Featured
-
-
Review Article |
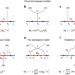 Renormalization group running of neutrino parameters
Renormalization group running of neutrino parameters
Neutrinos are ghost-like particles that interact only very weakly with other particles. As ongoing experiments to measure their properties improve, Ohlsson and Zhou review neutrino mass models and the renormalization group running of neutrino parameters that aim to understand the origin of neutrino mass.
- Tommy Ohlsson
- & Shun Zhou
-
Article |
 High-quality electron beams from a helical inverse free-electron laser accelerator
High-quality electron beams from a helical inverse free-electron laser accelerator
Electrons moving in strongly curved paths emit radiation that is used in free-electron laser designs. Here, the authors demonstrate the inverse force principle, where a laser light field is used in a compact experimental design to accelerate electrons to produce high-quality electron beams.
- J. Duris
- , P. Musumeci
- & V. Yakimenko
-
Article |
 Conversion of magnetic energy in the magnetic reconnection layer of a laboratory plasma
Conversion of magnetic energy in the magnetic reconnection layer of a laboratory plasma
Magnetic reconnection is believed to play a key role in the acceleration and heating of particles in astrophysical plasmas but the details are unclear. Yamada et al. study reconnection in a laboratory plasma, enabling them to determine the exact mechanisms of energy flow from magnetic field to particles.
- Masaaki Yamada
- , Jongsoo Yoo
- & Clayton E. Myers
-
Article |
 Topological excitations in a kagome magnet
Topological excitations in a kagome magnet
Topological excitations in insulating magnets have recently attracted great interest from a fundamental and applied perspective. Here, Pereiro et al.report on the conditions to generate, stabilize and control skyrmions, even at room temperature, in a kagome magnet.
- Manuel Pereiro
- , Dmitry Yudin
- & Anders Bergman
-
Article
| Open Access A moiré deflectometer for antimatter
A moiré deflectometer for antimatter
Measuring forces on antimatter is vital to testing our understanding of fundamental physics. Towards this aim, Aghion et al.present a method to measure the deflection of antiprotons based on an atom optical tool, the moiré deflectometer, which could be extended to future antihydrogen gravity measurements.
- S. Aghion
- , O. Ahlén
- & J. Zmeskal
-
Article |
 Momentum-resolved hidden-order gap reveals symmetry breaking and origin of entropy loss in URu2Si2
Momentum-resolved hidden-order gap reveals symmetry breaking and origin of entropy loss in URu2Si2
URu2Si2 undergoes a prominent phase transition to an ordered state of unknown nature. Using high-resolution 3D ARPES, Bareille et al. image an abrupt symmetry reconstruction of its heavy-fermion electronic structure that could explain the origin of the ordered state and its missing entropy.
- C. Bareille
- , F. L. Boariu
- & A. F. Santander-Syro
-
Article |
 Searching for exotic particles in high-energy physics with deep learning
Searching for exotic particles in high-energy physics with deep learning
High-energy particle colliders are important for finding new particles, but huge volumes of data must be searched through to locate them. Here, the authors show the use of deep-learning methods on benchmark data sets as an approach to improving such new particle searches.
- P. Baldi
- , P. Sadowski
- & D. Whiteson
-
Article
| Open Access An experimental limit on the charge of antihydrogen
An experimental limit on the charge of antihydrogen
Fundamental theories do not predict a difference between the properties of matter and antimatter, but experimental tests of this are still in their infancy. To this end, this study analyses the effects of electric fields on antihydrogen atoms in the ALPHA trap to place a bound on the charge of antihydrogen.
- C. Amole
- , M. D. Ashkezari
- & A. E. Charman
-
Article |
 Single bunch X-ray pulses on demand from a multi-bunch synchrotron radiation source
Single bunch X-ray pulses on demand from a multi-bunch synchrotron radiation source
Although synchrotron facilities routinely operate in a multi-bunch regime for maximum average brilliance, studies relying on time-of-flight schemes require single-bunch operation. Here, Holldack et al.isolate and apply single bunch X-ray pulses from multibunch radiation using pulse picking by resonant excitation.
- K. Holldack
- , R. Ovsyannikov
- & A. Föhlisch
-
Article |
 Bose–Einstein condensation in an ultra-hot gas of pumped magnons
Bose–Einstein condensation in an ultra-hot gas of pumped magnons
In contrast to real atoms, Bose–Einstein condensation of quasi-particles does not require low temperature, but is obtained via external pumping. Here, the authors show an unexpected transitional dynamics of a Bose–Einstein condensate of magnons due to a nonlinear evaporative supercooling mechanism.
- Alexander A. Serga
- , Vasil S. Tiberkevich
- & Burkard Hillebrands
-
Article |
 Self-organization into quantized eigenstates of a classical wave-driven particle
Self-organization into quantized eigenstates of a classical wave-driven particle
The coupling of particles with physical waves is a generic phenomenon observed in various systems, but its differentiation from quantum effect is still unclear. Perrard et al.address this issue using a bouncing liquid drop confined in a magnetic potential well, where quantized motions are obtained.
