Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access 0.5-keV Soft X-ray attosecond continua
0.5-keV Soft X-ray attosecond continua
Attosecond soft X-ray pulses hold promise for probing electronic dynamics in real time, but it is challenging to achieve element sensitivity while maintaining temporal resolution. Teichmann et al. report the cover of carbon, nitrogen and oxygen absorption edges with an isolated pulse supporting 13 as duration.
- S. M. Teichmann
- , F. Silva
- & J. Biegert
-
Article
| Open Access Mapping quantum state dynamics in spontaneous emission
Mapping quantum state dynamics in spontaneous emission
The evolution of a quantum state undergoing radiative decay depends on how the emission is detected. Here, the authors demonstrate how continuous field detection, as opposed to the more common detection of energy quanta, allows control of the back-action on the emitter’s state.
- M. Naghiloo
- , N. Foroozani
- & K. W. Murch
-
Article
| Open Access Giant photon bunching, superradiant pulse emission and excitation trapping in quantum-dot nanolasers
Giant photon bunching, superradiant pulse emission and excitation trapping in quantum-dot nanolasers
Classical light sources are characterized by their intensity and coherence, whereas quantum light sources are described by photon correlations. Here, the authors provide a connection between the two for the case of superradiant emission from quantum dots in a nanolaser.
- Frank Jahnke
- , Christopher Gies
- & Sven Höfling
-
Article
| Open Access Nonlocality-driven supercontinuum white light generation in plasmonic nanostructures
Nonlocality-driven supercontinuum white light generation in plasmonic nanostructures
A theoretical description of the nonlinear response of metals is complicated due to their complex electron behavior. Here, Krasavin et al. use a hydrodynamic model coupled with Maxwell's equations and demonstrate higher harmonics and supercontinuum generation from metal Archimedean spiral shapes
- A. V. Krasavin
- , P. Ginzburg
- & A. V. Zayats
-
Article
| Open Access Controlling the volatility of the written optical state in electrochromic DNA liquid crystals
Controlling the volatility of the written optical state in electrochromic DNA liquid crystals
Electrochromism, the dependence of light absorption upon electronic control, finds a wide range of applications in smart materials. Here, Liu et al. show an electrochromic DNA–surfactant liquid crystal system that exhibits electrically tunable optical absorption and thermally tunable memory.
- Kai Liu
- , Justin Varghese
- & Andreas Herrmann
-
Article
| Open Access Giant photoluminescence enhancement in tungsten-diselenide–gold plasmonic hybrid structures
Giant photoluminescence enhancement in tungsten-diselenide–gold plasmonic hybrid structures
Two-dimensional materials have excellent electrical properties, but poor luminescence limits their application in optoelectronics. Here, the authors demonstrate a plasmon-induced 20,000-fold enhancement in photoluminescence from tungsten diselenide suspended across a nanometre-scale gap.
- Zhuo Wang
- , Zhaogang Dong
- & Andrew T. S. Wee
-
Article
| Open Access Active mode locking of quantum cascade lasers in an external ring cavity
Active mode locking of quantum cascade lasers in an external ring cavity
Compact, integrated mode-locked lasers can produce ultrashort pulses of light in the visible and near infrared, but are more difficult to achieve in the mid-infrared. Here, the authors demonstrate active mode locking of an external-cavity quantum cascade laser emitting at 5.2 micrometres at room temperature.
- D. G. Revin
- , M. Hemingway
- & A. Belyanin
-
Article
| Open Access A 14 × 14 μm2 footprint polarization-encoded quantum controlled-NOT gate based on hybrid waveguide
A 14 × 14 μm2 footprint polarization-encoded quantum controlled-NOT gate based on hybrid waveguide
Photonic circuits often require separate components to manipulate light with orthogonal polarization, but this increases the chip size. Here, the authors create a polarization-dependent beam-splitter that uses dielectric loaded plasmonic waveguides to handle both polarizations in the same component.
