Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access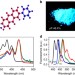 High mobility emissive organic semiconductor
High mobility emissive organic semiconductor
Organic semiconductors with high mobility and strong fluorescence are necessary for optoelectronic devices. Here, Liu et al. show an organic semiconductor, 2,6-diphenylanthracene, satisfying both requirements with mobility of 34 cm2 V−1 s−1 and emission of 6,627 cd m−2at a turn-on voltage of 2.8 V.
- Jie Liu
- , Hantang Zhang
- & Alan J. Heeger
-
Article
| Open Access High yield and ultrafast sources of electrically triggered entangled-photon pairs based on strain-tunable quantum dots
High yield and ultrafast sources of electrically triggered entangled-photon pairs based on strain-tunable quantum dots
Quantum communications require sources of entangled photons. Electrically triggered sources usually suffer from low entangled-emission efficiency. Here, the authors use piezoelectric strains to tune the fine structure of quantum dot emitters, and increase the entanglement probability and fidelity.
- Jiaxiang Zhang
- , Johannes S. Wildmann
- & Oliver G. Schmidt
-
Article
| Open Access Enhanced optoelectronic quality of perovskite thin films with hypophosphorous acid for planar heterojunction solar cells
Enhanced optoelectronic quality of perovskite thin films with hypophosphorous acid for planar heterojunction solar cells
An imbalance in I/Pb stoichiometry is thought to lead to defects in metal halide films. Here, Zhang et al. show that the addition of hypophosphorous acid in the precursor solution can significantly improve the film quality and enhance the photoluminescence intensity, leading to improved photovoltaic devices.
- Wei Zhang
- , Sandeep Pathak
- & Henry J. Snaith
-
Article
| Open Access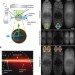 Confocal multiview light-sheet microscopy
Confocal multiview light-sheet microscopy
Multiview light-sheet microscopy is a powerful tool for imaging relatively large biological samples over long periods of time, but scattering can limit image quality. Here, the authors combine multiview light-sheet imaging with electronic confocal slit detection to improve image quality, double acquisition speed and streamline data fusion.
- Gustavo de Medeiros
- , Nils Norlin
- & Lars Hufnagel
-
Article
| Open Access Optical focusing inside scattering media with time-reversed ultrasound microbubble encoded light
Optical focusing inside scattering media with time-reversed ultrasound microbubble encoded light
Focusing light inside biological tissue is challenging due to its strong scattering nature. Here, the authors develop a technique that uses ultrasonically destroyed microbubbles to assist in the computation of a wavefront solution which forms optical foci at the microbubble destruction sites.
- Haowen Ruan
- , Mooseok Jang
- & Changhuei Yang
-
Article
| Open Access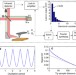 Scattering-type scanning near-field optical microscopy with reconstruction of vertical interaction
Scattering-type scanning near-field optical microscopy with reconstruction of vertical interaction
Conventionally, scattering-type scanning near-field optical microscopy does not provide information on the vertical characteristic of near-field responses. Here, Xu et al. develop a method to reconstruct the vertical interaction response between the tip and the sample using this near-field technique.
- Le Wang
- & Xiaoji G. Xu
-
Article
| Open Access Highly tunable hybrid metamaterials employing split-ring resonators strongly coupled to graphene surface plasmons
Highly tunable hybrid metamaterials employing split-ring resonators strongly coupled to graphene surface plasmons
Realizing tunable metamaterials across a broad spectral range is of great interest. Here, Liu et al. introduce hybrid structures comprising graphene plasmonic resonators strongly coupled to conventional split-ring resonators and reach 60% transmission modulation with an operating speed above 40 MHz.
- Peter Q. Liu
- , Isaac J. Luxmoore
- & Geoffrey R. Nash
-
Article
| Open Access Reliable quantum certification of photonic state preparations
Reliable quantum certification of photonic state preparations
Photonic quantum technologies rely on the creation and manipulation of continuous variables states whose experimental preparation needs to be verified- a noteworthy impractical task. Here, the authors present a protocol that allows to certify continuous variables states with limited experimental overhead.
