Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Dynamic imaging of interfacial electrochemistry on single Ag nanowires by azimuth-modulated plasmonic scattering interferometry
Dynamic imaging of interfacial electrochemistry on single Ag nanowires by azimuth-modulated plasmonic scattering interferometry
Direct visualization of the chemical dynamics of surfaces in solution is essential to gain mechanistic insights into nanocatalysis and electrochemistry. Here, the authors demonstrate the imaging of dynamic interfacial changes on a single nanowire during chemical reactions using azimuthally modulated plasmonic scattering interferometry.
- Gang Wu
- , Chen Qian
- & Xian-Wei Liu
-
Article
| Open Access Large depth-of-field ultra-compact microscope by progressive optimization and deep learning
Large depth-of-field ultra-compact microscope by progressive optimization and deep learning
Traditional optical microscope, while bulky, often fails to deliver optimal performance. Here, the authors have engineered an integrated microscope of 0.15 cm3 in volume and a weight of 0.5 g, which outperforms a commercial microscope and can be seamlessly integrated with a smartphone.
- Yuanlong Zhang
- , Xiaofei Song
- & Qionghai Dai
-
Article
| Open Access High-speed scanless entire bandwidth mid-infrared chemical imaging
High-speed scanless entire bandwidth mid-infrared chemical imaging
The authors present a fast mid-infrared hyperspectral chemical imaging technique that uses chirped pulse upconversion of sub-cycle pulses at the image plane, with lateral resolution of 15 µm and an adjustable field of view and large spectral range. They demonstrate identification and mapping different components in a microfluidic device, plant cell, and mouse embryo.
- Yue Zhao
- , Shota Kusama
- & Takao Fuji
-
Article
| Open Access Non-line-of-sight snapshots and background mapping with an active corner camera
Non-line-of-sight snapshots and background mapping with an active corner camera
Most non-line-of-sight imaging requires scanned illumination, limiting applicability for dynamic scenes. Here the authors exploit occlusion and a sensor array to estimate locations and sizes of moving foreground objects and a static background map.
- Sheila Seidel
- , Hoover Rueda-Chacón
- & Vivek K Goyal
-
Article
| Open Access Imaging the field inside nanophotonic accelerators
Imaging the field inside nanophotonic accelerators
The optical field inside a nanophotonic particle accelerator is revealed. To this end, the authors developed a field imaging technique for spatial and spectral resolution on the nanometer scale.
- Tal Fishman
- , Urs Haeusler
- & Ido Kaminer
-
Article
| Open Access Direct laser writing of 3D electrodes on flexible substrates
Direct laser writing of 3D electrodes on flexible substrates
This report describes a 3D microelectrode array integrated on a thin-film flexible cable using traditional thin-film processing techniques and direct laser writing of 3D structures at micron resolution via two-photon lithography for neural recording.
- Morgan A. Brown
- , Kara M. Zappitelli
- & Timothy J. Gardner
-
Article
| Open Access Deep learning-based incoherent holographic camera enabling acquisition of real-world holograms for holographic streaming system
Deep learning-based incoherent holographic camera enabling acquisition of real-world holograms for holographic streaming system
The authors develop a deep learning-based incoherent holographic camera system in order to deliver visually enhanced holograms in real-time. The neural network filters the noise in the captured holograms, and by integrating a holographic camera and a display, they demonstrate a holographic streaming system.
- Hyeonseung Yu
- , Youngrok Kim
- & Hong-Seok Lee
-
Article
| Open Access A chip-scale atomic beam clock
A chip-scale atomic beam clock
Compact atomic clocks and atom interferometers are desired for on-chip integration. Here the authors demonstrate a chip-scale atomic beam of 87Rb atoms and its application as an atomic beam clock
- Gabriela D. Martinez
- , Chao Li
- & William R. McGehee
-
Article
| Open Access Coherent Stokes Raman scattering microscopy (CSRS)
Coherent Stokes Raman scattering microscopy (CSRS)
Coherent Stokes Raman scattering (CSRS) has never been explored previously for chemical imaging due to a strong fluorescence background. Here, the authors demonstrate the first fluorescence-free CSRS laser scanning microscope and predict CSRS’ unique backscattering properties.