- S. M. Wang
- , Q. Q. Cheng
- & S. N. Zhu
-
Article
| Open Access Enhanced nonlinear interactions in quantum optomechanics via mechanical amplification
Enhanced nonlinear interactions in quantum optomechanics via mechanical amplification
Optomechanics harnesses the interaction between mechanical resonators and light, but weak matter–single-photon interactions limit studies to the linear regime. Here, the authors show that the interaction can be enhanced by modulating the spring constant of the resonator.
- Marc-Antoine Lemonde
- , Nicolas Didier
- & Aashish A. Clerk
-
Correspondence
| Open Access Correspondence: Reply to ‘Quantitative evaluation of X-ray dark-field images for microcalcification analysis in mammography’
Correspondence: Reply to ‘Quantitative evaluation of X-ray dark-field images for microcalcification analysis in mammography’
- Zhentian Wang
- , Nik Hauser
- & Marco Stampanoni
-
Article
| Open Access Experimental realization of Bloch oscillations in a parity-time synthetic silicon photonic lattice
Experimental realization of Bloch oscillations in a parity-time synthetic silicon photonic lattice
Bloch oscillations are a fundamental electron transport phenomenon in condensed matter. Here, the authors experimentally realize spatial Bloch oscillations in a non-Hermitian integrated photonic system using CMOS compatible fabrication processes, contributing to improving the understanding of non-Hermitian transport phenomena.
- Ye-Long Xu
- , William S. Fegadolli
- & Yan-Feng Chen
-
Article
| Open Access Guided post-acceleration of laser-driven ions by a miniature modular structure
Guided post-acceleration of laser-driven ions by a miniature modular structure
Intense laser-driven acceleration mechanisms are promising for the realization of compact particle accelerators. Here, the authors present a miniature linear accelerating module for laser-driven protons from a foil that addresses limitation in terms of peak energy, bandwidth and beam divergence.
- Satyabrata Kar
- , Hamad Ahmed
- & Marco Borghesi
-
Article
| Open Access Experimental perfect state transfer of an entangled photonic qubit
Experimental perfect state transfer of an entangled photonic qubit
Transferring quantum information is a fundamental task, but doing so with high fidelity is a challenging task. Here, the authors implement the perfect state transfer protocol to a photonic qubit, entangled with a second one in a different location, across eleven coupled waveguides.
- Robert J. Chapman
- , Matteo Santandrea
- & Alberto Peruzzo
-
Article
| Open Access Free-carrier-induced soliton fission unveiled by in situ measurements in nanophotonic waveguides
Free-carrier-induced soliton fission unveiled by in situ measurements in nanophotonic waveguides
Solitons are nonlinear waves that exist in diverse forms of matter. Here, Husko et al. use near-field measurements to observe the spatio-temporal evolution of optical pulses in a nanophotonic semiconductor waveguide, demonstrating that nonlinear photo-carrier generation can induce fission of solitons.
- Chad Husko
- , Matthias Wulf
- & L. Kuipers
-
Article
| Open Access Enhancing coherent transport in a photonic network using controllable decoherence
Enhancing coherent transport in a photonic network using controllable decoherence
The efficiency of coherent transport can be enhanced through interaction between the system and a noisy environment. Here, Biggerstaff et al. report an experimental simulation of environment assisted coherent transport using laser-written waveguides, showing that controllable decoherence yields an increase in transport efficiency.
- Devon N. Biggerstaff
- , René Heilmann
- & Ivan Kassal
-
Article
| Open Access Plasmonic piezoelectric nanomechanical resonator for spectrally selective infrared sensing
Plasmonic piezoelectric nanomechanical resonator for spectrally selective infrared sensing
Plasmonic metasurfaces can provide exciting optical functionalities. Here, Hui et al. demonstrate an infrared sensor by combining plasmonic and piezoelectric electromechanical resonances, demonstrating efficient transduction of vibration with a strong and polarization-independent absorption over an ultrathin thickness.
- Yu Hui
- , Juan Sebastian Gomez-Diaz
- & Matteo Rinaldi
-
Article
| Open Access Femtosecond electron imaging of defect-modulated phonon dynamics
Femtosecond electron imaging of defect-modulated phonon dynamics
Phonons—crystal lattice vibrations—interact with crystal defects on the nanometre spatial scale and femtosecond timescale. Here, the authors demonstrate direct, real-space imaging of the nucleation, emergence and dispersion of single-phonon wavefronts at individual atomic-scale defects in semiconductors.
