Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Broadband miniaturized spectrometers with a van der Waals tunnel diode
Broadband miniaturized spectrometers with a van der Waals tunnel diode
Here, the authors report a high-performance broadband spectrometer based on a van der Waals heterostructure tunnel diode containing MoS2 and and black phosphorus, leveraging their electrically tunable photoresponse and advanced computational algorithms for spectral reconstruction.
- Md Gius Uddin
- , Susobhan Das
- & Zhipei Sun
-
Article
| Open Access Differential perovskite hemispherical photodetector for intelligent imaging and location tracking
Differential perovskite hemispherical photodetector for intelligent imaging and location tracking
Differential spectrometers recognise different wavelength via their differential photodetector responsivity. The authors combine an 8-pixel hemispherical perovskite photodetector with neural network algorithms to realise 3D trajectory tracking and 2D location tacking with colour classification.
- Xiaopeng Feng
- , Chenglong Li
- & Haotong Wei
-
Article
| Open Access Cochaperones convey the energy of ATP hydrolysis for directional action of Hsp90
Cochaperones convey the energy of ATP hydrolysis for directional action of Hsp90
The precise role of cochaperones and ATP hydrolysis in driving Hsp90’s chaperone cycle is largely unclear. Here, the authors use single-molecule FRET to show that several cochaperones are necessary to establish directionality in Hsp90’s conformational cycle.
- Leonie Vollmar
- , Julia Schimpf
- & Thorsten Hugel
-
Article
| Open Access High-speed and energy-efficient non-volatile silicon photonic memory based on heterogeneously integrated memresonator
High-speed and energy-efficient non-volatile silicon photonic memory based on heterogeneously integrated memresonator
Photonic integrated circuits have grown as potential hardware for neural networks and quantum computing, yet the tuning speed and large power consumption limited the application. Here, authors introduce the memresonator, a memristor heterogeneously integrated with a microring resonator, as a non-volatile silicon photonic phase shifter to address these limitations.
- Bassem Tossoun
- , Di Liang
- & Raymond G. Beausoleil
-
Article
| Open Access Photonic Stochastic Emergent Storage for deep classification by scattering-intrinsic patterns
Photonic Stochastic Emergent Storage for deep classification by scattering-intrinsic patterns
Photonic Stochastic Emergent Storage is a neuromorphic photonic device for image storage and classification based on scattering-intrinsic patterns. Here, the authors show emergent storage employs stochastic prototype scattering-induced light patterns to generate categories corresponding to emergent archetypes.
- Marco Leonetti
- , Giorgio Gosti
- & Giancarlo Ruocco
-
Article
| Open Access Giant intrinsic photovoltaic effect in one-dimensional van der Waals grain boundaries
Giant intrinsic photovoltaic effect in one-dimensional van der Waals grain boundaries
The intrinsic photovoltaic effect (IPVE) in noncentrosymmetric materials has the potential to overcome the limitations of traditional photovoltaic devices. Here, the authors report the observation of a strong and gate-tunable IPVE in 1D grain boundaries of a van der Waals semiconductor, ReS2.
- Yongheng Zhou
- , Xin Zhou
- & Xiaolong Chen
-
Article
| Open Access Distributed quantum sensing of multiple phases with fewer photons
Distributed quantum sensing of multiple phases with fewer photons
Enhanced sensitivity is a key parameter in quantum metrology. Here the authors demonstrate a distributed quantum phase sensing method that uses fewer photons than the number of parameters needed, and an enhanced quantum sensitivity is achieved.
- Dong-Hyun Kim
- , Seongjin Hong
- & Hyang-Tag Lim
-
Article
| Open Access Scalable integrated two-dimensional Fourier-transform spectrometry
Scalable integrated two-dimensional Fourier-transform spectrometry
The authors propose and demonstrate a novel integrated spectrometer that measures any arbitrary spectrum with two-dimensional Fourier transform, breaking the scalability limit in chip-scale spectrometry.