- Sandro Heuke
- & Hervé Rigneault
-
Article
| Open Access Drug screening at single-organoid resolution via bioprinting and interferometry
Drug screening at single-organoid resolution via bioprinting and interferometry
Traditional 2D cell culture platforms do not accurately reflect the physiology of human tumors. Here, authors combine bioprinting and high-speed live cell interferometry with machine learning to measure drug sensitivity at single-organoid resolution in a label-free manner.
- Peyton J. Tebon
- , Bowen Wang
- & Alice Soragni
-
Article
| Open Access Giant optomechanical spring effect in plasmonic nano- and picocavities probed by surface-enhanced Raman scattering
Giant optomechanical spring effect in plasmonic nano- and picocavities probed by surface-enhanced Raman scattering
Extreme confinement of light in plasmonic nanocavities strongly enhances the optomechanical coupling of light with molecular vibrations. Here, the authors use a giant optical spring effect to reversibly weaken molecular bonds.
- Lukas A. Jakob
- , William M. Deacon
- & Jeremy J. Baumberg
-
Article
| Open Access Characterization of diffusing sub-10 nm nano-objects using single anti-resonant element optical fibers
Characterization of diffusing sub-10 nm nano-objects using single anti-resonant element optical fibers
Characterizing diffusing species is increasingly important for revealing nanoscale processes. Here, the authors uncover the potential of fiber-assisted nanoparticle tracking analysis by characterizing nanoparticles as small as 9 nm at record precision levels, reaching fundamental limits.
- Torsten Wieduwilt
- , Ronny Förster
- & Markus A. Schmidt
-
Article
| Open Access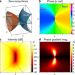 Point singularity array with metasurfaces
Point singularity array with metasurfaces
Optical singularities are typically 1D structures like vortices. This study used metasurfaces to position ten identical point singularities with tight confinement. This could miniaturize optical systems for super-resolution microscopy and dark traps.
- Soon Wei Daniel Lim
- , Joon-Suh Park
- & Federico Capasso
-
Article
| Open Access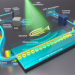 Parallel interrogation of the chalcogenide-based micro-ring sensor array for photoacoustic tomography
Parallel interrogation of the chalcogenide-based micro-ring sensor array for photoacoustic tomography
The authors report a highly sensitive chalcogenide-based micro-ring sensor array for photoacoustic tomography and develops a compatible parallel interrogation means by synthesizing a digital optical frequency comb. Imaging is demonstrated on fast-moving objects, leaf veins, and live zebrafish.
- Jingshun Pan
- , Qiang Li
- & Zhaohui Li
-
Article
| Open Access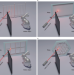 Non-line-of-sight imaging with arbitrary illumination and detection pattern
Non-line-of-sight imaging with arbitrary illumination and detection pattern
The authors propose a confocal complemented signal-object collaborative regularization method for non-line-of-sight (NLOS) imaging without specific requirements on the spatial pattern of measurement points. The method extends the application range of NLOS imaging.
- Xintong Liu
- , Jianyu Wang
- & Lingyun Qiu
-
Article
| Open Access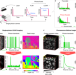 CASPI: collaborative photon processing for active single-photon imaging
CASPI: collaborative photon processing for active single-photon imaging
The sparse, noisy, and distorted raw photon data captured by single-photon cameras make it difficult to estimate scene properties under challenging illumination conditions. Here, the authors present Collaborative photon processing for Active Single-Photon Imaging (CASPI), a technology-agnostic, application-agnostic, and training-free photon processing pipeline for high-resolution single-photon cameras.
- Jongho Lee
- , Atul Ingle
- & Mohit Gupta
-
Article
| Open Access Hybrid achromatic microlenses with high numerical apertures and focusing efficiencies across the visible
Hybrid achromatic microlenses with high numerical apertures and focusing efficiencies across the visible
Creating compact, lightweight and powerful optics that work well under visible light has been challenging. Here, the authors 3D print optically transparent polymers inside nanoporous glass in order to densely integrate refractive and diffractive elements, forming thin, high-performance hybrid achromatic imaging micro-optics.