- Leandro Aolita
- , Christian Gogolin
- & Jens Eisert
-
Article
| Open Access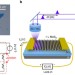 Ultrafast response of monolayer molybdenum disulfide photodetectors
Ultrafast response of monolayer molybdenum disulfide photodetectors
Two-dimensional transition-metal dichalcogenides are useful for optoelectronic applications, but the ultimate limit on the speed of photodetector operation is unknown. Here, the authors show that the optical response time of monolayer molybdenum disulfide can be as short as three picoseconds.
- Haining Wang
- , Changjian Zhang
- & Farhan Rana
-
Article
| Open Access Direct observation and imaging of a spin-wave soliton with p-like symmetry
Direct observation and imaging of a spin-wave soliton with p-like symmetry
Injecting spin-polarized current into a ferromagnetic thin film via a nanocontact is expected to generate a radially-symmetric spin wave soliton. Here, the authors use time-resolved x-ray microscopy and micromagnetic simulations to demonstrate the occurrence of p-like symmetry associated with non-uniform magnetic fields in the nanocontact region.
- S. Bonetti
- , R. Kukreja
- & H. A. Dürr
-
Article
| Open Access Hybrid graphene plasmonic waveguide modulators
Hybrid graphene plasmonic waveguide modulators
The combination of graphene with plasmonic waveguides remains largely unexplored. Here, Ansell et al. report the fabrication of hybrid graphene plasmonic waveguide modulators working in the telecom range, with a modulation depth greater than 0.03 dB μm−1and with comparable characteristics to silicon-based devices.
- D. Ansell
- , I. P. Radko
- & A. N. Grigorenko
-
Article
| Open Access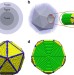 Atomistic electrodynamics simulations of bare and ligand-coated nanoparticles in the quantum size regime
Atomistic electrodynamics simulations of bare and ligand-coated nanoparticles in the quantum size regime
Investigating the properties of metallic nanoparticles in the 2–10 nm range is a computational challenge. Here, the authors introduce an atomistic electrodynamics model to describe bare and coated particles and dimers, and show that the ligand layer modifies the near-field properties of the particles.
- Xing Chen
- , Justin E. Moore
- & Lasse Jensen
-
Article
| Open Access Planar-integrated single-crystalline perovskite photodetectors
Planar-integrated single-crystalline perovskite photodetectors
Single crystals of organolead halide perovskites exhibit large carrier mobilities and long diffusion lengths. Here, the authors succeed in growing the single crystals on planar substrates and integrate them as the active layer of visible photodetectors with a large gain-bandwidth product.
- Makhsud I. Saidaminov
- , Valerio Adinolfi
- & Osman M. Bakr
-
Article
| Open Access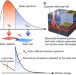 A hot-electron thermophotonic solar cell demonstrated by thermal up-conversion of sub-bandgap photons
A hot-electron thermophotonic solar cell demonstrated by thermal up-conversion of sub-bandgap photons
The efficiency of single junction solar cells is limited by their inability to absorb photons with an energy smaller than the bandgap. Here, the authors surpass the Shockley-Queisser limit by using an integrated hot-electron thermophotonic emitter to thermally up-convert sub-bandgap photons.
- Daniel J. Farrell
- , Hassanet Sodabanlu
- & Yoshitaka Okada
-
Article
| Open Access Stable ultrathin partially oxidized copper film electrode for highly efficient flexible solar cells
Stable ultrathin partially oxidized copper film electrode for highly efficient flexible solar cells
Light enters and exits optoelectronic devices through transparent conductive electrodes, which are one of their most expensive components. Here, the authors develop stable transparent conductive electrodes based on copper and oxide layers that lead to efficient flexible organic solar cells.
- Guoqing Zhao
- , Wei Wang
- & Jungheum Yun
-
Article
| Open Access Spectral splitting photovoltaics using perovskite and wideband dye-sensitized solar cells
Spectral splitting photovoltaics using perovskite and wideband dye-sensitized solar cells
Lead halide perovskite solar cells have a limited spectral response in the near infrared. Here, the authors present ruthenium dyes with extended near infrared absorbance and combine perovskite and dye-based solar cells by spectral splitting to obtain broadband, 21.5% efficient solar cells.