- Daniel R. Cremons
- , Dayne A. Plemmons
- & David J. Flannigan
-
Article
| Open Access Magnetic-free non-reciprocity based on staggered commutation
Magnetic-free non-reciprocity based on staggered commutation
Components such as isolators, circulators and gyrators are non-reciprocal in that they allow electromagnetic waves to flow in one direction but not the other. Here, the authors demonstrate a radio-frequency circulator that is compatible with and integrated in a complementary metal-oxide semiconductor integrated circuit.
- Negar Reiskarimian
- & Harish Krishnaswamy
-
Article
| Open Access Near optimal graphene terahertz non-reciprocal isolator
Near optimal graphene terahertz non-reciprocal isolator
Optical isolators, or optical diodes, allow electromagnetic radiation to travel in one direction but not the other. Here, the authors achieve unidirectional propagation of terahertz waves by taking advantage of the non-reciprocal nature of optical conductivity in magnetostatically biased graphene.
- Michele Tamagnone
- , Clara Moldovan
- & Julien Perruisseau-Carrier
-
Article
| Open Access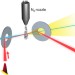 Diffractive imaging of a rotational wavepacket in nitrogen molecules with femtosecond megaelectronvolt electron pulses
Diffractive imaging of a rotational wavepacket in nitrogen molecules with femtosecond megaelectronvolt electron pulses
Imaging changes in molecular geometries with sufficient temporal and spatial resolution to image nuclei is a critical challenge in the chemical sciences. Here the authors report gasphase Megaelectronvolt electron diffraction with 100 fs temporal resolution and subAngstrom spatial resolution.
- Jie Yang
- , Markus Guehr
- & Xijie Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Frequency and bandwidth conversion of single photons in a room-temperature diamond quantum memory
Frequency and bandwidth conversion of single photons in a room-temperature diamond quantum memory
Controlling the spectral properties of single photons is important for emerging optical quantum technologies, but doing so in a frequency-multiplexed framework is challenging. Here, the authors demonstrate quantum frequency conversion with a Raman quantum memory in room-temperature diamond.
- Kent A. G. Fisher
- , Duncan G. England
- & Benjamin J. Sussman
-
Article
| Open Access Giant photostriction in organic–inorganic lead halide perovskites
Giant photostriction in organic–inorganic lead halide perovskites
The photophysics of lead halide perovskites is under intense investigation. Here, the authors use force microscopy on single crystals to show that light induces drastic lattice changes, and propose that the weakening of the hydrogen coupling under illumination is responsible for the lattice dilatation.
- Yang Zhou
- , Lu You
- & Junling Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Real-time high dynamic range laser scanning microscopy
Real-time high dynamic range laser scanning microscopy
Confocal and multiphoton fluorescence microscopy often suffers from low dynamic range. Here the authors develop a high dynamic range, laser scanning fluorescence technique by simultaneously recording different light intensity ranges. The method can be adapted to commercial systems.
- C. Vinegoni
- , C. Leon Swisher
- & R. Weissleder
-
Article
| Open Access Active temporal multiplexing of indistinguishable heralded single photons
Active temporal multiplexing of indistinguishable heralded single photons
Deterministically generated single photons are useful for quantum communications, but the processes that create such light are often non-deterministic. Here, the authors enhance the single-photon output probability by multiplexing photons from four temporal modes using fibre-integrated optics.
- C. Xiong
- , X. Zhang
- & B. J. Eggleton
-
Article
| Open Access Exciton localization in solution-processed organolead trihalide perovskites
Exciton localization in solution-processed organolead trihalide perovskites
The recombination dynamics of photogenerated carriers in organolead trihalide perovskites are not well understood. Here, He et al.report that the recombination of photogenerated carriers in solution-processed methylammonium-lead-halide films is dominated by excitons weakly localized in band tail states.
