Featured
-
-
Article |
 Bandgap tunability at single-layer molybdenum disulphide grain boundaries
Bandgap tunability at single-layer molybdenum disulphide grain boundaries
Molybdenum disulphide is a two-dimensional material that, unlike graphene, has a nonzero bandgap. Here, the authors demonstrate that the bandgap of single-layer molybdenum disulphide grown on graphite by chemical vapour deposition changes with distance from the grain boundary
- Yu Li Huang
- , Yifeng Chen
- & Andrew T. S. Wee
-
Article |
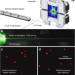 Imaging single cells in a beam of live cyanobacteria with an X-ray laser
Imaging single cells in a beam of live cyanobacteria with an X-ray laser
Imaging live cells at nanometre resolution is challenging because radiation damage kills the cells during exposure. Here, the authors overcome this difficulty in a ‘diffraction before destruction’ experiment using an X-ray laser and record signal to 4 nm resolution on a free-flying cell.
- Gijs van der Schot
- , Martin Svenda
- & Tomas Ekeberg
-
Article |
 Wide-angle planar microtracking for quasi-static microcell concentrating photovoltaics
Wide-angle planar microtracking for quasi-static microcell concentrating photovoltaics
Concentrating photovoltaics (PVs) offer a route to lower the cost of solar power, but their scale has been incompatible with roof top installation. Here, Price et al.demonstrate quasi-static concentrating PVs that achieve >200 × flux concentration over a full day in the form factor of a standard PV panel.
- Jared S. Price
- , Xing Sheng
- & Noel C. Giebink
-
Article
| Open Access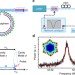 Brillouin-scattering-induced transparency and non-reciprocal light storage
Brillouin-scattering-induced transparency and non-reciprocal light storage
Stimulated Brillouin scattering is a non-linear interaction that allows light to be stored as coherent acoustic waves. Here, the authors report on Brillouin scattering-induced transparency in an optical microresonator whose high quality allows for long-lifetime non-reciprocal light storage.
- Chun-Hua Dong
- , Zhen Shen
- & Guang-Can Guo
-
Article |
 Single-pixel imaging by means of Fourier spectrum acquisition
Single-pixel imaging by means of Fourier spectrum acquisition
Single-pixel imaging can capture a scene without a direct line of sight to the object but high-quality imaging has proven challenging. Here, by acquiring their Fourier spectrum, Zhang et al. demonstrate indirect, high-quality single-pixel imaging in the presence of noisy environmental illumination.
- Zibang Zhang
- , Xiao Ma
- & Jingang Zhong
-
Article
| Open Access Spatiotemporal noise characterization for chirped-pulse amplification systems
Spatiotemporal noise characterization for chirped-pulse amplification systems
High-field physics experiments are often plagued by noise in the driving laser, which remains poorly characterized. Ma et al. study the noise in a pulse stretcher and compressor system in the spatiotemporal domain and find that noise from the stretcher elements governs the pulse contrast at the laser focus.
- Jingui Ma
- , Peng Yuan
- & Liejia Qian
-
Article
| Open Access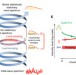 Wave kinetics of random fibre lasers
Wave kinetics of random fibre lasers
Kinetic theory is a mathematical framework that is used to describe non-linear systems with a large number of degrees of freedom. Here, the authors develop a concept of active wave kinetics of cyclic systems and describe the function of random fibre laser.
- D V. Churkin
- , I V. Kolokolov
- & S K. Turitsyn
-
Article |
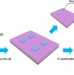 Seeded growth of highly crystalline molybdenum disulphide monolayers at controlled locations
Seeded growth of highly crystalline molybdenum disulphide monolayers at controlled locations
Although synthesis of high-quality MoS2 has been demonstrated, growth of monolayer MoS2at controlled locations is highly desirable for applications. Here, the authors introduce a method where patterned seeds of molybdenum source material are used to grow isolated flakes at predetermined locations.