- Stéphane Perrard
- , Matthieu Labousse
- & Yves Couder
-
Article
| Open Access A source of antihydrogen for in-flight hyperfine spectroscopy
A source of antihydrogen for in-flight hyperfine spectroscopy
Comparing hydrogen and antihydrogen—its antimatter counterpart—provides important tests of fundamental symmetries in the Standard Model. Kuroda et al. present a source of antihydrogen atoms that may provide high-precision in-flight measurements of their ground-state hyperfine splitting.
- N. Kuroda
- , S. Ulmer
- & Y. Yamazaki
-
Article |
 Fusion reactions initiated by laser-accelerated particle beams in a laser-produced plasma
Fusion reactions initiated by laser-accelerated particle beams in a laser-produced plasma
The nuclear fusion of hydrogen and boron nuclei has potential advantages over the fusion of deuterium and tritium for energy production as it produces no neutrons. Labaune et al. report progress towards achieving this by colliding a laser-driven particle beam into a laser-generated plasma.
- C. Labaune
- , C. Baccou
- & J. Rafelski
-
Article
| Open Access Description and first application of a new technique to measure the gravitational mass of antihydrogen
Description and first application of a new technique to measure the gravitational mass of antihydrogen
One intriguing question about antimatter that is yet to be directly answered is whether or not it behaves exactly the same as matter under gravity. Here, a direct experimental method is presented to measure the ratio of inertial to gravitational mass for antihydrogen under free-fall conditions.
- C. Amole
- , M. D. Ashkezari
- & A. E. Charman
-
Article |
 Universal current-velocity relation of skyrmion motion in chiral magnets
Universal current-velocity relation of skyrmion motion in chiral magnets
Current-induced motion of skyrmions is attracting attention due to its low critical current density, however, its microscopic mechanisms have not been elucidated yet. Using numerical simulations, the authors demonstrate a universal current-velocity relation of skyrmion motion, independent of disorder or nonadiabatic effects.
- Junichi Iwasaki
- , Masahito Mochizuki
- & Naoto Nagaosa
-
Article |
 Ultrasensitive magnetic field detection using a single artificial atom
Ultrasensitive magnetic field detection using a single artificial atom
For the ultrasensitive detection of magnetic fields either atomic transitions or superconducting circuits are used. Bal et al. combine such approaches and demonstrate a superconducting device functioning as an artificial atom for magnetic field detection with high sensitivity and spatial resolution.
- M. Bal
- , C. Deng
- & A. Lupascu
-
Article
| Open Access Relativistic frequency upshift to the extreme ultraviolet regime using self-induced oscillatory flying mirrors
Relativistic frequency upshift to the extreme ultraviolet regime using self-induced oscillatory flying mirrors
Generation of ultrafast X-rays using lab-based laser sources is promising for numerous spectroscopic and imaging techniques. By generating a long underdense plasma in a solid, Kim et al.show relativistic frequency upshift of a laser pulse to 4.9 nm, caused by reflection from electron nanosheets.
- I Jong Kim
- , Ki Hong Pae
- & Jongmin Lee
-
Article |
 Measuring the size of individual particles from three-dimensional imaging experiments
Measuring the size of individual particles from three-dimensional imaging experiments
The degree of polydispersity of colloidal suspensions is known to have consequences for their physical properties. Kuritaet al. present a general method for determining the sizes of individual particles, and thus the polydispersity, using only the coordinates of the centre positions of spherical particles.
- Rei Kurita
- , David B. Ruffner
- & Eric R. Weeks
-
Article
| Open Access Direct observation of prompt pre-thermal laser ion sheath acceleration
Direct observation of prompt pre-thermal laser ion sheath acceleration
High-intensity laser-plasma ion generation is promising as a compact proton source for applications like ion beam therapy. Using a femtosecond table-top laser system, Zeilet al. show that protons efficiently gain energy in the pre-thermal intra-pulse phase of the generation process.
- K. Zeil
- , J. Metzkes
- & U. Schramm
-
Article
| Open Access Electric field-induced chemical locomotion of conducting objects
Electric field-induced chemical locomotion of conducting objects
External electric fields have been used to control the motion of small objects through electrostatic repulsion. Here, electric fields are used to polarize conducting objects, triggering their movement by spatially separated electrochemical reactions leading to directionally controlled bubble evolution.
- Gabriel Loget
- & Alexander Kuhn
-
Article
| Open Access Measurement of the inelastic proton–proton cross-section at √s=7 TeV with the ATLAS detector
Measurement of the inelastic proton–proton cross-section at √s=7 TeV with the ATLAS detector
The measurement of the total cross-section of proton–proton collisions is of fundamental importance for particle physics. Here, the first measurement of the inelastic cross-section is presented for proton–proton collisions at an energy of 7 teraelectronvolts using the ATLAS detector at the Large Hadron Collider.
- G. Aad
- , B. Abbott
- & L. Zwalinski
-
Article |
 Quasi-two-dimensional Skyrmion lattices in a chiral nematic liquid crystal
Quasi-two-dimensional Skyrmion lattices in a chiral nematic liquid crystal
Skyrmions are particle-like topological entities in a continuous field that have a role in various condensed matter systems. Here, numerical methods are used to show that a chiral nematic liquid crystal could be used as a model system to facilitate direct structural investigation of Skyrmions.
- Jun-ichi Fukuda
- & Slobodan Žumer

 The quantum nature of skyrmions and half-skyrmions in Cu2OSeO3
The quantum nature of skyrmions and half-skyrmions in Cu2OSeO3