- Haiping He
- , Qianqian Yu
- & Zhizhen Ye
-
Article
| Open Access Collective atomic scattering and motional effects in a dense coherent medium
Collective atomic scattering and motional effects in a dense coherent medium
Light scattering from a dense coherent medium is determined by the interplay of dispersive and radiative dipole–dipole interactions. Here, the authors control the motional effects that obscure the coherence of scattered light and study collective emission in a driven gas of cold strontium-88 atoms.
- S. L. Bromley
- , B. Zhu
- & J. Ye
-
Article
| Open Access Optically responsive supramolecular polymer glasses
Optically responsive supramolecular polymer glasses
The ability to heal whilst maintaining original functionality is important for establishing materials with superior longevity. Here, the authors demonstrate a supramolecular polymeric coating which exhibits excellent optical and mechanical properties, even following damage repair.
- Diederik W. R. Balkenende
- , Christophe A. Monnier
- & Christoph Weder
-
Article
| Open Access Polarized three-photon-pumped laser in a single MOF microcrystal
Polarized three-photon-pumped laser in a single MOF microcrystal
Higher-order multi-photon pumped polarized lasers promise application in future optoelectronic and biomedical applications. Here, the authors demonstrate a polarized three-photon pumped (3PP) microcavity laser in a single host-guest composite MOF crystal via a controllable in situ self-assembly strategy.
- Huajun He
- , En Ma
- & Guodong Qian
-
Article
| Open Access Photoacoustics of single laser-trapped nanodroplets for the direct observation of nanofocusing in aerosol photokinetics
Photoacoustics of single laser-trapped nanodroplets for the direct observation of nanofocusing in aerosol photokinetics
Aerosol droplets have significant effects on atmospheric photochemistry, however measuring absorption from single droplets is a challenge. Here, the authors report a method to measure absorption of nanodroplets with attolitre sensitivity, showing rate enhancements for light focusing in photolysis reactions.
- Johannes W. Cremer
- , Klemens M. Thaler
- & Ruth Signorell
-
Article
| Open Access Damage-free vibrational spectroscopy of biological materials in the electron microscope
Damage-free vibrational spectroscopy of biological materials in the electron microscope
Use of electron microscopy to determine morphology, or find where functionally significant biomolecules are located with high spatial resolution is of great interest. Here, Rez, Cohen et al. use aloof electron beam vibrational spectroscopy to probe different bonds in biological samples with no significant radiation damage.
- Peter Rez
- , Toshihiro Aoki
- & Hagai Cohen
-
Article
| Open Access Selectively enhanced photocurrent generation in twisted bilayer graphene with van Hove singularity
Selectively enhanced photocurrent generation in twisted bilayer graphene with van Hove singularity
Graphene has the high carrier mobility and short photoresponse time required for efficient photodetection, but broad and weak optical absorption are severe drawbacks. Here, the authors show that twisted bilayer graphene with van Hove singularities exhibits a strong light-matter interaction and selectively enhanced photocurrent generation.
- Jianbo Yin
- , Huan Wang
- & Zhongfan Liu
-
Article
| Open Access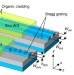 Lasing in silicon–organic hybrid waveguides
Lasing in silicon–organic hybrid waveguides
On-chip light sources for silicon photonic circuits remain a challenge since the indirect bandgap of silicon prevents efficient light emission. The authors demonstrate that lasing can be achieved by combining standard silicon-on-insulator waveguides with dye-doped organic cladding materials to provide optical gain.
- Dietmar Korn
- , Matthias Lauermann
- & Christian Koos
-
Article
| Open Access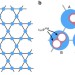 Topological phase transitions and chiral inelastic transport induced by the squeezing of light
Topological phase transitions and chiral inelastic transport induced by the squeezing of light
Most known topological states of light are in the end closely analogous to fermionic states. Here, the authors show that the squeezing of light can lead to the formation of photonic topological states which do not have any fermionic counterpart yet support unusual chiral edge states.
- Vittorio Peano
- , Martin Houde
- & Aashish A. Clerk
-
Article
| Open Access Intensifying the response of distributed optical fibre sensors using 2D and 3D image restoration
Intensifying the response of distributed optical fibre sensors using 2D and 3D image restoration
Optical fibres offer a way of sensing across a wide area, providing a spatial and temporal map of the measured parameter. Here, the authors use image and video processing to remove noise and increase the contrast in such a distributed optical fibre sensor, improving the signal-to-noise ratio by a factor of 100.