- Hongnan Xu
- , Yue Qin
- & Hon Ki Tsang
-
Article
| Open Access Scalable nano-architecture for stable near-blackbody solar absorption at high temperatures
Scalable nano-architecture for stable near-blackbody solar absorption at high temperatures
Nanostructures are generally unstable above 850 °C in air, limiting their use in high-temperature solar thermal applications. Here, a scalable ceramic nano-architecture layer can significantly enhance and stabilise the absorption of an arbitrary solar absorber.
- Yifan Guo
- , Kaoru Tsuda
- & Juan F. Torres
-
Article
| Open Access Drone-based displacement measurement of infrastructures utilizing phase information
Drone-based displacement measurement of infrastructures utilizing phase information
Drones are an effective and flexible tool for safety assessment of aging infrastructure, especially in locations with challenging accessibility. Here, authors demonstrate a phase-based sampling moiré technique with a drone for measurement of millimeter-scale infrastructural displacement in bridges.
- Shien Ri
- , Jiaxing Ye
- & Norihiko Ogura
-
Article
| Open Access Single-cell mapping of lipid metabolites using an infrared probe in human-derived model systems
Single-cell mapping of lipid metabolites using an infrared probe in human-derived model systems
Current metabolic imaging studies are limited by low resolution and low specificity. Here, the authors present a single-cell metabolic imaging platform to monitor lipid metabolism with high specificity in various human-derived 2D and 3D culture systems.
- Yeran Bai
- , Carolina M. Camargo
- & Kenneth S. Kosik
-
Article
| Open Access Theory predicts 2D chiral polaritons based on achiral Fabry–Pérot cavities using apparent circular dichroism
Theory predicts 2D chiral polaritons based on achiral Fabry–Pérot cavities using apparent circular dichroism
2D chiral polaritons are light-matter states with select angular momentum holding technological promise. Here, the authors present the theory of such states, and propose their realisation based on a phenomenon called “apparent circular dichroism”.
- Andrew H. Salij
- , Randall H. Goldsmith
- & Roel Tempelaar
-
Article
| Open Access Creating pairs of exceptional points for arbitrary polarization control: asymmetric vectorial wavefront modulation
Creating pairs of exceptional points for arbitrary polarization control: asymmetric vectorial wavefront modulation
The authors report the chiral inversion of exceptional points (EPs) through a structural mirror-symmetric operation, extending the application of EP to any desired polarization states, surpassing the inherent limitation of conventional EP systems.
- Zijin Yang
- , Po-Sheng Huang
- & Qinghua Song
-
Article
| Open Access Direct laser-written optomechanical membranes in fiber Fabry-Perot cavities
Direct laser-written optomechanical membranes in fiber Fabry-Perot cavities
Authors showcase 3D direct laser writing to fabricate optically interfaced mechanical resonators. The membrane-type structures are placed inside fiber Fabry-Perot cavities to realize a miniaturized optical cavity. Further, the optomechanical properties reveal the coupling mechanism and a significant tuning of the mechanical resonator frequency.
- Lukas Tenbrake
- , Alexander Faßbender
- & Hannes Pfeifer
-
Article
| Open Access Electrical tuning of branched flow of light
Electrical tuning of branched flow of light
Here the authors experimentally realize the electrical tuning of branched flow of light in nematic liquid crystals. The statistical properties and the polarization effect of the branched flow of light in the film are systematically studied adding fundamental insights on branched flow of light.
- Shan-shan Chang
- , Ke-Hui Wu
- & Jin-hui Chen
-
Article
| Open Access Turnkey photonic flywheel in a microresonator-filtered laser
Turnkey photonic flywheel in a microresonator-filtered laser
Here the authors demonstrate a universal approach to achieve turnkey dissipative Kerr soliton (DKS) frequency comb. Phase insensitivity, self-healing capability, deterministic selection of DKS state, and access to ultralow noise are all successfully accomplished.