- Takumi Kinoshita
- , Kazuteru Nonomura
- & Hiroshi Segawa
-
Article
| Open Access Implementation of continuous-variable quantum key distribution with composable and one-sided-device-independent security against coherent attacks
Implementation of continuous-variable quantum key distribution with composable and one-sided-device-independent security against coherent attacks
When quantum key distribution is composed with other secure protocols the overall security has to be guaranteed, which adds further security requirements. Here, the authors demonstrate continuous-variable quantum key distribution with composable security and one-sided-device independence.
- Tobias Gehring
- , Vitus Händchen
- & Roman Schnabel
-
Article
| Open Access Ultra-high modulation depth exceeding 2,400% in optically controlled topological surface plasmons
Ultra-high modulation depth exceeding 2,400% in optically controlled topological surface plasmons
For optical control of plasmons metals require a large amount of power in the control pulse, yielding a small modulation depth. Here, Sim et al. fabricate arrays of Bi2Se3 and report a modulation depth of 2,400% at 1.5 THz with an optical fluence of 45 μJ/cm2, demonstrating a novel route for controlling plasmons.
- Sangwan Sim
- , Houk Jang
- & Hyunyong Choi
-
Article
| Open Access High-performing nonlinear visualization of terahertz radiation on a silicon charge-coupled device
High-performing nonlinear visualization of terahertz radiation on a silicon charge-coupled device
The absence of an imaging device in the low frequency terahertz range has hindered the advance of applications. Here, Shalabyet al. introduce a silicon based charge coupled device allowing the visualization of terahertz radiation in real time and at high spatial detail.
- Mostafa Shalaby
- , Carlo Vicario
- & Christoph P. Hauri
-
Article
| Open Access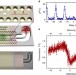 Single-photon non-linear optics with a quantum dot in a waveguide
Single-photon non-linear optics with a quantum dot in a waveguide
Interacting light beams are required for all-optical information processing, but such nonlinear effects are tiny at the single-photon level. Here, the authors show that a single quantum dot in a photonic-crystal waveguide enables the necessary giant optical nonlinearity.
- A. Javadi
- , I. Söllner
- & P. Lodahl
-
Article
| Open Access Microsecond-sustained lasing from colloidal quantum dot solids
Microsecond-sustained lasing from colloidal quantum dot solids
To date, lasing in colloidal quantum dot solids has been limited to the nanosecond temporal range, limiting the potential for solution-processed lasers. Here, the authors combine thermal management with low amplified spontaneous emission threshold to produce microsecond-sustained lasing.
- Michael M. Adachi
- , Fengjia Fan
- & Edward H. Sargent
-
Article
| Open Access Zeolite-like liquid crystals
Zeolite-like liquid crystals
Zeolites with regular porous structures are widely used as gas adsorbents and scaffolding for catalysts. Poppe et al. report a liquid crystal with zeolite-like structure by self-assembly of polyphilic molecules with π-conjugated rod-like cores into a honeycomb formed by pentagonal/octagonal channels.
- Silvio Poppe
- , Anne Lehmann
- & Carsten Tschierske
-
Article
| Open Access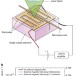 Photoelectric detection of electron spin resonance of nitrogen-vacancy centres in diamond
Photoelectric detection of electron spin resonance of nitrogen-vacancy centres in diamond
Nitrogen-vacancy colour centre defects in diamond are one possible host for qubits, but such an application requires a method for reading out the colour centre spin state. Here, the authors demonstrate a photoelectric readout technique of the magnetic resonances of these colour centres.
- E. Bourgeois
- , A. Jarmola
- & M. Nesladek
-
Article
| Open Access Directly measuring mean and variance of infinite-spectrum observables such as the photon orbital angular momentum
Directly measuring mean and variance of infinite-spectrum observables such as the photon orbital angular momentum
The more degrees of freedom a quantum observable has, the more complicated it is to measure its probability distribution. Here, the authors deduce the mean and variance of an infinite-dimensional variable, the orbital angular momentum of light, from a two-dimensional one: spin angular momentum.
- Bruno Piccirillo
- , Sergei Slussarenko
- & Enrico Santamato
-
Article
| Open Access Storage of multiple single-photon pulses emitted from a quantum dot in a solid-state quantum memory
Storage of multiple single-photon pulses emitted from a quantum dot in a solid-state quantum memory
Quantum repeaters are critical components for distributing entanglement over long distances, and they can be improved by the elimination of multi-photon-pair events. Here, the authors demonstrate the storage of single photons emitted by a quantum dot in a polarization maintaining solid-state memory.