- Marcelo A. Soto
- , Jaime A. Ramírez
- & Luc Thévenaz
-
Article
| Open Access Direct single-shot phase retrieval from the diffraction pattern of separated objects
Direct single-shot phase retrieval from the diffraction pattern of separated objects
Short X-ray pulses from free-electron lasers enable coherent diffractive imaging of noncrystalline objects such as single molecules. Here, the authors reconstructing full image information from a single-shot diffraction pattern by using two sufficiently separated objects to act as references for each other.
- Ben Leshem
- , Rui Xu
- & Oren Raz
-
Article
| Open Access Pure-quartic solitons
Pure-quartic solitons
Optical solitons are pulses that propagate undistorted. Here, the authors demonstrate a class of soliton arising from the interaction of self-phase modulation with quartic dispersion, rather than with quadratic dispersion as occurs in conventional solitons.
- Andrea Blanco-Redondo
- , C. Martijn de Sterke
- & Chad Husko
-
Article
| Open Access Wavelength-tunable entangled photons from silicon-integrated III–V quantum dots
Wavelength-tunable entangled photons from silicon-integrated III–V quantum dots
Deterministic sources of entangled photons are important for photonic quantum networks, but many applications are only possible when their wavelengths are tunable. Here, the authors use on-chip strain engineering to demonstrate such a source with silicon-integrated InAs/GaAs quantum dots.
- Yan Chen
- , Jiaxiang Zhang
- & Oliver G. Schmidt
-
Article
| Open Access High-contrast and fast electrochromic switching enabled by plasmonics
High-contrast and fast electrochromic switching enabled by plasmonics
Slow switching speeds in device configurations have severely limited the applications of electrochromic materials. Here, Xu et al. use plasmonic nanoslit arrays and demonstrate fast, high-contrast, monochromatic and full-colour electrochromic switching using two different electrochromic polymers.
- Ting Xu
- , Erich C. Walter
- & A. Alec Talin
-
Article
| Open Access Demonstration of a near-IR line-referenced electro-optical laser frequency comb for precision radial velocity measurements in astronomy
Demonstration of a near-IR line-referenced electro-optical laser frequency comb for precision radial velocity measurements in astronomy
Laser frequency combs emit a spectrum of equally spaced peaks that can provide precise frequency references useful for astronomy. Here, the authors demonstrate a frequency comb using electro-optical modulation, which has a line spacing that is resolvable using grating spectrographs unlike the mode-locking approach.
- X. Yi
- , K. Vahala
- & C. Beichman
-
Article
| Open Access Wavelength-tunable sources of entangled photons interfaced with atomic vapours
Wavelength-tunable sources of entangled photons interfaced with atomic vapours
Quantum dots can produce entangled photons, but careful control over photon wavelength is required for real-life applications. Here, the authors use three-directional strain engineering to overcome this problem and to interface entangled photons from quantum dots with a cloud of natural atoms.
- Rinaldo Trotta
- , Javier Martín-Sánchez
- & Armando Rastelli
-
Article
| Open Access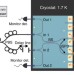 Quantum interference in heterogeneous superconducting-photonic circuits on a silicon chip
Quantum interference in heterogeneous superconducting-photonic circuits on a silicon chip
Scaling photonic quantum information processing approaches remains challenging for integrated quantum optics. Here, Schuck et al.develop a hybrid superconducting-photonic circuit system to show how quantum interference and single-photon detectors can be combined in a scalable fashion on a silicon chip.
- C. Schuck
- , X. Guo
- & H. X. Tang
-
Article
| Open Access Substantial bulk photovoltaic effect enhancement via nanolayering
Substantial bulk photovoltaic effect enhancement via nanolayering
Spontaneous polarization in ferroelectric materials leads to their use as photovoltaic devices. Here, the authors show by first-principles calculations how nanolayering of PbTiO3with nickel ions and oxygen vacancies can result in enhanced photocurrents due to smaller bandgaps and photocurrent alignment.