- Gang Hee Han
- , Nicholas J. Kybert
- & A. T. Charlie Johnson
-
Article |
 Coherent spin control of a nanocavity-enhanced qubit in diamond
Coherent spin control of a nanocavity-enhanced qubit in diamond
Nitrogen-vacancy centres in diamond have established themselves as excellent candidates for solid-state quantum memories due to their optical addressability and long coherence times. Here, the authors report on a diamond-nanocavity system with improved spin-photon interface performances.
- Luozhou Li
- , Tim Schröder
- & Dirk Englund
-
Article |
 Detecting noise with shot noise using on-chip photon detector
Detecting noise with shot noise using on-chip photon detector
The detection of high-frequency radiation emitted by a quantum conductor is promising but current approaches exhibit limited sensitivity. Here, Jompol et al. propose on-chip radiation detection based on photo-assisted shot noise and show the response to be independent of the nature and geometry of the quantum conductor.
- Y. Jompol
- , P. Roulleau
- & D. C. Glattli
-
Article
| Open Access A strong-field driver in the single-cycle regime based on self-compression in a kagome fibre
A strong-field driver in the single-cycle regime based on self-compression in a kagome fibre
Single-cycle and sub-cycle field transients are typically generated by external pulse compression where a combination of nonlinear broadening followed up by dispersion compensation is used. Here, Balciunas et al. use self-compression in a Kagome fibre to generate phase-controlled single-cycle pulses.
- T. Balciunas
- , C. Fourcade-Dutin
- & F. Benabid
-
Article
| Open Access Multi-channel electronic and vibrational dynamics in polyatomic resonant high-order harmonic generation
Multi-channel electronic and vibrational dynamics in polyatomic resonant high-order harmonic generation
Strong-field ionization in molecules is more complex than in atoms with multiple channel dynamics and a coherent superposition of electronic states. Here, Ferré et al. develop multi-modal spectroscopy to measure those dynamics and reveal a resonant to non-resonant high-harmonic generation transition.
- A. Ferré
- , A. E. Boguslavskiy
- & Y. Mairesse
-
Article
| Open Access Femtosecond all-optical synchronization of an X-ray free-electron laser
Femtosecond all-optical synchronization of an X-ray free-electron laser
Few-femtosecond synchronization at free-electron lasers is key for nearly all experimental applications, stable operation and future light source development. Here, Schulz et al. demonstrate all-optical synchronization of the soft X-ray FEL FLASH to better than 30 fs and illustrate a pathway to sub-10 fs.
- S. Schulz
- , I. Grguraš
- & A. L. Cavalieri
-
Article |
 Forbidden atomic transitions driven by an intensity-modulated laser trap
Forbidden atomic transitions driven by an intensity-modulated laser trap
Atomic spectroscopy is typically based on multipole atom-field interactions that obey established selection rules. Using Rydberg atoms as an example, Moore et al. show that the quadratic (ponderomotive) interaction can provide both more flexible selection rules and greater spatial addressability.
- Kaitlin R. Moore
- , Sarah E. Anderson
- & Georg Raithel
-
Article
| Open Access Dip-pen patterning of poly(9,9-dioctylfluorene) chain-conformation-based nano-photonic elements
Dip-pen patterning of poly(9,9-dioctylfluorene) chain-conformation-based nano-photonic elements
The optoelectronic properties of semiconducting polymers are controlled by altering chemical structure and/or inter-chain order. Perevedentsev et al. propose a nanopatterning approach whereby the geometry of polymer chain segments is modified to engineer metamaterial structures for visible light.
- Aleksandr Perevedentsev
- , Yannick Sonnefraud
- & Donal D. C. Bradley
-
Article |
 Photoswitchable semiconductor nanocrystals with self-regulating photochromic Förster resonance energy transfer acceptors
Photoswitchable semiconductor nanocrystals with self-regulating photochromic Förster resonance energy transfer acceptors
Photochromic Förster resonance energy transfer endows nanosensors with photoswitchable fluorescence properties. Diaz et al. present a system with two photostationary end states, one of which exhibits constant quenching of the quantum dot donor independent of its mean distance to the photochromic acceptors.