- Jian-Shun Tang
- , Zong-Quan Zhou
- & Guang-Can Guo
-
Article
| Open Access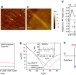 Planar carbon nanotube–graphene hybrid films for high-performance broadband photodetectors
Planar carbon nanotube–graphene hybrid films for high-performance broadband photodetectors
Graphene has excellent electronic properties but its photoresponsivity is limited by low absorption and the ultrafast recombination of photoexcited carriers. Here, the authors demonstrate fast, high responsivity and broadband photodetectors by combining graphene with single-wall carbon nanotubes.
- Yuanda Liu
- , Fengqiu Wang
- & Rong Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access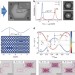 Dynamic acousto-optic control of a strongly coupled photonic molecule
Dynamic acousto-optic control of a strongly coupled photonic molecule
Dynamic control of components is required for large-scale quantum photonic networks. Here, Kapfingeret al. show dynamic control of the interaction between two coupled photonic crystal nanocavities forming a photonic molecule. Tuning is achieved by using an electrically generated radio frequency surface acoustic wave.
- Stephan Kapfinger
- , Thorsten Reichert
- & Hubert J. Krenner
-
Article
| Open Access Flexible coherent control of plasmonic spin-Hall effect
Flexible coherent control of plasmonic spin-Hall effect
Conventional methods to control surface plasmon polaritons with light offer limited tunability or complex design parameters. Here, Xiao et al. demonstrate coherent and independent control of surface plasmon polariton orbitals for two opposite spins using multiple rings of nano-slots on a metasurface
- Shiyi Xiao
- , Fan Zhong
- & Jensen Li
-
Article
| Open Access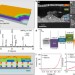 Light-induced pyroelectric effect as an effective approach for ultrafast ultraviolet nanosensing
Light-induced pyroelectric effect as an effective approach for ultrafast ultraviolet nanosensing
Zinc oxide is potentially a useful material for ultraviolet detectors, but a relatively long response time hinders practical implementation. Here, the authors demonstrate a zinc oxide nanowire/perovskite heterostructure detector with a five orders of magnitude improvement in both rising and falling edge time.
- Zhaona Wang
- , Ruomeng Yu
- & Zhong Lin Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Hot-carrier cooling and photoinduced refractive index changes in organic–inorganic lead halide perovskites
Hot-carrier cooling and photoinduced refractive index changes in organic–inorganic lead halide perovskites
The use of organic–inorganic metal-halide perovskites in hot-carrier devices depends on deepening the understanding of photoexcitations in these materials. Here, Price et al. use transient absorption spectroscopy to study hot-carrier distributions in CH3NH3PbI3and quantify key semiconductors parameters.
- Michael B. Price
- , Justinas Butkus
- & Felix Deschler
-
Article
| Open Access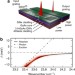 Ultra-low-power hybrid light–matter solitons
Ultra-low-power hybrid light–matter solitons
Harnessing nonlinear optics in optoelectronic devices requires a platform that exhibits both giant optical nonlinearity and is compatible with photonic-circuit fabrication. Here, the authors demonstrate such a system that uses strong light–matter coupling between waveguide photons and quantum-well excitons.
- P. M. Walker
- , L. Tinkler
- & D. N. Krizhanovskii
-
Article
| Open Access Proposal for a room-temperature diamond maser
Proposal for a room-temperature diamond maser
Maser applications are hindered by their demanding working conditions. Here, Jinet al. theoretically propose a room-temperature maser based on nitrogen vacancy centres in diamond. This numerical study demonstrates that the operation of the maser under readily accessible conditions is feasible.
- Liang Jin
- , Matthias Pfender
- & Ren-Bao Liu
-
Article
| Open Access Efficient direct solar-to-hydrogen conversion by in situ interface transformation of a tandem structure
Efficient direct solar-to-hydrogen conversion by in situ interface transformation of a tandem structure
A future carbon-free energy economy requires an efficient photocatalytic route to hydrogen generation. Here, the authors employ surface modification techniques to raise the performance of an unassisted solar water splitting device to achieve exceptional performances.