- Mingming Nie
- , Jonathan Musgrave
- & Shu-Wei Huang
-
Article
| Open Access Direct and integrating sampling in terahertz receivers from wafer-scalable InAs nanowires
Direct and integrating sampling in terahertz receivers from wafer-scalable InAs nanowires
Authors report on nanofacet engineering of wafer‐scalable InAs nanowires enabling the operation of THz photodetectors in direct or integrating sampling mode, with performance comparable to commercial InP technology.
- Kun Peng
- , Nicholas Paul Morgan
- & Michael B. Johnston
-
Perspective
| Open Access Planar hyperbolic polaritons in 2D van der Waals materials
Planar hyperbolic polaritons in 2D van der Waals materials
In this Perspective, the authors illustrate the physics of hyperbolic polaritons in anisotropic 2D and 1D materials, proposing new potential material candidates, forward looking opportunities and technological applications.
- Hongwei Wang
- , Anshuman Kumar
- & Tony Low
-
Article
| Open Access Dual-wavelength metalens enables Epi-fluorescence detection from single molecules
Dual-wavelength metalens enables Epi-fluorescence detection from single molecules
The requirement for sophisticated objective lenses hinders the miniaturisation of single molecule fluorescence spectroscopy for portable sensing applications. Here, the authors demonstrate a dual-wavelength metalens for real-time monitoring of individual fluorescent nanoparticles.
- Aleksandr Barulin
- , Yeseul Kim
- & Inki Kim
-
Article
| Open Access A mode-locked random laser generating transform-limited optical pulses
A mode-locked random laser generating transform-limited optical pulses
Pulses of adjustable duration are generated by a mode-locked random fibre laser that can drive advances in sensing. Rayleigh backscattering from cm-long sections of telecom fibre provides laser feedback and spectral selectivity to the Fourier limit.
- Jean Pierre von der Weid
- , Marlon M. Correia
- & Walter Margulis
-
Article
| Open Access Quantum plasmonics pushes chiral sensing limit to single molecules: a paradigm for chiral biodetections
Quantum plasmonics pushes chiral sensing limit to single molecules: a paradigm for chiral biodetections
Chiroptic sensing of single molecule is extremely challenging. Here the authors unveil an extreme nanophotonic system based on nanoparticle-on-mirror shows exceptional high sensitivity of chiral supramolecules, which can resolve enantiomer access of a racemate monolayer, exhibiting great potential for single chiral molecule sensing.
- Chi Zhang
- , Huatian Hu
- & Tao Ding
-
Article
| Open Access AI-driven projection tomography with multicore fibre-optic cell rotation
AI-driven projection tomography with multicore fibre-optic cell rotation
Conventional optical tomography can have disadvantages, including anisotropic resolution and incomplete imaging of cellular structures. Here, the authors propose an AI-driven 3D cell imaging system with a cell rotator, which offers improved resolution and automated processing.
- Jiawei Sun
- , Bin Yang
- & Juergen W. Czarske
-
Article
| Open Access Ultrafast entropy production in pump-probe experiments
Ultrafast entropy production in pump-probe experiments
Ultrafast spectroscopy enables characterization and control of non-equilibrium states. Here the authors introduce a stochastic thermodynamics approach to calculate entropy production in a material under ultrafast excitation, using ionic displacement data from time-resolved X-ray scattering experiments.
- Lorenzo Caprini
- , Hartmut Löwen
- & R. Matthias Geilhufe
-
Article
| Open Access Waveguide holography for 3D augmented reality glasses
Waveguide holography for 3D augmented reality glasses
Near-eye displays are pivotal for building augmented and virtual reality platforms, but hurdles remain in achieving comfort and realistic visual experiences. Here, authors demonstrate compact 3D holographic glasses with focus cues by combining merits of waveguide displays and holographic displays.
- Changwon Jang
- , Kiseung Bang
- & Douglas Lanman
-
Article
| Open Access Photogating-assisted tunneling boosts the responsivity and speed of heterogeneous WSe2/Ta2NiSe5 photodetectors
Photogating-assisted tunneling boosts the responsivity and speed of heterogeneous WSe2/Ta2NiSe5 photodetectors
Photodetectors based on 2D materials can exhibit high photoresponsivity, but usually at the cost of their response speed. Here, the authors report a strategy based on photogating-assisted tunneling to overcome this trade-off in WSe2/Ta2NiSe5 heterostructures.