- Corey A. Richards
- , Christian R. Ocier
- & Paul V. Braun
-
Article
| Open Access Deep learning enables satellite-based monitoring of large populations of terrestrial mammals across heterogeneous landscape
Deep learning enables satellite-based monitoring of large populations of terrestrial mammals across heterogeneous landscape
This study presents a deep learning pipeline to automatically locate and count large herds of migratory ungulates (wildebeest and zebra) in the Serengeti-Mara ecosystem using fine resolution satellite imagery. The results achieve accurate detection of nearly 500,000 individuals across thousands of square kilometers and multiple habitat types.
- Zijing Wu
- , Ce Zhang
- & Tiejun Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Imaging quantized vortex rings in superfluid helium to evaluate quantum dissipation
Imaging quantized vortex rings in superfluid helium to evaluate quantum dissipation
Quantum vortices exist in superfluid and play important role in superfluid characteristics. Here the authors determine quantum dissipation caused by mutual friction in superfluid by filming the motion of quantized vortex rings in superfluid helium.
- Yuan Tang
- , Wei Guo
- & Toshiaki Kanai
-
Article
| Open Access Single-frame deep-learning super-resolution microscopy for intracellular dynamics imaging
Single-frame deep-learning super-resolution microscopy for intracellular dynamics imaging
Multi-frame super-resolution microscopy is hampered by long acquisition times and phototoxicity, which hinder its use for live-cell imaging. Here, authors propose a deep-learning-based single-frame super-resolution approach to image cellular dynamics with high spatiotemporal resolution.
- Rong Chen
- , Xiao Tang
- & Shuhuai Yao
-
Article
| Open Access Measurement-induced collective vibrational quantum coherence under spontaneous Raman scattering in a liquid
Measurement-induced collective vibrational quantum coherence under spontaneous Raman scattering in a liquid
Spontaneous Raman scattering is classically understood as an incoherent process. Here, the authors demonstrate that macroscopic quantum coherence among billions of vibrating molecules in a liquid is generated when single photon detection and single spatio-temporal mode excitation are implemented.
- Valeria Vento
- , Santiago Tarrago Velez
- & Christophe Galland
-
Article
| Open Access 3D-patterned inverse-designed mid-infrared metaoptics
3D-patterned inverse-designed mid-infrared metaoptics
The authors show computationally optimized, multilayer scattering structures in the mid-infrared for high efficiency imaging. Multispectral and polarization sorting devices are fabricated via two-photon lithography and characterized optically.
- Gregory Roberts
- , Conner Ballew
- & Andrei Faraon
-
Article
| Open Access Direct nano-imaging of light-matter interactions in nanoscale excitonic emitters
Direct nano-imaging of light-matter interactions in nanoscale excitonic emitters
Authors investigate quasi-2D nanoscale emitters on different substrates with tapping mode tip-enhanced spectroscopy. They visualize in-plane near-field and radiative energy propagation via Surface plasmon polaritons launched by the nanoscale emitters on dielectric/Au or SiO2/Si substrates.
- Kiyoung Jo
- , Emanuele Marino
- & Deep Jariwala
-
Article
| Open Access Single-pulse terahertz spectroscopy monitoring sub-millisecond time dynamics at a rate of 50 kHz
Single-pulse terahertz spectroscopy monitoring sub-millisecond time dynamics at a rate of 50 kHz
Single-pulse THz spectroscopy at 50 kHz is performed with a table-top system to extract rapid changes of a material’s complex dielectric function. This technique is demonstrated by monitoring carrier accumulation and relaxation dynamics in silicon.
- Nicolas Couture
- , Wei Cui
- & Jean-Michel Ménard
-
Article
| Open Access Triboelectric-induced ion mobility for artificial intelligence-enhanced mid-infrared gas spectroscopy
Triboelectric-induced ion mobility for artificial intelligence-enhanced mid-infrared gas spectroscopy
Isopropyl alcohol can play a significant role in anti-virus diagnosis but generally yields limited response in conventional detection. Here, authors propose a methodology of AI-enhanced ion mobility and mid-infrared spectroscopy for accurate gas identification despite presence different carbon-based gases.
