Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access The AT-hook is an evolutionarily conserved auto-regulatory domain of SWI/SNF required for cell lineage priming
The AT-hook is an evolutionarily conserved auto-regulatory domain of SWI/SNF required for cell lineage priming
This study demonstrates that an evolutionary conserved, autoregulatory ‘AT-hook’ domain of SWI/SNF regulates gene transcription and enhancer activation by modulating SWI/SNF intrinsic catalytic activity and is critical for cell lineage priming.
- Dhurjhoti Saha
- , Solomon Hailu
- & Blaine Bartholomew
-
Article
| Open Access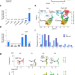 PCGF1-PRC1 links chromatin repression with DNA replication during hematopoietic cell lineage commitment
PCGF1-PRC1 links chromatin repression with DNA replication during hematopoietic cell lineage commitment
Here the authors show that a Polycomb Repressive Complex 1 (PRC1) containing PCGF1 prevents excessive loading of transcriptional activators and chromatin remodelers on nascent DNA, allowing proper deposition of nucleosomes immediately after the passage of the DNA replication fork to optimize downstream chromatin configurations in hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells (HSPCs).
- Junichiro Takano
- , Shinsuke Ito
- & Tomokatsu Ikawa
-
Article
| Open Access Nucleosome-directed replication origin licensing independent of a consensus DNA sequence
Nucleosome-directed replication origin licensing independent of a consensus DNA sequence
Most eukaryotes do not use a consensus DNA sequence as binding sites for the origin recognition complex (ORC) to initiate DNA replication, however budding yeast do. Here the authors show S. cerevisiae ORC can bind nucleosomes near nucleosome-free regions and recruit replicative helicases to form a pre-replication complex independent of the DNA sequence.
- Sai Li
- , Michael R. Wasserman
- & Shixin Liu
-
Article
| Open Access Dynamic nucleosome landscape elicits a noncanonical GATA2 pioneer model
Dynamic nucleosome landscape elicits a noncanonical GATA2 pioneer model
Here the authors provide a multi-omic study of the nucleosome landscape in LNCaP cells and observe nine functional nucleosome states each with characteristic nucleosome footprints. Upon androgen stimulation, they observed changes in these nucleosome states accompanied by changes in binding and function of pioneer factors, including GATA2.
- Tianbao Li
- , Qi Liu
- & Victor X. Jin
-
Article
| Open Access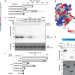 Tousled-like kinase 2 targets ASF1 histone chaperones through client mimicry
Tousled-like kinase 2 targets ASF1 histone chaperones through client mimicry
Tousled-like kinase 2 (TLK2) phosphorylates ASF1 histone chaperones to promote nucleosome assembly in S phase. Here, the authors show that TLK2 targets ASF1 by simulating its client protein histone H3, exploiting a primordial protein interaction surface for regulatory control.
- Bertrand Simon
- , Hua Jane Lou
- & David A. Calderwood
-
Article
| Open Access Ruler elements in chromatin remodelers set nucleosome array spacing and phasing
Ruler elements in chromatin remodelers set nucleosome array spacing and phasing
Although chromatin remodelers have been shown to align nucleosome arrays to barriers and to generate spacing regularity among nucleosomes within arrays, it has remained unclear how the distance to barrier and the spacing length are determined in absolute terms. Here, the authors reveal that remodelers contain a ‘ruler’ element that sets remodeler-specific alignment and spacing distances when generating nucleosome arrays.
- Elisa Oberbeckmann
- , Vanessa Niebauer
- & Philipp Korber
-
Article
| Open Access Nucleosome plasticity is a critical element of chromatin liquid–liquid phase separation and multivalent nucleosome interactions
Nucleosome plasticity is a critical element of chromatin liquid–liquid phase separation and multivalent nucleosome interactions
Resolving nucleosomes with chemical accuracy inside sub-Mb chromatin provides molecular insight into the modulation of chromatin structure and its liquid–liquid phase separation (LLPS). By developing a multiscale chromatin model, the authors find that DNA breathing enhances the valency, heterogeneity, and dynamics of nucleosomes, promoting disordered folding and LLPS.