- Sebastián A. Díaz
- , Florencia Gillanders
- & Thomas M. Jovin
-
Article |
 Experimental evidence of replica symmetry breaking in random lasers
Experimental evidence of replica symmetry breaking in random lasers
Replica symmetry breaking, in which identical systems subject to identical conditions evolve to different end states, has been predicted to occur in many contexts but has yet to be observed experimentally. Ghofraniha et al.report evidence for its occurrence in the pulse-to-pulse variations of a random laser.
- N. Ghofraniha
- , I. Viola
- & C. Conti
-
Article
| Open Access Dark-field X-ray microscopy for multiscale structural characterization
Dark-field X-ray microscopy for multiscale structural characterization
The internal structure of materials determines many of their physical and mechanical properties. Here, the authors have developed a non-destructive X-ray microscopy technique for layer-by-layer mapping of crystallographic orientations and stresses to obtain a three-dimensional reconstruction of a material.
- H. Simons
- , A. King
- & H. F. Poulsen
-
Article
| Open Access Coherent coupling of molecular resonators with a microcavity mode
Coherent coupling of molecular resonators with a microcavity mode
Coherent coupling of light with electronic transitions has led to phenomena such as polariton lasing and superfluidity. Shalabney et al.now couple the optical modes of micro-cavity to the vibrational modes of a molecule at room temperature and thereby alter the chemical behaviour of the molecule.
- A. Shalabney
- , J. George
- & T. W. Ebbesen
-
Article |
 A borane laser
A borane laser
Solution-processed blue lasers are used in many applications such as spectroscopy or material processing. Here, the authors demonstrate a borane solution-based blue laser that offers a high efficiency and a photostability that is superior to commercial laser dyes.
- Luis Cerdán
- , Jakub Braborec
- & Michael G. S. Londesborough
-
Article
| Open Access Reconfigurable radio-frequency arbitrary waveforms synthesized in a silicon photonic chip
Reconfigurable radio-frequency arbitrary waveforms synthesized in a silicon photonic chip
Performing radio-frequency arbitrary waveform generation in the optical domain offers advantages over electronic-based methods but suffers from lack of integration and slow speed. Here, Wang et al. propose a fast-reconfigurable, radio-frequency arbitrary waveform generator fully integrated in a silicon chip.
- Jian Wang
- , Hao Shen
- & Minghao Qi
-
Article
| Open Access On-chip detection of non-classical light by scalable integration of single-photon detectors
On-chip detection of non-classical light by scalable integration of single-photon detectors
The integration of single-photon detectors, as superconducting nanowire single-photon detectors, in photonic-integrated circuits is a goal of quantum information science. Here, Najafi et al.introduce a micrometer-scale flip-chip process enabling such a integration in a scalable way.
- Faraz Najafi
- , Jacob Mower
- & Dirk Englund
-
Article
| Open Access Generation of spin currents by surface plasmon resonance
Generation of spin currents by surface plasmon resonance
Optical methods allow for the excitation of diverse magnetic phenomena in nanostructured materials. Here, Uchida et al. demonstrate how pure spin current may be generated across a Pt/BiY2Fe5O12thin film interface by optically exciting surface plasmon resonance in embedded gold nanoparticles.
- K. Uchida
- , H. Adachi
- & E. Saitoh
-
Article |
 Phase steps and resonator detuning measurements in microresonator frequency combs
Phase steps and resonator detuning measurements in microresonator frequency combs
The nonlinear dynamic interaction between optical comb frequencies and microresonator modes are not yet fully understood. Here, the authors demonstrate a method to characterize microcomb states and observe discrete phase steps that have not been observed in conventional frequency combs.
- Pascal Del’Haye
- , Aurélien Coillet
- & Scott A. Diddams
-
Article |
 Dirac leaky-wave antennas for continuous beam scanning from photonic crystals
Dirac leaky-wave antennas for continuous beam scanning from photonic crystals
Directive and scannable radiation patterns beyond the microwave region are desirable but leaky-wave antennas in the terahertz and optical range are unavailable. Here, Memarian and Eleftheriades demonstrate continuously scanned leaky-wave radiation from the interface of a photonic crystal with a Dirac-type dispersion.