- Matthias M. May
- , Hans-Joachim Lewerenz
- & Thomas Hannappel
-
Article
| Open Access Nanophotonic coherent light–matter interfaces based on rare-earth-doped crystals
Nanophotonic coherent light–matter interfaces based on rare-earth-doped crystals
Quantum light–matter interfaces connecting stationary qubits to photons are fundamental elements of future quantum optical networks. Here, the authors report a quantum interface based on highly coherent rare-earth ions—the solid-state qubits—coupled to a nanophotonic cavity fabricated in the host crystal.
- Tian Zhong
- , Jonathan M. Kindem
- & Andrei Faraon
-
Article
| Open Access Cross-polarized photon-pair generation and bi-chromatically pumped optical parametric oscillation on a chip
Cross-polarized photon-pair generation and bi-chromatically pumped optical parametric oscillation on a chip
On-chip nonlinear optics devices find a number of applications in modern optics from spectroscopy to communications. Here, the authors increase the degrees of freedom for frequency mixing by demonstrating the nonlinear interaction of perpendicularly-polarized modes in an integrated microring resonator.
- Christian Reimer
- , Michael Kues
- & Roberto Morandotti
-
Article
| Open Access Transform-limited single photons from a single quantum dot
Transform-limited single photons from a single quantum dot
Photons emitted from a quantum dot typically have slightly different frequencies owing to various sources of noise. Here, the authors suppress the noise, notably the noise arising from the nuclear spins, and demonstrate single-photon emission with a transform-limited optical linewidth.
- Andreas V. Kuhlmann
- , Jonathan H. Prechtel
- & Richard J. Warburton
-
Article
| Open Access Two-photon-like microscopy with orders-of-magnitude lower illumination intensity via two-step fluorescence
Two-photon-like microscopy with orders-of-magnitude lower illumination intensity via two-step fluorescence
Two-photon fluorescence gives a quadratic response, which improves imaging in thick samples but requires extremely intense illumination. Here, the authors describe two-step fluorescent imaging, a much lower intensity approach to quadratic excitation, via reversible photoswitchable fluorophores.
- Maria Ingaramo
- , Andrew G. York
- & George H. Patterson
-
Article
| Open Access Integration of photonic nanojets and semiconductor nanoparticles for enhanced all-optical switching
Integration of photonic nanojets and semiconductor nanoparticles for enhanced all-optical switching
The terabit-per-second rates of optical fibres exceed the capability of electronics, but all-optical switches are needed to alleviate the bottleneck in these networks. Here, Born et al.describe such a switch using dielectric spheres, yielding femtojoule switching energy and femtosecond switching times.
- Brandon Born
- , Jeffrey D. A. Krupa
- & Jonathan F. Holzman
-
Article
| Open Access Single-shot spectro-temporal characterization of XUV pulses from a seeded free-electron laser
Single-shot spectro-temporal characterization of XUV pulses from a seeded free-electron laser
X-ray free-electron laser is a power probe for materials, but it is challenging to measure the spectro-temporal characters of individual pulses. Here, De Ninno et al.implement an interferometric method allowing one to characterize and control the ultrashort XUV pulses seeded by a femtosecond laser.
- Giovanni De Ninno
- , David Gauthier
- & Matija Stupar
-
Article
| Open Access Visualizing nanoscale excitonic relaxation properties of disordered edges and grain boundaries in monolayer molybdenum disulfide
Visualizing nanoscale excitonic relaxation properties of disordered edges and grain boundaries in monolayer molybdenum disulfide
Understanding the dynamics of light-induced carriers is vital for employing two-dimensional materials in optoelectronic applications. Here, the authors use a sub diffraction-limit optical technique to reveal the excitonic properties of monolayer molybdenum disulfide at the nanoscale.
- Wei Bao
- , Nicholas J. Borys
- & P. James Schuck
-
Article
| Open Access Field propagation-induced directionality of carrier-envelope phase-controlled photoemission from nanospheres
Field propagation-induced directionality of carrier-envelope phase-controlled photoemission from nanospheres
The localized enhancement of laser light in optical near-fields of nanostructures enables the steering of ultrafast electronic motion. Here, the authors employ field propagation in nanospheres to obtain directional tunability and attosecond control of near-field-induced strong-field photoemission.