- Stephen E. Farr
- , Esmae J. Woods
- & Rosana Collepardo-Guevara
-
Article
| Open Access Histone dynamics mediate DNA unwrapping and sliding in nucleosomes
Histone dynamics mediate DNA unwrapping and sliding in nucleosomes
Nucleosomes tightly wrap ~147 DNA base pairs around an octamer of histone proteins, but how nucleosome structural dynamics affect genome functioning is not completely clear. Here authors employ all-atom molecular dynamics simulations of nucleosome core particles and observe that octamer dynamics and plasticity enable DNA unwrapping and sliding.
- Grigoriy A. Armeev
- , Anastasiia S. Kniazeva
- & Alexey K. Shaytan
-
Article
| Open Access Structural and dynamic mechanisms of CBF3-guided centromeric nucleosome formation
Structural and dynamic mechanisms of CBF3-guided centromeric nucleosome formation
Chromosome segregation requires the association of the kinetochore protein complex with a specialized nucleosome at the centromere. Here, the authors present cryo-EM and mutational studies that provide insights into the structure of the budding yeast centromeric nucleosome and how the centromere CBF3 protein complex guides its formation.
- Ruifang Guan
- , Tengfei Lian
- & Yawen Bai
-
Article
| Open Access Dinucleosome specificity and allosteric switch of the ISW1a ATP-dependent chromatin remodeler in transcription regulation
Dinucleosome specificity and allosteric switch of the ISW1a ATP-dependent chromatin remodeler in transcription regulation
Here the authors show that the preference of yeast chromatin remodeler ISW1a for dinucleosomes hinges on conformational changes that occur in the transition from binding mononucleosomes to dinucleosomes. These changes are critical for ISW1a organizing chromatin at promoters and regulating transcription in conjunction with other chromatin remodelers.
- Saurabh K. Bhardwaj
- , Solomon G. Hailu
- & Blaine Bartholomew
-
Article
| Open Access Molecular mechanism of the MORC4 ATPase activation
Molecular mechanism of the MORC4 ATPase activation
Human Microrchidia 4 (MORC4) ATPase has been implicated in acute and chronic pancreatitis, inflammatory disorders and cancer. Here the authors describe the structure–function relationship of MORC4 and define the molecular mechanism for MORC4 activation.
- Adam H. Tencer
- , Khan L. Cox
- & Tatiana G. Kutateladze
-
Article
| Open Access Multivalent interactions drive nucleosome binding and efficient chromatin deacetylation by SIRT6
Multivalent interactions drive nucleosome binding and efficient chromatin deacetylation by SIRT6
SIRT6 plays essential roles in metabolism, tumor suppression, and DNA repair through the deacetylation of histone substrates. Here the authors use biophysical methods to investigate the molecular basis for SIRT6 interaction with the nucleosome core particle.
- Wallace H. Liu
- , Jie Zheng
- & John M. Denu
-
Article
| Open Access Near-atomic resolution structures of interdigitated nucleosome fibres
Near-atomic resolution structures of interdigitated nucleosome fibres
Crystal structures of nucleosome fibres assembled from cohesive-ended dinucleosomes with and without linker histone reveal open zigzag conformations that are interdigitated with one another, and suggest the role that linker DNA plays in observed variable fibre configurations and packing.
- Zenita Adhireksan
- , Deepti Sharma
- & Curt A. Davey
-
Article
| Open Access Interaction of the pioneer transcription factor GATA3 with nucleosomes
Interaction of the pioneer transcription factor GATA3 with nucleosomes
GATA 3 functions as a pioneer factor during cellular reprogramming. Here the authors delineate nucleosome positioning relative to GATA3 binding motifs and describe the structure of a GATA3–nucleosome complex; providing insight into how a pioneer factor interacts with nucleosomes and catalyze their local remodelling to produce an accessible enhancer.
