sudarsan Mugunthan
- , Lan Li Wong
- & Thomas Seviour
-
Article
| Open Access Distributed genotyping and clustering of Neisseria strains reveal continual emergence of epidemic meningococcus over a century
Distributed genotyping and clustering of Neisseria strains reveal continual emergence of epidemic meningococcus over a century
Core genome multilocus sequence typing (cgMLST) is used to classify bacterial strains for epidemiological applications. Here, the authors describe a distributed cgMLST scheme that does not require a central database of allelic sequences, and apply it to study evolutionary patterns of epidemic and endemic strains of the genus Neisseria.
- Ling Zhong
- , Menghan Zhang
- & Zhemin Zhou
-
Article
| Open Access Regulation of the physiology and virulence of Ralstonia solanacearum by the second messenger 2′,3′-cyclic guanosine monophosphate
Regulation of the physiology and virulence of Ralstonia solanacearum by the second messenger 2′,3′-cyclic guanosine monophosphate
Nucleotide second messengers are employed by many bacterial species to regulate various cellular processes. Here, the authors demonstrate that 2',3'-cyclic guanosine monophosphate (2',3'-cGMP) controls the important biological functions and virulence in Ralstonia solanacearum by abolishing the interaction between a transcriptional regulator and the promoters of target genes.
- Xia Li
- , Wenfang Yin
- & Yinyue Deng
-
Article
| Open Access A smooth tubercle bacillus from Ethiopia phylogenetically close to the Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex
A smooth tubercle bacillus from Ethiopia phylogenetically close to the Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex
The Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex (MTBC) includes several pathogens thought to have originated in East Africa from an ancestor closely related to Mycobacterium canettii. Here, the authors describe a clinical tuberculosis strain isolated in Ethiopia that has typical M. canettii features but is phylogenetically much closer to the MTBC clade, supporting that the emergence of MTBC pathogens is a recent evolutionary event.
- Bazezew Yenew
- , Arash Ghodousi
- & Daniela Maria Cirillo
-
Article
| Open Access c-di-GMP inhibits the DNA binding activity of H-NS in Salmonella
c-di-GMP inhibits the DNA binding activity of H-NS in Salmonella
H-NS is a global regulatory protein that represses expression of many genes in bacteria. Here, Li et al. show that a second messenger, cyclic di-GMP, binds to H-NS and inhibits its binding to DNA, thus relieving H-NS-mediated transcriptional silencing.
- Shuyu Li
- , Qinmeng Liu
- & Lei Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Synthetic genetic oscillators demonstrate the functional importance of phenotypic variation in pneumococcal-host interactions
Synthetic genetic oscillators demonstrate the functional importance of phenotypic variation in pneumococcal-host interactions
Here, Rueff et al engineered a CRISPRi-based oscillator to rewire capsule production in Streptococcus pneumoniae from its native control. They show that heterogeneity in capsule production is beneficial for fitness in several virulence associated traits.
- Anne-Stéphanie Rueff
- , Renske van Raaphorst
- & Jan-Willem Veening
-
Article
| Open Access Glutamine metabolism inhibition has dual immunomodulatory and antibacterial activities against Mycobacterium tuberculosis
Glutamine metabolism inhibition has dual immunomodulatory and antibacterial activities against Mycobacterium tuberculosis
Parveen et al., using immunological, and metabolomics-based assays, demonstrate the importance of host glutamine metabolism in tuberculosis pathogenesis and show host-directed activity against tuberculosis.
- Sadiya Parveen
- , Jessica Shen
- & William R. Bishai
-
Article
| Open Access Enterohaemorrhagic E. coli utilizes host- and microbiota-derived L-malate as a signaling molecule for intestinal colonization
Enterohaemorrhagic E. coli utilizes host- and microbiota-derived L-malate as a signaling molecule for intestinal colonization
Here, Liu et al show that enterohaemorrhagic Escherichia coli utilizes host- and microbiota-derived L-malate as an essential nutrient and signalling molecule to promote its growth and colonization in the large intestine.
- Bin Liu
- , Lingyan Jiang
- & Bin Yang
-
Article
| Open Access Mutational spectra are associated with bacterial niche
Mutational spectra are associated with bacterial niche
Mutagens and DNA repair defects generate context-specific mutational signatures in cancer cells. Here, Ruis et al. provide evidence of similar processes in bacteria, showing that mutational spectra may be associated with sites of bacterial replication when mutagen exposures differ, and can be used in these cases to infer transmission routes.
- Christopher Ruis
- , Aaron Weimann
- & Julian Parkhill

 Salmonella exploits membrane reservoirs for invasion of host cells
Salmonella exploits membrane reservoirs for invasion of host cells