- Mingxiu Liu
- , Jingxuan Wei
- & Shaojuan Li
-
Article
| Open Access Organohydrogel-based transparent terahertz absorber via ionic conduction loss
Organohydrogel-based transparent terahertz absorber via ionic conduction loss
Transparent absorbers for electromagnetic interference shielding are sought in the terahertz frequency range. The authors demonstrate organohydrogel-elastomer composites based on permittivity gradients, with strong ionic conduction loss, showing high absorption in the 0.5–4.5 THz band.
- Wenke Xie
- , Qian Tang
- & Qiye Wen
-
Article
| Open Access Probing optical anapoles with fast electron beams
Probing optical anapoles with fast electron beams
Optical anapoles in nanoresonators result in strong suppression of the electromagnetic radiation, which is challenging to detect in ideal settings. Here, the authors show that fast electrons are a powerful tool to circumvent this challenge due to their ability to access dark modes.
- Carlos Maciel-Escudero
- , Andrew B. Yankovich
- & Timur O. Shegai
-
Article
| Open Access High quality factor metasurfaces for two-dimensional wavefront manipulation
High quality factor metasurfaces for two-dimensional wavefront manipulation
Wavefront manipulation with metasurfaces is typically limited to low quality factors. Here, the authors show how higher-order Mie modes can be leveraged to design high quality factor optical metasurfaces for wavefront manipulation in two dimensions.
- Claudio U. Hail
- , Morgan Foley
- & Harry A. Atwater
-
Article
| Open Access Ultra-narrow inhomogeneous spectral distribution of telecom-wavelength vanadium centres in isotopically-enriched silicon carbide
Ultra-narrow inhomogeneous spectral distribution of telecom-wavelength vanadium centres in isotopically-enriched silicon carbide
Several solid-state defect platforms have been proposed for application as a spin-photon interface in quantum communication networks. Here the authors report spin-selective optical transitions and narrow inhomogeneous spectral distribution of V centers in isotopically-enriched SiC emitting in the telecom O-band.
- Pasquale Cilibrizzi
- , Muhammad Junaid Arshad
- & Cristian Bonato
-
Article
| Open Access Orbital perspective on high-harmonic generation from solids
Orbital perspective on high-harmonic generation from solids
Here the authors identify real-space contributions to the characteristics of high-harmonic generation in ReS2 and demonstrate the possibility of laser-controlled emission. They find that the spectrum is not just determined by the band structure, but also by the interference between HHG signals coming from different atoms within the unit cell.
- Álvaro Jiménez-Galán
- , Chandler Bossaer
- & Giulio Vampa
-
Article
| Open Access UV-curable thiol-ene system for broadband infrared transparent objects
UV-curable thiol-ene system for broadband infrared transparent objects
Processing of conventional infrared-transparent materials limits their applicability. The authors demonstrate 3D printing of thiol-ene optical components with mid- and long-wave infrared transparency with applications such as reaction temperature monitoring.
- Piaoran Ye
- , Zhihan Hong
- & Rongguang Liang
-
Article
| Open Access All-optical geometric image transformations enabled by ultrathin metasurfaces
All-optical geometric image transformations enabled by ultrathin metasurfaces
Metasurfaces enable all-optical geometric coordinate transformations, converting images with altered pixel spatial relations, which can facilitate fast, energy-efficient preprocessing for tasks like object tracking, or aid in laser manufacturing.
- Xingwang Zhang
- , Xiaojie Zhang
- & Xingjie Ni
-
Article
| Open Access Coherent light scattering from a telecom C-band quantum dot
Coherent light scattering from a telecom C-band quantum dot
Developing quantum networks would require reliable sources of coherent quantum light at telecom wavelengths. Here, the authors employ elastic scattering of excitation laser photons on InAs/InP quantum dots to demonstrate the emission of telecom photons with coherence times longer than the Fourier limit.