- Hiroki Tanaka
- , Yoshimasa Takizawa
- & Hitoshi Kurumizaka
-
Article
| Open Access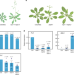 NAP1-RELATED PROTEIN1 and 2 negatively regulate H2A.Z abundance in chromatin in Arabidopsis
NAP1-RELATED PROTEIN1 and 2 negatively regulate H2A.Z abundance in chromatin in Arabidopsis
The histone variant H2A.Z is deposited by the SWR1 complex to replace H2A in Arabidopsis, but the mechanism of H2A.Z removal is unclear. Here, the authors show that NRP proteins can regulate gene expression by counteracting SWR1 and prevent excessive accumulation of H2A.Z.
- Yafei Wang
- , Zhenhui Zhong
- & Israel Ausin
-
Article
| Open Access Histone H2A variants alpha1-extension helix directs RNF168-mediated ubiquitination
Histone H2A variants alpha1-extension helix directs RNF168-mediated ubiquitination
Histone ubiquitination plays a critical role in the DNA damage response pathway. Here the authors reveal how RNF168 ubiquitinates the H2A family including noncanonical variants, H2AZ and macroH2A1/2, at the divergent N-terminal tail lysine residue.
- Jessica L. Kelliher
- , Kirk L. West
- & Justin W. C. Leung
-
Article
| Open Access CHD4 slides nucleosomes by decoupling entry- and exit-side DNA translocation
CHD4 slides nucleosomes by decoupling entry- and exit-side DNA translocation
Chromatin remodellers hydrolyse ATP to move nucleosomal DNA against histone octamers. Here, the authors use single-molecule assays to examine the mechanism of action of CHD4 remodeller, and provide evidence that CHD4 slides nucleosomes by decoupling entry- and exit-side DNA translocation.
- Yichen Zhong
- , Bishnu P. Paudel
- & Joel P. Mackay
-
Article
| Open Access Nucleosome positioning stability is a modulator of germline mutation rate variation across the human genome
Nucleosome positioning stability is a modulator of germline mutation rate variation across the human genome
Nucleosome organization has been suggested to affect local mutation rates in the genome. Here, the authors analyse data on >300,000 human de novo mutations and high-resolution nucleosome maps and provide evidence that nucleosome positioning stability modulates germline mutation rate variation across the human genome.
- Cai Li
- & Nicholas M. Luscombe
-
Article
| Open Access Role of cell-type specific nucleosome positioning in inducible activation of mammalian promoters
Role of cell-type specific nucleosome positioning in inducible activation of mammalian promoters
Nucleosome organisation plays important roles in regulating functional genomic elements. Here, the authors use high-resolution profiling to analyse dynamic nucleosome positioning at inducible and cell-type-specific promoters, providing a global view of chromatin architecture at inducible promoters.
- Agata Oruba
- , Simona Saccani
- & Dominic van Essen
-
Article
| Open Access Mechanisms governing the pioneering and redistribution capabilities of the non-classical pioneer PU.1
Mechanisms governing the pioneering and redistribution capabilities of the non-classical pioneer PU.1
PU.1 is a master TF of hematopoietic lineage differentiation. Here the authors analyse properties of PU.1 DNA-binding in vitro and genome-wide in vivo across different cell types with native or ectopic PU.1 expression, and uncover the mechanisms governing the pioneering and redistribution capabilities of the non-classical pioneer PU.1.
- Julia Minderjahn
- , Andreas Schmidt
- & Michael Rehli
-
Article
| Open Access Structural basis of nucleosome assembly by the Abo1 AAA+ ATPase histone chaperone
Structural basis of nucleosome assembly by the Abo1 AAA+ ATPase histone chaperone
ATAD2 AAA+ ATPases are a family of histone chaperones that regulate nucleosome density and chromatin dynamics. Here, authors find that the fission yeast ATAD2 homolog Abo1 deposits histone H3–H4 onto DNA in an ATP-hydrolysis-dependent manner, and present the cryo-EM structure of an ATAD2 family ATPase to reveal the structural basis of nucleosome assembly by Abo1.