- Jianxiong Zhu
- , Shanling Ji
- & Chengkuo Lee
-
Article
| Open Access A sensitive high repetition rate arrival time monitor for X-ray free electron lasers
A sensitive high repetition rate arrival time monitor for X-ray free electron lasers
In time-resolved measurements it is crucial to know the time delay between the exciting and probing light pulses. Here the authors demonstrate a self-referencing common-path interferometer method measuring the arrival time between the X-ray free electron laser and the optical pulse to the target and thus their inherent timing jitter.
- Michael Diez
- , Henning Kirchberg
- & Christian Bressler
-
Article
| Open Access Quantum microscopy of cells at the Heisenberg limit
Quantum microscopy of cells at the Heisenberg limit
The authors present a method for super-resolution quantum microscopy at the Heisenberg limit by using pairs of entangled photons with balanced pathlengths. They improve the spatial resolution, imaging speed, and contrast-to-noise ratio in practice while providing a theoretical interpretation of the super-resolution feature.
- Zhe He
- , Yide Zhang
- & Lihong V. Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Single-shot isotropic differential interference contrast microscopy
Single-shot isotropic differential interference contrast microscopy
The authors present a metasurface-assisted isotropic DIC microscopy technique. It is based on an original pattern of radial shear interferometry, that converts rectilinear shear into rotationally symmetric radial shear, enabling single-shot isotropic imaging capabilities.
- Xinwei Wang
- , Hao Wang
- & Xumin Ding
-
Article
| Open Access All-optical control of high-purity trions in nanoscale waveguide
All-optical control of high-purity trions in nanoscale waveguide
The authors induce a nanoscale strain gradient in monolayer MoS2 suspended on a waveguide and take advantage of propagating surface plasmon polaritons to localize hot electrons in the suspended area. They funnel excitons in the waveguide, facilitating all-optical control of exciton-to-trion conversion.
- Hyeongwoo Lee
- , Yeonjeong Koo
- & Kyoung-Duck Park
-
Article
| Open Access Confocal interferometric scattering microscopy reveals 3D nanoscopic structure and dynamics in live cells
Confocal interferometric scattering microscopy reveals 3D nanoscopic structure and dynamics in live cells
Label-free imaging is crucial to life sciences, but it can be hampered by the lack of 3D imaging capability and low nanoscopic sensitivity. Here, authors show a confocal interferometric scattering microscopy approach allowing the quantification of nanometric topography and intracellular dynamics.
- Michelle Küppers
- , David Albrecht
- & Vahid Sandoghdar
-
Article
| Open Access Meta-optics empowered vector visual cryptography for high security and rapid decryption
Meta-optics empowered vector visual cryptography for high security and rapid decryption
Usual methods for optical encryption suffer from a tradeoff between the level of security and the complexity of operation given by multiple optical measurements or digital postprocessing. Here, the authors show a multi-d.o.f. metasurface-based vector optical manipulation protocol enabling secure decryption in real time.
- Fei Zhang
- , Yinghui Guo
- & Xiangang Luo
-
Article
| Open Access Imaging-based intelligent spectrometer on a plasmonic rainbow chip
Imaging-based intelligent spectrometer on a plasmonic rainbow chip
The authors develop an imaging-based intelligent spectrometer on a plasmonic “rainbow” chip. It can accurately and precisely determine the spectroscopic and polarimetric information of the illumination spectrum using a single image assisted by suitably trained deep learning algorithms.
- Dylan Tua
- , Ruiying Liu
- & Qiaoqiang Gan
-
Article
| Open Access Ultrafast light targeting for high-throughput precise control of neuronal networks
Ultrafast light targeting for high-throughput precise control of neuronal networks
Current holographic approaches for neuronal stimulation have limitations in their temporal resolution and the number of targeted neurons. Here, the authors demonstrate an approach for ultra-fast holographic light targeting which, combined with optogenetics, enables sub-millisecond control of sequential neuronal activation and high throughput simultaneous multicell illumination.