- Mohammad Memarian
- & George V. Eleftheriades
-
Article
| Open Access Imaging with a small number of photons
Imaging with a small number of photons
Advances in low-light-level imaging techniques have shown that imaging in the one photon per pixel regime is possible. Here, Morris et al. demonstrate high-quality image reconstruction using ghost and heralded imaging with less than one photon per image pixel with a time-gated intensified camera.
- Peter A. Morris
- , Reuben S. Aspden
- & Miles J. Padgett
-
Article |
 Topological solitons as addressable phase bits in a driven laser
Topological solitons as addressable phase bits in a driven laser
In nonlinear optical systems, self-localized bistable packets of light exist as controllable intensity pulses in the longitudinal or transverse dimension. Here, Garbin et al. experimentally demonstrate the existence of localized longitudinal states existing in the phase of laser light.
- Bruno Garbin
- , Julien Javaloyes
- & Stéphane Barland
-
Article |
 Optical focusing deep inside dynamic scattering media with near-infrared time-reversed ultrasonically encoded (TRUE) light
Optical focusing deep inside dynamic scattering media with near-infrared time-reversed ultrasonically encoded (TRUE) light
Shaping the incident wavefront allows optical focusing deep inside scattering media, but its application in dynamic media is hindered by its low speed. Here, Liu et al. improve the speed by two orders of magnitude and demonstrate in vivolight focusing inside dynamic scattering media.
- Yan Liu
- , Puxiang Lai
- & Lihong V. Wang
-
Article |
 Tunable ferroelectric polarization and its interplay with spin–orbit coupling in tin iodide perovskites
Tunable ferroelectric polarization and its interplay with spin–orbit coupling in tin iodide perovskites
Halide perovskites are widely studied as components in photovoltaic cells. Here, the authors show that these materials also possess a tunable ferroelectric polarization as well as relativistic spin-splitting effects suggesting additional functionalities, for example, as spintronic and optoelectronic devices.
- Alessandro Stroppa
- , Domenico Di Sante
- & Silvia Picozzi
-
Article
| Open Access Modulator-free quadrature amplitude modulation signal synthesis
Modulator-free quadrature amplitude modulation signal synthesis
Quadrature amplitude modulation signalling is currently enabling rapid data transfer capacity growth, but it still has associated drawbacks. Here, Liu et al.use optical injection locking to generate complex modulation format signals with reduced consumption, small footprint and easy integration.
- Zhixin Liu
- , Joseph Kakande
- & Radan Slavík
-
Article
| Open Access Photonic quasi-crystal terahertz lasers
Photonic quasi-crystal terahertz lasers
Various vertical surface emitting, terahertz quantum-cascade lasers have been proposed recently but these suffer from power cancellations in the far-field and limited extraction efficiencies. Here, Vitiello et al.circumvent these issues using two-dimensional photonic quasi-crystalline resonators.
- Miriam Serena Vitiello
- , Michele Nobile
- & A. Giles Davies
-
Article |
 Coherent two-dimensional photocurrent spectroscopy in a PbS quantum dot photocell
Coherent two-dimensional photocurrent spectroscopy in a PbS quantum dot photocell
Two-dimensional photocurrent spectroscopy can identify coherent electronic dynamics and offers promise for studies of numerous material systems. Karki et al. now show that the method can be used to study ultrafast carrier processes in lead sulphide quantum dots, such as multiple exciton generation.
- Khadga J. Karki
- , Julia R. Widom
- & Andrew H. Marcus
-
Article |
 Solution-processed multilayer small-molecule light-emitting devices with high-efficiency white-light emission
Solution-processed multilayer small-molecule light-emitting devices with high-efficiency white-light emission
High-efficiency organic light-emitting devices usually require the growth of many layers of different materials by vapour deposition in vacuum. Naoya Aizawa et al. demonstrate the fabrication of high-efficiency multilayer organic LEDs from solution.