- Carol Cho
- , Juwon Jang
- & Ji-Joon Song
-
Article
| Open Access JASPer controls interphase histone H3S10 phosphorylation by chromosomal kinase JIL-1 in Drosophila
JASPer controls interphase histone H3S10 phosphorylation by chromosomal kinase JIL-1 in Drosophila
The chromosomal kinase JIL-1 is responsible for interphase histone H3S10 phosphorylation and has been proposed to protect active chromatin from heterochromatinisation. Here, the authors show that JIL-1 is stabilized and anchored to active genes and telomeric transposons by JASPer, which binds to H3K36me3 nucleosomes via its PWWP domain.
- Christian Albig
- , Chao Wang
- & Catherine Regnard
-
Article
| Open Access Histone H3K23-specific acetylation by MORF is coupled to H3K14 acylation
Histone H3K23-specific acetylation by MORF is coupled to H3K14 acylation
Acetylation of histone H3K23 has emerged as an essential posttranslational modification, yet this epigenetic mark remains poorly understood. Here, the authors identify the native MORF complex as a histone H3K23-specific acetyltransferase and show that interaction of the MORF subunit with acylated H3K14 promotes acetylation of H3K23 by this complex to activate transcription.
- Brianna J. Klein
- , Suk Min Jang
- & Tatiana G. Kutateladze
-
Article
| Open Access Mechanism of centromere recruitment of the CENP-A chaperone HJURP and its implications for centromere licensing
Mechanism of centromere recruitment of the CENP-A chaperone HJURP and its implications for centromere licensing
The CENP-A chaperone HJURP associates with Mis18α, Mis18β, and M18BP1 to target centromeres and deposit new CENP-A. Here the authors provide evidence that two repeats in human HJURP previously proposed to be functionally distinct are interchangeable and bind concomitantly to the 4:2:2 Mis18α:Mis18β:M18BP1 complex without dissociating it.
- Dongqing Pan
- , Kai Walstein
- & Andrea Musacchio
-
Article
| Open Access NF-Y controls fidelity of transcription initiation at gene promoters through maintenance of the nucleosome-depleted region
NF-Y controls fidelity of transcription initiation at gene promoters through maintenance of the nucleosome-depleted region
The mechanisms underlying specific TSS selection in mammals remain unclear. Here the authors show that the ubiquitously expressed transcription factor NF-Y regulate fidelity of transcription initiation at gene promoters, maintaining the region upstream of TSSs in a nucleosome-depleted state, while protecting this region from ectopic transcription initiation.
- Andrew J. Oldfield
- , Telmo Henriques
- & Raja Jothi
-
Article
| Open Access Structure and function of the Orc1 BAH-nucleosome complex
Structure and function of the Orc1 BAH-nucleosome complex
The Origin Recognition Complex (ORC) plays conserved and diverse roles in eukaryotes. Here the authors present the structure of a chromatin interacting domain of yeast Orc1 in complex with the nucleosome core particle, revealing that Orc1 interacts with the histone H4 tail irrespective of K16 acetylation; a modification that regulates accessibility to chromatin.
- Pablo De Ioannes
- , Victor A. Leon
- & Karim-Jean Armache
-
Article
| Open Access Theoretical analysis of Polycomb-Trithorax systems predicts that poised chromatin is bistable and not bivalent
Theoretical analysis of Polycomb-Trithorax systems predicts that poised chromatin is bistable and not bivalent
Polycomb and Trithorax group proteins regulate silent and active gene expression states, but also allow poised states in pluripotent cells. Here the authors present a mathematical model that integrates data on Polycomb/ Trithorax biochemistry into a single coherent framework which predicts that poised chromatin is not bivalent as previously proposed, but is bistable, meaning that the system switches frequently between stable active and silent states.
- Kim Sneppen
- & Leonie Ringrose
-
Article
| Open Access The CENP-A centromere targeting domain facilitates H4K20 monomethylation in the nucleosome by structural polymorphism
The CENP-A centromere targeting domain facilitates H4K20 monomethylation in the nucleosome by structural polymorphism
Kinetochore function depends on H4K20 monomethylation in centromeric nucleosomes but the underlying mechanism is unclear. Here, the authors provide evidence that the centromere-specific nucleosome subunit CENP-A facilitates H4K20 methylation by enabling a conformational change of the H4 N-terminal tail.