- Giulia Faini
- , Dimitrii Tanese
- & Valentina Emiliani
-
Article
| Open Access Exploiting volumetric wave correlation for enhanced depth imaging in scattering medium
Exploiting volumetric wave correlation for enhanced depth imaging in scattering medium
The authors achieve ultrahigh resolution and depth volumetric imaging in complex media by recording a volumetric reflection matrix covering individual wavelengths and angles and developing reconstruction algorithms based on volumetric wave correlation.
- Ye-Ryoung Lee
- , Dong-Young Kim
- & Wonshik Choi
-
Article
| Open Access Super-resolution orbital angular momentum holography
Super-resolution orbital angular momentum holography
The resolution of orbital angular momentum holography is limited by a fundamental sampling criterion. Here, the authors break the resolution barrier by temporal multiplexing of binary holograms and enhance the resolution and capacity by several times.
- Zijian Shi
- , Zhensong Wan
- & Xing Fu
-
Article
| Open Access Single-shot polarimetry of vector beams by supervised learning
Single-shot polarimetry of vector beams by supervised learning
The authors demonstrate a single shot polarimetry of vector beams without requiring polarization optics. They map the beam polarization content into a spatial intensity distribution and utilize supervised learning for single-shot measurements of multiple polarizations.
- Davide Pierangeli
- & Claudio Conti
-
Article
| Open Access Single-shot ultrafast terahertz photography
Single-shot ultrafast terahertz photography
The authors demonstrate a single-shot ultrafast terahertz (THz) photography system that can provide both the 2D spatial and 1D temporal imaging capabilities of ultrashort transient scenes with sub-picosecond temporal resolutions by engineering the electro-optic detection system.
- Junliang Dong
- , Pei You
- & Roberto Morandotti
-
Article
| Open Access Evanescent field trapping and propulsion of Janus particles along optical nanofibers
Evanescent field trapping and propulsion of Janus particles along optical nanofibers
Manipulation of Janus particles is challenging and has limited precision. Here, the authors propose manipulation of Janus particles by optical forces in the evanescent field of an optical nanofiber, and demonstrate that they exhibit strong transverse localization on the nanofiber and much faster propulsion compared to all-dielectric particles of the same size.
- Georgiy Tkachenko
- , Viet Giang Truong
- & Síle Nic Chormaic
-
Article
| Open Access Real-time single-molecule 3D tracking in E. coli based on cross-entropy minimization
Real-time single-molecule 3D tracking in E. coli based on cross-entropy minimization
Single-molecule 3D tracking is critical to understand macromolecular dynamics but achieving this at a sub-millisecond resolution remains challenging. Here the authors present a 3D tracking method based on cross-entropy minimization and the true excitation point spread function.
- Elias Amselem
- , Bo Broadwater
- & Johan Elf
-
Article
| Open Access A general highly efficient synthesis of biocompatible rhodamine dyes and probes for live-cell multicolor nanoscopy
A general highly efficient synthesis of biocompatible rhodamine dyes and probes for live-cell multicolor nanoscopy
Rhodamines are privileged fluorescent dyes for labelling intracellular structures in living cells. Here, the authors present a facile protecting-group-free synthesis permitting generation of a wide range of symmetrical and unsymmetrical 4-carboxyrhodamines covering the whole visible spectrum.
- Jonas Bucevičius
- , Rūta Gerasimaitė
- & Gražvydas Lukinavičius
-
Article
| Open Access Extracting particle size distribution from laser speckle with a physics-enhanced autocorrelation-based estimator (PEACE)
Extracting particle size distribution from laser speckle with a physics-enhanced autocorrelation-based estimator (PEACE)
The authors demonstrate a real-time, non-invasive, far-field optical probe to monitor particle size distribution in pharmaceutical manufacturing. It characterizes the speckle scattered from the surface using machine learning weaved into optical physics.