- L. Wells
- , T. Müller
- & A. J. Shields
-
Article
| Open Access Tracking exceptional points above the lasing threshold
Tracking exceptional points above the lasing threshold
The authors report on the experimental observation and characterization of exceptional points above the lasing threshold in photonic crystal nanocavities.
- Kaiwen Ji
- , Qi Zhong
- & Alejandro M. Yacomotti
-
Article
| Open Access Quantum transport of high-dimensional spatial information with a nonlinear detector
Quantum transport of high-dimensional spatial information with a nonlinear detector
High-dimensional quantum states allow for several advantages in quantum communication, but protocols such as teleportation require additional entangled photons as the dimension increases. Here, the authors show how to transport a high-dimensional quantum state from a bright coherent laser field to a single photon, using two entangled photons as the quantum channel.
- Bereneice Sephton
- , Adam Vallés
- & Andrew Forbes
-
Article
| Open Access Remote transport of high-dimensional orbital angular momentum states and ghost images via spatial-mode-engineered frequency conversion
Remote transport of high-dimensional orbital angular momentum states and ghost images via spatial-mode-engineered frequency conversion
Remote transport of high-dimensional-encoded photonic states could in principle be achieved via quantum teleportation, but with considerable experimental effort. Here, instead, the authors exploit spatial-mode engineered frequency conversion between a coherent wave packet and a single photon to remotely transfer the HD OAM states, also providing a strategy for quantum imaging.
- Xiaodong Qiu
- , Haoxu Guo
- & Lixiang Chen
-
Article
| Open Access Hyperbolic exciton polaritons in a van der Waals magnet
Hyperbolic exciton polaritons in a van der Waals magnet
Hyperbolic exciton polaritons (HEPs) are anisotropic light-matter excitations with promising applications, but their steady-state observation is challenging. Here, the authors report experimental evidence of HEPs in a van der Waals magnet, CrSBr, via cryogenic infrared near-field microscopy.
- Francesco L. Ruta
- , Shuai Zhang
- & D. N. Basov
-
Comment
| Open Access Excitonic Complexes in Two-Dimensional Transition Metal Dichalcogenides
Excitonic Complexes in Two-Dimensional Transition Metal Dichalcogenides
The enhanced Coulomb interaction in two dimensions leads to not only tightly bound excitons but also many-particle excitonic complexes: excitons interacting with other quasiparticles, which results in improved and even new exciton properties with better controls. Here, we summarize studies of excitonic complexes in monolayer transition metal dichalcogenides and their moiré heterojunctions, envisioning how to utilize them for exploring quantum many-body physics.
- Xiaotong Chen
- , Zhen Lian
- & Su-Fei Shi
-
Article
| Open Access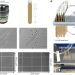 ComplexEye: a multi-lens array microscope for high-throughput embedded immune cell migration analysis
ComplexEye: a multi-lens array microscope for high-throughput embedded immune cell migration analysis
Video microscopy is key in studying cell migration, but accomplishing this in a high-throughput manner is still challenging. Here, the authors present an array microscope that can track the movements of thousands of individual cells simultaneously, and that can be used for drug screening studies.
- Zülal Cibir
- , Jacqueline Hassel
- & Matthias Gunzer
-
Article
| Open Access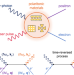 Nanophotonics for pair production
Nanophotonics for pair production
The authors propose electron-positron creation by scattering of gamma-rays and polaritons, enabling the synthesis of ultrafast, localized positron sources and introducing the possibility to exploit nanophotonics for particle physics.
- Valerio Di Giulio
- & F. Javier García de Abajo
-
Article
| Open Access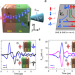 Ultrafast THz probing of nonlocal orbital current in transverse multilayer metallic heterostructures
Ultrafast THz probing of nonlocal orbital current in transverse multilayer metallic heterostructures
By optically driving the magnetization in a magnetic system, terahertz emission can be induced from an adjacent normal metal, as a result of spin-to-charge conversion. Here, Kumar and Kumar successfully show the equivalent effect arising from orbital-to-charge conversion.