- Yasuhiro Arimura
- , Hiroaki Tachiwana
- & Hitoshi Kurumizaka
-
Article
| Open Access Structure of transcribing RNA polymerase II-nucleosome complex
Structure of transcribing RNA polymerase II-nucleosome complex
Eukaryotic transcription requires passage of RNA polymerase II (Pol II) through chromatin, which is impaired by nucleosomes. Here the authors report the cryo-EM structure of transcribing Pol II engaged with a downstream nucleosome core particle at an overall resolution of 4.4 Å, providing insights into the mechanism of chromatin transcription.
- Lucas Farnung
- , Seychelle M. Vos
- & Patrick Cramer
-
Article
| Open Access High precision FRET studies reveal reversible transitions in nucleosomes between microseconds and minutes
High precision FRET studies reveal reversible transitions in nucleosomes between microseconds and minutes
Nucleosomes compact the genome and regulate access to specific DNA sequences. Here the authors employ single-molecule FRET studies to characterize nucleosome dynamics at different salt concentrations and dissect nucleosome disassembly into elementary steps.
- Alexander Gansen
- , Suren Felekyan
- & Jörg Langowski
-
Article
| Open Access Intracellular nucleosomes constrain a DNA linking number difference of −1.26 that reconciles the Lk paradox
Intracellular nucleosomes constrain a DNA linking number difference of −1.26 that reconciles the Lk paradox
There had been an enduring discrepancy between theoretical and observed measurement of the DNA linking number (∆Lk) constrained by nucleosomes. Here the authors provide measurements of the ∆Lk constrained by individual nucleosomes in native chromatin that reconcile this discrepancy.
- Joana Segura
- , Ricky S. Joshi
- & Joaquim Roca
-
Article
| Open Access Mapping of histone-binding sites in histone replacement-completed spermatozoa
Mapping of histone-binding sites in histone replacement-completed spermatozoa
While a majority of histones are replaced by protamines during spermatogenesis, a small amount is retained in mammalian spermatozoa. Here the authors develop a method to purify histones from replacement-completed sperm (HRCS), completely solubilize histones from cross-linked HRCS without MNase digestion, and map histone-binding sites in these cells.
- Keisuke Yoshida
- , Masafumi Muratani
- & Shunsuke Ishii
-
Article
| Open Access Functional activity of the H3.3 histone chaperone complex HIRA requires trimerization of the HIRA subunit
Functional activity of the H3.3 histone chaperone complex HIRA requires trimerization of the HIRA subunit
The HIRA histone chaperone complex is involved in the deposition of the histone variant H3.3. Here the authors, by using biochemical and crystallographic approaches, report the homotrimerization of the HIRA subunit which is critical for the functional activity of the complex.
- Dominique Ray-Gallet
- , M. Daniel Ricketts
- & Geneviève Almouzni
-
Article
| Open Access Global profiling of protein–DNA and protein–nucleosome binding affinities using quantitative mass spectrometry
Global profiling of protein–DNA and protein–nucleosome binding affinities using quantitative mass spectrometry
Quantitative mass spectrometry enables the proteome-wide assessment of biomolecular binding affinities. While previous approaches mainly focused on protein–small molecule interactions, the authors here present a method to probe protein–DNA and protein–nucleosome binding affinities at proteome scale.
- Matthew M. Makowski
- , Cathrin Gräwe
- & Michiel Vermeulen
-
Article
| Open Access Functional crosstalk between histone H2B ubiquitylation and H2A modifications and variants
Functional crosstalk between histone H2B ubiquitylation and H2A modifications and variants
Ubiquitylation of H2B is associated with transcription and regulation of chromatin structure. Here, the authors perform an unbiased screen to identify the role of chromatin modifications on ubiquitylation of H2BK120 and characterize the crosstalk between H2BK120ub and H2A modifications and variants.