- F. Süßmann
- , L. Seiffert
- & T. Fennel
-
Article
| Open Access High spectral purity Kerr frequency comb radio frequency photonic oscillator
High spectral purity Kerr frequency comb radio frequency photonic oscillator
An optical frequency comb demodulated on a photodiode can generate a radio frequency signal with high spectral purity at a frequency corresponding to the comb spacing. Here, Liang et al.demonstrate a frequency-comb-based radio frequency photonic oscillator characterized with low phase noise and high frequency stability.
- W. Liang
- , D. Eliyahu
- & L. Maleki
-
Article |
 Super-resolution photoacoustic imaging through a scattering wall
Super-resolution photoacoustic imaging through a scattering wall
With wavefront shaping, imaging through scattering walls is possible, but this technique requires generating feedback from behind the wall. Here, Conkeyet al. use photoacoustic feedback for wavefront optimization for sub-acoustic resolution imaging behind a scattering wall with an improved signal-to-noise ratio.
- Donald B. Conkey
- , Antonio M. Caravaca-Aguirre
- & Rafael Piestun
-
Article |
 Diastereomeric liquid crystal domains at the mesoscale
Diastereomeric liquid crystal domains at the mesoscale
Helical nanofilaments—composed of achiral, bent core molecules—have been shown to assemble into left- and right-handed structures. Here, the authors show diastereomeric interactions on the mesocale between chiral liquid crystal guest compounds and helical nanofilament-based pores.
- Dong Chen
- , Michael R. Tuchband
- & Noel A. Clark
-
Article
| Open Access Qubit entanglement between ring-resonator photon-pair sources on a silicon chip
Qubit entanglement between ring-resonator photon-pair sources on a silicon chip
Scalable photonic devices for quantum information processing require on-chip quantum states engineering. Here the authors report the creation of entangled photon pairs on a silicon-on-insulator chip by integrating resonant photon sources, spectral demultiplexers and reconfigurable optics in a single device.
- J. W. Silverstone
- , R. Santagati
- & M. G. Thompson
-
Article
| Open Access Multiphoton harvesting metal–organic frameworks
Multiphoton harvesting metal–organic frameworks
Metal–organic frameworks (MOFs) combining the properties of the metal ions and organic ligands are been proposed for many applications. Here Quah et al. demonstrate multiphoton excitation fluorescence in MOF materials enhanced by high quantum yielding guest molecules and Förster resonance energy transfer.
- Hong Sheng Quah
- , Weiqiang Chen
- & Jagadese J. Vittal
-
Article
| Open Access Non-plasmonic nanoantennas for surface enhanced spectroscopies with ultra-low heat conversion
Non-plasmonic nanoantennas for surface enhanced spectroscopies with ultra-low heat conversion
Metallic nanoantennas can enhance and confine electromagnetic fields, however, localized heating hinders many applications. Here, Caldarola et al.demonstrate both high near-field enhancement and ultra-low heat conversion in the visible-near infrared region using silicon dimer nanoantennas with 20 nm gaps.
- Martín Caldarola
- , Pablo Albella
- & Stefan A. Maier
-
Article
| Open Access Direct observation of multistep energy transfer in LHCII with fifth-order 3D electronic spectroscopy
Direct observation of multistep energy transfer in LHCII with fifth-order 3D electronic spectroscopy
Photosynthesis is a complex process, involving the transfer of sunlight driven excitation energy to a reaction centre. Here, the authors directly observe the multistep excitation energy transitions in a light-harvesting complex using ultrafast fifth-order three-dimensional electronic spectroscopy.
- Zhengyang Zhang
- , Petar H. Lambrev
- & Howe-Siang Tan
-
Article
| Open Access Micromotors with asymmetric shape that efficiently convert light into work by thermocapillary effects
Micromotors with asymmetric shape that efficiently convert light into work by thermocapillary effects
The direct conversion of light into work allows the control of micromotors, but typically with low efficiencies and high power density requirements. Here, Maggiet al. demonstrate efficient thermocapillary propulsion of microgears on a liquid–air interface with wide-field, incoherent illumination.
- Claudio Maggi
- , Filippo Saglimbeni
- & Roberto Di Leonardo

 High-efficiency polymer solar cells with small photon energy loss
High-efficiency polymer solar cells with small photon energy loss