- Fenggong Wang
- , Steve M. Young
- & Andrew M. Rappe
-
Article
| Open Access Shaping the nonlinear near field
Shaping the nonlinear near field
While shaping of the electromagnetic fields around nanostructures is widely studied, the influence of the field inside the nanostructures is often overlooked. Here, Wolf et al. control the spatial distribution of third-harmonic emission in a plasmonic nanostructure, imaged by a far field Fourier method.
- Daniela Wolf
- , Thorsten Schumacher
- & Markus Lippitz
-
Article
| Open Access Widely tunable two-colour seeded free-electron laser source for resonant-pump resonant-probe magnetic scattering
Widely tunable two-colour seeded free-electron laser source for resonant-pump resonant-probe magnetic scattering
Two-colour X-ray free electron laser is a powerful tool for pump–probe measurements, but currently constrained by limited tunability. Here, Ferrari et al. develop a configuration that allows tuning both the pump and the probe to specific electronic excitations, providing element selectivity.
- Eugenio Ferrari
- , Carlo Spezzani
- & Maurizio Sacchi
-
Article
| Open Access Manipulation of charge transfer and transport in plasmonic-ferroelectric hybrids for photoelectrochemical applications
Manipulation of charge transfer and transport in plasmonic-ferroelectric hybrids for photoelectrochemical applications
Photoelectrochemical systems based on plasmonics require control of band bending at the interface as well as transport of hot carriers. Here, Wang et al. employ a ferroelectric material, Pb(Zr,Ti)O3, with gold on ITO to capture hot electrons from the metal and manipulate the photoexcited charges for energy conversion.
- Zhijie Wang
- , Dawei Cao
- & Yong Lei
-
Article
| Open Access Electromechanical control of nitrogen-vacancy defect emission using graphene NEMS
Electromechanical control of nitrogen-vacancy defect emission using graphene NEMS
Active control of optical fields at the nanoscale is difficult to achieve. Here, the authors fabricate an on-chip graphene NEMS suspended a few tens of nanometres above nitrogen vacancy centres and demonstrate electromechanical control of the photons emitted by electrostatic tuning of the graphene NEMS position.
- Antoine Reserbat-Plantey
- , Kevin G. Schädler
- & Frank H. L. Koppens
-
Article
| Open Access A series connection architecture for large-area organic photovoltaic modules with a 7.5% module efficiency
A series connection architecture for large-area organic photovoltaic modules with a 7.5% module efficiency
The fabrication of organic photovoltaic modules usually relies on patterning techniques which limit their efficiencies. Here, the authors propose a module structure that avoids the patterning steps, and use doctor-blade printing and slot-die coating to fabricate large-area modules reaching 7.5% efficiencies.
- Soonil Hong
- , Hongkyu Kang
- & Kwanghee Lee
-
Article
| Open Access Bio-recognitive photonics of a DNA-guided organic semiconductor
Bio-recognitive photonics of a DNA-guided organic semiconductor
BioLEDs is an emerging group of light-emitting diodes that use duplex-strand DNA to enhance luminescence intensity. Here, Back et al.show that only the specific binding between a pair of single-strand DNA can trigger the enhancement, which potentially makes BioLEDs an easy platform for DNA recognition.
- Seung Hyuk Back
- , Jin Hyuk Park
- & Dong June Ahn
-
Article
| Open Access Flexible thin-film black gold membranes with ultrabroadband plasmonic nanofocusing for efficient solar vapour generation
Flexible thin-film black gold membranes with ultrabroadband plasmonic nanofocusing for efficient solar vapour generation
Efficient steam generation under solar irradiation is of interest for energy harvesting applications. Here, Bae et al. develop a plasmonic nanofocusing film consisting of metal coated alumina nanowires to efficiently generate solar vapour with an efficiency up to 57% at 20 kWm−2.
- Kyuyoung Bae
- , Gumin Kang
- & Willie J. Padilla

 Photo-induced halide redistribution in organic–inorganic perovskite films
Photo-induced halide redistribution in organic–inorganic perovskite films