- Felix Wojcik
- , Geoffrey P. Dann
- & Tom W. Muir
-
Article
| Open Access Structural rearrangements of the histone octamer translocate DNA
Structural rearrangements of the histone octamer translocate DNA
Nucleosomes are dynamic and can move along DNA in an uncatalyzed manner but little is known about the mechanisms of histone octamer translocation. Here the authors present cryo-EM structures of nucleosomes in differently organized histone octamer and DNA states and show how histone octamers translocate DNA.
- Silvija Bilokapic
- , Mike Strauss
- & Mario Halic
-
Article
| Open Access scNMT-seq enables joint profiling of chromatin accessibility DNA methylation and transcription in single cells
scNMT-seq enables joint profiling of chromatin accessibility DNA methylation and transcription in single cells
Relationships between DNA methylation and transcription, and methylation and DNA accessibility can be probed but interrogating all three in the same single cells has not been possible. Here, the authors report the first single-cell method for parallel chromatin accessibility, DNA methylation and transcriptome profiling.
- Stephen J. Clark
- , Ricard Argelaguet
- & Wolf Reik
-
Article
| Open Access Dot1 regulates nucleosome dynamics by its inherent histone chaperone activity in yeast
Dot1 regulates nucleosome dynamics by its inherent histone chaperone activity in yeast
Dot1 is an evolutionarily conserved enzyme, responsible for histone H3K79 methylation in most eukaryotes. Here authors show that, in yeast, Dot1p has histone chaperone activity and regulates nucleosome dynamics via histone exchange in transcribed regions.
- Soyun Lee
- , Seunghee Oh
- & Daeyoup Lee
-
Article
| Open Access Microbiota derived short chain fatty acids promote histone crotonylation in the colon through histone deacetylases
Microbiota derived short chain fatty acids promote histone crotonylation in the colon through histone deacetylases
Histone post-translational modifications are known key regulators of gene expression. Here, the authors characterize histone crotonylation at histone H3 lysine 18 in intestinal epithelia and find that it is a highly dynamic cell cycle regulated mark under the regulation of the HDAC deacetylases.
- Rachel Fellows
- , Jérémy Denizot
- & Patrick Varga-Weisz
-
Article
| Open Access Nucleosome acidic patch-targeting binuclear ruthenium compounds induce aberrant chromatin condensation
Nucleosome acidic patch-targeting binuclear ruthenium compounds induce aberrant chromatin condensation
Histone H2A–H2B dimers in nucleosomes contain an acidic patch, a highly electronegative cleft. Here, the authors characterize a family of binuclear ruthenium compounds that selectively target the acidic patch, generating intra-nucleosomal H2A-H2B cross-links as well as inter-nucleosomal cross-links.
- Gabriela E. Davey
- , Zenita Adhireksan
- & Curt A. Davey
-
Article
| Open Access Accessibility of the histone H3 tail in the nucleosome for binding of paired readers
Accessibility of the histone H3 tail in the nucleosome for binding of paired readers
The chromatin remodeller CHD4 contains two PHD finger reader domains that have been shown to bivalently recognize H3 histone tails. Here, the authors describe a mechanism by which the PHD fingers bind to the intact nucleosome core particle, revealing both cooperative and individual interactions.
- Jovylyn Gatchalian
- , Xiaodong Wang
- & Tatiana G. Kutateladze
-
Article
| Open Access Structural and mechanistic insights into ATRX-dependent and -independent functions of the histone chaperone DAXX
Structural and mechanistic insights into ATRX-dependent and -independent functions of the histone chaperone DAXX
The ATRX-DAXX histone chaperone complex incorporates H3.3 in heterochromatin in a replication-independent manner. Here, the authors present a high-resolution x-ray crystal structure of an interaction surface between ATRX and DAXX, and characterize ATRX-dependent and-independent functions of DAXX.
- Dominik Hoelper
- , Hongda Huang
- & Peter W. Lewis
-
Article
| Open Access DNA binding drives the association of BRG1/hBRM bromodomains with nucleosomes
DNA binding drives the association of BRG1/hBRM bromodomains with nucleosomes
BRG1 and BRM are central components of the BAF (mSWI/SNF) chromatin remodelling complex, which is critical for regulation of chromatin structure. Here, the authors provide evidence that both the BRG1 and hBRM bromodomains have DNA-binding activity and bind to both DNA and H3K14ac simultaneously.