- Naoya Aizawa
- , Yong-Jin Pu
- & Junji Kido
-
Article |
 Experimental realization of photonic topological insulator in a uniaxial metacrystal waveguide
Experimental realization of photonic topological insulator in a uniaxial metacrystal waveguide
Photonic topological insulators have been theoretically predicted but their experimental demonstration has proven challenging. Here, Chen et al.experimentally realize a photonic topological insulator by embedding a non-bianisotropic and a non-resonant metacrystal into a waveguide.
- Wen-Jie Chen
- , Shao-Ji Jiang
- & C. T. Chan
-
Article |
 High quality-factor optical nanocavities in bulk single-crystal diamond
High quality-factor optical nanocavities in bulk single-crystal diamond
Single-crystal diamond is a promising material for applications in classical and quantum optics, but the lack of scalable fabrication remains an issue. Here, Burek et al. adapt angle-etching nanofabrication techniques to realize ring resonators and photonic crystal cavities in single crystal diamond with quality factors in excess of 105.
- Michael J. Burek
- , Yiwen Chu
- & Marko Lončar
-
Article |
 All-dielectric metasurface analogue of electromagnetically induced transparency
All-dielectric metasurface analogue of electromagnetically induced transparency
Electromagnetically induced transparency—an effect in atomic physics caused by interference between transitions—has found analogues in other areas, like nanophotonics. Yang et al. exploit this effect in an all-dielectric metasurface to produce high-Q-factor resonances ideal for refractive index sensing.
- Yuanmu Yang
- , Ivan I. Kravchenko
- & Jason Valentine
-
Article |
 Manifestation of unconventional biexciton states in quantum dots
Manifestation of unconventional biexciton states in quantum dots
Artificial atoms usually constitute an orbital structure for trapped charge carriers. Here, Hönig et al. demonstrate that polarization fields and large charge carrier masses can dilute the common orbital conception and find a hybrid-biexciton molecule that enables anomalous spin configurations.
- Gerald Hönig
- , Gordon Callsen
- & Axel Hoffmann
-
Article
| Open Access Dynamically controlling the emission of single excitons in photonic crystal cavities
Dynamically controlling the emission of single excitons in photonic crystal cavities
Controlling the coherent evolution of cavity quantum electrodynamics systems is key for future quantum networks. Here Pagliano et al.demonstrate dynamic control of the coupling of a single exciton to a photonic micro-resonator using electrical tuning of the exciton energy in a photonic crystal cavity diode.
- Francesco Pagliano
- , YongJin Cho
- & Andrea Fiore
-
Article
| Open Access Quantum state-controlled directional spontaneous emission of photons into a nanophotonic waveguide
Quantum state-controlled directional spontaneous emission of photons into a nanophotonic waveguide
Nanoscale confinement in an optical fibre induces coupling between a photon’s spin and orbital angular momentum. Here, the authors use this effect to control the direction of photons spontaneously emitted from trapped caesium atoms into a nanofibre.
- R. Mitsch
- , C. Sayrin
- & A. Rauschenbeutel
-
Article |
 Electrically tunable nonlinear plasmonics in graphene nanoislands
Electrically tunable nonlinear plasmonics in graphene nanoislands
Plasmons in metallic nanostructures provide light enhancement that amplifies their nonlinear optical response. This study shows that graphene nanoislands also give rise to an amplified nonlinear polarizability that can be tuned electrically to surpass those of other nonlinear media by orders of magnitude.
- Joel D. Cox
- & F. Javier García de Abajo
-
Article
| Open Access Assembling programmable FRET-based photonic networks using designer DNA scaffolds
Assembling programmable FRET-based photonic networks using designer DNA scaffolds
DNA is a useful molecule with which to construct nanomaterials with controllable functionalities. Here, the authors fabricate photonic wires by appending dye molecules at set positions along DNA structures, and show how FRET performance can be tuned by modifying dye separation.