- Sandeep Kumar
- & Sunil Kumar
-
Article
| Open Access Real-time photonic blind interference cancellation
Real-time photonic blind interference cancellation
The authors demonstrate real-time blind photonic interference cancellation using FPGA-photonic coordinated processing with zero calibration micro-ring resonator control and sub-second cancellation weight identification.
- Joshua C. Lederman
- , Weipeng Zhang
- & Paul R. Prucnal
-
Article
| Open Access Photon-phonon collaboratively pumped laser
Photon-phonon collaboratively pumped laser
Ultrahigh-efficiency and low-threshold yet tunable and compact laser devices are at the base of new functional devices. Here the authors harness a new temperature degree of freedom to realize a tunable photon-phonon collaboratively pumped laser.
- Yu Fu
- , Fei Liang
- & Yan-Feng Chen
-
Article
| Open Access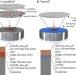 Mid-infrared supermirrors with finesse exceeding 400 000
Mid-infrared supermirrors with finesse exceeding 400 000
The researchers showcase all-crystalline and hybrid mid-infrared supermirrors with the lowest optical losses ever demonstrated in this wavelength range, representing an unprecedented improvement over any existing mirrors made with any production technology.
- Gar-Wing Truong
- , Lukas W. Perner
- & Garrett D. Cole
-
Article
| Open Access Direct identification of interfacial degradation in blue OLEDs using nanoscale chemical depth profiling
Direct identification of interfacial degradation in blue OLEDs using nanoscale chemical depth profiling
Understanding the degradation mechanism of organic light-emitting diodes is essential to improve device performance and stability. Here, authors present a high-resolution diagnostic method to obtain molecular information with 7-nm depth resolution and analyse devices at different degradation levels.
- Gustavo F. Trindade
- , Soohwan Sul
- & Ian S. Gilmore
-
Article
| Open Access Plasmon mediated coherent population oscillations in molecular aggregates
Plasmon mediated coherent population oscillations in molecular aggregates
The authors uncover a coherent, long-range transport of excitons in organic semiconductors that are strongly coupled to spatially structured plasmon fields by tracing ultrafast Rabi oscillations using two-dimensional electronic spectroscopy.
- Daniel Timmer
- , Moritz Gittinger
- & Christoph Lienau
-
Article
| Open Access Fluorescence lifetime Hong-Ou-Mandel sensing
Fluorescence lifetime Hong-Ou-Mandel sensing
Standard techniques for Fluorescence Lifetime Imaging Microscopy are limited by the electronics to 100’s of picoseconds time resolution. Here, the authors show how to use two-photon interference to perform fluorescence lifetime sensing with picosecond-scale resolution.
- Ashley Lyons
- , Vytautas Zickus
- & Daniele Faccio
-
Article
| Open Access Blazed oblique plane microscopy reveals scale-invariant inference of brain-wide population activity
Blazed oblique plane microscopy reveals scale-invariant inference of brain-wide population activity
Recording neuronal activity at cellular resolution across an entire adult vertebrate brain is challenging. Here, the authors develop a blazed oblique plane microscope to perform brain-wide activity measurements in an adult vertebrate at high cellular resolution.
- Maximilian Hoffmann
- , Jörg Henninger
- & Benjamin Judkewitz
-
Article
| Open Access Polariton design and modulation via van der Waals/doped semiconductor heterostructures
Polariton design and modulation via van der Waals/doped semiconductor heterostructures
The photonic applications of hyperbolic phonon polaritons (HPhPs) in anisotropic van der Waals materials are currently limited by their low tunability. Here, the authors report the static and ultrafast wavevector modulation of HPhPs in hexagonal boron nitride by tuning the plasma frequency of doped semiconductor substrates.
- Mingze He
- , Joseph R. Matson
- & Joshua D. Caldwell

 Giant optical polarisation rotations induced by a single quantum dot spin
Giant optical polarisation rotations induced by a single quantum dot spin