- Emma A. Morrison
- , Julio C. Sanchez
- & Catherine A. Musselman
-
Article
| Open Access A bromodomain–DNA interaction facilitates acetylation-dependent bivalent nucleosome recognition by the BET protein BRDT
A bromodomain–DNA interaction facilitates acetylation-dependent bivalent nucleosome recognition by the BET protein BRDT
Many chromatin modifying proteins, including BRDT, contain bromodomains, which are known to interact with nucleosomes. Here, the authors find that BRDT interacts with nucleosomes via only one of its two bromodomains, and that the interaction involves contacts with DNA as well as acetylated histones.
- Thomas C. R. Miller
- , Bernd Simon
- & Christoph W. Müller
-
Article
| Open Access MNase titration reveals differences between nucleosome occupancy and chromatin accessibility
MNase titration reveals differences between nucleosome occupancy and chromatin accessibility
Nucleosome positioning and chromatin accessibility are important contributors to the regulation of gene expression. Here the authors describe a method that allows the simultaneous measurement of nucleosome occupancy and chromatin accessibility in the same assay, revealing new features of chromatin organization linked to gene regulation.
- Jakub Mieczkowski
- , April Cook
- & Michael Y. Tolstorukov
-
Article
| Open Access Effects of cytosine modifications on DNA flexibility and nucleosome mechanical stability
Effects of cytosine modifications on DNA flexibility and nucleosome mechanical stability
Cytosine modifications are important epigenetic markers yet their physical influence on DNA is not well understood. Here, Ngo et al. show that different alterations affect DNA flexibility, suggesting a mechanism where modifications change accessibility of nucleosome bound DNA.
- Thuy T. M. Ngo
- , Jejoong Yoo
- & Taekjip Ha
-
Article
| Open Access BAP1/ASXL1 recruitment and activation for H2A deubiquitination
BAP1/ASXL1 recruitment and activation for H2A deubiquitination
The tumor suppressor BAP1 is activated by ASXL1 to deubiquitinate mono-ubiquitinated H2A at K119 in Polycomb gene repression. Here, the authors show how BAP1’s C-terminal extension auto-recruits it to nucleosomes, where the DEUBAD domain of ASXL1 increases BAP1’s affinity for ubiquitin to drive deubiquitination.
- Danny D. Sahtoe
- , Willem J. van Dijk
- & Titia K. Sixma
-
Article
| Open Access Linker histone H1 and H3K56 acetylation are antagonistic regulators of nucleosome dynamics
Linker histone H1 and H3K56 acetylation are antagonistic regulators of nucleosome dynamics
The linker histone H1 is highly abundant and regulates DNA accessibility by compacting chromatin. Here the authors analyze transcription factor binding to nucleosomes and show that histone H1 suppresses unwrapping but does not directly block the binding of transcription factors.
- Morgan Bernier
- , Yi Luo
- & Michael G. Poirier
-
Article
| Open Access Generation of a synthetic GlcNAcylated nucleosome reveals regulation of stability by H2A-Thr101 GlcNAcylation
Generation of a synthetic GlcNAcylated nucleosome reveals regulation of stability by H2A-Thr101 GlcNAcylation
Post-translational modification of histones has been implicated in gene regulation. Here, Lercher et al. generate synthetic GlcNAcylated histone 2A and nucleosomes and show that this modification can cause nucleosome destabilization, suggesting histone 2A O-GlcNAcylation may promote an open chromatin state and increase transcription.
- Lukas Lercher
- , Ritu Raj
- & Benjamin G. Davis

 Two DOT1 enzymes cooperatively mediate efficient ubiquitin-independent histone H3 lysine 76 tri-methylation in kinetoplastids
Two DOT1 enzymes cooperatively mediate efficient ubiquitin-independent histone H3 lysine 76 tri-methylation in kinetoplastids