- Susan Buckhout-White
- , Christopher M Spillmann
- & Igor L. Medintz
-
Article |
 Long-term stable polymer solar cells with significantly reduced burn-in loss
Long-term stable polymer solar cells with significantly reduced burn-in loss
Efficiency and stability are two major concerns in polymer-based solar cell development. Here Kong et al.report that the lifetime of a bulk heterojunction polymer can be improved by removing its low-molecular-weight components, which leads to a substantially reduced burn-in loss under photo-aging conditions.
- Jaemin Kong
- , Suhee Song
- & Kwanghee Lee
-
Article |
 Bio-inspired networks for optoelectronic applications
Bio-inspired networks for optoelectronic applications
Biological systems, subject to evolutionary optimization over millions of years, have been a source of ingenious solutions in many areas of science. Here, Han et al. develop transparent electrodes inspired by two such systems: a leaf venation and a spider’s web.
- Bing Han
- , Yuanlin Huang
- & Jinwei Gao
-
Article |
 Strong coupling between chlorosomes of photosynthetic bacteria and a confined optical cavity mode
Strong coupling between chlorosomes of photosynthetic bacteria and a confined optical cavity mode
Photosynthetic bacteria growing in low light environments have evolved to use small amounts of light with high efficiency. Here, Coles et al. demonstrate strong exciton–photon coupling of about 1,000 chlorosomes to a confined cavity mode thus modifying the energy levels of the light-harvesting process.
- David M. Coles
- , Yanshen Yang
- & Jason M. Smith
-
Article |
 Photon energy upconversion through thermal radiation with the power efficiency reaching 16%
Photon energy upconversion through thermal radiation with the power efficiency reaching 16%
Energy transfer upconversion can increase the absorption efficiency but has been limited by multiphonon relaxation. Here, Wang et al. demonstrate that photon energy upconversion by thermal radiation benefits from multiphonon relaxation and achieves efficiencies as high as 16%.
- Junxin Wang
- , Tian Ming
- & Chun-Hua Yan
-
Article
| Open Access Photon-assisted tunnelling with nonclassical light
Photon-assisted tunnelling with nonclassical light
Coherently coupling microwave photons to quantum electronic conductors could provide a useful platform for quantum information processing. Souquet et al. now theoretically demonstrate that such systems can also act as sensitive probes of the quantum properties of non-classical microwave radiation.
- J. -R. Souquet
- , M. J. Woolley
- & A. A. Clerk
-
Article
| Open Access Ultralow mode-volume photonic crystal nanobeam cavities for high-efficiency coupling to individual carbon nanotube emitters
Ultralow mode-volume photonic crystal nanobeam cavities for high-efficiency coupling to individual carbon nanotube emitters
Efficient coupling to photonic structures is essential to exploit the emission properties of carbon nanotubes (CNTs). Here, Miura et al.demonstrate spontaneous emission coupling efficiency exceeding 85% from a single CNT to a silicon photonic crystal nanobeam cavity with an ultralow mode-volume.
- R. Miura
- , S. Imamura
- & Y. K. Kato
-
Article |
 Repurposing Blu-ray movie discs as quasi-random nanoimprinting templates for photon management
Repurposing Blu-ray movie discs as quasi-random nanoimprinting templates for photon management
Quasi-random nanostructures are being considered for many photon management applications but their use has been limited by their costly fabrication. Here, Smith et al. show that the quasi-random patterns on Blu-ray movie discs are already near-optimized for light-trapping applications in solar cells.
- Alexander J. Smith
- , Chen Wang
- & Jiaxing Huang
-
Article |
 Power-controlled transition from standard to negative refraction in reorientational soft matter
Power-controlled transition from standard to negative refraction in reorientational soft matter
Anisotropic media have interesting effects, particularly at interfaces. Piccardi et al.show that optical refraction in nonlinear nematic liquid crystals can be tuned from positive to negative by acting on beam power, altering the distribution of the optic axis and the energy flux.
- Armando Piccardi
- , Alessandro Alberucci
- & Gaetano Assanto

 Visualization of molecular fluorescence point spread functions via remote excitation switching fluorescence microscopy
Visualization of molecular fluorescence point spread functions via remote excitation switching fluorescence microscopy