- Qihang Zhang
- , Janaka C. Gamekkanda
- & George Barbastathis
-
Article
| Open Access Mid-infrared single-pixel imaging at the single-photon level
Mid-infrared single-pixel imaging at the single-photon level
The authors present an implementation of mid-infrared single-photon computational imaging with a single-element silicon detector. In addition to unique features of single-pixel simplicity and room-temperature operation, the infrared imager offers a superior sensitivity at the single-photon level.
- Yinqi Wang
- , Kun Huang
- & Heping Zeng
-
Article
| Open Access Bright Tm3+-based downshifting luminescence nanoprobe operating around 1800 nm for NIR-IIb and c bioimaging
Bright Tm3+-based downshifting luminescence nanoprobe operating around 1800 nm for NIR-IIb and c bioimaging
Fluorescence imaging in the near-infrared region yields high-quality images that overcome the current depth limitations. Here, the authors report a Tm3 + -based nanoprobe for NIR-IIb/c imaging, providing references to future bioimaging beyond 1700 nm.
- Yulei Chang
- , Haoren Chen
- & Xianggui Kong
-
Article
| Open Access Theoretical and experimental analysis of circularly polarized luminescence spectrophotometers for artifact-free measurements using a single CCD camera
Theoretical and experimental analysis of circularly polarized luminescence spectrophotometers for artifact-free measurements using a single CCD camera
The authors present an artifact-free circularly polarized luminescence spectrophotometer using a single camera and two polarization encoding paths. The spectra are measured in a few seconds without the need of calibration by inverting the role of the paths.
- Bruno Baguenard
- , Amina Bensalah-Ledoux
- & Stéphan Guy
-
Article
| Open Access Mid-infrared cross-comb spectroscopy
Mid-infrared cross-comb spectroscopy
The authors introduce and demonstrate cross-comb spectroscopy in the mid-infrared as a variant of dual-comb spectroscopy. It provides enhanced performance and allows mid-infrared spectral information to be obtained by near-infrared detection.
- Mingchen Liu
- , Robert M. Gray
- & Alireza Marandi
-
Article
| Open Access Monocular metasurface camera for passive single-shot 4D imaging
Monocular metasurface camera for passive single-shot 4D imaging
The authors present a monocular camera equipped with a single-layer metalens for passive single-shot 4D imaging. It can simultaneously perform high-accuracy depth sensing and highfidelity polarization imaging over an extended depth of field.
- Zicheng Shen
- , Feng Zhao
- & Yuanmu Yang
-
Article
| Open Access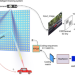 Intelligent metasurface system for automatic tracking of moving targets and wireless communications based on computer vision
Intelligent metasurface system for automatic tracking of moving targets and wireless communications based on computer vision
The authors present an intelligent metasurface system that uses a target detection algorithm combined with a depth camera, to automatically detect the position of moving targets and achieve real-time wireless communications. The system can operate for multiple targets in limited ambient light, outdoor and other realistic environments.
- Weihan Li
- , Qian Ma
- & Tie Jun Cui
-
Article
| Open Access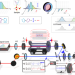 Dual-comb optical activity spectroscopy for the analysis of vibrational optical activity induced by external magnetic field
Dual-comb optical activity spectroscopy for the analysis of vibrational optical activity induced by external magnetic field
Dual-comb spectroscopy was first applied to the measurement of magnetic optical activity spectroscopy, realizing Doppler-limited gas-phase molecular analysis, and was further extended to the rapid measurement of liquid-phase chiroptical activity.
- Daowang Peng
- , Chenglin Gu
- & Wenxue Li
-
Article
| Open Access Visualizing orthogonal RNAs simultaneously in live mammalian cells by fluorescence lifetime imaging microscopy (FLIM)
Visualizing orthogonal RNAs simultaneously in live mammalian cells by fluorescence lifetime imaging microscopy (FLIM)
No multi-color RNA fluorescent tags are currently available for use in live cells. Here, the authors show that fluorescence lifetime imaging microscopy is advantageous for multiplexed RNA visualization while achieving robust cellular contrast.
- Nadia Sarfraz
- , Emilia Moscoso
- & Esther Braselmann

 Label-free adaptive optics single-molecule localization microscopy for whole zebrafish
Label-free adaptive optics single-molecule localization microscopy for whole zebrafish